f8a8d6249439d7de9b86f03fcf41f404.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Perioperative Medical Evaluation for Gynecological Surgery Cullen Archer, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology June 2006
Perioperative Medical Evaluation for Gynecological Surgery Cullen Archer, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology June 2006
 6 Key Elements to Medicine Preop • • • Cardiac Risk Pulmonary Risk DVT Risk and Prevention Endocarditis Prophylaxis Perioperative Delirium Steroids
6 Key Elements to Medicine Preop • • • Cardiac Risk Pulmonary Risk DVT Risk and Prevention Endocarditis Prophylaxis Perioperative Delirium Steroids
 Topics • • Preoperative Cardiovascular Evaluation Antibiotic Prophylaxis Endocarditis Prophylaxis DVT Prophylaxis
Topics • • Preoperative Cardiovascular Evaluation Antibiotic Prophylaxis Endocarditis Prophylaxis DVT Prophylaxis
 Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation • Evaluation tailored to circumstances • H+P and ECG should identify potentially serious cardiac disorders • Define disease severity, stability, and prior treatment
Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation • Evaluation tailored to circumstances • H+P and ECG should identify potentially serious cardiac disorders • Define disease severity, stability, and prior treatment
 Clinical Predictors of Increased Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk (Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Death) • Major – Unstable coronary syndromes • Acute or recent myocardial infarction* with evidence of important ischemic risk by clinical symptoms or noninvasive study • Unstable or severe† angina (Canadian class III or IV)‡ – Decompensated heart failure – Significant arrhythmias • High-grade atrioventricular block • Symptomatic ventricular arrhythmias in the presence of underlying heart disease • Supraventricular arrhythmias with uncontrolled ventricular rate – Severe valvular disease *The American College of Cardiology National Database Library defines recent MI as greater than 7 days but less than or equal to 1 month (30 days); acute MI is within 7 days. †May include “stable” angina in patients who are unusually sedentary. ‡Campeau L. Grading of angina pectoris. Circulation. 1976; 54: 522– 523.
Clinical Predictors of Increased Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk (Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Death) • Major – Unstable coronary syndromes • Acute or recent myocardial infarction* with evidence of important ischemic risk by clinical symptoms or noninvasive study • Unstable or severe† angina (Canadian class III or IV)‡ – Decompensated heart failure – Significant arrhythmias • High-grade atrioventricular block • Symptomatic ventricular arrhythmias in the presence of underlying heart disease • Supraventricular arrhythmias with uncontrolled ventricular rate – Severe valvular disease *The American College of Cardiology National Database Library defines recent MI as greater than 7 days but less than or equal to 1 month (30 days); acute MI is within 7 days. †May include “stable” angina in patients who are unusually sedentary. ‡Campeau L. Grading of angina pectoris. Circulation. 1976; 54: 522– 523.
 Clinical Predictors of Increased Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk (Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Death) • Intermediate – Mild angina pectoris (Canadian class I or II) – Previous myocardial infarction by history or pathological Q waves – Compensated or prior heart failure – Diabetes mellitus (particularly insulindependent) – Renal insufficiency
Clinical Predictors of Increased Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk (Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Death) • Intermediate – Mild angina pectoris (Canadian class I or II) – Previous myocardial infarction by history or pathological Q waves – Compensated or prior heart failure – Diabetes mellitus (particularly insulindependent) – Renal insufficiency
 Clinical Predictors of Increased Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk (Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Death) • Minor – Advanced age – Abnormal ECG (left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle-branch block, ST-T abnormalities) – Rhythm other than sinus (e. g. , atrial fibrillation) – Low functional capacity (e. g. , inability to climb one flight of stairs with a bag of groceries) – History of stroke – Uncontrolled systemic hypertension
Clinical Predictors of Increased Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk (Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Death) • Minor – Advanced age – Abnormal ECG (left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle-branch block, ST-T abnormalities) – Rhythm other than sinus (e. g. , atrial fibrillation) – Low functional capacity (e. g. , inability to climb one flight of stairs with a bag of groceries) – History of stroke – Uncontrolled systemic hypertension
 Functional Capacity 1 MET Can you take care of yourself? Eat, dress, or use the toilet? Walk indoors around the house? Walk a block or two on level ground at 2 -3 mph (4. 8 kph) 4 MET Do light work around the house like dusting or washing dishes? Climb a flight of stairs or walk up a hill? Run a short distance? Do heavy work around the house like scrubbing floors or lifting or moving heavy furniture Participate in moderate recreational activities like golf, bowling, dancing, doubles tennis, or throwing a baseball or football? >10 Participate in strenuous sports like swimming, singles tennis, football, basketball, or skiing?
