1f646ebf2fc88312820ec93f75d74aa6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 158

Personal Protective Equipment Vincent J. Giblin, General President 1293 Airport Road Beaver, WV 25813 Phone: (304) 253 -8674 Fax: (304) 253 -7758 E-mail: hazmat@iuoeiettc. org

This material was produced under grant number 46 C 5 -HT 16 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U. S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U. S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U. S. Government. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program

Personal Protective Equipment General Requirements n Application l Hazards of processes l Chemical hazards l Radiological hazards l Mechanical irritants Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 3

Personal Protective Equipment General Requirements n Employee-owned equipment l Employer must assure 4 Adequacy 4 Proper maintenance 4 Proper sanitation Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 4

Personal Protective Equipment General Requirements n Design l Shall be of safe design and construction so as not to be a hazard to the employee in itself Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 5

Personal Protective Equipment General Requirements n Hazard assessment and equipment selection l Identifying hazards that require PPE 4 Requires written certification l Selecting PPE shall be based on 4 Hazard assessment 4 Proper fit l Communicate selection decision to each affected employee Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 6

Personal Protective Equipment General Requirements n Training l Everyone required to wear PPE shall be trained to know at least the following 4 When PPE is necessary 4 What PPE is necessary 4 How to don, doff, adjust and wear PPE 4 Limitations of PPE 4 Proper care, use and maintenance Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 7

Personal Protective Equipment General Requirements n Training l Each employee shall demonstrate understanding and skill required in training l Written certification required Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 8
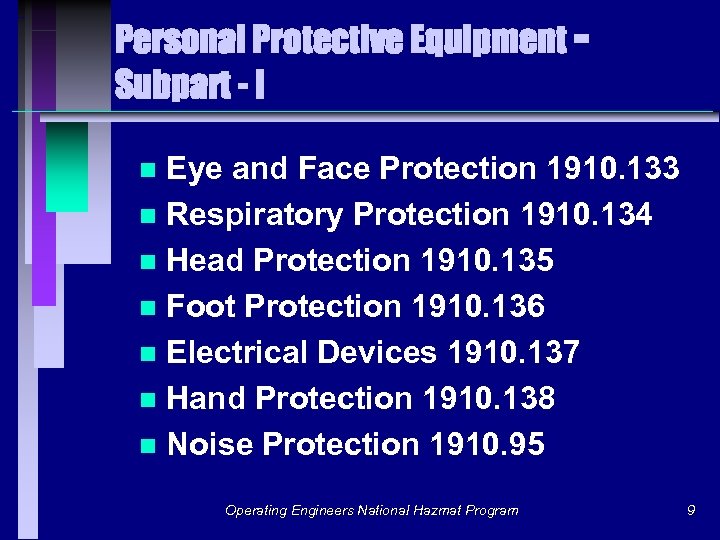
Personal Protective Equipment Subpart - I Eye and Face Protection 1910. 133 n Respiratory Protection 1910. 134 n Head Protection 1910. 135 n Foot Protection 1910. 136 n Electrical Devices 1910. 137 n Hand Protection 1910. 138 n Noise Protection 1910. 95 n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 9

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 10

Eye & Face Protection n The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses appropriate eye or face protection when exposed to eye or face hazards from flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 11

Eye & Face Protection n The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses eye protection that provides side protection when there is a hazard from flying objects. Detachable side protectors (e. g. clip-on or slide-on side shields) meeting the pertinent requirements of this section are acceptable. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 12

Eye & Face Protection n The employer shall ensure that each affected employee who wears prescription lenses while engaged in operations that involve eye hazards wears eye protection that incorporates the prescription in its design, or…. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 13

Eye & Face Protection Wears eye protection that can be worn over the prescription lenses without disturbing the proper position of the prescription lenses or the protective lenses. n Eye and face PPE shall be distinctly marked to facilitate identification of the manufacturer. n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 14

Eye & Face Protection n The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses equipment with filter lenses that have a shade number appropriate for the work being performed for protection from injurious light radiation. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 15

