a0012887084b6749ba0998a33fa10720.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Perkins IV Program Design Taskforce Day Two & Three Offsite 26 -27 July 2007 With Session Notes Included Taskforce Responses Shown In GREEN Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 1
Perkins IV Program Design Taskforce Day Two & Three Offsite 26 -27 July 2007 With Session Notes Included Taskforce Responses Shown In GREEN Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 1
 PDTF 26 -27 July Agenda Day Two: Ø Ø Ø Day Three: Welcome & Logistics Meeting Objectives for Day Two Recap of Day One (12 July) Tying the Pieces Together Breakout Team Instructions Breakout #1 (Three Teams) Building the CTE Vision v Leveraging Successful Foundation Blocks v Prioritizing & Addressing Obstacles v Report Back to PDTF Ø Group Discussion Ø Expectations for Day Three Recap of Day One (12 July) Ø Breakout #2; Continuing the Work Ø Building the CTE Vision v Leveraging Successful Foundation Blocks v Prioritizing & Addressing Obstacles v Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Report Back to PDTF Group Discussion Optional Breakout #3 Group Discussion of Open Issues Initiating the 4 th Team v Translating Team outputs into Perkins Next Steps for PDTF & Teams Ø Brief Audit Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 2
PDTF 26 -27 July Agenda Day Two: Ø Ø Ø Day Three: Welcome & Logistics Meeting Objectives for Day Two Recap of Day One (12 July) Tying the Pieces Together Breakout Team Instructions Breakout #1 (Three Teams) Building the CTE Vision v Leveraging Successful Foundation Blocks v Prioritizing & Addressing Obstacles v Report Back to PDTF Ø Group Discussion Ø Expectations for Day Three Recap of Day One (12 July) Ø Breakout #2; Continuing the Work Ø Building the CTE Vision v Leveraging Successful Foundation Blocks v Prioritizing & Addressing Obstacles v Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Report Back to PDTF Group Discussion Optional Breakout #3 Group Discussion of Open Issues Initiating the 4 th Team v Translating Team outputs into Perkins Next Steps for PDTF & Teams Ø Brief Audit Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 2
 Welcome, New Introductions & Logistics Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 3
Welcome, New Introductions & Logistics Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 3
 Thoughts Since 12 July? Ø Still confused at how we get there from here v From each Taskforce to the Policy Advisory Committee v How does it tie together v Especially Accountability, Program Design & Special Populations v Link to Professional Development Ø 12 July was a Broad Journey on CTE vs. Perkins — what is our scope? Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 4
Thoughts Since 12 July? Ø Still confused at how we get there from here v From each Taskforce to the Policy Advisory Committee v How does it tie together v Especially Accountability, Program Design & Special Populations v Link to Professional Development Ø 12 July was a Broad Journey on CTE vs. Perkins — what is our scope? Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 4
 Objectives, Groundrules. Assumptions & Expectations Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 5
Objectives, Groundrules. Assumptions & Expectations Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 5
 PDTF Objectives Ø Ø Ø Ø Create a compelling vision of CTE's future Use that vision to think strategically about the biggest opportunities in front of us Identify major challenges/obstacles that need to be overcome Build on past efforts and not reinvent the wheel (including the Transition Taskforce, SB 364, etc. ) Address those challenges that we have control over or can influence (vs. those we have no impact on) Develop specific strategies to make our Vision a reality Translate the above into the Perkins IV 5 -Year Plan Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 6
PDTF Objectives Ø Ø Ø Ø Create a compelling vision of CTE's future Use that vision to think strategically about the biggest opportunities in front of us Identify major challenges/obstacles that need to be overcome Build on past efforts and not reinvent the wheel (including the Transition Taskforce, SB 364, etc. ) Address those challenges that we have control over or can influence (vs. those we have no impact on) Develop specific strategies to make our Vision a reality Translate the above into the Perkins IV 5 -Year Plan Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 6
 Groundrules Assumptions Be here 100% of the time — phones, pagers & Blackberrys off Ø Constructive dialog & even disagreement are welcome Ø Lots to do — please get to the point Ø Respect our diversity — backgrounds, experience, capabilities and uniqueness Ø Aligned, we can get almost anything accomplished v Misaligned, we will melt down Ø v Ø If you miss a meeting Please prepare anyway v Send us your thoughts & proxy v Review the session notes to stay current v No substitutes or stand-ins v Revised 30 July 2007 Perkins IV Funding Distribution Formula Your Role: Active participation v Open minds; honest discussion v Yellow vs. Green Hat v v Ø Off-the-Table for the PDTF: Ø My Role: Help drive us toward our goals v Bring in outside perspective v For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 7
Groundrules Assumptions Be here 100% of the time — phones, pagers & Blackberrys off Ø Constructive dialog & even disagreement are welcome Ø Lots to do — please get to the point Ø Respect our diversity — backgrounds, experience, capabilities and uniqueness Ø Aligned, we can get almost anything accomplished v Misaligned, we will melt down Ø v Ø If you miss a meeting Please prepare anyway v Send us your thoughts & proxy v Review the session notes to stay current v No substitutes or stand-ins v Revised 30 July 2007 Perkins IV Funding Distribution Formula Your Role: Active participation v Open minds; honest discussion v Yellow vs. Green Hat v v Ø Off-the-Table for the PDTF: Ø My Role: Help drive us toward our goals v Bring in outside perspective v For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 7
 Expectations Ø Build on the recommendations of recent efforts — not reinvent the wheel Transition Taskforce v SB 364 v PTE Symposium of 2004 v Ø We are not looking for a one-size-fits-all solution or a cookiecutter approach to CTE Our diversity is our strength — in demographics, local needs, what has worked in the past v We have lots of “good practice” models out there v Ø We are looking for how CTE can/must become: v More responsive to the evolving needs of students & the workforce q v High Skill, High Wage, High Demand More seamless across the spectrum of PK-20 Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 8
Expectations Ø Build on the recommendations of recent efforts — not reinvent the wheel Transition Taskforce v SB 364 v PTE Symposium of 2004 v Ø We are not looking for a one-size-fits-all solution or a cookiecutter approach to CTE Our diversity is our strength — in demographics, local needs, what has worked in the past v We have lots of “good practice” models out there v Ø We are looking for how CTE can/must become: v More responsive to the evolving needs of students & the workforce q v High Skill, High Wage, High Demand More seamless across the spectrum of PK-20 Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 8
 Brief Recap of Day One (12 July Kickoff) Tying the Pieces Together Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 9
Brief Recap of Day One (12 July Kickoff) Tying the Pieces Together Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 9
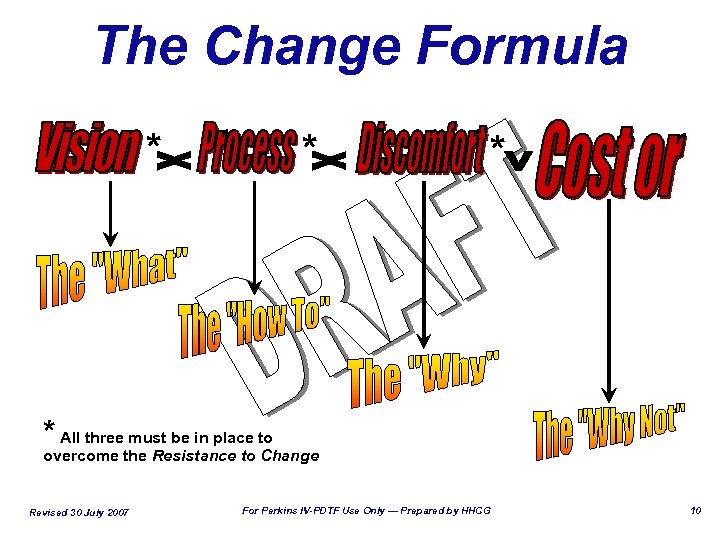 The Change Formula * * All three must be in place to overcome the Resistance to Change Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 10
The Change Formula * * All three must be in place to overcome the Resistance to Change Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 10
 Recap of Day One Ø Discomfort — “The Why” v Feedback from the interviews & the focus group v Trends/big issues facing CTE v What failure looks like Ø Vision — “The What” v Opportunity for CTE v Our 2012 Vision for CTE v Foundation blocks; leverage opportunities Ø Cost or Resistance — “The Why Not” v Challenges/Obstacles for CTE Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 11
Recap of Day One Ø Discomfort — “The Why” v Feedback from the interviews & the focus group v Trends/big issues facing CTE v What failure looks like Ø Vision — “The What” v Opportunity for CTE v Our 2012 Vision for CTE v Foundation blocks; leverage opportunities Ø Cost or Resistance — “The Why Not” v Challenges/Obstacles for CTE Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 11
 The Work of Days Two & Three Ø Refine and flesh out: v Our Vision of 2012 v Foundation Blocks — Leverage Opportunities v Obstacles Ø Translate into the Perkins IV Five Year Plan for CTE Transformation Ø Process — “The How To” v Develop Implementation Strategies & Actions Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 12
The Work of Days Two & Three Ø Refine and flesh out: v Our Vision of 2012 v Foundation Blocks — Leverage Opportunities v Obstacles Ø Translate into the Perkins IV Five Year Plan for CTE Transformation Ø Process — “The How To” v Develop Implementation Strategies & Actions Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 12
 Day One Next Steps Data mine for relevant input to the PDTF Ø Add Industry/Program specific Focus Groups as a strategic & periodic tool to: Ø Solicit feedback from recent grads (2 -to-3 yrs out) v Solicit feedback from employers v Help keep curriculum developers as well as Instructors current and relevant v Help foster stronger ties with industry Ø All PDTF Members — please: Review these notes and suggest clarifications/changes v Look for emerging themes regarding: v Vision q Leverage Foundation Blocks q Challenges & Obstacles q v Revised 30 July 2007 v Try to find that pithy, compelling statement that captures the hearts and minds of CTE’s vision Example: We help people become whole again q One suggestion already: Preparing Our Future Workforce through Effective Learning Systems q For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 13
Day One Next Steps Data mine for relevant input to the PDTF Ø Add Industry/Program specific Focus Groups as a strategic & periodic tool to: Ø Solicit feedback from recent grads (2 -to-3 yrs out) v Solicit feedback from employers v Help keep curriculum developers as well as Instructors current and relevant v Help foster stronger ties with industry Ø All PDTF Members — please: Review these notes and suggest clarifications/changes v Look for emerging themes regarding: v Vision q Leverage Foundation Blocks q Challenges & Obstacles q v Revised 30 July 2007 v Try to find that pithy, compelling statement that captures the hearts and minds of CTE’s vision Example: We help people become whole again q One suggestion already: Preparing Our Future Workforce through Effective Learning Systems q For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 13