Functional Capacity 1 MET Can you take care of yourself? Eat, dress, or use the toilet? Walk indoors around the house? Walk a block or two on level ground at 2 -3 mph (4. 8 kph) 4 MET Do light work around the house like dusting or washing dishes? Climb a flight of stairs or walk up a hill? Run a short distance? Do heavy work around the house like scrubbing floors or lifting or moving heavy furniture Participate in moderate recreational activities like golf, bowling, dancing, doubles tennis, or throwing a baseball or football? >10 Participate in strenuous sports like swimming, singles tennis, football, basketball, or skiing?
 Cardiac Risk* Stratification for Noncardiac Surgical Procedures • • • High (Reported cardiac risk often greater than 5%) • Emergent major operations, particularly in the elderly • Aortic and other major vascular surgery • Peripheral vascular surgery • Anticipated prolonged surgical procedures associated with large fluid shifts and/or blood loss Intermediate (Reported cardiac risk generally less than 5%) • Carotid endarterectomy • Head and neck surgery • Intraperitoneal and intrathoracic surgery • Orthopedic surgery • Prostate surgery Low† (Reported cardiac risk generally less than 1%) • Endoscopic procedures • Superficial procedure • Cataract surgery • Breast surgery *Combined incidence of cardiac death and nonfatal myocardial infarction. †Do not generally require further preoperative cardiac testing.
Cardiac Risk* Stratification for Noncardiac Surgical Procedures • • • High (Reported cardiac risk often greater than 5%) • Emergent major operations, particularly in the elderly • Aortic and other major vascular surgery • Peripheral vascular surgery • Anticipated prolonged surgical procedures associated with large fluid shifts and/or blood loss Intermediate (Reported cardiac risk generally less than 5%) • Carotid endarterectomy • Head and neck surgery • Intraperitoneal and intrathoracic surgery • Orthopedic surgery • Prostate surgery Low† (Reported cardiac risk generally less than 1%) • Endoscopic procedures • Superficial procedure • Cataract surgery • Breast surgery *Combined incidence of cardiac death and nonfatal myocardial infarction. †Do not generally require further preoperative cardiac testing.
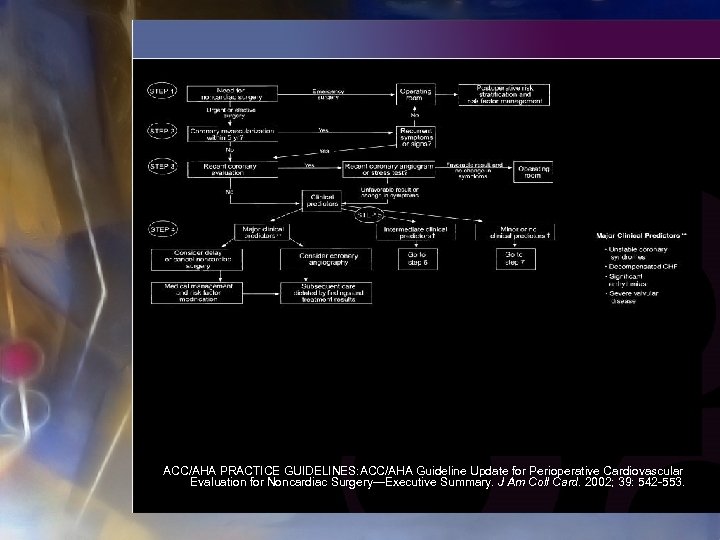 ACC/AHA PRACTICE GUIDELINES: ACC/AHA Guideline Update for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation for Noncardiac Surgery—Executive Summary. J Am Coll Card. 2002; 39: 542 -553.
ACC/AHA PRACTICE GUIDELINES: ACC/AHA Guideline Update for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation for Noncardiac Surgery—Executive Summary. J Am Coll Card. 2002; 39: 542 -553.
 ACC/AHA PRACTICE GUIDELINES: ACC/AHA Guideline Update for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation for Noncardiac Surgery—Executive Summary. J Am Coll Card. 2002; 39: 542 -553.
ACC/AHA PRACTICE GUIDELINES: ACC/AHA Guideline Update for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation for Noncardiac Surgery—Executive Summary. J Am Coll Card. 2002; 39: 542 -553.
 ACC/AHA PRACTICE GUIDELINES: ACC/AHA Guideline Update for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation for Noncardiac Surgery—Executive Summary. J Am Coll Card. 2002; 39: 542 -553.
ACC/AHA PRACTICE GUIDELINES: ACC/AHA Guideline Update for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation for Noncardiac Surgery—Executive Summary. J Am Coll Card. 2002; 39: 542 -553.
