4955cf1e794a3225420865bc59a45a2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 PERSONAL FINANCE Unit 1: Saving and Investing
PERSONAL FINANCE Unit 1: Saving and Investing
 Chapter 1: Savings
Chapter 1: Savings
 Savings Money Facts: • 70% of people live paycheck to paycheck. • Only 41% of Americans save regularly. • Half of American households live on less than $46, 326 a year. • 19% of people who make over $100, 000 live paycheck to paycheck!
Savings Money Facts: • 70% of people live paycheck to paycheck. • Only 41% of Americans save regularly. • Half of American households live on less than $46, 326 a year. • 19% of people who make over $100, 000 live paycheck to paycheck!
 Savings The Seven Baby Steps (These are the steps you should take to reach financial peace!) • 1. $1, 000 in an emergency fund (or $500 if you make less than $20, 000/yr. ) • 2. Pay off all debt except the house utilizing the debt snowball (focus on one debt at a time beginning with smallest debt to gain momentum).
Savings The Seven Baby Steps (These are the steps you should take to reach financial peace!) • 1. $1, 000 in an emergency fund (or $500 if you make less than $20, 000/yr. ) • 2. Pay off all debt except the house utilizing the debt snowball (focus on one debt at a time beginning with smallest debt to gain momentum).
 Savings • 3. 3 – 6 months expenses in savings. • 4. Invest 15% of your household income into retirement plans. • 5. College funding. • 6. Pay off your home early. • 7. Build wealth and give! • (These steps are meant to be achieved one at a time, in order. )
Savings • 3. 3 – 6 months expenses in savings. • 4. Invest 15% of your household income into retirement plans. • 5. College funding. • 6. Pay off your home early. • 7. Build wealth and give! • (These steps are meant to be achieved one at a time, in order. )
 Savings • Saving must become a priority, but always pay yourself first. • The United States has a negative savings rate. • This means that we have more debt than we have savings! • Money is amoral, meaning it is neither good nor bad.
Savings • Saving must become a priority, but always pay yourself first. • The United States has a negative savings rate. • This means that we have more debt than we have savings! • Money is amoral, meaning it is neither good nor bad.
 Why save money? • Three basic reasons to save money: • 1. Emergency Fund • 2. Purchases • 3. Wealth Building
Why save money? • Three basic reasons to save money: • 1. Emergency Fund • 2. Purchases • 3. Wealth Building
 Why Save Money? • 1. Emergency Funds • Murphy’s Law: Anything that can go wrong, will go wrong! • Emergencies will happen, so plan on it. • A great place to keep your emergency fund is in a Money Market account from a mutual fund company. • You will earn a higher interest rate, which means more money.
Why Save Money? • 1. Emergency Funds • Murphy’s Law: Anything that can go wrong, will go wrong! • Emergencies will happen, so plan on it. • A great place to keep your emergency fund is in a Money Market account from a mutual fund company. • You will earn a higher interest rate, which means more money.
 Why Save Money? • Money Market: Returns a higher interest rates than a savings account, but also requires more of a minimum deposit. • Do not use your emergency fund for purchases. • Purchases are the second thing you save money for.
Why Save Money? • Money Market: Returns a higher interest rates than a savings account, but also requires more of a minimum deposit. • Do not use your emergency fund for purchases. • Purchases are the second thing you save money for.
 Why Save Money? 2. Purchases • Instead of borrowing to purchase, pay cash. • Borrowing money will mean you have to pay an interest on the money, which means you pay more in the long run. • When you pay cash, you can usually negotiate a lower price.
Why Save Money? 2. Purchases • Instead of borrowing to purchase, pay cash. • Borrowing money will mean you have to pay an interest on the money, which means you pay more in the long run. • When you pay cash, you can usually negotiate a lower price.
 Why Save Money? 3. Wealth Building • Building wealth takes time and discipline. • Part of building wealth is investing your savings. • Interest is the key to investing. This is the percent of your money you will receive in return for allowing someone to hold your money.
Why Save Money? 3. Wealth Building • Building wealth takes time and discipline. • Part of building wealth is investing your savings. • Interest is the key to investing. This is the percent of your money you will receive in return for allowing someone to hold your money.
 Savings Investing • Interest: a fee paid to you by the entity holding your money. Usually a percentage of the money you allow them to hold. • Ex. Invest $1000 at 10% interest. • 10% of $1000 is $100, so at the end of the year, you will have $1, 100. • (Secret of how rich get richer!)
Savings Investing • Interest: a fee paid to you by the entity holding your money. Usually a percentage of the money you allow them to hold. • Ex. Invest $1000 at 10% interest. • 10% of $1000 is $100, so at the end of the year, you will have $1, 100. • (Secret of how rich get richer!)