 Definitions Mission = "our purpose for being”, raison d’etre Ø Vision = "we are aspiring to become; a vivid idealized description of a desired outcome that inspires, energizes and helps us create a mental picture of our target. " Ø v Ø We will KNOW when the right Vision comes along Foundation Blocks = current good-practices, pilots, models, etc. that have the potential to be leveraged across the Oregon CTE system — adapted for local conditions Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 14
Definitions Mission = "our purpose for being”, raison d’etre Ø Vision = "we are aspiring to become; a vivid idealized description of a desired outcome that inspires, energizes and helps us create a mental picture of our target. " Ø v Ø We will KNOW when the right Vision comes along Foundation Blocks = current good-practices, pilots, models, etc. that have the potential to be leveraged across the Oregon CTE system — adapted for local conditions Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 14
 A Compelling Vision for CTE Vision Candidates: 1. CTE: Adding value to your employment skills 2. CTE: Providing employment skills for today and tomorrow 3. CTE: Increasing employment options 4. CTE: Meeting students needs for successful transitions in life 5. CTE: Engagement, Achievement, Transition 6. CTE: Career preparation today for a secure future tomorrow 7. CTE: Creating a future of opportunities 8. CTE: Planning for a future of opportunities 9. CTE: An integral part of public education; designed to educate about, through, and for careers Revised 30 July 2007 10. CTE: We connect education and careers! 11. CTE: A key partner in Oregon Economic Development 12. CTE: Providing the tools to build careers 13. CTE: Building careers, prosperity, and self respect 14. CTE: Preparing youth for life 15. CTE: We build careers 16. CTE: Strategies for success 17. CTE: The bridge to prosperity 18. CTE: The link between learning and life 19. CTE: Preparing today's youth for tomorrow's careers 20. CTE: Preparing Our Future Workforce through Effective Learning Systems For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 15
A Compelling Vision for CTE Vision Candidates: 1. CTE: Adding value to your employment skills 2. CTE: Providing employment skills for today and tomorrow 3. CTE: Increasing employment options 4. CTE: Meeting students needs for successful transitions in life 5. CTE: Engagement, Achievement, Transition 6. CTE: Career preparation today for a secure future tomorrow 7. CTE: Creating a future of opportunities 8. CTE: Planning for a future of opportunities 9. CTE: An integral part of public education; designed to educate about, through, and for careers Revised 30 July 2007 10. CTE: We connect education and careers! 11. CTE: A key partner in Oregon Economic Development 12. CTE: Providing the tools to build careers 13. CTE: Building careers, prosperity, and self respect 14. CTE: Preparing youth for life 15. CTE: We build careers 16. CTE: Strategies for success 17. CTE: The bridge to prosperity 18. CTE: The link between learning and life 19. CTE: Preparing today's youth for tomorrow's careers 20. CTE: Preparing Our Future Workforce through Effective Learning Systems For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 15
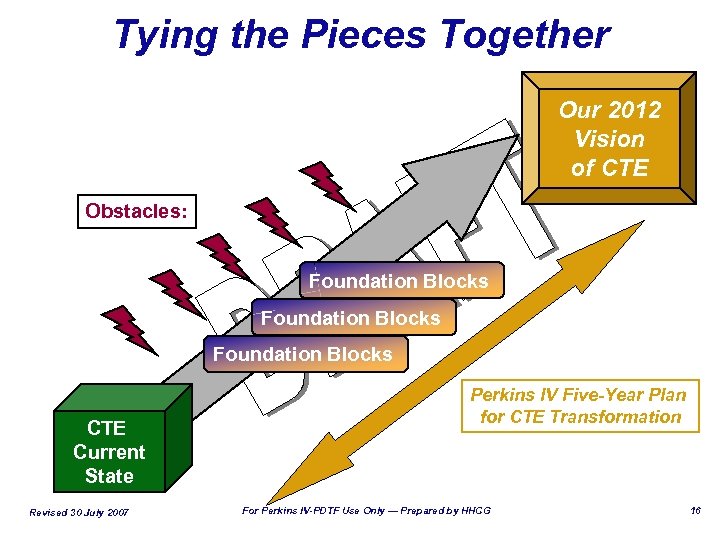 Tying the Pieces Together Our 2012 Vision of CTE Obstacles: Foundation Blocks CTE Current State Revised 30 July 2007 Perkins IV Five-Year Plan for CTE Transformation For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 16
Tying the Pieces Together Our 2012 Vision of CTE Obstacles: Foundation Blocks CTE Current State Revised 30 July 2007 Perkins IV Five-Year Plan for CTE Transformation For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 16
 Breakout Instructions * Building Our CTE Vision * Leveraging Foundation Blocks * Addressing Obstacles Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 17
Breakout Instructions * Building Our CTE Vision * Leveraging Foundation Blocks * Addressing Obstacles Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 17
 Team A. Building Our CTE Vision Ø Tasks: v Pick a Scribe and a Presenter v Group the points from the Vision brainstorming 12 July into themes v Get rid of duplications and redundancies v Pick/develop the Top-Five Compelling & Pithy Statements v What key actions would help make our Vision a reality? v Explore how to best package this Vision for others — marketing tactics q Format: Narrative vs. Day-in-the-Life vs. Other q Identify your major audiences (e. g. , CTE candidates, local Boards, Faculty, Parents, Employers/Industry Associations) q Strategize on how CTE should communicate this Vision to each of these audiences Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 18
Team A. Building Our CTE Vision Ø Tasks: v Pick a Scribe and a Presenter v Group the points from the Vision brainstorming 12 July into themes v Get rid of duplications and redundancies v Pick/develop the Top-Five Compelling & Pithy Statements v What key actions would help make our Vision a reality? v Explore how to best package this Vision for others — marketing tactics q Format: Narrative vs. Day-in-the-Life vs. Other q Identify your major audiences (e. g. , CTE candidates, local Boards, Faculty, Parents, Employers/Industry Associations) q Strategize on how CTE should communicate this Vision to each of these audiences Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 18
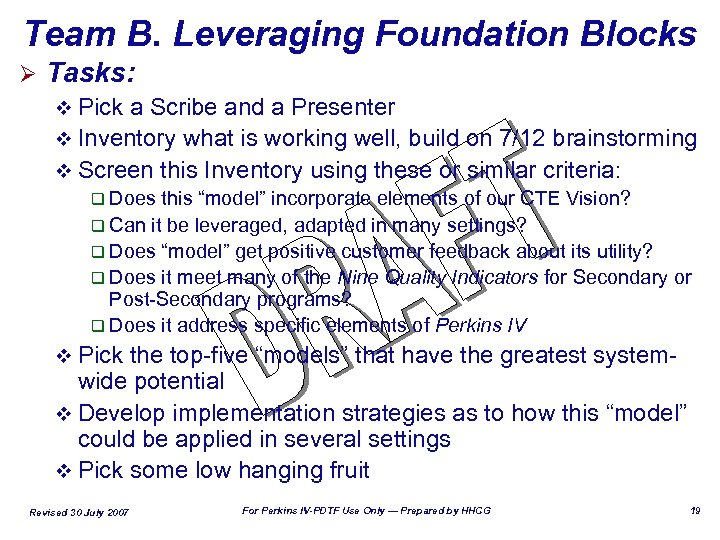 Team B. Leveraging Foundation Blocks Ø Tasks: v Pick a Scribe and a Presenter v Inventory what is working well, build on 7/12 brainstorming v Screen this Inventory using these or similar criteria: q Does this “model” incorporate elements of our CTE Vision? q Can it be leveraged, adapted in many settings? q Does “model” get positive customer feedback about its utility? q Does it meet many of the Nine Quality Indicators for Secondary or Post-Secondary programs? q Does it address specific elements of Perkins IV v Pick the top-five “models” that have the greatest system- wide potential v Develop implementation strategies as to how this “model” could be applied in several settings v Pick some low hanging fruit Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 19
Team B. Leveraging Foundation Blocks Ø Tasks: v Pick a Scribe and a Presenter v Inventory what is working well, build on 7/12 brainstorming v Screen this Inventory using these or similar criteria: q Does this “model” incorporate elements of our CTE Vision? q Can it be leveraged, adapted in many settings? q Does “model” get positive customer feedback about its utility? q Does it meet many of the Nine Quality Indicators for Secondary or Post-Secondary programs? q Does it address specific elements of Perkins IV v Pick the top-five “models” that have the greatest system- wide potential v Develop implementation strategies as to how this “model” could be applied in several settings v Pick some low hanging fruit Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 19
 Team C. Addressing Obstacles Ø Tasks: v Pick a Scribe and a Presenter v Categorize into three groups q Which obstacles do we have direct control over? q Which ones can we influence? q Which one do we have no impact or control over? v Choose the “deal-breakers”, those obstacles whose resolution are pre-requisites to our achieving our Vision v Set priorities for the first two buckets (control over & can influence) v Start with the “deal-breakers”, i. e. , top-priorities q Clearly define the obstacle & who are the key parties involved q Who else needs to be at the table to help overcome this obstacle? q Develop the case for change (cost-benefit, tradeoffs) q Develop work-arounds where relevant Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 20
Team C. Addressing Obstacles Ø Tasks: v Pick a Scribe and a Presenter v Categorize into three groups q Which obstacles do we have direct control over? q Which ones can we influence? q Which one do we have no impact or control over? v Choose the “deal-breakers”, those obstacles whose resolution are pre-requisites to our achieving our Vision v Set priorities for the first two buckets (control over & can influence) v Start with the “deal-breakers”, i. e. , top-priorities q Clearly define the obstacle & who are the key parties involved q Who else needs to be at the table to help overcome this obstacle? q Develop the case for change (cost-benefit, tradeoffs) q Develop work-arounds where relevant Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 20
 Perkins IV Program Design Taskforce Day Three Offsite 27 July 2007 Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 21
Perkins IV Program Design Taskforce Day Three Offsite 27 July 2007 Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 21
 PDTF 26 -27 July Agenda Day Two: Ø Ø Ø Day Three: Welcome & Logistics Meeting Objectives for Day Two Recap of Day One (12 July) Tying the Pieces Together Breakout Team Instructions Breakout #1 (Three Teams) Ø Ø Ø Building the CTE Vision v Leveraging Successful Foundation Ø Blocks v Prioritizing & Addressing Obstacles v Report Back to PDTF Ø Group Discussion Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Recap of Day One (12 July) Knowledge-Based Economy Breakout #2; Continuing the Work Report Back to PDTF Group Discussion of Some Key Issues Path Forward v Initiating the 4 th Team Translating Team Outputs into Perkins Brief Audit Ø Meeting Close Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 22
PDTF 26 -27 July Agenda Day Two: Ø Ø Ø Day Three: Welcome & Logistics Meeting Objectives for Day Two Recap of Day One (12 July) Tying the Pieces Together Breakout Team Instructions Breakout #1 (Three Teams) Ø Ø Ø Building the CTE Vision v Leveraging Successful Foundation Ø Blocks v Prioritizing & Addressing Obstacles v Report Back to PDTF Ø Group Discussion Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Recap of Day One (12 July) Knowledge-Based Economy Breakout #2; Continuing the Work Report Back to PDTF Group Discussion of Some Key Issues Path Forward v Initiating the 4 th Team Translating Team Outputs into Perkins Brief Audit Ø Meeting Close Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 22
 KBE Economy (Knowledge-Based Enterprises) Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 23
KBE Economy (Knowledge-Based Enterprises) Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 23
 “The World is Flat” — 10 Flatteners 1. Berlin Wall Comes Down November 1989 2. When Netscape Went Public, August 1995 from PC to Internet Based Platform 3. Workflow software enables a global supply chain 4. Open Sourcing — Shareware 5. Outsourcing — Y 2 K; Using telecom to contract to another firm in another country 6. Off Shoring — Moving a U. S. factory to another country 7. Supply Chaining — Connected throughout the chain without owner control 8. In Sourcing — UPS into your company 9. Informing — The ability to build and deploy your own personal supply chain; a supply chain of information, knowledge, and entertainment. (Google, Yahoo, MSN Web Search) 10. The Steroids — Digital, Mobile, Wireless, Personal and Virtual Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 24