 Specific Preoperative Conditions Hypertension – ≥ 180/110 should be controlled preoperatively – Perioperative antagonists Valvular Heart Disease Myocardial Disease Arrhythmias
Specific Preoperative Conditions Hypertension – ≥ 180/110 should be controlled preoperatively – Perioperative antagonists Valvular Heart Disease Myocardial Disease Arrhythmias
 Specific Preoperative Conditions • Implantable Pacemakers and Interventricular Conduction Devices – unipolar or bipolar pacemaker leads – Electrocautery: bipolar or unipolar ? • ICD devices should be programmed off immediately before surgery and then on again postoperatively
Specific Preoperative Conditions • Implantable Pacemakers and Interventricular Conduction Devices – unipolar or bipolar pacemaker leads – Electrocautery: bipolar or unipolar ? • ICD devices should be programmed off immediately before surgery and then on again postoperatively
 Surgical Site Prophylaxis Antimicrobial Prophylactic Regimens by Procedure Antibiotic Vaginal/abdominal cefazolin hysterectomy* Cefoxitin Cefotetan Metronidazole Laparoscopy None Laparotomy None Hysteroscopy None Hysterosalpingogram Doxycycline† IUD insertion None Endometrial biopsy None Induced abortion/D&C Doxycycline Metronidazole Urodynamics Dose 1 or 2 g single dose IV 500 mg single dose IV 100 mg po BID x 5 days 100 mg orally 1 hour before and 200 mg orally after the procedure 500 mg po BID for 5 days None *A convenient time to administer antibiotic prophylaxis is just before induction of anesthesia †If hysterosalpingogram demonstrates dilated tubes. No prophylaxis is indicated for a normal study. ACOG Practice Bulletin 23, January 2001
Surgical Site Prophylaxis Antimicrobial Prophylactic Regimens by Procedure Antibiotic Vaginal/abdominal cefazolin hysterectomy* Cefoxitin Cefotetan Metronidazole Laparoscopy None Laparotomy None Hysteroscopy None Hysterosalpingogram Doxycycline† IUD insertion None Endometrial biopsy None Induced abortion/D&C Doxycycline Metronidazole Urodynamics Dose 1 or 2 g single dose IV 500 mg single dose IV 100 mg po BID x 5 days 100 mg orally 1 hour before and 200 mg orally after the procedure 500 mg po BID for 5 days None *A convenient time to administer antibiotic prophylaxis is just before induction of anesthesia †If hysterosalpingogram demonstrates dilated tubes. No prophylaxis is indicated for a normal study. ACOG Practice Bulletin 23, January 2001
 Endocarditis Prophylaxis Endocarditis prophylaxis recommended Respiratory tract Tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy Surgical operations that involve respiratory mucosa Bronchoscopy with a rigid bronchoscope Gastrointestinal tract 1 Sclerotherapy for esophageal varices Esophageal stricture dilation Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography with biliary obstruction Biliary tract surgery Surgical operations that involve intestinal mucosa Genitourinary tract Prostatic surgery Cystoscopy Urethral dilation 1 Prophylaxis is recommended for high-risk patients; it is optimal for medium-risk patients. Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997; 96: 358 -366.
Endocarditis Prophylaxis Endocarditis prophylaxis recommended Respiratory tract Tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy Surgical operations that involve respiratory mucosa Bronchoscopy with a rigid bronchoscope Gastrointestinal tract 1 Sclerotherapy for esophageal varices Esophageal stricture dilation Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography with biliary obstruction Biliary tract surgery Surgical operations that involve intestinal mucosa Genitourinary tract Prostatic surgery Cystoscopy Urethral dilation 1 Prophylaxis is recommended for high-risk patients; it is optimal for medium-risk patients. Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997; 96: 358 -366.
 Endocarditis Prophylaxis Endocarditis prophylaxis not recommended Respiratory tract Endotracheal intubation Bronchoscopy with a flexible bronchoscope, with or without biopsy 2 Tympanostomy tube insertion Gastrointestinal tract Transesophageal echocardiography 2 Endoscopy with or without gastrointestinal biopsy 2 Genitourinary tract Vaginal hysterectomy 2 Vaginal delivery 2 Cesarean section In uninfected tissue: Urethral catheterization Uterine dilatation and curettage Therapeutic abortion Sterilization procedures Insertion or removal of intrauterine devices Other Cardiac catheterization, including balloon angioplasty Implanted cardiac pacemakers, implanted defibrillators, and coronary stents Incision or biopsy of surgically scrubbed skin Circumcision 2 Prophylaxis is optional for high-risk patients Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997; 96: 358 -366.