Eye & Face Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 16

Eye & Face Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 17

Eye & Face Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 18

Eye & Face Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 19

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 20

Permissible Practice Employer shall provide: Engineering Controls (if feasible) n Respiratory Protection Program n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 21

Definitions n Thirty-five definitions have been added to the new final rule. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 22

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are necessary: Written program n Worksite-specific procedures n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 23

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are necessary: Must include following provisions: l Procedures for selecting respirators l Medical evaluations l Fit testing procedures l Procedures for ensuring air quality and quantity Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 24

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are necessary: l Procedures and schedules for cleaning, disinfecting, storing, inspecting, repairing, discarding and maintaining respirators l Employee training in respiratory hazards Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 25

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are necessary: n Employee training in respiratory hazards in both routine use and emergencies n Employee training in the proper use of respirators including donning, doffing, and limitations n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 26

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are necessary: n Procedures for evaluating the effectiveness of the program Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 27

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are not necessary: n Employers may provide respirators n or may permit employees to use their own respirator if employer determines that the use will not in itself create a hazard Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 28

Respiratory Protection Program Where respirators are not necessary: n If employer permits voluntary usage they must: Provide users with Appendix D l Establish written program for: l 4 Medical Qualifications 4 Respirator Maintenance Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 29

Respiratory Protection Program Employer must designate a Program Administrator n Employer must provide respirators, training, medical evaluations at no cost to the employees n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 30

Selection of Respirators Employer must: l Select from NIOSH-certified respirators l Base respirator selection on workplace respiratory hazards l Identify and evaluate workplace respiratory hazards Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 31

Selection of Respirators If employer cannot identify or reasonably estimate employee exposure, shall consider atmosphere to be IDLH n Employer shall select respirators from a sufficient number of models and sizes so that the respirator is acceptable and fits the user n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 32

Selection of Respirators n n Respirators for IDLH Atmospheres Full-face pressure demand SCBA (minimum 30 minutes) Full-face pressure demand SAR-E Escape-only respirators must be NIOSH-certified Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 33

Selection of Respirators for IDLH Atmospheres n Oxygen-deficient atmospheres shall be considered IDLH n l Exception: If employer can guarantee that the oxygen level can be maintained within specified ranges in Table II, then any SAR may be used Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 34

Selection of respirators n Respirator shall be correct for chemical state and form Gases l Vapors l Particulate l Other l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 35

Selection of Respirators For Protection against Gases and Vapors n n SCBA, SAR-E, SAR APR if: l ESLI (End-of-service-life indicator) or l Change schedule that ensures changes are made before end of cartridge service life Breakthrough is no longer an acceptable measure for cartridge change Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 36

Medical Evaluation Why: n Employer shall provide medical evaluation to determine the employee’s ability to use a respirator Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 37

Medical Evaluation When: n Employer shall provide medical evaluation prior to fit test or required use of respirator n Employer may discontinue when employee no longer requires respirator Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 38

Medical Evaluation Who: n Employer shall identify a physician or other licensed health care professional (PLHCP) Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 39

Medical Evaluation What: n The medical evaluation shall obtain the information requested by the questionnaire in Sections 1 and 2, Part A of Appendix C. n PLHCP may use medical exam or a questionnaire to obtain information Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 40

Medical Evaluation Follow-up exam required if: n Any positive response to questions 1 -8 Section 2, Part A, Appendix C n Initial medical exam demonstrates the need n Exam shall include any test the PLHCP deems necessary Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 41

Medical Evaluation n n Exams shall be kept confidential and be administered during the employee’s normal working hours or at a time and place convenient to the employee Employee shall have opportunity to discuss questionnaire or exam results with PLHCP Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 42

Medical Evaluation Supplemental Information: n Type and weight of respirator n Duration and frequency of use n Expected physical work effort n Additional protective clothing n Temperature and humidity extremes n Written respirator program Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 43

Medical Determination n Obtain written evaluation from PLHCP including the following: l Limitations on respirator use related to: 4 Medical condition of employee 4 Workplace conditions 4 Whether or not employee is medically able to wear respirator Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 44

