47bdb60bfdc33ee3e28e5d8e81ac9320.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts A short explanation and a comparisson by W. D. Schram MSc
Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts A short explanation and a comparisson by W. D. Schram MSc
 Overview Introduction on Roman aqueducts Introduction about Persian qanats Special topics Comparison Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Overview Introduction on Roman aqueducts Introduction about Persian qanats Special topics Comparison Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Aqueducts: basic elements Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Aqueducts: basic elements Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Aqueducts: tunnel Note: a masonry channel inside a tunnel (Cave de Curé, Gier aqueduct, Lyon, France) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Aqueducts: tunnel Note: a masonry channel inside a tunnel (Cave de Curé, Gier aqueduct, Lyon, France) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Aqueducts: bridges The world known aqueduct bridge Pont du Gard, part of the aqueduct (50 km) of Nimes (France). Also represented on a banknote of 5 euro Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Aqueducts: bridges The world known aqueduct bridge Pont du Gard, part of the aqueduct (50 km) of Nimes (France). Also represented on a banknote of 5 euro Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Aqueducts: arcade Two (!) aqueduct channels (70 and 88 km long, mainly subterranean) on top of a series of arches (Rome, Italy) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Aqueducts: arcade Two (!) aqueduct channels (70 and 88 km long, mainly subterranean) on top of a series of arches (Rome, Italy) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 The Roman empire Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
The Roman empire Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Aqueducts: some 750 Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Aqueducts: some 750 Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Aqueducts: the users Local fountain (Gerasa, Jordan) Baths (reconstruction) (Xanten, Germany) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Aqueducts: the users Local fountain (Gerasa, Jordan) Baths (reconstruction) (Xanten, Germany) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
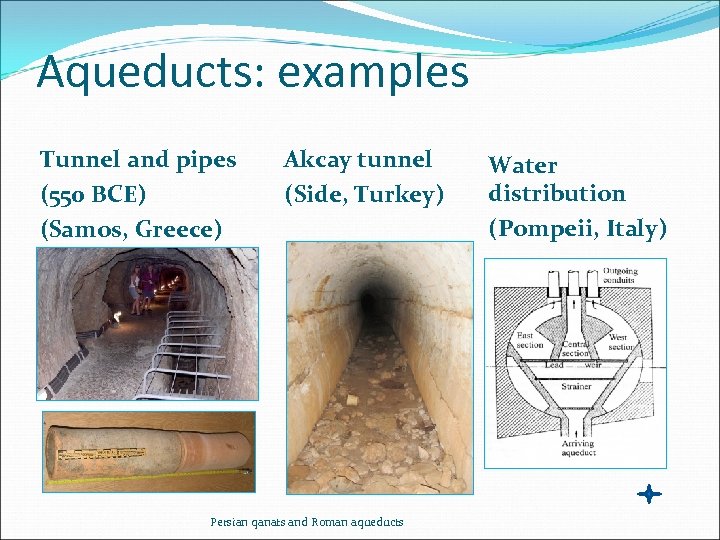 Aqueducts: examples Tunnel and pipes (550 BCE) (Samos, Greece) Akcay tunnel (Side, Turkey) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Water distribution (Pompeii, Italy)
Aqueducts: examples Tunnel and pipes (550 BCE) (Samos, Greece) Akcay tunnel (Side, Turkey) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Water distribution (Pompeii, Italy)