Endocarditis Prophylaxis Endocarditis prophylaxis not recommended Respiratory tract Endotracheal intubation Bronchoscopy with a flexible bronchoscope, with or without biopsy 2 Tympanostomy tube insertion Gastrointestinal tract Transesophageal echocardiography 2 Endoscopy with or without gastrointestinal biopsy 2 Genitourinary tract Vaginal hysterectomy 2 Vaginal delivery 2 Cesarean section In uninfected tissue: Urethral catheterization Uterine dilatation and curettage Therapeutic abortion Sterilization procedures Insertion or removal of intrauterine devices Other Cardiac catheterization, including balloon angioplasty Implanted cardiac pacemakers, implanted defibrillators, and coronary stents Incision or biopsy of surgically scrubbed skin Circumcision 2 Prophylaxis is optional for high-risk patients Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997; 96: 358 -366.
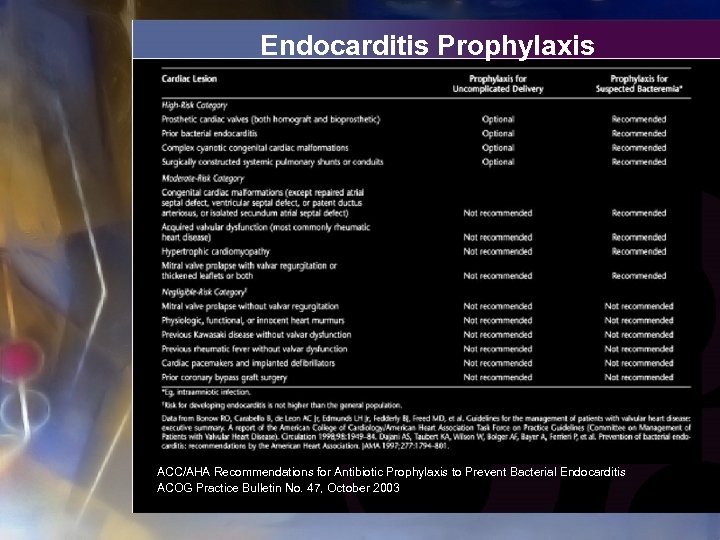 Endocarditis Prophylaxis ACC/AHA Recommendations for Antibiotic Prophylaxis to Prevent Bacterial Endocarditis ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 47, October 2003
Endocarditis Prophylaxis ACC/AHA Recommendations for Antibiotic Prophylaxis to Prevent Bacterial Endocarditis ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 47, October 2003
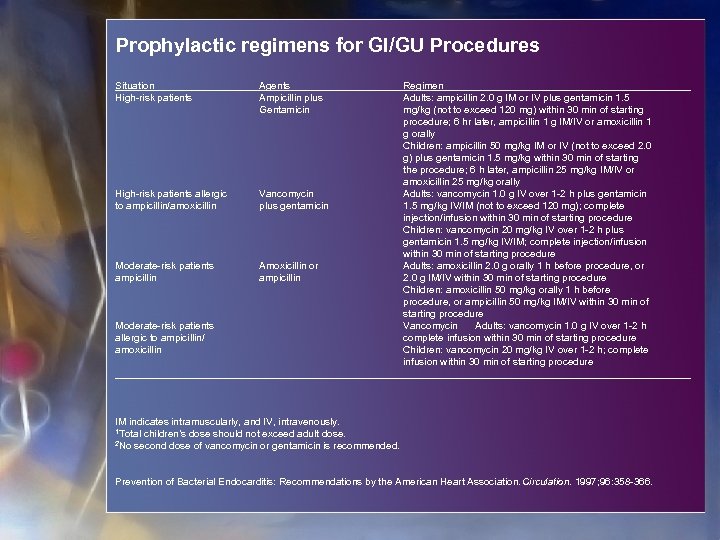 Prophylactic regimens for GI/GU Procedures Situation High-risk patients Agents Ampicillin plus Gentamicin High-risk patients allergic to ampicillin/amoxicillin Vancomycin plus gentamicin Moderate-risk patients ampicillin Amoxicillin or ampicillin Moderate-risk patients allergic to ampicillin/ amoxicillin Regimen Adults: ampicillin 2. 0 g IM or IV plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg (not to exceed 120 mg) within 30 min of starting procedure; 6 hr later, ampicillin 1 g IM/IV or amoxicillin 1 g orally Children: ampicillin 50 mg/kg IM or IV (not to exceed 2. 0 g) plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg within 30 min of starting the procedure; 6 h later, ampicillin 25 mg/kg IM/IV or amoxicillin 25 mg/kg orally Adults: vancomycin 1. 0 g IV over 1 -2 h plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg IV/IM (not to exceed 120 mg); complete injection/infusion within 30 min of starting procedure Children: vancomycin 20 mg/kg IV over 1 -2 h plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg IV/IM; complete injection/infusion within 30 min of starting procedure Adults: amoxicillin 2. 0 g orally 1 h before procedure, or 2. 0 g IM/IV within 30 min of starting procedure Children: amoxicillin 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure, or ampicillin 50 mg/kg IM/IV within 30 min of starting procedure Vancomycin Adults: vancomycin 1. 0 g IV over 1 -2 h complete infusion within 30 min of starting procedure Children: vancomycin 20 mg/kg IV over 1 -2 h; complete infusion within 30 min of starting procedure IM indicates intramuscularly, and IV, intravenously. 1 Total children’s dose should not exceed adult dose. 2 No second dose of vancomycin or gentamicin is recommended. Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997; 96: 358 -366.