“The World is Flat” — 10 Flatteners 1. Berlin Wall Comes Down November 1989 2. When Netscape Went Public, August 1995 from PC to Internet Based Platform 3. Workflow software enables a global supply chain 4. Open Sourcing — Shareware 5. Outsourcing — Y 2 K; Using telecom to contract to another firm in another country 6. Off Shoring — Moving a U. S. factory to another country 7. Supply Chaining — Connected throughout the chain without owner control 8. In Sourcing — UPS into your company 9. Informing — The ability to build and deploy your own personal supply chain; a supply chain of information, knowledge, and entertainment. (Google, Yahoo, MSN Web Search) 10. The Steroids — Digital, Mobile, Wireless, Personal and Virtual Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 24
 KBE Economy Hypothesis: Every person, company or organization has unique knowledge with KBE market value KBE Definition and Characteristics: Ø A KBE economy is driven by the production, distribution and use of knowledge for growth, wealth creation and employment increases Ø KBE competition is based in innovation rather than price as in classical economies Ø Countries and regions that show more evidence of innovation are richer and grow faster Ø Companies that show more evidence of innovation post better financial performance Ø Innovation is the productive use of knowledge Ø Innovation is largely connecting existing ideas in a new way — not inventing Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 25
KBE Economy Hypothesis: Every person, company or organization has unique knowledge with KBE market value KBE Definition and Characteristics: Ø A KBE economy is driven by the production, distribution and use of knowledge for growth, wealth creation and employment increases Ø KBE competition is based in innovation rather than price as in classical economies Ø Countries and regions that show more evidence of innovation are richer and grow faster Ø Companies that show more evidence of innovation post better financial performance Ø Innovation is the productive use of knowledge Ø Innovation is largely connecting existing ideas in a new way — not inventing Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 25
 Key Components & Strategies of a KBE Economy Education Level l Percentage of College graduates is a primary driver to higher per capita income — but not the only one Science and Technology Activity Innovation Across Industries and Sectors l. Productivity gains do not depend on what region an industry competes in, but rather how it competes Talent Strategy l 75% or personal income growth during the 90’s tied to technology output Export-Oriented Industries l Industries oriented to national/global markets produce higher value products and pay more l. Regions that promote talent across industries are most likely to become economic winners Reduction of Poverty and Inequality l. Broad-based well-being of residents Entrepreneurial Initiative l 90% of the new jobs created in the and decreased poverty are important for sustained increases in economic growth new economy will be generated by companies of 10 or less employees Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 26
Key Components & Strategies of a KBE Economy Education Level l Percentage of College graduates is a primary driver to higher per capita income — but not the only one Science and Technology Activity Innovation Across Industries and Sectors l. Productivity gains do not depend on what region an industry competes in, but rather how it competes Talent Strategy l 75% or personal income growth during the 90’s tied to technology output Export-Oriented Industries l Industries oriented to national/global markets produce higher value products and pay more l. Regions that promote talent across industries are most likely to become economic winners Reduction of Poverty and Inequality l. Broad-based well-being of residents Entrepreneurial Initiative l 90% of the new jobs created in the and decreased poverty are important for sustained increases in economic growth new economy will be generated by companies of 10 or less employees Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: Vi. TAL Economy 26
 What Does This Mean for CTE? Taskforce Responses: Ø Are we preparing people for our region or for a KBE Economy? ” Ø For what labor market are we preparing our students? Ø v Ø Ø Ø Some regions have 95% companies with 5 or less (Rogue Valley) Ø How do we address a highly diversified market? School-based Enterprises movement — marketing, finances, skills Cultural diversity needs to be embedded in our knowledge and skills Ø We may have an increasing disparity in rich-vs. -poor Ø Need students who are well-rounded, have diversified skills, generalists v Ø How to sell & present themselves Secondary vs. Post-Secondary responsibilities are different Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Problem-solving and creativity are also important Challenges us to think about how we define “Program” v CTE opportunities vs. CTE programs May shift the training and professional development for Student Services Team To allow students to design their own programs v AGS can be oriented to this v Those programs do not require approval — components are identified locally v Challenges us to think about resource allocation Self-Employment data not included in Labor Dept data Must teach self-created, self-directed working world; selling self For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 27
What Does This Mean for CTE? Taskforce Responses: Ø Are we preparing people for our region or for a KBE Economy? ” Ø For what labor market are we preparing our students? Ø v Ø Ø Ø Some regions have 95% companies with 5 or less (Rogue Valley) Ø How do we address a highly diversified market? School-based Enterprises movement — marketing, finances, skills Cultural diversity needs to be embedded in our knowledge and skills Ø We may have an increasing disparity in rich-vs. -poor Ø Need students who are well-rounded, have diversified skills, generalists v Ø How to sell & present themselves Secondary vs. Post-Secondary responsibilities are different Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Problem-solving and creativity are also important Challenges us to think about how we define “Program” v CTE opportunities vs. CTE programs May shift the training and professional development for Student Services Team To allow students to design their own programs v AGS can be oriented to this v Those programs do not require approval — components are identified locally v Challenges us to think about resource allocation Self-Employment data not included in Labor Dept data Must teach self-created, self-directed working world; selling self For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 27
 Reportouts & Discussion * Building Our CTE Vision * Leveraging Foundation Blocks * Addressing Obstacles Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 28
Reportouts & Discussion * Building Our CTE Vision * Leveraging Foundation Blocks * Addressing Obstacles Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 28
 Team A. Building Our CTE Vision Taskforce Responses: Process went well Ø Lots of brainstorming Ø Washington State efforts = a good source of ideas Ø Marketing strategy Ø By target audience v Message content v Delivery ideas v Working on the pithy statement Ø CTE: Learning for life Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 29
Team A. Building Our CTE Vision Taskforce Responses: Process went well Ø Lots of brainstorming Ø Washington State efforts = a good source of ideas Ø Marketing strategy Ø By target audience v Message content v Delivery ideas v Working on the pithy statement Ø CTE: Learning for life Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 29
 Team B. Leveraging Foundation Blocks Taskforce Responses: Ø Grouped our work into three areas: v q Advising tools for students; make this The “Green Category” v Student Support v a part of a POS q Connect to proficiencies q Robust Student Support Centers v Ø What if the POS could be articulated across the 2 ndary/Post 2 ndary interface? v Talk about “block-transfer” rather than course-by-course v Curriculum Group Discussion: v What we need to improve: q More consistency q Proficiency base orientation q Broader transferability q More formalized 2 ndary/Post-2 ndary re assessing technical skills — this is a policy issue (beyond Perkins, beyond CTE) Coalescing elements of Programs of Study with Professional Development v Lots of implications beyond Perkins — transforming CTE, supporting our system work, setting policy v Revised 30 July 2007 Roadmaps Ø Process: Really interested in working on the Student Support Systems and addressing “deficits” v Coordinating student plans v Electronic delivery of instruction & guidance v Work ethics & leadership — strengthen our organizations that represent different pieces of curriculum (FFA, DECA, etc. ) v For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 30
Team B. Leveraging Foundation Blocks Taskforce Responses: Ø Grouped our work into three areas: v q Advising tools for students; make this The “Green Category” v Student Support v a part of a POS q Connect to proficiencies q Robust Student Support Centers v Ø What if the POS could be articulated across the 2 ndary/Post 2 ndary interface? v Talk about “block-transfer” rather than course-by-course v Curriculum Group Discussion: v What we need to improve: q More consistency q Proficiency base orientation q Broader transferability q More formalized 2 ndary/Post-2 ndary re assessing technical skills — this is a policy issue (beyond Perkins, beyond CTE) Coalescing elements of Programs of Study with Professional Development v Lots of implications beyond Perkins — transforming CTE, supporting our system work, setting policy v Revised 30 July 2007 Roadmaps Ø Process: Really interested in working on the Student Support Systems and addressing “deficits” v Coordinating student plans v Electronic delivery of instruction & guidance v Work ethics & leadership — strengthen our organizations that represent different pieces of curriculum (FFA, DECA, etc. ) v For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 30
 Team C. Addressing Obstacles Taskforce Responses: Ø Discussed the obstacles to death Root causes a long list v Isolated top five v Ø Some solutions have been identified Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 31
Team C. Addressing Obstacles Taskforce Responses: Ø Discussed the obstacles to death Root causes a long list v Isolated top five v Ø Some solutions have been identified Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 31