 Qanats: basic elements Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: basic elements Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: channel and shafts Qanat shaft (near Yazd) Shaft tops Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: channel and shafts Qanat shaft (near Yazd) Shaft tops Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: from the air Persepolis Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: from the air Persepolis Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: the users Place to scoop water Water distribution Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: the users Place to scoop water Water distribution Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: works of art Qanat bridge (Kharanaq, Yazd) Ice house (Yazd) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: works of art Qanat bridge (Kharanaq, Yazd) Ice house (Yazd) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
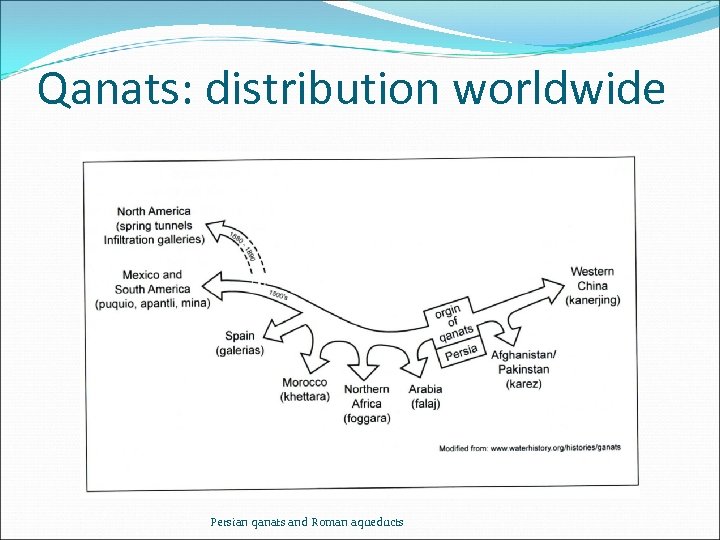 Qanats: distribution worldwide Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: distribution worldwide Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
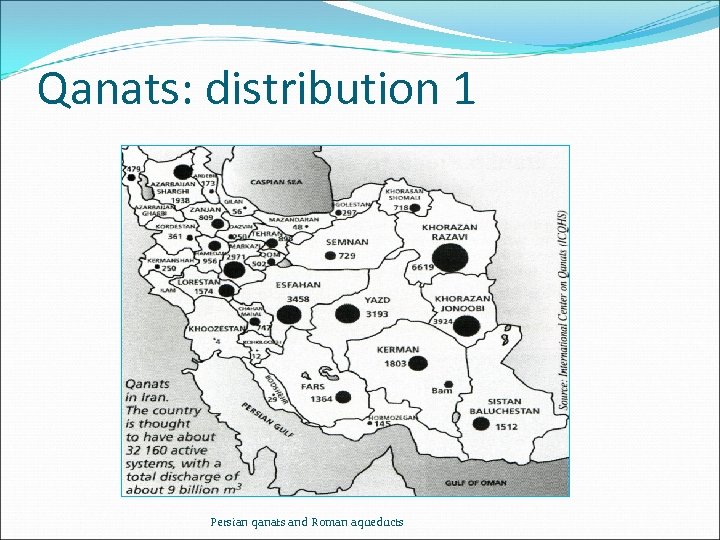 Qanats: distribution 1 Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: distribution 1 Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: distribution 2 Tehran (ca 1960 CE) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Isfahan (1942 CE)
Qanats: distribution 2 Tehran (ca 1960 CE) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Isfahan (1942 CE)
 Qanats: distribution 3 Tafilalt (Maroc) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Qanats in Syria
Qanats: distribution 3 Tafilalt (Maroc) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Qanats in Syria
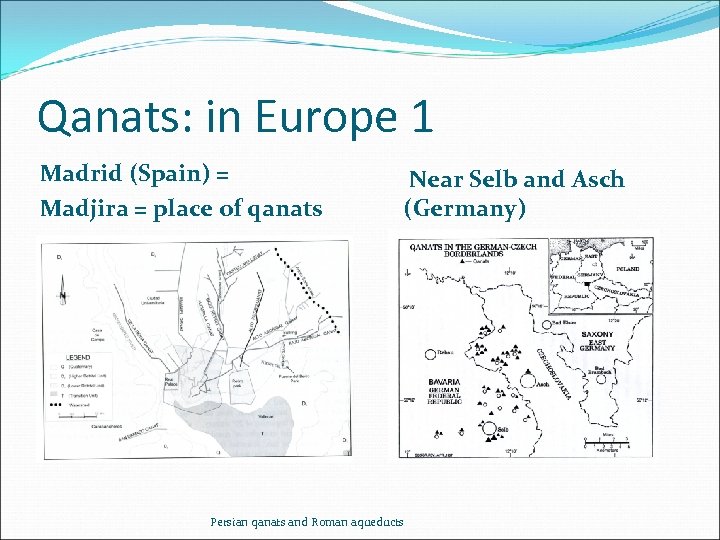 Qanats: in Europe 1 Madrid (Spain) = Madjira = place of qanats Near Selb and Asch (Germany) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: in Europe 1 Madrid (Spain) = Madjira = place of qanats Near Selb and Asch (Germany) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: in Europe 2 The qanat of Walferdange (Luxemburg) with stepped channel and access shafts Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Qanats: in Europe 2 The qanat of Walferdange (Luxemburg) with stepped channel and access shafts Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Qanats: construction Muqanni Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Clay rings for reinforcements
Qanats: construction Muqanni Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Clay rings for reinforcements
 Storage Water storage site Entrance Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Storage Water storage site Entrance Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