Medical Determination n Obtain written evaluation from PLHCP l The need for follow-up examination l Statement that the PLHCP provided the employee with a copy of the written recommendation Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 45

Medical Determination If negative pressure APR used, PLHCP may recommend PAPR n Employer must comply n After subsequent exams PLHCP may change recommendation n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 46

Fit Testing - Appendix A Required if any negative- or positive-pressure tight-fitting respirators used must be in negative-pressure mode n Employee must pass fit test n l Qualitative (100 ff or lower) (f)(6) l Quantitative (Half- or full-face) (f)(7) 4 full-face = 500 fit factor 4 half-face = 100 fit factor Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 47

Fit Testing - Appendix A n Testing will be repeated annually, unless employee’s condition changes enough to warrant a retest: Facial Scarring l Dental changes l Cosmetic surgery l Obvious weight change l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 48

Fit Testing - Appendix A n n After a passed fit test, employee may notify employer that respirator fit is unacceptable Employer must allow employee to re-select and retest Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 49

Respirator Use n Facepiece seal protection l No facial hair in seal or valves l Nothing may interfere with seal n User must perform seal check prior to each use. (Appendix B-1) Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 50

Respirator Use n IDLH Atmospheres One or more employees located outside l Visual, voice, or signal line communication must be maintained l Outside employee must be trained and equipped for emergency rescue l Must notify employer prior to entry to provide emergency rescue l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 51

Respirator Use n IDLH Atmospheres Outside employees must be equipped with: l Pressure demand SCBA or SAR-E l Appropriate retrieval equipment l Equivalent means for rescue, if retrieval system is more hazardous Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 52

Respirator Use n Interior structural firefighting l All IDLH requirements plus: 4 Two employees enter IDLH atmosphere together and maintain visual or voice contact 4 At least two outside employees 4 All employees in this situation must use SCBA’s Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 53

Maintenance and Care n Cleaning and Disinfecting Intervals: One user - As often as necessary to maintain sanitary condition l Two or more users - Before being used by different user l Emergency use - After each use l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 54

Maintenance and Care n Storage (Routine use) Protect from damage, contamination, dust, sunlight, extreme temperatures, excessive moisture, damaging chemicals l Prevent deformation l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 55

Maintenance and Care n Storage (Emergency use) Protected from damage, contamination, dust, sunlight, extreme temperatures, excessive moisture, damaging chemicals l Stored to prevent deformation l Kept accessible to work place l Stored in compartments or in covers marked EMERGENCY RESPIRATORS l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 56

Maintenance and Care n Inspection l Routine Use - 4 After each use and during cleaning l Emergency Use- 4 At least monthly 4 Function test before and after each use Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 57

Maintenance and Care n n Inspection must include: (Routine Use) l Function l Tightness of connections l Component condition l Elasticity SCBA’s monthly l Fully charged l recharged when pressure falls below 90% l Regulator and warning device condition Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 58

Maintenance and Care n For emergency use, the employer must certify the respirator by documenting: l Date of Inspection l Name of Inspector l Findings l Required remedial action l Serial number of respirator l Provide this information on a tag or label Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 59

Maintenance and Care n Repairs Performed by trained personnel only l According to manufacturer’s specifications l Using only NIOSH approved parts l Reducing and admission valves, regulator, and alarms - by manufacturer or technician trained by manufacturer l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 60

Breathing Air Quality n Must meet requirements of ANSI/Compressed Gas Association Commodity Specification for Air G -7. 1 -1989 (Type 1 -Grade D) Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 61

Breathing Air Quality n Type 1 -Grade D l Oxygen content - 19. 5% - 23. 5% l Hydrocarbon - 5 mg/m 3 or less l Carbon monoxide (CO) - 10 ppm or less l Carbon dioxide (CO 2) - 1, 000 ppm or less l Lack of noticeable odor Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 62

Breathing Air Quality No compressed oxygen and compressed air mixing n Oxygen concentrations above 23. 5% to be used for oxygen service only n Cylinders must comply with 49 CFR Part 173 and Part 178 n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 63