 Key Discussion Items Ø Programs of Study provide the framework in which Perkins funded CTE will be designed and implemented. What is your vision of Oregon’s model (Perkins) Program of Study? Are there additional elements (beyond the Perkins Act specifications) that Oregon should incorporate to achieve this model Program of Study? Is co-approval of secondary and post secondary Programs of Study possible and useful? v What role should curriculum alignment and articulation (transfer of credit) play in the Program of Study framework? v What refinements are necessary in the Quality Assurance standards to support the implementation of the Program of Study? v What are the “wrap around” student services that are necessary to fully implement the Perkins Programs of Study? v Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 32
Key Discussion Items Ø Programs of Study provide the framework in which Perkins funded CTE will be designed and implemented. What is your vision of Oregon’s model (Perkins) Program of Study? Are there additional elements (beyond the Perkins Act specifications) that Oregon should incorporate to achieve this model Program of Study? Is co-approval of secondary and post secondary Programs of Study possible and useful? v What role should curriculum alignment and articulation (transfer of credit) play in the Program of Study framework? v What refinements are necessary in the Quality Assurance standards to support the implementation of the Program of Study? v What are the “wrap around” student services that are necessary to fully implement the Perkins Programs of Study? v Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 32
 Key Discussion Item #1 Ø Ø What is your vision of Oregon’s model (Perkins) Program of Study? Are there additional elements (beyond the Perkins Act specifications) that Oregon should incorporate to achieve this model Program of Study? Is co-approval of secondary and post secondary Programs of Study possible and useful? Revised 30 July 2007 Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 33
Key Discussion Item #1 Ø Ø What is your vision of Oregon’s model (Perkins) Program of Study? Are there additional elements (beyond the Perkins Act specifications) that Oregon should incorporate to achieve this model Program of Study? Is co-approval of secondary and post secondary Programs of Study possible and useful? Revised 30 July 2007 Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 33
 Key Discussion Item #2 Ø Ø What role should curriculum alignment and articulation (transfer of credit) play in the Program of Study framework? Revised 30 July 2007 Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 34
Key Discussion Item #2 Ø Ø What role should curriculum alignment and articulation (transfer of credit) play in the Program of Study framework? Revised 30 July 2007 Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 34
 Key Discussion Item #3 What refinements are necessary in the Quality Assurance standards to support the implementation of the Program of Study? Taskforce Responses: Ø Ø Ø Need to expand this to include Post. Secondary CTE Programs Driven by local control A self-reflective process What’s Working: Process makes you go through lots of steps to analyze what’s going on in the classroom v It gets Administrators up to speed on the classroom setting; is CTE in our schoolimprovement plan (e. g. , contextual learning) v Serves as a quality improvement tool Ø Ideas: v v Ø What’s Not Working: Revised 30 July 2007 v v It’s easy to put down stuff, but not do it v Only tied/customized to CTE/Perkins v Programs are teacher-dependent; attrition hurts v v Needs greater district-level tie-in Needs to have more ‘meat’ and follow-through Needs good oversight and consequences for not doing it (e. g. , tied to teacher-evaluation) Could be adapted to fit non-CTE Programs Link to the Legislative requirement of School Districts to have/implement an improvement plan Exit exams/criteria ought to be included in the future For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 35
Key Discussion Item #3 What refinements are necessary in the Quality Assurance standards to support the implementation of the Program of Study? Taskforce Responses: Ø Ø Ø Need to expand this to include Post. Secondary CTE Programs Driven by local control A self-reflective process What’s Working: Process makes you go through lots of steps to analyze what’s going on in the classroom v It gets Administrators up to speed on the classroom setting; is CTE in our schoolimprovement plan (e. g. , contextual learning) v Serves as a quality improvement tool Ø Ideas: v v Ø What’s Not Working: Revised 30 July 2007 v v It’s easy to put down stuff, but not do it v Only tied/customized to CTE/Perkins v Programs are teacher-dependent; attrition hurts v v Needs greater district-level tie-in Needs to have more ‘meat’ and follow-through Needs good oversight and consequences for not doing it (e. g. , tied to teacher-evaluation) Could be adapted to fit non-CTE Programs Link to the Legislative requirement of School Districts to have/implement an improvement plan Exit exams/criteria ought to be included in the future For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 35
 Key Discussion Item #4 (1 of 2) Ø What are the robust student services system that are necessary to fully implement the Perkins Programs of Study? Taskforce Responses: Bigger than the counselors Ø Inclusive — all students: Ø Secondary v Post-Secondary v Special Populations v Ø What’s working? v v v Many elements are in place somewhere Career-related standards as a diploma requirement Tutoring labs are in place at all CCs in some shape or form Many campuses have cultural-diversity ctrs, offering special help Special ambassador programs Internships Ideas — critical need for more professional development Ø Make sure funding follows policy Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 36
Key Discussion Item #4 (1 of 2) Ø What are the robust student services system that are necessary to fully implement the Perkins Programs of Study? Taskforce Responses: Bigger than the counselors Ø Inclusive — all students: Ø Secondary v Post-Secondary v Special Populations v Ø What’s working? v v v Many elements are in place somewhere Career-related standards as a diploma requirement Tutoring labs are in place at all CCs in some shape or form Many campuses have cultural-diversity ctrs, offering special help Special ambassador programs Internships Ideas — critical need for more professional development Ø Make sure funding follows policy Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 36
 Key Discussion Item #4 (2 of 2) Ø What are the robust student services system that are necessary to fully implement the Perkins Programs of Study? Taskforce Responses: Ø What’s not working or lacking? v v v v v There isn’t a comprehensive system across the CTE spectrum Plan-profiles aren’t carried through Lack a system-wide electronic portfolio In many student services dept. ’s the focus is still on college No correlation between HS assessment test and College placement test Huge gap between HS grad requirements and Post-secondary entry or career readiness Lack of integration of academic with career counseling — gets worse as you go up in years Deficiency in personnel especially re special populations Transition between 2 ndary and Post-2 ndary for students with disabilities Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 37
Key Discussion Item #4 (2 of 2) Ø What are the robust student services system that are necessary to fully implement the Perkins Programs of Study? Taskforce Responses: Ø What’s not working or lacking? v v v v v There isn’t a comprehensive system across the CTE spectrum Plan-profiles aren’t carried through Lack a system-wide electronic portfolio In many student services dept. ’s the focus is still on college No correlation between HS assessment test and College placement test Huge gap between HS grad requirements and Post-secondary entry or career readiness Lack of integration of academic with career counseling — gets worse as you go up in years Deficiency in personnel especially re special populations Transition between 2 ndary and Post-2 ndary for students with disabilities Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 37
 Path Forward & Wrapup Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 38
Path Forward & Wrapup Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 38
 Path Forward Each Team — Staff to “clean-up” Word file from Day’s Two and Three, then Stan to integrate Ø Based on feedback from the PDTF and the above integrated file, design Days Four and Five Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 39
Path Forward Each Team — Staff to “clean-up” Word file from Day’s Two and Three, then Stan to integrate Ø Based on feedback from the PDTF and the above integrated file, design Days Four and Five Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 39
 Perkins IV Program Design Taskforce Day Two Offsite 26 July 2007 BACKUP SLIDES Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 40
Perkins IV Program Design Taskforce Day Two Offsite 26 July 2007 BACKUP SLIDES Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 40
 Perkins IV Ø The Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 provides funding for approved high school and community college career and technical education programs v Ø The purpose of this reauthorized Act is to develop the academic, career and technical knowledge, and skills of secondary and postsecondary students who elect to enroll in career and technical education programs. Each state that seeks funding under this Act must submit a one-year State Transition Plan (2007 -08) followed by a fiveyear State Plan (2008 -2013) v The development of the State Plan must allow for input from a broad array of stakeholders including: teachers, counselors, administrators, parents, students, institutions of higher education, members of Tech Prep consortiums, the State Workforce Investment Board, interested community members, representatives from special populations, business and industry, and labor. Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 41
Perkins IV Ø The Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 provides funding for approved high school and community college career and technical education programs v Ø The purpose of this reauthorized Act is to develop the academic, career and technical knowledge, and skills of secondary and postsecondary students who elect to enroll in career and technical education programs. Each state that seeks funding under this Act must submit a one-year State Transition Plan (2007 -08) followed by a fiveyear State Plan (2008 -2013) v The development of the State Plan must allow for input from a broad array of stakeholders including: teachers, counselors, administrators, parents, students, institutions of higher education, members of Tech Prep consortiums, the State Workforce Investment Board, interested community members, representatives from special populations, business and industry, and labor. Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 41
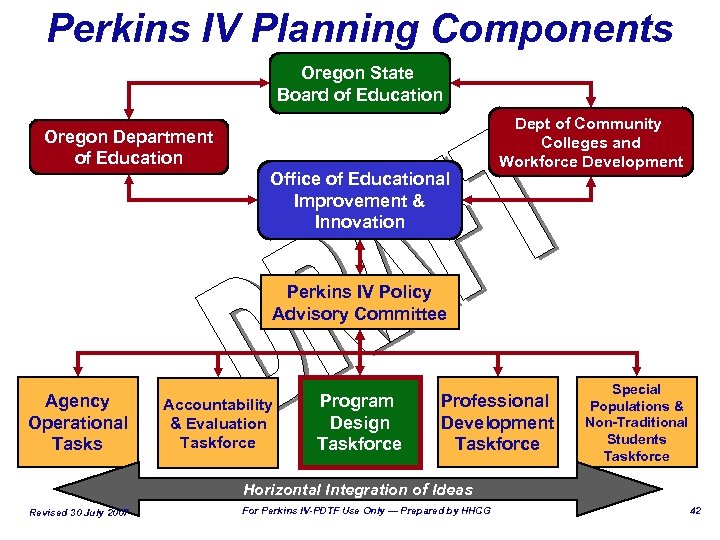 Perkins IV Planning Components Oregon State Board of Education Oregon Department of Education Office of Educational Improvement & Innovation Dept of Community Colleges and Workforce Development Perkins IV Policy Advisory Committee Agency Operational Tasks Accountability & Evaluation Taskforce Program Design Taskforce Professional Development Taskforce Special Populations & Non-Traditional Students Taskforce Horizontal Integration of Ideas Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 42