 Savings • Compound Interest: interest paid on interest previously earned. • Ex. You now have $1, 100 after one year. At the end of the next year you will have… • $1, 100 x 10% = $110 • So you will now have $1, 210. • Year 3: $1, 210 x 10% = $121 • So after year 3, you have $1, 331…
Savings • Compound Interest: interest paid on interest previously earned. • Ex. You now have $1, 100 after one year. At the end of the next year you will have… • $1, 100 x 10% = $110 • So you will now have $1, 210. • Year 3: $1, 210 x 10% = $121 • So after year 3, you have $1, 331…
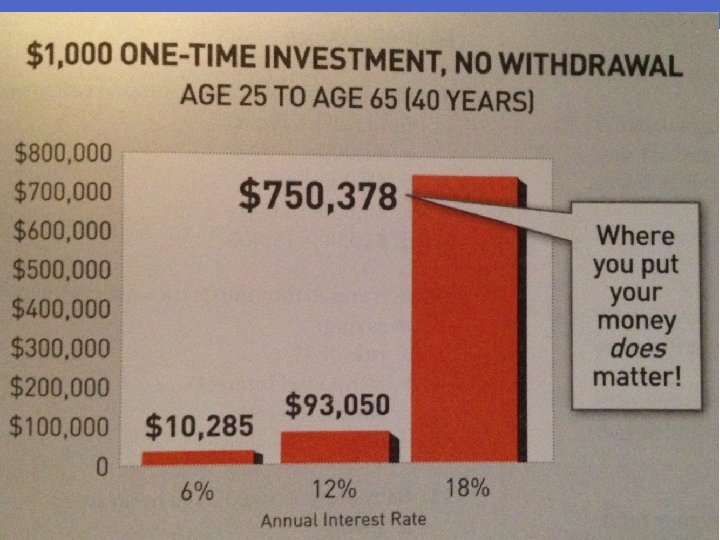
 Savings • How to Calculate Compound Interest: • FV = PV (1 + r/m)mt • FV is the future value • PV is the present value • r is the annual interest rate as a decimal. • m is the number of times a year the interest is compounded (monthly – 12, yearly – 1…) • t is the number of years you invest.
Savings • How to Calculate Compound Interest: • FV = PV (1 + r/m)mt • FV is the future value • PV is the present value • r is the annual interest rate as a decimal. • m is the number of times a year the interest is compounded (monthly – 12, yearly – 1…) • t is the number of years you invest.
 Savings • Ex. You invest $5, 000 for 5 years at 12% compounded yearly. • FV = PV (1 + r/m)mt • FV = 5000(1 +. 12/1)1(5) • FV = 5000(1. 12)5 • FV = 5000(1. 76) • FV = $8, 800 • So after 5 years, you would have $8, 800
Savings • Ex. You invest $5, 000 for 5 years at 12% compounded yearly. • FV = PV (1 + r/m)mt • FV = 5000(1 +. 12/1)1(5) • FV = 5000(1. 12)5 • FV = 5000(1. 76) • FV = $8, 800 • So after 5 years, you would have $8, 800
 Savings The Story of Ben and Arthur • Both save $2, 000 per year at 12% interest. • Ben starts putting in money at age 19 and stops at age 26. • Arthur starts putting in money at age 27 and stops at age 65. • Who will have the most money at the age of 65?
Savings The Story of Ben and Arthur • Both save $2, 000 per year at 12% interest. • Ben starts putting in money at age 19 and stops at age 26. • Arthur starts putting in money at age 27 and stops at age 65. • Who will have the most money at the age of 65?
 Chapter 2: Investment Options
Chapter 2: Investment Options
 Investment Options • KISS: Keep It Simple Stupid! • Don’t put money in anything you don’t understand, and investing does not have to be complex. • Diversification: to spread around your investment dollars among several different things to lower risk. • When you have all of your money in one place, the risk is higher.
Investment Options • KISS: Keep It Simple Stupid! • Don’t put money in anything you don’t understand, and investing does not have to be complex. • Diversification: to spread around your investment dollars among several different things to lower risk. • When you have all of your money in one place, the risk is higher.