Prophylactic regimens for GI/GU Procedures Situation High-risk patients Agents Ampicillin plus Gentamicin High-risk patients allergic to ampicillin/amoxicillin Vancomycin plus gentamicin Moderate-risk patients ampicillin Amoxicillin or ampicillin Moderate-risk patients allergic to ampicillin/ amoxicillin Regimen Adults: ampicillin 2. 0 g IM or IV plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg (not to exceed 120 mg) within 30 min of starting procedure; 6 hr later, ampicillin 1 g IM/IV or amoxicillin 1 g orally Children: ampicillin 50 mg/kg IM or IV (not to exceed 2. 0 g) plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg within 30 min of starting the procedure; 6 h later, ampicillin 25 mg/kg IM/IV or amoxicillin 25 mg/kg orally Adults: vancomycin 1. 0 g IV over 1 -2 h plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg IV/IM (not to exceed 120 mg); complete injection/infusion within 30 min of starting procedure Children: vancomycin 20 mg/kg IV over 1 -2 h plus gentamicin 1. 5 mg/kg IV/IM; complete injection/infusion within 30 min of starting procedure Adults: amoxicillin 2. 0 g orally 1 h before procedure, or 2. 0 g IM/IV within 30 min of starting procedure Children: amoxicillin 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure, or ampicillin 50 mg/kg IM/IV within 30 min of starting procedure Vancomycin Adults: vancomycin 1. 0 g IV over 1 -2 h complete infusion within 30 min of starting procedure Children: vancomycin 20 mg/kg IV over 1 -2 h; complete infusion within 30 min of starting procedure IM indicates intramuscularly, and IV, intravenously. 1 Total children’s dose should not exceed adult dose. 2 No second dose of vancomycin or gentamicin is recommended. Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997; 96: 358 -366.
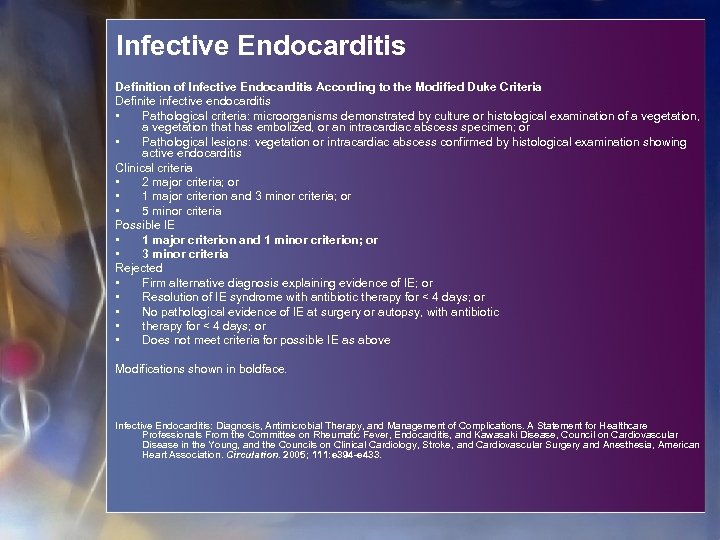 Infective Endocarditis Definition of Infective Endocarditis According to the Modified Duke Criteria Definite infective endocarditis • Pathological criteria: microorganisms demonstrated by culture or histological examination of a vegetation, a vegetation that has embolized, or an intracardiac abscess specimen; or • Pathological lesions: vegetation or intracardiac abscess confirmed by histological examination showing active endocarditis Clinical criteria • 2 major criteria; or • 1 major criterion and 3 minor criteria; or • 5 minor criteria Possible IE • 1 major criterion and 1 minor criterion; or • 3 minor criteria Rejected • Firm alternative diagnosis explaining evidence of IE; or • Resolution of IE syndrome with antibiotic therapy for < 4 days; or • No pathological evidence of IE at surgery or autopsy, with antibiotic • therapy for < 4 days; or • Does not meet criteria for possible IE as above Modifications shown in boldface. Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications. A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association. Circulation. 2005; 111: e 394 -e 433.