Perkins IV Planning Components Oregon State Board of Education Oregon Department of Education Office of Educational Improvement & Innovation Dept of Community Colleges and Workforce Development Perkins IV Policy Advisory Committee Agency Operational Tasks Accountability & Evaluation Taskforce Program Design Taskforce Professional Development Taskforce Special Populations & Non-Traditional Students Taskforce Horizontal Integration of Ideas Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 42
 Who Are Our Customers? Ø Who we each consider to be our customers helps determine the degree of alignment across the CTE spectrum: Intermediate-Customers? Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Our Org’s Management Local School Board State Agency (ODE, CCWD, etc. ) State Board of Education Feds Next Org in Line Students Workforce Oregon Employers Society Revised 30 July 2007 End-Customers? Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Our Org’s Management Local School Board State Agency (ODE, CCWD, etc. ) State Board of Education Feds Next Org in Line Students Workforce Oregon Employers Society For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 43
Who Are Our Customers? Ø Who we each consider to be our customers helps determine the degree of alignment across the CTE spectrum: Intermediate-Customers? Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Our Org’s Management Local School Board State Agency (ODE, CCWD, etc. ) State Board of Education Feds Next Org in Line Students Workforce Oregon Employers Society Revised 30 July 2007 End-Customers? Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Our Org’s Management Local School Board State Agency (ODE, CCWD, etc. ) State Board of Education Feds Next Org in Line Students Workforce Oregon Employers Society For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 43
 Discussion of the Opportunity for CTE Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 44
Discussion of the Opportunity for CTE Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 44
 Important Trends Ø Education Week 12 June ‘ 07: v “Employers interviewed said they were able to redesign jobs around academic-skills deficiencies, but not soft-skills deficiencies” v “One of the biggest crises facing CTE is a teacher shortage. It’s a huge issue” v “For some kids, it is awfully important that they see a job at the end of a sequence of classes” v “We need to dramatically increase postsecondary attainment, especially among underserved groups. Without them, we simply cannot produce enough workers for the jobs of the future, and we risk further expanding the American family-income divide” v “Aiming to prepare 100% of students for the 40% of society’s jobs that require [4 -year] college skills makes good politics, but bad economics, and it will create a lot of disappointment” Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 45
Important Trends Ø Education Week 12 June ‘ 07: v “Employers interviewed said they were able to redesign jobs around academic-skills deficiencies, but not soft-skills deficiencies” v “One of the biggest crises facing CTE is a teacher shortage. It’s a huge issue” v “For some kids, it is awfully important that they see a job at the end of a sequence of classes” v “We need to dramatically increase postsecondary attainment, especially among underserved groups. Without them, we simply cannot produce enough workers for the jobs of the future, and we risk further expanding the American family-income divide” v “Aiming to prepare 100% of students for the 40% of society’s jobs that require [4 -year] college skills makes good politics, but bad economics, and it will create a lot of disappointment” Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 45
 Important Trends, cont’d Ø Diplomas Count 2007 — A Conversation with the Experts 20 June ‘ 07: v “Why isn't vocational education being better understood? Children not interested in heading off to college can learn real skills in a well-run vocational setting q The world will always need carpenters and plumbers. . . these jobs are plentiful, honorable and pay well q It seems to me we could be providing real opportunities for so many of our youth if vocational education were given more respect and more dollars” q Ø Bureau of Labor Statistics: “There will be a shortfall of 10 million workers by 2010” v “A demographic crunch is coming and will be exacerbated by a talent crunch that threatens to stall the very engines of economic growth” v Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 46
Important Trends, cont’d Ø Diplomas Count 2007 — A Conversation with the Experts 20 June ‘ 07: v “Why isn't vocational education being better understood? Children not interested in heading off to college can learn real skills in a well-run vocational setting q The world will always need carpenters and plumbers. . . these jobs are plentiful, honorable and pay well q It seems to me we could be providing real opportunities for so many of our youth if vocational education were given more respect and more dollars” q Ø Bureau of Labor Statistics: “There will be a shortfall of 10 million workers by 2010” v “A demographic crunch is coming and will be exacerbated by a talent crunch that threatens to stall the very engines of economic growth” v Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 46
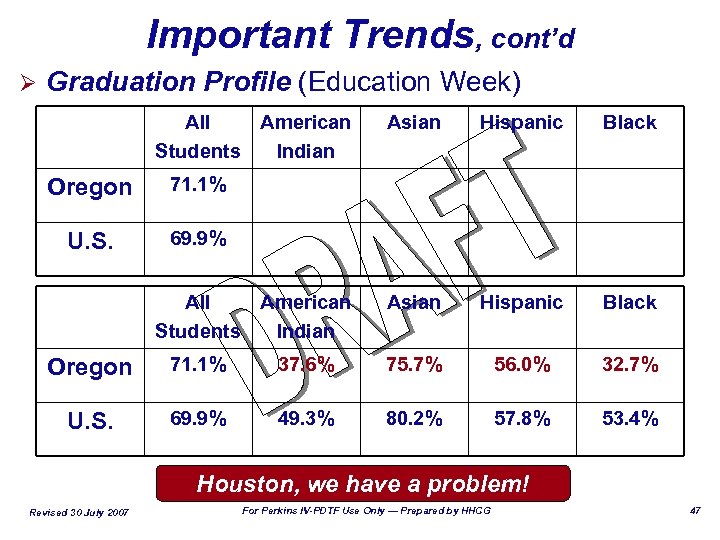 Important Trends, cont’d Ø Graduation Profile (Education Week) All American Students Indian Oregon Hispanic Black Asian Hispanic Black 71. 1% U. S. Asian 69. 9% All American Students Indian Oregon 71. 1% 37. 6% 75. 7% 56. 0% 32. 7% U. S. 69. 9% 49. 3% 80. 2% 57. 8% 53. 4% Houston, we have a problem! Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 47
Important Trends, cont’d Ø Graduation Profile (Education Week) All American Students Indian Oregon Hispanic Black Asian Hispanic Black 71. 1% U. S. Asian 69. 9% All American Students Indian Oregon 71. 1% 37. 6% 75. 7% 56. 0% 32. 7% U. S. 69. 9% 49. 3% 80. 2% 57. 8% 53. 4% Houston, we have a problem! Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 47
 Important Trends, cont’d Ø Graduation Profile (Education Week) v Discussion: q Graduation #’s only tell a small part of the story q Relevance & utility of education received is key — whether academic or CTE or both q The PDTF needs to looks more carefully at different aspects of this issue Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 48
Important Trends, cont’d Ø Graduation Profile (Education Week) v Discussion: q Graduation #’s only tell a small part of the story q Relevance & utility of education received is key — whether academic or CTE or both q The PDTF needs to looks more carefully at different aspects of this issue Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 48
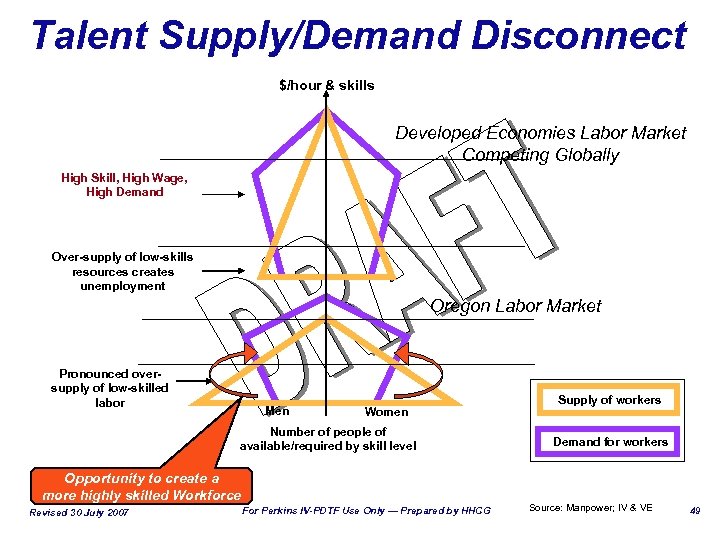 Talent Supply/Demand Disconnect $/hour & skills Developed Economies Labor Market Competing Globally High Skill, High Wage, High Demand Over-supply of low-skills resources creates unemployment Oregon Labor Market Pronounced oversupply of low-skilled labor Men Women Number of people of available/required by skill level Opportunity to create a more highly skilled Workforce Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Supply of workers Demand for workers Source: Manpower; IV & VE 49
Talent Supply/Demand Disconnect $/hour & skills Developed Economies Labor Market Competing Globally High Skill, High Wage, High Demand Over-supply of low-skills resources creates unemployment Oregon Labor Market Pronounced oversupply of low-skilled labor Men Women Number of people of available/required by skill level Opportunity to create a more highly skilled Workforce Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Supply of workers Demand for workers Source: Manpower; IV & VE 49
 The Opportunity for CTE? Task force responses: Contextualized Learning Outcomes Ø Real World Experiences Ø Integration/Systems Ø Curricular learning opportunities v Systems learning — making connections re problem-solving v Strike while the iron is hot! This is very timely Ø Cooperate & co-opt with other educational areas — 3 R’s Ø Employers are coming to the table with resources Ø Opportunity to engage earlier grades — it’s coming back National piece — baby boom Ø International piece — economic stakes are high Ø Save the world! Ø To change perceptions about CTE (via marketing, etc. ) Ø v Ø Revised 30 July 2007 To start removing boundaries between career-oriented vs. learning For seamlessness between PK and 16, especially in HS Ø Capture the middle students that may not be destined to college Ø Redesign programs so that they are transitional to 4 -yr degrees Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 50
The Opportunity for CTE? Task force responses: Contextualized Learning Outcomes Ø Real World Experiences Ø Integration/Systems Ø Curricular learning opportunities v Systems learning — making connections re problem-solving v Strike while the iron is hot! This is very timely Ø Cooperate & co-opt with other educational areas — 3 R’s Ø Employers are coming to the table with resources Ø Opportunity to engage earlier grades — it’s coming back National piece — baby boom Ø International piece — economic stakes are high Ø Save the world! Ø To change perceptions about CTE (via marketing, etc. ) Ø v Ø Revised 30 July 2007 To start removing boundaries between career-oriented vs. learning For seamlessness between PK and 16, especially in HS Ø Capture the middle students that may not be destined to college Ø Redesign programs so that they are transitional to 4 -yr degrees Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 50
 The Opportunity for CTE? Taskforce Responses: Ø Ø Ø Marketing CTE opportunities re hightech industry Make sure students understand that the skills they acquire in CTE are utilized The opportunity is for students utilizing CTE not the other way around Use a variety of data to drive our thinking To reshape CTE — restructuring, using words/ideas that are not as divisive; and closer to the way the world works Ref: Workforce side — Work Readiness Certificate v Career-related learning standards Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Define CTE — it’s a very broad topic Professional-side v Lifelong learning, skill-upgrading v The labels we use are important — we need to be clear & consistent Ø Perkins may have brought us together — but this discussion is needed now anyway! Ø Ties into the new diploma requirements being implemented now — super-timely Ø v How do we take better advantage of these (2012)? We have an opportunity to define the whole K-16 CTE spectrum Ø For CTE to addressed the work & college readiness transferring from HS Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 51