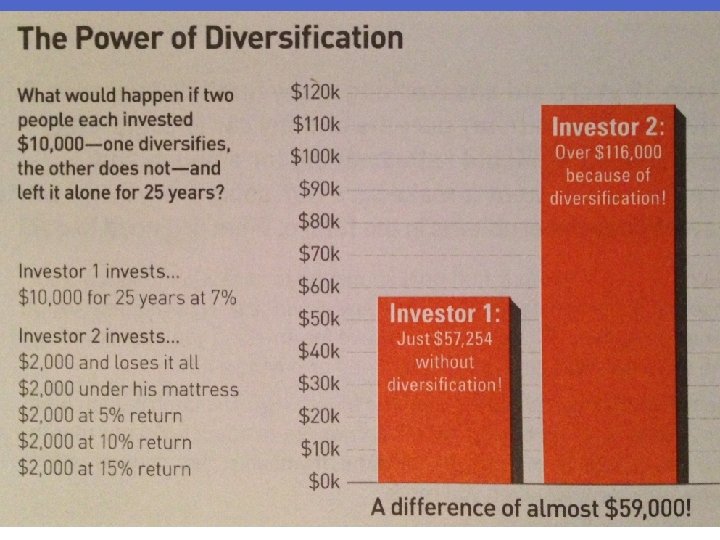
 Investment Options • With almost all investments, as the risk goes up, so does the potential return. • Liquidity: how quickly you can turn the investment into cash. • With more liquidity, the return on investment is less. • Savings accounts are very liquid, so the interest rates are usually lower.
Investment Options • With almost all investments, as the risk goes up, so does the potential return. • Liquidity: how quickly you can turn the investment into cash. • With more liquidity, the return on investment is less. • Savings accounts are very liquid, so the interest rates are usually lower.
 Investment Options • Types of Investments: • 1. Money Markets • 2. Single Stocks • 3. Bonds • 4. Mutual Funds • 5. Real Estate • 6. Annuities
Investment Options • Types of Investments: • 1. Money Markets • 2. Single Stocks • 3. Bonds • 4. Mutual Funds • 5. Real Estate • 6. Annuities
 Investment Options • 1. Money Markets • CD (Certificate of Deposit), usually bought at a bank. • Money market mutual funds are low risk. • Some have check writing privileges. • Great investment for emergency funds. • Very liquid.
Investment Options • 1. Money Markets • CD (Certificate of Deposit), usually bought at a bank. • Money market mutual funds are low risk. • Some have check writing privileges. • Great investment for emergency funds. • Very liquid.
 Investment Options • 2. Single Stocks • Extremely high degree of risk. • When you buy stock, you are buying a small piece of ownership in the company. • Your return comes as the company increases in value or pays you some of the profits (dividends).
Investment Options • 2. Single Stocks • Extremely high degree of risk. • When you buy stock, you are buying a small piece of ownership in the company. • Your return comes as the company increases in value or pays you some of the profits (dividends).
 Investment Options • 3. Bonds • A bond is a debt by which the company owes you money. • Your return is the fluctuation in price and the interest rate paid. • It is like an I. O. U. where the company borrows money from you and pays you interest on the money they borrow.
Investment Options • 3. Bonds • A bond is a debt by which the company owes you money. • Your return is the fluctuation in price and the interest rate paid. • It is like an I. O. U. where the company borrows money from you and pays you interest on the money they borrow.
 Investment Options • 4. Mutual Funds • Investors pool their money to invest. • Portfolio managers manage the pool of money or fund. • Your return comes as the value of the fund is increased. • Mutual funds are good long-term investments.
Investment Options • 4. Mutual Funds • Investors pool their money to invest. • Portfolio managers manage the pool of money or fund. • Your return comes as the value of the fund is increased. • Mutual funds are good long-term investments.
 Investment Options • 5. Real Estate • Least liquid investment! • You should have lots of cash before using real estate as an investment. • Buy property and hold it until it increases in value and then sell it at a higher price. • Risky because of the fluctuations in the price of properties.
Investment Options • 5. Real Estate • Least liquid investment! • You should have lots of cash before using real estate as an investment. • Buy property and hold it until it increases in value and then sell it at a higher price. • Risky because of the fluctuations in the price of properties.
 Investment Options • 6. Annuities • Annuities are savings accounts with an insurance company. • You pay regularly into an account over a long period of time and receive the return at a later point in time. • Mostly used to save for retirement. • Lower risk
Investment Options • 6. Annuities • Annuities are savings accounts with an insurance company. • You pay regularly into an account over a long period of time and receive the return at a later point in time. • Mostly used to save for retirement. • Lower risk
 Building wealth takes time. There are very few people who get rich quickly! If you do, give me some money!
Building wealth takes time. There are very few people who get rich quickly! If you do, give me some money!
 Chapter 3: Wealth Building and College Savings
Chapter 3: Wealth Building and College Savings
 Wealth Building and College Savings • Average graduate of a four year college has student loan debt of $19, 237. • Graduate students: $114, 000 • 46% of Americans have less than $10, 000 saved for retirement. • 13% of teens know what a 401(k) is. • 29% of teens know how to pay for college.
