Lecture Career.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 «Personnel Development & Career»
«Personnel Development & Career»
 TRADITIONAL POINT OF VIEW measures, that include learning &training (повышение квалификации), retraining (переподготовка) of the personnel
TRADITIONAL POINT OF VIEW measures, that include learning &training (повышение квалификации), retraining (переподготовка) of the personnel
 MODERN POINT OF VIEW structural change (numerical, age distribution, qualification structure) of the personnel & alignment with company's strategic goals
MODERN POINT OF VIEW structural change (numerical, age distribution, qualification structure) of the personnel & alignment with company's strategic goals
 This activity is both focused upon, and evaluated against, the job that an individual currently holds. Training: This activity focuses upon the jobs that an individual may potentially hold in the future, and is evaluated against those jobs. Development:
This activity is both focused upon, and evaluated against, the job that an individual currently holds. Training: This activity focuses upon the jobs that an individual may potentially hold in the future, and is evaluated against those jobs. Development:
 «CORPORATIVE UNIVERSITIES» Scientific basis- concept of “Learning Organization” Appeared at 1960 -s at the USA One of the most efficient technologies of personnel development
«CORPORATIVE UNIVERSITIES» Scientific basis- concept of “Learning Organization” Appeared at 1960 -s at the USA One of the most efficient technologies of personnel development
 «CORPORATIVE UNIVERSITIES» Based on Corporative needs & values Creation common corporative culture, corporative standards, corporative values
«CORPORATIVE UNIVERSITIES» Based on Corporative needs & values Creation common corporative culture, corporative standards, corporative values
 LEARNING ORGANIZATIONS (PETER SENGE) are those organizations, where people continually expand their capacity to create the results, the truly desire, where new & expansive patterns of thinking … & where people are continually learning ©
LEARNING ORGANIZATIONS (PETER SENGE) are those organizations, where people continually expand their capacity to create the results, the truly desire, where new & expansive patterns of thinking … & where people are continually learning ©
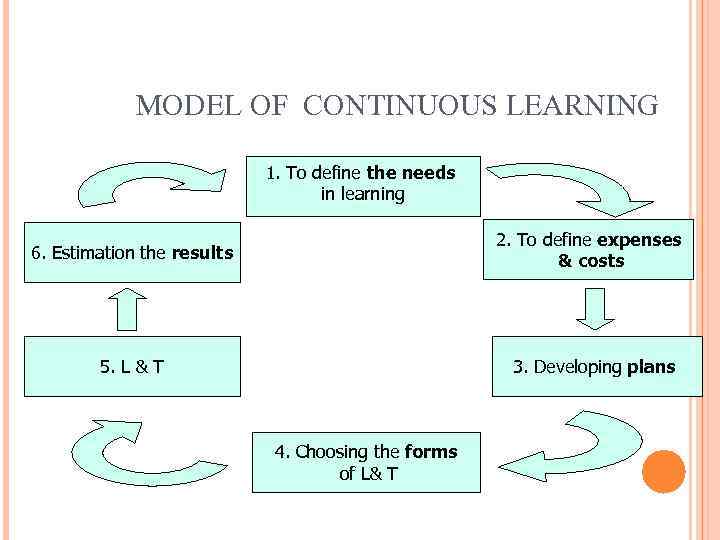 MODEL OF CONTINUOUS LEARNING 1. To define the needs in learning 2. To define expenses & costs 6. Estimation the results 5. L & T 3. Developing plans 4. Choosing the forms of L& T
MODEL OF CONTINUOUS LEARNING 1. To define the needs in learning 2. To define expenses & costs 6. Estimation the results 5. L & T 3. Developing plans 4. Choosing the forms of L& T
 WAYS OF L&T Primary While changing the career Task-oriented Рlanned Developing
WAYS OF L&T Primary While changing the career Task-oriented Рlanned Developing
 CAREER COURSE OR PROGRESS THROUGH LIFE OR DISTINCT PERIOD OF LIFE
CAREER COURSE OR PROGRESS THROUGH LIFE OR DISTINCT PERIOD OF LIFE
 TYPES Professional Inter-organizational institutional) Intra-organizational Horizontal Vertical Latent = Hidden (inter-
TYPES Professional Inter-organizational institutional) Intra-organizational Horizontal Vertical Latent = Hidden (inter-
 WHY DO PEOPLE CHANGE CAREER The downsizing or the restructuring of an organization (54%). New challenges or opportunities that arise (30%). Poor or ineffective leadership (25%). Having a poor relationship with a manager(s) (22%). For the improvement of a better work/life balance (21%). Contributions are not being recognized (21%). For better compensation and benefits (18%), For better alignment with personal and organizational values (17%). Personal strengths and capabilities are not a good fit with an organization (16%). The financial instability of an organization (13%). An organization relocated (12%). [6]
WHY DO PEOPLE CHANGE CAREER The downsizing or the restructuring of an organization (54%). New challenges or opportunities that arise (30%). Poor or ineffective leadership (25%). Having a poor relationship with a manager(s) (22%). For the improvement of a better work/life balance (21%). Contributions are not being recognized (21%). For better compensation and benefits (18%), For better alignment with personal and organizational values (17%). Personal strengths and capabilities are not a good fit with an organization (16%). The financial instability of an organization (13%). An organization relocated (12%). [6]