Infective Endocarditis Definition of Infective Endocarditis According to the Modified Duke Criteria Definite infective endocarditis • Pathological criteria: microorganisms demonstrated by culture or histological examination of a vegetation, a vegetation that has embolized, or an intracardiac abscess specimen; or • Pathological lesions: vegetation or intracardiac abscess confirmed by histological examination showing active endocarditis Clinical criteria • 2 major criteria; or • 1 major criterion and 3 minor criteria; or • 5 minor criteria Possible IE • 1 major criterion and 1 minor criterion; or • 3 minor criteria Rejected • Firm alternative diagnosis explaining evidence of IE; or • Resolution of IE syndrome with antibiotic therapy for < 4 days; or • No pathological evidence of IE at surgery or autopsy, with antibiotic • therapy for < 4 days; or • Does not meet criteria for possible IE as above Modifications shown in boldface. Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications. A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association. Circulation. 2005; 111: e 394 -e 433.
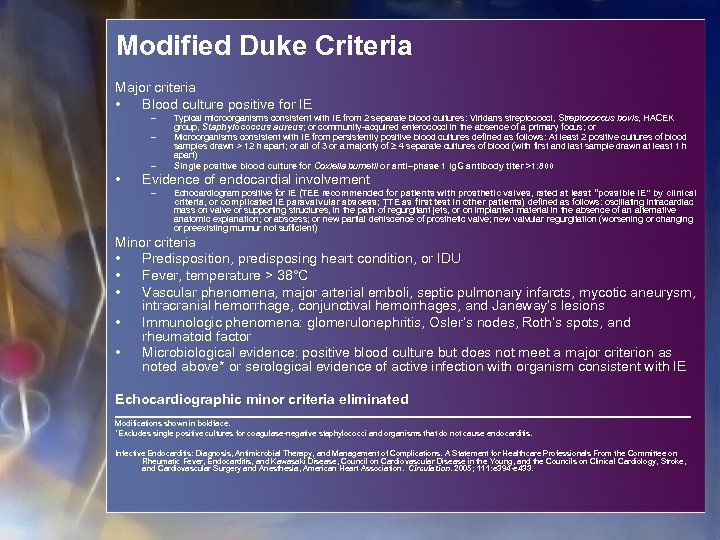 Modified Duke Criteria Major criteria • Blood culture positive for IE – – – • Typical microorganisms consistent with IE from 2 separate blood cultures: Viridans streptococci, Streptococcus bovis, HACEK group, Staphylococcus aureus; or community-acquired enterococci in the absence of a primary focus; or Microorganisms consistent with IE from persistently positive blood cultures defined as follows: At least 2 positive cultures of blood samples drawn > 12 h apart; or all of 3 or a majority of ≥ 4 separate cultures of blood (with first and last sample drawn at least 1 h apart) Single positive blood culture for Coxiella burnetii or anti–phase 1 Ig. G antibody titer >1: 800 Evidence of endocardial involvement – Echocardiogram positive for IE (TEE recommended for patients with prosthetic valves, rated at least “possible IE” by clinical criteria, or complicated IE paravalvular abscess; TTE as first test in other patients) defined as follows: oscillating intracardiac mass on valve or supporting structures, in the path of regurgitant jets, or on implanted material in the absence of an alternative anatomic explanation; or abscess; or new partial dehiscence of prosthetic valve; new valvular regurgitation (worsening or changing or preexisting murmur not sufficient) Minor criteria • Predisposition, predisposing heart condition, or IDU • Fever, temperature > 38°C • Vascular phenomena, major arterial emboli, septic pulmonary infarcts, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhages, and Janeway’s lesions • Immunologic phenomena: glomerulonephritis, Osler’s nodes, Roth’s spots, and rheumatoid factor • Microbiological evidence: positive blood culture but does not meet a major criterion as noted above* or serological evidence of active infection with organism consistent with IE Echocardiographic minor criteria eliminated Modifications shown in boldface. *Excludes single positive cultures for coagulase-negative staphylococci and organisms that do not cause endocarditis. Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications. A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association. Circulation. 2005; 111: e 394 -e 433.