Wealth Building and College Savings • Average graduate of a four year college has student loan debt of $19, 237. • Graduate students: $114, 000 • 46% of Americans have less than $10, 000 saved for retirement. • 13% of teens know what a 401(k) is. • 29% of teens know how to pay for college.
 Wealth Building and College Savings • Lottery Stories! • William Post won $16. 2 million! • His former girlfriend sued him and won part of his winnings. • His brother was arrested for hiring a hit man to kill him for his money. • His other sibling harassed him to invest in businesses and they failed. • After 1 year, he was $1 million in debt!
Wealth Building and College Savings • Lottery Stories! • William Post won $16. 2 million! • His former girlfriend sued him and won part of his winnings. • His brother was arrested for hiring a hit man to kill him for his money. • His other sibling harassed him to invest in businesses and they failed. • After 1 year, he was $1 million in debt!
 Wealth Building and College Savings • Suzanne Mullins won $4. 2 million • Borrowed $200, 000 using her lottery winnings as collateral. • Stopped making payments on the loan. • Company sued her and won. • Today she has no assets.
Wealth Building and College Savings • Suzanne Mullins won $4. 2 million • Borrowed $200, 000 using her lottery winnings as collateral. • Stopped making payments on the loan. • Company sued her and won. • Today she has no assets.
 Wealth Building and College Savings • William Hurt won $3. 1 million. • He spent his money on a divorce and crack cocaine. • Two years later, he was broke and facing murder charges.
Wealth Building and College Savings • William Hurt won $3. 1 million. • He spent his money on a divorce and crack cocaine. • Two years later, he was broke and facing murder charges.
 Wealth Building and College Savings • Baby Step #4: Invest 15% of your household income into Roth IRAs and pre-tax retirement plans. • Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) – government is responsible for insuring or guaranteeing deposits in banks and savings institutions. • Created in 1933 to restore confidence in banks after thousands of them failed
Wealth Building and College Savings • Baby Step #4: Invest 15% of your household income into Roth IRAs and pre-tax retirement plans. • Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) – government is responsible for insuring or guaranteeing deposits in banks and savings institutions. • Created in 1933 to restore confidence in banks after thousands of them failed
 Wealth Building and College Savings • The Federal Reserve (The Fed) – Central banking system of the United States and has four main duties: • 1. Controls the supply of money. • 2. Supervises and regulates banks. • 3. Maintains the stability of the financial system. • 4. Provides financial services to banks.
Wealth Building and College Savings • The Federal Reserve (The Fed) – Central banking system of the United States and has four main duties: • 1. Controls the supply of money. • 2. Supervises and regulates banks. • 3. Maintains the stability of the financial system. • 4. Provides financial services to banks.
 Wealth Building and College Savings • Individual Retirement Arrangement (IRA) – provides tax advantages for retirement savings in the United States. • Roth IRA – After tax IRA that grows tax free. • It provides you with money, tax-free, in retirement, if you follow certain rules. • Tax free money is the best money!
Wealth Building and College Savings • Individual Retirement Arrangement (IRA) – provides tax advantages for retirement savings in the United States. • Roth IRA – After tax IRA that grows tax free. • It provides you with money, tax-free, in retirement, if you follow certain rules. • Tax free money is the best money!
 Wealth Building and College Savings • 401(k), 403(b), & 457 Retirement Plans • You have money deducted from your paycheck before or after taxes toward retirement. • Compounds interests with delayed taxation. • Employers sometimes match your contributions.
Wealth Building and College Savings • 401(k), 403(b), & 457 Retirement Plans • You have money deducted from your paycheck before or after taxes toward retirement. • Compounds interests with delayed taxation. • Employers sometimes match your contributions.
 Wealth Building and College Savings • If you leave a job, rollover your retirement plan to an IRA when you leave so you continue saving for retirement. • Never borrow from your retirement plan. • Summary: Invest for your retirement as soon as you can!
Wealth Building and College Savings • If you leave a job, rollover your retirement plan to an IRA when you leave so you continue saving for retirement. • Never borrow from your retirement plan. • Summary: Invest for your retirement as soon as you can!
 Wealth Building and College Savings College Funding • Save for your children’s education using tax-favored plans. • Educational Savings Accounts (ESA) – You can save $2, 000 per year for 18 years. • You would invest a total of $36, 000, but at 12% growth, your child would have $126, 000 for college – TAX FREE!
Wealth Building and College Savings College Funding • Save for your children’s education using tax-favored plans. • Educational Savings Accounts (ESA) – You can save $2, 000 per year for 18 years. • You would invest a total of $36, 000, but at 12% growth, your child would have $126, 000 for college – TAX FREE!