 For the improvement of a better work/life balance (21%). Contributions are not being recognized (21%). For better compensation and benefits (18%), For better alignment with personal and organizational values (17%).
For the improvement of a better work/life balance (21%). Contributions are not being recognized (21%). For better compensation and benefits (18%), For better alignment with personal and organizational values (17%).
 Personal strengths and capabilities are not a good fit with an organization (16%). The financial instability of an organization (13%). An organization relocated (12%)
Personal strengths and capabilities are not a good fit with an organization (16%). The financial instability of an organization (13%). An organization relocated (12%)
 STAGES OF CAREER Preliminary period–(age 25 -28) “Предварительный” Formation period - (age 25 -30) “Этап становления” Promotion period – (age 30 -45) “Этап продвижения” Saving Period – (age 45 -60) “Этап сохранения” Retirement –(age 60 -70) “Этап завершения”
STAGES OF CAREER Preliminary period–(age 25 -28) “Предварительный” Formation period - (age 25 -30) “Этап становления” Promotion period – (age 30 -45) “Этап продвижения” Saving Period – (age 45 -60) “Этап сохранения” Retirement –(age 60 -70) “Этап завершения”
 CAREER DEVELOPMENT IS: " . . . the total constellation of psychological, sociological, educational, physical, economic, and chance factors that combine to influence the nature and significance of work in the total lifespan of any given individual. "
CAREER DEVELOPMENT IS: " . . . the total constellation of psychological, sociological, educational, physical, economic, and chance factors that combine to influence the nature and significance of work in the total lifespan of any given individual. "
 CAREER DEVELOPMENT IS: ". . . the lifelong psychological and behavioral processes as well as contextual influences shaping one’s career over the life span. As such, career development involves the person’s creation of a career pattern, decision-making style, integration of life roles, values expression, and liferole self concepts. "
CAREER DEVELOPMENT IS: ". . . the lifelong psychological and behavioral processes as well as contextual influences shaping one’s career over the life span. As such, career development involves the person’s creation of a career pattern, decision-making style, integration of life roles, values expression, and liferole self concepts. "
 Professional Career Guidance/counseling Centres Coaching is a teaching or training process in which an individual gets support while learning to achieve a specific personal or professional result or goal
Professional Career Guidance/counseling Centres Coaching is a teaching or training process in which an individual gets support while learning to achieve a specific personal or professional result or goal
 TALENT MANAGEMENT Talent management refers to the anticipation of required human capital the organization needs at the time then setting a plan to meet those needs Companies that engage in talent management are strategic and deliberate in how they source, attract, select, train, develop, retain, promote, and move employees through the organization.
TALENT MANAGEMENT Talent management refers to the anticipation of required human capital the organization needs at the time then setting a plan to meet those needs Companies that engage in talent management are strategic and deliberate in how they source, attract, select, train, develop, retain, promote, and move employees through the organization.
 Competencies are defined as observable abilities, skills, knowledge, motivations or traits defined in terms of the behaviours needed for successful job performance.
Competencies are defined as observable abilities, skills, knowledge, motivations or traits defined in terms of the behaviours needed for successful job performance.