Breathing Air Quality Cylinders of air purchased must have a certificate of analysis for Type 1 -Grade D air n On-site compressors must: n l Be situated to prevent contamination l Minimize moisture content so Dew point at 1 atm. is 10 below ambient temperature Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 64

Breathing Air Quality n On-site compressors must: l Have sorbent beds and filters to ensure air quality l Sorbent beds must be refurbished or replaced according to manufacturer’s instructions l Must have a tag with person authorized to perform the change John Doe Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 65

Breathing Air Quality On-site compressors that are not oil-lubricated - employer shall ensure CO levels no higher than 10 ppm n On-site compressors that are oillubricated - employer shall ensure CO levels no higher than 10 ppm and monitor air temperature n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 66

Breathing Air Quality n Employer shall ensure that breathing air couplings are incompatible with all nonrespirable cylinder outlets Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 67

Identification of Filters, Cartridges, and Canisters Color Coded n NIOSH Approval label n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 68

Training n Employers shall ensure that each employee can demonstrate knowledge of at least the following: l Why respirators are necessary l How improper fit, usage, or maintenance can affect protection l Limitations and capabilities l Proper inspection procedures Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 69

Training n Employers shall ensure that each employee can demonstrate knowledge of at least the following: l Proper donning and doffing procedures l Proper seal check procedure l Maintenance and storage l Medical signs and symptoms Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 70

Training n If new employee has had training within the previous 12 months, employer may waive initial training and retrain the employee within 12 months of his or her previous training Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 71

Training n Retraining shall be annual and when l Changes in workplace or respirator render previous training obsolete l Employee demonstrates inadequacies in respirator usage Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 72

Training n Appendix D shall be provided, in either written or oral format, when voluntary respirator usage is allowed by employer Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 73

Program Evaluation n Employer must conduct evaluations to determine: l Respiratory program is being properly implemented l Proper respirator usage l Respirator program effectiveness Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 74

Program Evaluation n Employer must consult with employees to assess employee views and to identify: Respirator program effectiveness l Any problems l Respirator fit l Appropriate respirator selection l Respirator usage l Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 75

Recordkeeping n Medical evaluation l The medical record for each employee shall be preserved and maintained for at least the duration of employment plus thirty (30) years. 29 CFR 1910. 1020 (d)(1)(i) Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 76

Recordkeeping n Medical evaluation l The medical records of employees who have worked for less than one year for the employer need not be retained beyond the term of employment if they are provided to the employee upon the termination of employment. 29 CFR 1910. 1020 (d)(1)(i)(C) Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 77

Recordkeeping n Fit testing records must include: l Employee name or ID l Type of fit test l Respirator make, model, size l Date of test l Pass/Fail results Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 78

Recordkeeping Fit testing records must be retained until next fit test n A written copy of respirator program shall be retained by employer n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 79

Dates Effective date: April 8, 1998 n Compliance date: September 8, 1998 n Employer may use existing training, fit testing, medical evaluations, and program evaluations. If conducted within twelve months of April 8, 1998 n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 80

Appendices Appendix A - Fit testing procedures Appendix B-1 - User seal check Appendix B-2 - Cleaning procedures Appendix C - Medical evaluation/questionnaire Appendix D - (non-mandatory) - Information for voluntary respirator usage Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 81

RESPIRATOR TYPES Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 82

Air-Purifying Respirators Types of Filtration n Mechanical n Chemical n Combination n Gas Mask Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 83

Air-Purifying Respirators Types n Paper Disposable APF-5 Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 84

Air-Purifying Respirators Types n 1/2 Mask APF-10 Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 85

Air-Purifying Respirators Types n Full-Face (FF) APF-50 Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 86

Air-Purifying Respirators Types n PAPR APF-100 Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 87

Air-Purifying Respirators Limitations n Limitations l. Correct Cartridge l. Cartridge Life l. Battery Life (PAPR) n Weak Spots l. Face to Facepiece seal l. Exhalation Valve Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 88

Air-Purifying Respirators Limitations n Unacceptable Conditions l Never use in IDLH l Never use in unknowns l Never use in oxygen-deficient atmospheres l Never with substances with low warning properties l Never above MUL or MUC Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 89