Modified Duke Criteria Major criteria • Blood culture positive for IE – – – • Typical microorganisms consistent with IE from 2 separate blood cultures: Viridans streptococci, Streptococcus bovis, HACEK group, Staphylococcus aureus; or community-acquired enterococci in the absence of a primary focus; or Microorganisms consistent with IE from persistently positive blood cultures defined as follows: At least 2 positive cultures of blood samples drawn > 12 h apart; or all of 3 or a majority of ≥ 4 separate cultures of blood (with first and last sample drawn at least 1 h apart) Single positive blood culture for Coxiella burnetii or anti–phase 1 Ig. G antibody titer >1: 800 Evidence of endocardial involvement – Echocardiogram positive for IE (TEE recommended for patients with prosthetic valves, rated at least “possible IE” by clinical criteria, or complicated IE paravalvular abscess; TTE as first test in other patients) defined as follows: oscillating intracardiac mass on valve or supporting structures, in the path of regurgitant jets, or on implanted material in the absence of an alternative anatomic explanation; or abscess; or new partial dehiscence of prosthetic valve; new valvular regurgitation (worsening or changing or preexisting murmur not sufficient) Minor criteria • Predisposition, predisposing heart condition, or IDU • Fever, temperature > 38°C • Vascular phenomena, major arterial emboli, septic pulmonary infarcts, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhages, and Janeway’s lesions • Immunologic phenomena: glomerulonephritis, Osler’s nodes, Roth’s spots, and rheumatoid factor • Microbiological evidence: positive blood culture but does not meet a major criterion as noted above* or serological evidence of active infection with organism consistent with IE Echocardiographic minor criteria eliminated Modifications shown in boldface. *Excludes single positive cultures for coagulase-negative staphylococci and organisms that do not cause endocarditis. Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications. A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association. Circulation. 2005; 111: e 394 -e 433.
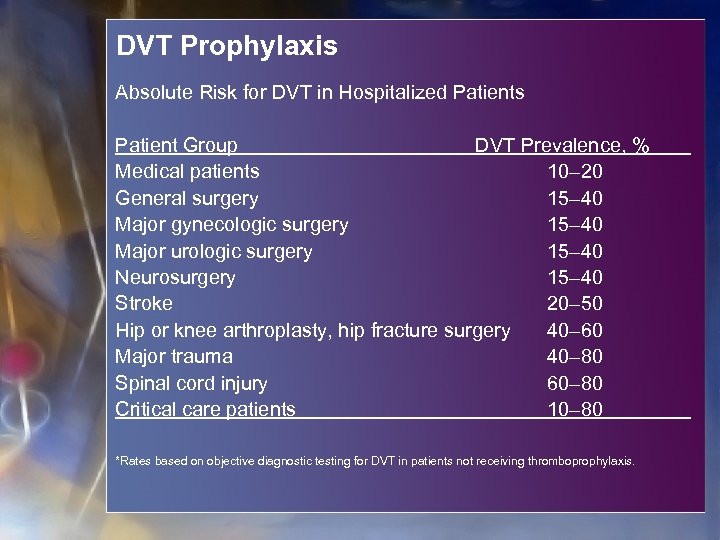 DVT Prophylaxis Absolute Risk for DVT in Hospitalized Patients Patient Group DVT Prevalence, % Medical patients 10– 20 General surgery 15– 40 Major gynecologic surgery 15– 40 Major urologic surgery 15– 40 Neurosurgery 15– 40 Stroke 20– 50 Hip or knee arthroplasty, hip fracture surgery 40– 60 Major trauma 40– 80 Spinal cord injury 60– 80 Critical care patients 10– 80 *Rates based on objective diagnostic testing for DVT in patients not receiving thromboprophylaxis.
DVT Prophylaxis Absolute Risk for DVT in Hospitalized Patients Patient Group DVT Prevalence, % Medical patients 10– 20 General surgery 15– 40 Major gynecologic surgery 15– 40 Major urologic surgery 15– 40 Neurosurgery 15– 40 Stroke 20– 50 Hip or knee arthroplasty, hip fracture surgery 40– 60 Major trauma 40– 80 Spinal cord injury 60– 80 Critical care patients 10– 80 *Rates based on objective diagnostic testing for DVT in patients not receiving thromboprophylaxis.