 Human capital is the stock of competencies, knowledge and personality attributes embodied in the ability to perform labor so as to produce economic value. Human capital is vitally important for an organization's success Human capital costs a certain expense, repays that expense with a profit
Human capital is the stock of competencies, knowledge and personality attributes embodied in the ability to perform labor so as to produce economic value. Human capital is vitally important for an organization's success Human capital costs a certain expense, repays that expense with a profit
 GENERAL TERMS Knowledge is gleaned by organizing information. Typically, information evolves to knowledge by the learner's gaining context, perspective and scope about the information. Skills are applying knowledge in an efficient manner to get something done. One notices skills in an employee by their behaviors. Simply put, continuous learning is the ability to learn. Learning need not be a linear event where a learner goes to a formal learning program, gains areas of knowledge and skills about a process, and then the learning ceases. If the learner can view life (including work) as a "learning program", then the learner can continue to learn from almost everything in life. As a result, the learner continues to expand his or her capacity for living, including working.
GENERAL TERMS Knowledge is gleaned by organizing information. Typically, information evolves to knowledge by the learner's gaining context, perspective and scope about the information. Skills are applying knowledge in an efficient manner to get something done. One notices skills in an employee by their behaviors. Simply put, continuous learning is the ability to learn. Learning need not be a linear event where a learner goes to a formal learning program, gains areas of knowledge and skills about a process, and then the learning ceases. If the learner can view life (including work) as a "learning program", then the learner can continue to learn from almost everything in life. As a result, the learner continues to expand his or her capacity for living, including working.
 PECULIARITIES: COMPETENCE IS Expandable and self generating with use Transportable and shareable
PECULIARITIES: COMPETENCE IS Expandable and self generating with use Transportable and shareable
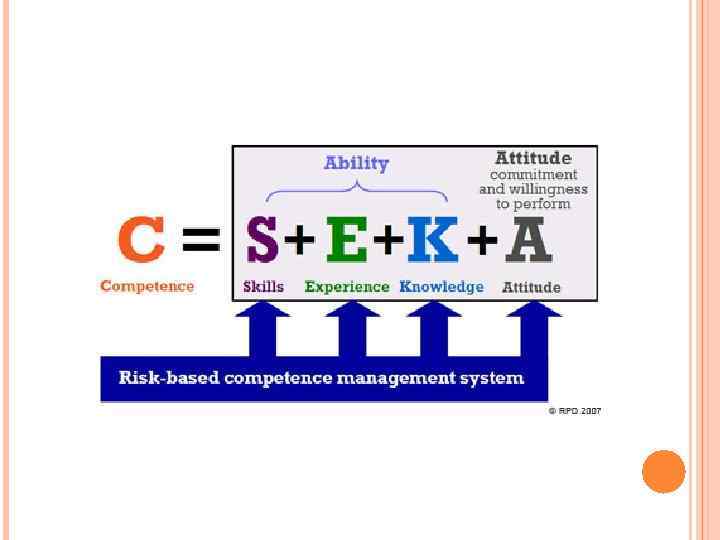
 COMPETENCE MANAGEMENT Competence - the ability to sustain the coordinated deployment of resources in ways that helps an organization achieve its goals (creating and distributing value to customers and stakeholders).
COMPETENCE MANAGEMENT Competence - the ability to sustain the coordinated deployment of resources in ways that helps an organization achieve its goals (creating and distributing value to customers and stakeholders).
 The "stakeholders" in training and development are categorized into several classes. The sponsors of training and development are senior managers. The clients of training and development are business planners. Line managers are responsible for coaching, resources, and performance. The participants are those who actually undergo the processes. The facilitators are Human Resource Management staff. And the providers are specialists in the field. Each of these groups has its own agenda and motivations, which sometimes conflict with the agendas and motivations of the others.
The "stakeholders" in training and development are categorized into several classes. The sponsors of training and development are senior managers. The clients of training and development are business planners. Line managers are responsible for coaching, resources, and performance. The participants are those who actually undergo the processes. The facilitators are Human Resource Management staff. And the providers are specialists in the field. Each of these groups has its own agenda and motivations, which sometimes conflict with the agendas and motivations of the others.