Air-Purifying Respirators Protection Factors n Maximum Use Levels APF x PEL=MUL n Maximum Use Concentration concentration above cartridge approval (NIOSH) Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 90

Supplied-Air Respirator W / SCBA Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 91

Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 92

Summary n YOU should be able to l Identify the types of respirators l Explain how a respirator operates l Properly inspect a respirator l Don an APR, SCBA and SAR -E/SCBA l Ask pertinent questions Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 93

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 94

Head Protection General requirements n The employer shall ensure that each affected employee wears a protective helmet when working in areas where there is a potential for injury to the head from falling objects n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 95

Head Protection n The employer shall ensure that a protective helmet designed to reduce electrical shock hazard is worn by each such affected employee when near exposed electrical conductors which could contact the head Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 96

Head Protection Criteria for protective helmets n Protective helmets purchased after July 5, 1994 shall comply with Personnel Protection-Protective Headwear for Industrial Workers. Requirements, "ANSI Z 89. 1 -1986, or shall be demonstrated to be equally effective Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 97

Head Protection n Protective helmets purchased before July 5, 1994 shall comply with the Requirements for Industrial Head Protection, " ANSI Z 89. 1 -1969, or shall be demonstrated by the employer to be equally effective Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 98

Head Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 99

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 100

Foot Protection n The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries due to falling or rolling objects, or objects piercing the sole, and where such employee's feet are exposed to electrical hazards Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 101

Foot Protection Criteria for protective footwear n Protective footwear purchased after July 5, 1994 shall comply with ANSI Z 41 -1991, or shall be demonstrated by the employer to be equally effective Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 102

Foot Protection n Protective footwear purchased before July 5, 1994 shall comply with the ANSI standard "USA Standard for Men's Safety-Toe Footwear, " Z 41. 1 -1967, or shall be demonstrated by the employer to be equally effective Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 103

Foot Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 104

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 105

Hand Protection n Employers shall select and require employees to use appropriate hand protection when employees' hands are exposed to hazards such as those from skin absorption of harmful substances; severe cuts or lacerations; severe abrasions; punctures; chemical burns; thermal burns; and harmful temperature extremes. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 106

Hand Protection n Employers shall base the selection of the appropriate hand protection on an evaluation of the performance characteristics of the hand protection relative to the task(s) to be performed, conditions present, duration of use, and the hazards and potential hazards identified. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 107

Hand Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 108

Hand Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 109

Hand Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 110

Hand Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 111

Hand Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 112

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 113

Limitations n There is no such thing as impermeable protective clothing n There is no one clothing material for all chemicals n Certain chemicals or combinations = less than an hour of protection following contact Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 114

Purpose CPC is worn to protect the skin and eyes from harmful chemicals n One must select a material with the most protection from the chemical encountered and consider the style of suit as well n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 115

Types of CPC n Fully-Encapsulating Suit (FES) n Non-encapsulating Suit Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 116

Protective Material Elastomers Butyl Rubber n Chlorinated Polyethylene n Natural Rubber n Teflon n Neoprene n Nitrile Rubber n Vitron n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 117

Protective Material Non - Elastomers Tyvek n Polyethylene n Saranex n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 118

Performance Requirements Chemical Resistance n Durability n Flexibility n Temperature Resistance n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 119

Performance Requirements Service Life n Ability to clean n Design - Size - Color - Cost n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 120

Chemical Resistance n Penetration : The transportation of chemicals through openings in a garment Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 121

Chemical Resistance n Degradation : A chemical action involving the molecular breakdown of the material due to chemical contact Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 122

Chemical Resistance n Permeation : A chemical action involving the movement of chemicals on a molecular level, through intact material Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 123

Chemical Resistance n Breakthrough Time: The elapsed time between initial contact of a chemical with the outside surface and the detection at the inside surface of the material Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 124

Selection of CPC The best protective material is one with a low permeation rate and a long breakthrough time !! Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 125

Physical Stress n Heat Stress n Accident Proneness n Fatigue Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 126

Heat Stress n Heat Cramps n Heat Exhaustion n Heat Stroke Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 127