 DVT Prophylaxis Risk Factors for VTE • • • • • • Surgery Trauma (major or lower extremity) Immobility, paresis Malignancy Cancer therapy (hormonal, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy) Previous VTE Increasing age Pregnancy and the postpartum period Estrogen-containing oral contraception or hormone replacement therapy Selective estrogen receptor modulators Acute medical illness Heart or respiratory failure Inflammatory bowel disease Nephrotic syndrome Myeloproliferative disorders Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Obesity Smoking Varicose veins Central venous catheterization Inherited or acquired thrombophilia
DVT Prophylaxis Risk Factors for VTE • • • • • • Surgery Trauma (major or lower extremity) Immobility, paresis Malignancy Cancer therapy (hormonal, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy) Previous VTE Increasing age Pregnancy and the postpartum period Estrogen-containing oral contraception or hormone replacement therapy Selective estrogen receptor modulators Acute medical illness Heart or respiratory failure Inflammatory bowel disease Nephrotic syndrome Myeloproliferative disorders Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Obesity Smoking Varicose veins Central venous catheterization Inherited or acquired thrombophilia
 ACCP Grading Recommendations Applying the Grades of Recommendation for Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. CHEST 2004; 126: 179 S– 187 S)
ACCP Grading Recommendations Applying the Grades of Recommendation for Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. CHEST 2004; 126: 179 S– 187 S)
 DVT Prophylaxis - Recommendations Minor Surgery • < 30 minutes for benign disease • Recommend against use if specific prophylaxis other than early and persistent mobilization (Grade 1 C). Laparoscopy • If VTE risk factors are present, we recommend the use of thromboprophylaxis with one or more of the following: LDUH, LMWH, IPC, or GCS (all Grade 1 C)
DVT Prophylaxis - Recommendations Minor Surgery • < 30 minutes for benign disease • Recommend against use if specific prophylaxis other than early and persistent mobilization (Grade 1 C). Laparoscopy • If VTE risk factors are present, we recommend the use of thromboprophylaxis with one or more of the following: LDUH, LMWH, IPC, or GCS (all Grade 1 C)
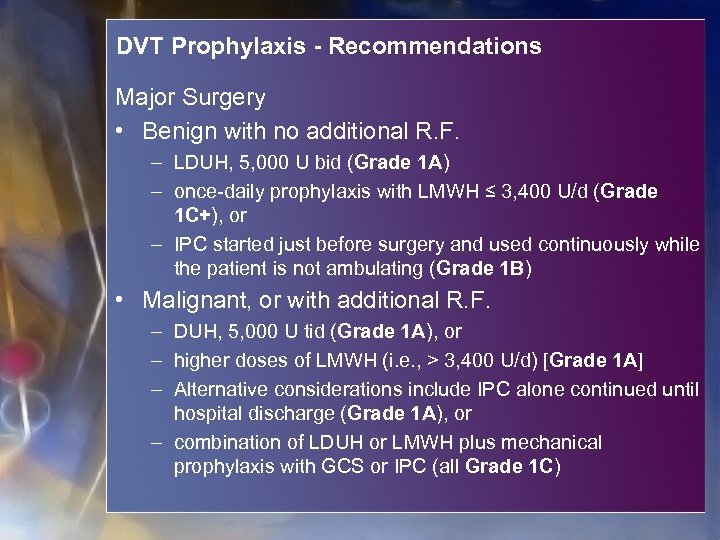 DVT Prophylaxis - Recommendations Major Surgery • Benign with no additional R. F. – LDUH, 5, 000 U bid (Grade 1 A) – once-daily prophylaxis with LMWH ≤ 3, 400 U/d (Grade 1 C+), or – IPC started just before surgery and used continuously while the patient is not ambulating (Grade 1 B) • Malignant, or with additional R. F. – DUH, 5, 000 U tid (Grade 1 A), or – higher doses of LMWH (i. e. , > 3, 400 U/d) [Grade 1 A] – Alternative considerations include IPC alone continued until hospital discharge (Grade 1 A), or – combination of LDUH or LMWH plus mechanical prophylaxis with GCS or IPC (all Grade 1 C)
DVT Prophylaxis - Recommendations Major Surgery • Benign with no additional R. F. – LDUH, 5, 000 U bid (Grade 1 A) – once-daily prophylaxis with LMWH ≤ 3, 400 U/d (Grade 1 C+), or – IPC started just before surgery and used continuously while the patient is not ambulating (Grade 1 B) • Malignant, or with additional R. F. – DUH, 5, 000 U tid (Grade 1 A), or – higher doses of LMWH (i. e. , > 3, 400 U/d) [Grade 1 A] – Alternative considerations include IPC alone continued until hospital discharge (Grade 1 A), or – combination of LDUH or LMWH plus mechanical prophylaxis with GCS or IPC (all Grade 1 C)
 DVT Prophylaxis - Recommendations Duration of Prophylaxis • until discharge from the hospital (Grade 1 C) • if particularly high risk, including those who have undergone cancer surgery and are > 60 years of age or have previously experienced VTE, prophylaxis for 2 to 4 weeks after hospital discharge (Grade 2 C)
DVT Prophylaxis - Recommendations Duration of Prophylaxis • until discharge from the hospital (Grade 1 C) • if particularly high risk, including those who have undergone cancer surgery and are > 60 years of age or have previously experienced VTE, prophylaxis for 2 to 4 weeks after hospital discharge (Grade 2 C)