The Opportunity for CTE? Taskforce Responses: Ø Ø Ø Marketing CTE opportunities re hightech industry Make sure students understand that the skills they acquire in CTE are utilized The opportunity is for students utilizing CTE not the other way around Use a variety of data to drive our thinking To reshape CTE — restructuring, using words/ideas that are not as divisive; and closer to the way the world works Ref: Workforce side — Work Readiness Certificate v Career-related learning standards Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Define CTE — it’s a very broad topic Professional-side v Lifelong learning, skill-upgrading v The labels we use are important — we need to be clear & consistent Ø Perkins may have brought us together — but this discussion is needed now anyway! Ø Ties into the new diploma requirements being implemented now — super-timely Ø v How do we take better advantage of these (2012)? We have an opportunity to define the whole K-16 CTE spectrum Ø For CTE to addressed the work & college readiness transferring from HS Ø For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 51
 The Opportunity for CTE? Taskforce Responses: Ø With the CTE Teacher shortage, we can look at all of this in a fresh way v Ø Ref: “Reinventing the American HS for the 21 st Century” v Ø Can look at extending CTE into teacher education programs Some wonderful ideas re: changing how we deliver education & qualify teachers Marketing what? Piggyback on other opportunities Ø Initial Themes: Ø Ø Potential integration of CTE with Academics v Collaboration/cooperation among the different levels of CTE v Need to build on prior work re: many of the above points — build some common understanding Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 52
The Opportunity for CTE? Taskforce Responses: Ø With the CTE Teacher shortage, we can look at all of this in a fresh way v Ø Ref: “Reinventing the American HS for the 21 st Century” v Ø Can look at extending CTE into teacher education programs Some wonderful ideas re: changing how we deliver education & qualify teachers Marketing what? Piggyback on other opportunities Ø Initial Themes: Ø Ø Potential integration of CTE with Academics v Collaboration/cooperation among the different levels of CTE v Need to build on prior work re: many of the above points — build some common understanding Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 52
 What Failure Looks Like Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 53
What Failure Looks Like Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 53
 What Failure Looks Like Ø Purpose: v Stir negative-discomfort by looking at the costs of not taking full advantage of this opportunity to transform CTE Ø Process: v Imagine the effects of not succeeding in addressing the current & emerging workforce needs v How would this impact your organization? v How would this impact tomorrow’s students? v How would this affect you personally? v Write a couple of Headlines about the failure of CTE Ø Share results with the group Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 54
What Failure Looks Like Ø Purpose: v Stir negative-discomfort by looking at the costs of not taking full advantage of this opportunity to transform CTE Ø Process: v Imagine the effects of not succeeding in addressing the current & emerging workforce needs v How would this impact your organization? v How would this impact tomorrow’s students? v How would this affect you personally? v Write a couple of Headlines about the failure of CTE Ø Share results with the group Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 54
 What Failure Looks Like Taskforce Responses: Student Impact Organization Impact Ø Higher dropout rate Ø Congress will drop funding Ø Lost opportunities (all kinds) Ø ODE loses staff Ø Misperception of what’s broken Ø Focus more on NCLB Ø CTE will become available in the private sector at a higher cost & Ø Schools become irrelevant or longer time status-quo continues Ø Some students will be left out Ø Perkins awarded to ITT to train altogether citizens from India and Canada to Ø Lost of relevancy — re experiencing work for American companies — the world of work CTE is outsourced! Ø Loss of roots Ø Will see more remediation needs Ø Lost income Ø Less flexibility; less opportunity to at HS, CC & 4 -yr experiment; less transferability Ø Greater barriers for risk populations especially students of color Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 55
What Failure Looks Like Taskforce Responses: Student Impact Organization Impact Ø Higher dropout rate Ø Congress will drop funding Ø Lost opportunities (all kinds) Ø ODE loses staff Ø Misperception of what’s broken Ø Focus more on NCLB Ø CTE will become available in the private sector at a higher cost & Ø Schools become irrelevant or longer time status-quo continues Ø Some students will be left out Ø Perkins awarded to ITT to train altogether citizens from India and Canada to Ø Lost of relevancy — re experiencing work for American companies — the world of work CTE is outsourced! Ø Loss of roots Ø Will see more remediation needs Ø Lost income Ø Less flexibility; less opportunity to at HS, CC & 4 -yr experiment; less transferability Ø Greater barriers for risk populations especially students of color Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 55
 What Failure Looks Like Taskforce Responses: Personal Impact Ø Lose my secure society Ø High cost of repair, technical services Ø It would really jeopardize my ability to engage with local businesses — nothing to offer v Ø Ø Ø I would mourn this Lower standard of living I wouldn’t feel as safe Army recruitment would rise for the wrong reasons Our own kids & grandkids won’t have the same opportunities that we had Growing gap between haves & havenots Oregon = has-been, used to be a nice place to live Revised 30 July 2007 Headlines Ø CTE is outsourced! Ø Intel closes due to lack of technicians Ø Gates is right — the Education System is broken! Ø Average cost of BS degree now reaching $100 k Ø The Monthly Auto-Repair Barge is leaving for India Ø Waiting list for Nursing Home is 10 -years Ø Academia Learns Technical Skills For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 56
What Failure Looks Like Taskforce Responses: Personal Impact Ø Lose my secure society Ø High cost of repair, technical services Ø It would really jeopardize my ability to engage with local businesses — nothing to offer v Ø Ø Ø I would mourn this Lower standard of living I wouldn’t feel as safe Army recruitment would rise for the wrong reasons Our own kids & grandkids won’t have the same opportunities that we had Growing gap between haves & havenots Oregon = has-been, used to be a nice place to live Revised 30 July 2007 Headlines Ø CTE is outsourced! Ø Intel closes due to lack of technicians Ø Gates is right — the Education System is broken! Ø Average cost of BS degree now reaching $100 k Ø The Monthly Auto-Repair Barge is leaving for India Ø Waiting list for Nursing Home is 10 -years Ø Academia Learns Technical Skills For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 56
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 57
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 57
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE In small groups — pick a scribe & presenter Ø Put yourself into the future Ø v Without any of the limitations or issues of today v Imagine that by 2012 Oregon becomes widely known as a World Class Model for Career & Technical Education Ø A team of observers arrives: v What would they see? v How would recent grads describe their experience? v Employers? v Educators? v Parents? Ø Share results with the group Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 58
Our 2012 Vision of CTE In small groups — pick a scribe & presenter Ø Put yourself into the future Ø v Without any of the limitations or issues of today v Imagine that by 2012 Oregon becomes widely known as a World Class Model for Career & Technical Education Ø A team of observers arrives: v What would they see? v How would recent grads describe their experience? v Employers? v Educators? v Parents? Ø Share results with the group Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 58
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Recent Grads Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Taskforce Responses: Very relevant to their jobs They love what they do Prepared for advancement Know how to seek next steps Their job connects back to the school systems They equate their success with how well they were prepared Can’t wait to work as a part-time teacher I got a great job; I make a living wage & I owe it all to my school Everything I took applied to my 4 -yr degree I bought a new truck/hybrid Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 59
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Recent Grads Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Taskforce Responses: Very relevant to their jobs They love what they do Prepared for advancement Know how to seek next steps Their job connects back to the school systems They equate their success with how well they were prepared Can’t wait to work as a part-time teacher I got a great job; I make a living wage & I owe it all to my school Everything I took applied to my 4 -yr degree I bought a new truck/hybrid Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 59
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Taskforce Responses: Employers Ø Ø Ø Ø I’ve got employees that create great profit Job-ready day one Where did you get them from They want to contribute to their community My best employees come from local schools I meet with local educators a couple of times a year — they really listen; have the capacity to met our needs We are ready to invest in additional training Ø Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 I enjoy teaching at my HS/CC I have excellent candidates to interview 20% of my workforce are interns Can serve my community/customers better with my diverse workforce The grads know how to work as a team The grads are innovative & create better ways to do business We are growing at 20%/year I am voting for the bond measure to expand CTE For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 60
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Taskforce Responses: Employers Ø Ø Ø Ø I’ve got employees that create great profit Job-ready day one Where did you get them from They want to contribute to their community My best employees come from local schools I meet with local educators a couple of times a year — they really listen; have the capacity to met our needs We are ready to invest in additional training Ø Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 I enjoy teaching at my HS/CC I have excellent candidates to interview 20% of my workforce are interns Can serve my community/customers better with my diverse workforce The grads know how to work as a team The grads are innovative & create better ways to do business We are growing at 20%/year I am voting for the bond measure to expand CTE For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 60