Physical Stress n Ways to minimize adverse effects: l Medical surveillance program l Acclimated to work environment l Length of work period vs. . . rest period Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 128

Physical Stress n Ways to minimize adverse effects: l Schedule work for cooler time of day l Increase intake of fluids Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 129

Inspection of CPC Suit material n Zipper and flaps n Connecting devices n Signs of chemical exposure n Proper size n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 130

Inspection of CPC Fully- Encapsulating Exhalation valves n Suit facepiece n Waist belt and ankle strap n Gloves and boots n Leak detection n Air-line attachment n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 131

Record Keeping Who, when and any problems n Use conditions n Repair status n After each use and monthly n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 132

Levels of Protection n Level A - Maximum respiratory and maximum skin n Level B - Maximum respiratory and moderate skin n Level C - Moderate respiratory and moderate skin n Level D - No respiratory and minimum skin Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 133

Personal Protective Equipment Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 134

Personal Protective Equipment Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 135

Personal Protective Equipment Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 136

Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 137

Noise Protection n Noise l Defined as unwanted sound l The units to measure noise levels are decibels (d. Bs) 4 a very soft whisper is about 30 d. B 4 a jack hammer is about 100 d. B l At 140 d. B, noise can cause physical pain Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 138

Noise Protection n If employees are exposed to average noise levels above 85 d. B, OSHA requires employers to implement a hearing conservation program. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 139

Noise Protection n OSHA’s permissible exposure limit (PEL) for noise is 90 d. B as an 8 hour TWA Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 140

Noise Protection Engineering controls n Administrative controls n Personal protective equipment (PPE) n Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 141

Noise Protection n Action level 29 CFR 1910. 95 l (c)(1 -2) n Table G-16 a Monitoring program l 29 CFR 1910. 95 l Subparagraph (d)(1 -3) l Notification l Hearing tests Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 142

Noise Protection n Audiometric testing program (g)(1 -10) l Employer shall establish and maintain an audiometric testing program l The program shall be at no cost to the employee Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 143

Noise Protection n Audiometric testing program (g)(1 -10) l Audiometric testing shall be performed by a licensed or certified audiologist l Baseline audiogram l Annual audiogram Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 144

Noise Protection n Audiometric test requirements (h)(1 -5) l Shall be pure tone, air conduction, hearing threshold examinations with test frequencies including as a minimum 500, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000 and 6000 Hz Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 145

Noise Protection Audiometric test requirements (h)(1 -5) n Tests shall be taken for each ear n l Equipment shall meet the specifications of ANSI S 3. 6 -1969 l Equipment shall be calibrated Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 146

Noise Protection n Personal protective equipment (PPE) l Employers shall make hearing protectors available to all employees exposed to 85 decibels TWA or greater at no cost to employee Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 147

Noise Protection n Personal protective equipment (PPE) l Employees shall be given the opportunity to select their hearing protectors from a variety of suitable hearing protectors provided by the employer Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 148

Noise Protection n Personal protective equipment (PPE) l Training shall be provided in the use and care of all hearing protectors provided to employees l The employer shall ensure proper initial fitting and supervise the correct use of all hearing protectors Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 149

Noise Protection n Hearing protector attenuation (j)(1 -4) l The adequacy of hearing protector attenuation shall be reevaluated whenever noise exposure changes Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 150

Noise Protection n Hearing protector attenuation (j)(1 -4) l The employer shall institute a training program for all employees who are exposed to noise at or above an 8 -hour TWA of 85 decibels, and shall ensure employee participation in such program Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 151

Noise Protection n Recordkeeping (m)(1 -2) l Monitoring results l Audiometric tests Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 152

Noise Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 153

Noise Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 154

Noise Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 155

Noise Protection Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 156

This material was produced under grant number 46 C 5 -HT 16 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U. S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U. S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U. S. Government. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program

End n This publication was made possible by grant numbers 5 U 45 ES 06182 -13 AND 5 U 45 ES 0976313 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), NIH. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIEHS, NIH. Operating Engineers National Hazmat Program 158
1f646ebf2fc88312820ec93f75d74aa6.ppt