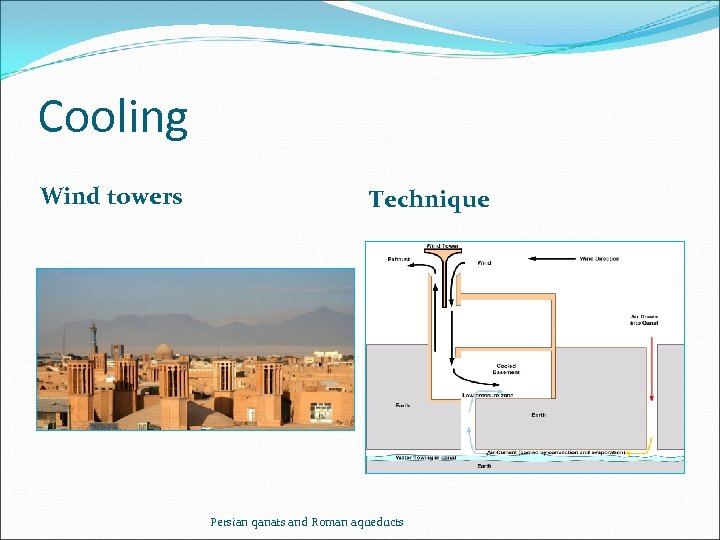 Cooling Wind towers Technique Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Cooling Wind towers Technique Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Ice house Meybod Cross-section Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Ice house Meybod Cross-section Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
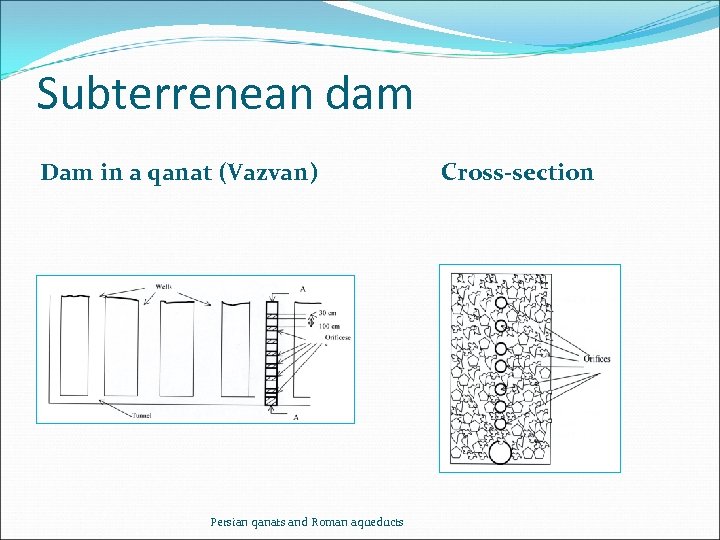 Subterrenean dam Dam in a qanat (Vazvan) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Cross-section
Subterrenean dam Dam in a qanat (Vazvan) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Cross-section
 Subterranean water mill Horizontal water wheel Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Subterranean water mill Horizontal water wheel Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Comparison 1 Element Iranian qanat Roman aqueduct Climate Mainly in arid regions In arid and semi-arid regions Source Aquifer River, spring or dam (by exception: well or aquifer) Place in the landscape 100% subterranean 20% above ground (arcades, substructions) Construction Shafts every 50 – 100 m plus connecting channel Masonry channel (or pipe), sometimes in qanat construction (shaft every 35 – 70 m) Course Straight line Sinuous, following the contour lines Works of art Exceptional: subterranean dams Bridges, tunnels, arcades, siphons Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Comparison 1 Element Iranian qanat Roman aqueduct Climate Mainly in arid regions In arid and semi-arid regions Source Aquifer River, spring or dam (by exception: well or aquifer) Place in the landscape 100% subterranean 20% above ground (arcades, substructions) Construction Shafts every 50 – 100 m plus connecting channel Masonry channel (or pipe), sometimes in qanat construction (shaft every 35 – 70 m) Course Straight line Sinuous, following the contour lines Works of art Exceptional: subterranean dams Bridges, tunnels, arcades, siphons Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Comparison 2 Element Iranian qanat Roman aqueduct Users Public and farmers (private houses, bath houses? ) Public and bathhouses. Also: houses, farmers, ornamental fountains (grainmills) Distribution Channels and sluices; for irrigation timesharing Distribution stations plus lead pipes inside the towns Status Utilitarian / lifeline Additional to other sources (wells, rainwater); luxury (Baths); showcase (Show of pride and power) Builders Well paid specialists Slave specialist, contractors, sometimes support from the military Ownership Coorperative ( 10 – 250 p) Town council Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Comparison 2 Element Iranian qanat Roman aqueduct Users Public and farmers (private houses, bath houses? ) Public and bathhouses. Also: houses, farmers, ornamental fountains (grainmills) Distribution Channels and sluices; for irrigation timesharing Distribution stations plus lead pipes inside the towns Status Utilitarian / lifeline Additional to other sources (wells, rainwater); luxury (Baths); showcase (Show of pride and power) Builders Well paid specialists Slave specialist, contractors, sometimes support from the military Ownership Coorperative ( 10 – 250 p) Town council Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Comparison 3 Element Iranian qanat Roman aqueduct Finance Members of the cooperation Local meacenas, the emperor, twon council Surplus water (only in winter): ? To flush the sewers and toilets, fullers Storage Local in modest volumes No, only behind some large bath houses (e. g. Rome) Basics: - cross-section - typical length - typical discharge - typical depth - typical fall 0, 6 – 1, 2 m 10 km 2. 000 m 3/day 10 – 50 m 0, 07 – 0, 1 % 0, 6 – 1, 2 m 20 km 20. 000 m 3/day 5 m 0, 1 – 0, 5 % Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Comparison 3 Element Iranian qanat Roman aqueduct Finance Members of the cooperation Local meacenas, the emperor, twon council Surplus water (only in winter): ? To flush the sewers and toilets, fullers Storage Local in modest volumes No, only behind some large bath houses (e. g. Rome) Basics: - cross-section - typical length - typical discharge - typical depth - typical fall 0, 6 – 1, 2 m 10 km 2. 000 m 3/day 10 – 50 m 0, 07 – 0, 1 % 0, 6 – 1, 2 m 20 km 20. 000 m 3/day 5 m 0, 1 – 0, 5 % Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Conclusions Although there are similarities, qanats are quite different from roman aqueducts Most striking: the difference in the sources qanat(s) are often the only source of water Roman aqueducts are all out of use Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Conclusions Although there are similarities, qanats are quite different from roman aqueducts Most striking: the difference in the sources qanat(s) are often the only source of water Roman aqueducts are all out of use Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
 Problems ? ! Nonius Datus (150 CE) (Saldae, Algeria) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Tehran (2009 CE)
Problems ? ! Nonius Datus (150 CE) (Saldae, Algeria) Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts Tehran (2009 CE)
 Usefull websites The International Center on Qanats and Historic Hydraulic Structures (ICQHS) in Yazd: http: //www. icqhs. org/English/Default. aspx The Water Museum in Yazd is part of the ICQHS Youtube film about qanats: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ie. BVMOPRYJ 0 Thank you Wilke Schram Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts
Usefull websites The International Center on Qanats and Historic Hydraulic Structures (ICQHS) in Yazd: http: //www. icqhs. org/English/Default. aspx The Water Museum in Yazd is part of the ICQHS Youtube film about qanats: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ie. BVMOPRYJ 0 Thank you Wilke Schram Persian qanats and Roman aqueducts