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Educators Ø Ø Ø Taskforce Responses: I have a raise Don’t care about PERS because I enjoy teaching so much I have more personal relationships with students 85% of my completing seniors have jobs! I go home everyday feeling rewarded for the work I do because my work is so successful I’m not burned out Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 I am a happy teacher Every year students ask me “what would it take for me to do what you do” I need more space/periods to serve all those wanting to be in the program I love teaching skills (vs. helping them catch-up) I work closely with the Math & English teachers I team-teach with business owners For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 61
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Educators Ø Ø Ø Taskforce Responses: I have a raise Don’t care about PERS because I enjoy teaching so much I have more personal relationships with students 85% of my completing seniors have jobs! I go home everyday feeling rewarded for the work I do because my work is so successful I’m not burned out Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 I am a happy teacher Every year students ask me “what would it take for me to do what you do” I need more space/periods to serve all those wanting to be in the program I love teaching skills (vs. helping them catch-up) I work closely with the Math & English teachers I team-teach with business owners For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 61
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Parents Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Taskforce Responses: Thank you! My child is out of the house, working & earning solid wages I’m jealous that I didn’t have this opportunity My tax $ have been well spent What is nano-technology? I am happy that my child has a career, not just a job FINALLY my kid is excited about school He/she makes more than I do! Now I’m back in school Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 62
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Parents Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Taskforce Responses: Thank you! My child is out of the house, working & earning solid wages I’m jealous that I didn’t have this opportunity My tax $ have been well spent What is nano-technology? I am happy that my child has a career, not just a job FINALLY my kid is excited about school He/she makes more than I do! Now I’m back in school Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 62
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Taskforce Responses: What is that Model? Ø Ø No delineation between CTE and other learning — Academic instruction services CTE Ø Easy transferable among the schools Ø All faculty periodically engaged in back-to-industry efforts Lots of on-line opportunities: Ø Program completers receive nextstep placement or are guaranteed a refresher course Ø Stds for teacher licenses are adapted to fit this paradigm with more opportunities for business environment Ø Different funding model — from contact hours to innovation, demandprograms, economic needs v Hybrid ed v Simulations v Distance-learning Ø No boundaries between different level of ed Ø Comprehensive advising system: v Ø Awareness => Exploration => Planning => Preparation Competency/outcome/proficiency based CTE -- vs contact hours, units Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 63
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Taskforce Responses: What is that Model? Ø Ø No delineation between CTE and other learning — Academic instruction services CTE Ø Easy transferable among the schools Ø All faculty periodically engaged in back-to-industry efforts Lots of on-line opportunities: Ø Program completers receive nextstep placement or are guaranteed a refresher course Ø Stds for teacher licenses are adapted to fit this paradigm with more opportunities for business environment Ø Different funding model — from contact hours to innovation, demandprograms, economic needs v Hybrid ed v Simulations v Distance-learning Ø No boundaries between different level of ed Ø Comprehensive advising system: v Ø Awareness => Exploration => Planning => Preparation Competency/outcome/proficiency based CTE -- vs contact hours, units Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 63
 Our 2012 Vision of CTE Taskforce Responses: What is that Model, cont’d: Ø Greater level of collaboration across the whole CTE+ spectrum Ø Respect for all sectors by all sectors Ø Students have lots of ways to apply their learning — contests, clubs, internships Ø Students K-20 all have plans that extend into the world of work Ø Model is financially responsible & sustainable Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Ø Ø Able to change with workforce needs — flexible, adaptable Teacher Ed is across the board delivered by CC, 4 -yr, & employers Profusion of mentorships for teachers & students Integrated Programs developed around career clusters & local business needs These opportunities are equally distributed around the State — on -site or via distance For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 64
Our 2012 Vision of CTE Taskforce Responses: What is that Model, cont’d: Ø Greater level of collaboration across the whole CTE+ spectrum Ø Respect for all sectors by all sectors Ø Students have lots of ways to apply their learning — contests, clubs, internships Ø Students K-20 all have plans that extend into the world of work Ø Model is financially responsible & sustainable Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Ø Ø Able to change with workforce needs — flexible, adaptable Teacher Ed is across the board delivered by CC, 4 -yr, & employers Profusion of mentorships for teachers & students Integrated Programs developed around career clusters & local business needs These opportunities are equally distributed around the State — on -site or via distance For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 64
 Foundation Blocks of Our Vision — Leverage Opportunities — Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 65
Foundation Blocks of Our Vision — Leverage Opportunities — Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 65
 Leverage Opportunities for CTE Taskforce Responses: Flexibility between big, little, urban, rural schools Ø Quality Assurance process (criteria) especially for HS level Ø Existing networks Ø Regional Coordinator Network v Counsel of Instructional Administrator v ODE/Local Ed Agency Ø Ø Ø v 2+2 & other transition programs — consistently applied Ø Local innovative model programs going on, e. g. : Ø v Ø Ø Ø Excellent relationships between CC and feeder HSs Strong business community connections Increased staffing ability at CCWD for accountability, etc. Active involvement with the implementation & reauthorization of NCLB Student Leadership Organizations in Oregon (esp. HS) Oregon Business Council budget framework OSU/LBCC Culinary Arts Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 66
Leverage Opportunities for CTE Taskforce Responses: Flexibility between big, little, urban, rural schools Ø Quality Assurance process (criteria) especially for HS level Ø Existing networks Ø Regional Coordinator Network v Counsel of Instructional Administrator v ODE/Local Ed Agency Ø Ø Ø v 2+2 & other transition programs — consistently applied Ø Local innovative model programs going on, e. g. : Ø v Ø Ø Ø Excellent relationships between CC and feeder HSs Strong business community connections Increased staffing ability at CCWD for accountability, etc. Active involvement with the implementation & reauthorization of NCLB Student Leadership Organizations in Oregon (esp. HS) Oregon Business Council budget framework OSU/LBCC Culinary Arts Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 66
 Leverage Opportunities for CTE Taskforce Responses: Systemic Innovative Programs Ø Small learning communities v Career Pathways Program Ø Ø v Ø Ø Ø Distance Education infrastructure Plan & Profile for K-12 can be built upon New diploma requirements 2007 & 2014 Credit for proficiencies (vs. time) Strong advisory committees Technological competence & career opportunities — value added within CTE Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Partnerships with Workforce Policy Board Connections with other policy entities — this is on people’s radar (State, National, etc. ) TSPC relationship — fertile ground of receptivity New legislatively funded CTE study Other funding sources — HR CREB, Incentive Grants, DOL Lots of existing data (needs analysis on CTE outcomes & labor needs) Federal Mandate to change For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 67
Leverage Opportunities for CTE Taskforce Responses: Systemic Innovative Programs Ø Small learning communities v Career Pathways Program Ø Ø v Ø Ø Ø Distance Education infrastructure Plan & Profile for K-12 can be built upon New diploma requirements 2007 & 2014 Credit for proficiencies (vs. time) Strong advisory committees Technological competence & career opportunities — value added within CTE Ø Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Partnerships with Workforce Policy Board Connections with other policy entities — this is on people’s radar (State, National, etc. ) TSPC relationship — fertile ground of receptivity New legislatively funded CTE study Other funding sources — HR CREB, Incentive Grants, DOL Lots of existing data (needs analysis on CTE outcomes & labor needs) Federal Mandate to change For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 67
 Achieving Our Vision — Challenges/Obstacles — Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 68
Achieving Our Vision — Challenges/Obstacles — Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 68
 Challenges/Obstacles for CTE Taskforce Responses: Changing the culture at schools Ø Big systems to change Ø Federal v State Ø Ø v Ø NCLB highly qualified teacher status Ø Ø State requirements for teacher approval Ø Ø Limited resources to rebuild our programs Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Student or youth culture issues Resistance from within CTE community — e. g. : with accountability Challenge re what is a mandate vs. local control In the end — everyone’s just fighting for the money People tied to existing formulas Contract & work rule issues For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 69
Challenges/Obstacles for CTE Taskforce Responses: Changing the culture at schools Ø Big systems to change Ø Federal v State Ø Ø v Ø NCLB highly qualified teacher status Ø Ø State requirements for teacher approval Ø Ø Limited resources to rebuild our programs Ø Ø Revised 30 July 2007 Student or youth culture issues Resistance from within CTE community — e. g. : with accountability Challenge re what is a mandate vs. local control In the end — everyone’s just fighting for the money People tied to existing formulas Contract & work rule issues For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 69
 Challenges/Obstacles for CTE Taskforce Responses: Some internal structures that get in the way of our being nimble Ø Pace — global economic changes Ø Lack of State Model really exists Ø Teacher workforce issues Ø Demographics v Aging v Ø Ø Articulation/transfer issues within the State Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Ø Huge learning issues with policy makers — politics Misinformation, misperceptions Lack of a communications structure and a teachingstructure Pipeline for succession planning for teachers and instructional leaders The changing demographics of rural areas — smaller schools For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 70
Challenges/Obstacles for CTE Taskforce Responses: Some internal structures that get in the way of our being nimble Ø Pace — global economic changes Ø Lack of State Model really exists Ø Teacher workforce issues Ø Demographics v Aging v Ø Ø Articulation/transfer issues within the State Revised 30 July 2007 Ø Ø Huge learning issues with policy makers — politics Misinformation, misperceptions Lack of a communications structure and a teachingstructure Pipeline for succession planning for teachers and instructional leaders The changing demographics of rural areas — smaller schools For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 70
 Appendix A — Focus Group Questions Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø What has been your work experience since graduating from school? Talk to me about how you moved in to your new job in the automotive industry? What were you most prepared to do once you starting working? And, what were you the least prepared to do? For example, talk to me about your ability to work with auto electronics and diagnostic equipment. How about computer skills, e. g. , your ability to go to manufacturer websites to get repair information? Let’s talk about how you did or didn’t learn to work together as a team to solve problems? And what about general communications, like working with customers? If you had to do it all over again, what would you like to see taught in automotive classes in high school and/or community college that it is not doing now? Are there things that you will like taught that would enhance you skills in today’s automotive repair business? Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 71
Appendix A — Focus Group Questions Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø What has been your work experience since graduating from school? Talk to me about how you moved in to your new job in the automotive industry? What were you most prepared to do once you starting working? And, what were you the least prepared to do? For example, talk to me about your ability to work with auto electronics and diagnostic equipment. How about computer skills, e. g. , your ability to go to manufacturer websites to get repair information? Let’s talk about how you did or didn’t learn to work together as a team to solve problems? And what about general communications, like working with customers? If you had to do it all over again, what would you like to see taught in automotive classes in high school and/or community college that it is not doing now? Are there things that you will like taught that would enhance you skills in today’s automotive repair business? Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 71
 Appendix A — Focus Group Questions, cont’d Ø Ø Ø Ø Do you get any training on repairing hybrid vehicles? How about training in dealerships? What types of training did they offer to you? Okay here’s a for instance…”I would have done better in the training that Toyota offered me…. if I had better preparation in school…or, I was really suffering because____________. Do you feel you learned independent skills to help you with problem solving, like figuring out options available and which is the correct one to choose? Did school help you to say, “How do I communicate options for car repair to the customer in a way they can understand? What is your assessment of the quality of your education and how they prepared you to work in the automotive industry? If you were King/queen for a day what would you change in the current education system to make automotive repair training the best it could possibly be? Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 72
Appendix A — Focus Group Questions, cont’d Ø Ø Ø Ø Do you get any training on repairing hybrid vehicles? How about training in dealerships? What types of training did they offer to you? Okay here’s a for instance…”I would have done better in the training that Toyota offered me…. if I had better preparation in school…or, I was really suffering because____________. Do you feel you learned independent skills to help you with problem solving, like figuring out options available and which is the correct one to choose? Did school help you to say, “How do I communicate options for car repair to the customer in a way they can understand? What is your assessment of the quality of your education and how they prepared you to work in the automotive industry? If you were King/queen for a day what would you change in the current education system to make automotive repair training the best it could possibly be? Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 72
 CTE Definitions CTE programs are an integral part of public education and are designed to educate about, through, and for careers From the National Centers for Career and Technical Education (NCCTE), funded by OVAE: Ø CTE engages all students in a dynamic and seamless learning experience resulting in their mastery of the career and academic knowledge and skills necessary to become productive contributing members of society From the California Career Technical Education Model Curriculum Standards and Framework) Ø CTE in Oregon provides basic technical skills to all students, skills specific to a broad career area to interested high school students and workforce training to community college students, and leverages substantive change in the education system Ø CTE programs that generate knowledge and innovation that prepare students for the demands of a global society Ø CTE: Where students learn in rich, contextual environments with the help of cutting-edge teaching and learning strategies, acquiring all of the technical and academic knowledge and skills they need to be successful on their life-long learning journey Ø Creating a seamless flow of information, innovations, funds and success through partnerships between business/industry, K-16 and state/federal agencies for PTE/CTE programs Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 73
CTE Definitions CTE programs are an integral part of public education and are designed to educate about, through, and for careers From the National Centers for Career and Technical Education (NCCTE), funded by OVAE: Ø CTE engages all students in a dynamic and seamless learning experience resulting in their mastery of the career and academic knowledge and skills necessary to become productive contributing members of society From the California Career Technical Education Model Curriculum Standards and Framework) Ø CTE in Oregon provides basic technical skills to all students, skills specific to a broad career area to interested high school students and workforce training to community college students, and leverages substantive change in the education system Ø CTE programs that generate knowledge and innovation that prepare students for the demands of a global society Ø CTE: Where students learn in rich, contextual environments with the help of cutting-edge teaching and learning strategies, acquiring all of the technical and academic knowledge and skills they need to be successful on their life-long learning journey Ø Creating a seamless flow of information, innovations, funds and success through partnerships between business/industry, K-16 and state/federal agencies for PTE/CTE programs Ø Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 73
 Knowledge Based Enterprise (KBE) Model Input Market Need Innovation Tech Transfer Transformational Process Outputs Human resource based Effort based production No fixed plant Service or Information Raw Material • Human Capital • History and Trends • Current Conditions • Forecasts for the Future • Local, Regional and Global Competition • Industry Best Practices & Innovations • Relevant University Research Tools Transactional • Judgment • Social Networks • Mentoring • Prediction Models Knowledge Based Community Characteristics • High-quality and skilled labor force • Close proximity to college and University knowledge base • Local amenities that support a high quality of life, including typography and water • 21 st century infrastructure; broadband • Regional connections with larger rural areas to connect with knowledge base Revised 30 July 2007 National and Global Markets For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: VE and Ron Duncan, S 5 COI Community Wealth $$$$$ 74
Knowledge Based Enterprise (KBE) Model Input Market Need Innovation Tech Transfer Transformational Process Outputs Human resource based Effort based production No fixed plant Service or Information Raw Material • Human Capital • History and Trends • Current Conditions • Forecasts for the Future • Local, Regional and Global Competition • Industry Best Practices & Innovations • Relevant University Research Tools Transactional • Judgment • Social Networks • Mentoring • Prediction Models Knowledge Based Community Characteristics • High-quality and skilled labor force • Close proximity to college and University knowledge base • Local amenities that support a high quality of life, including typography and water • 21 st century infrastructure; broadband • Regional connections with larger rural areas to connect with knowledge base Revised 30 July 2007 National and Global Markets For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG Source: VE and Ron Duncan, S 5 COI Community Wealth $$$$$ 74
 A Few Guiding Thoughts “The definition of insanity is doing the same thing over and over again, each time hoping for different results. ” W. Edwards Deming “The Future is already here; it’s just not widely distributed yet. ” William Gibson “By the strength of our common endeavor, we can accomplish more together, than we can alone. ” Tony Blair, Prime Minister of Great Britain “Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful committed people can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has. ” Margaret Mead Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 75
A Few Guiding Thoughts “The definition of insanity is doing the same thing over and over again, each time hoping for different results. ” W. Edwards Deming “The Future is already here; it’s just not widely distributed yet. ” William Gibson “By the strength of our common endeavor, we can accomplish more together, than we can alone. ” Tony Blair, Prime Minister of Great Britain “Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful committed people can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has. ” Margaret Mead Revised 30 July 2007 For Perkins IV-PDTF Use Only — Prepared by HHCG 75


