60657625fe4b1fbecbae6df0bc92abaf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

PERIOD 1 Ancient Period 8000 BCE to 600 BCE

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self-actualization (self-knowledge, fulfillment of personal potential) Esteem (autonomy, achievement, recognition) Social (belonging, affection) Safety (security, protection from harm) Physiological (Hunger, thirst, shelter)

Paleolithic to Neolithic n Paleolithic Age Humans had spread around globe n Humans were hunter-gatherers n Life style could not support large numbers n Man makes tools of stone, bone n n Began around 9, 000 BCE Rise of agriculture n Culture becomes increasingly complex n

RISE OF NEOLITHIC n Areas where Neolithic cultures arose Harsh environments n Water shortages n Few reliable sources of foodstuffs n n Causes of the Neolithic Revolution Development, spread of agriculture n Domestication of animals n Improvement of technology n

We begin at about 8, 000 BC when village life began in the New Stone Age. . . Also known as the Neolithic Revolution. NEW STONE AGE

A TOTALLY new way of living: From Hunter-Gatherers to Agriculture

ASPECTS OF NEOLITHIC AGE n Effects of Neolithic Age Sedentary culture develops n Surplus of food leads to increased populations n Rise of differentiated occupations n Complex cultures n Gender relations change n Humans begin to change environment n Communicable diseases become common n

PALEOLITHIC vs. NEOLITHIC n Many resist sedentarism Pastoralists n Hunter-Gatherers survive until 20 th century n Development uneven across regions n Change often slow n Indigenous development vs. diffusion n

INVENTION OF AGRICULTURE n Mesopotamians first to engage in agriculture n Around 8000 BC n Cereal crops n Wheat n Barley n Herd animals n Sheep n Goats

Human/Environmental interaction Tools and weapons n Social and political organization n Homes n n n n Lake houses in Switzerland Long houses along Danube Stone huts in Britain Reed lean-tos in Egypt Clay brick huts in Middle East Broad language groups appeared

POSSESSIONS n Needs of agriculture and stability n Clay pottery n Woven baskets n Woolen and linen clothing n Sophisticated tools and weapons n Plow

RESULTS OF AGRICULTURE n Required intensification of group organization n Neolithic farmers lived in settlements n Ranged from 150 (Jarmo) to 2000 (Jericho)

OUTSIDE CONTACTS n Neolithic communities had links n Walls indicate some fearful n Others were more peaceful Jericho
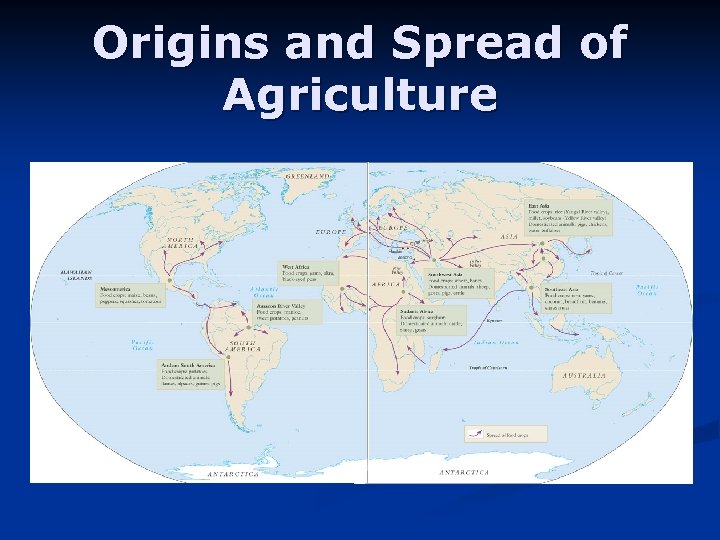
Origins and Spread of Agriculture

What does it mean to be civilized? n 18 th Century European Civilized vs. primitive n White vs. everyone else n n Historians have determined 6 characteristics of civilization: n Cities n Organized central governments n Complex religions n Social classes n Job specialization and the arts n Writing

CIVILIZATION’S 1 ST PHASE n Civilizations arose in few areas, spread out n Often arose around control of water n n n Called “hydraulic” (Hydro = water) civilizations Irrigation, flood control at center of power, changes Ancient period lasts generally to 1000 BCE

UNIQUENESS OF CIVILIZATION n Civilization was not simply next inevitable step from Neolithic Age n n Many peoples remained at simple foodraising stage for thousands of years— without developing any sort of civilization Only four locations developed civilizations entirely on their own n n China Indus River Valley Mesopotamia/Egypt Central America and Peru

Ancient River Valley Civilizations

Early River Valley Civilizations Environment • Flooding of Tigris and Euphrates unpredictable Mesopotamia • No natural barriers • Limited natural resources for making tools or buildings • Flooding of the Nile predictable Egypt • Nile an easy transportation link between Egypt’s villages • Deserts were natural barriers • Indus flooding unpredictable Indus River • Monsoon winds Valley • Mountains, deserts were natural barriers • Huang He flooding unpredictable China • Mountains, deserts natural barriers • Geographically isolated from other ancient civilizations Mesoamerica • Mountains and ocean natural barriers • Warm temperatures and moderate rainfall & Andes • Geographically isolated from other ancient civilizations

THE CULTURE OF CIVILIZATION n Permanent Institutions n n n n Religious: Theocracies, priesthoods, polytheism Political: Monarchy, aristocracy, militaries Social: Rise of classes Gender: Patriarchy Trade and Commerce Systems of Record Keeping Intellectual Traditions n n Arts, Architecture Literatures

WIDER CONTACTS Each civilization had particular patterns n Effects of Geography n Either facilitated, hindered communication n Strengthened, weakened local culture n n Contacts War, Trade, Diseases n Nomads n Migration n
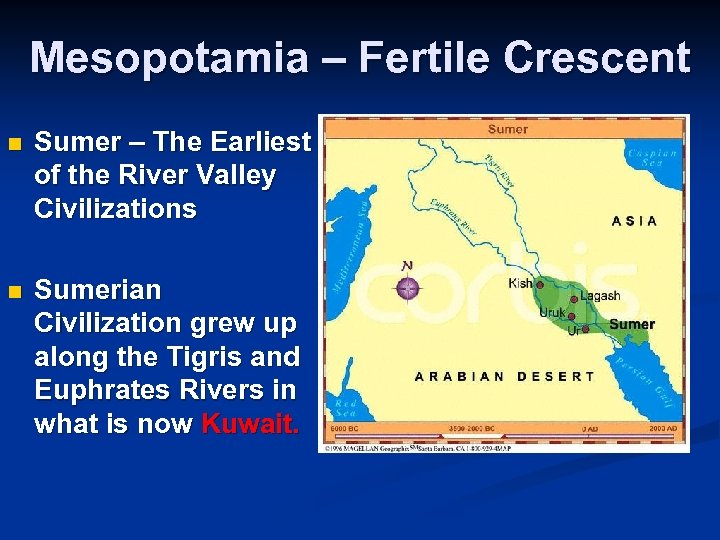
Mesopotamia – Fertile Crescent n Sumer – The Earliest of the River Valley Civilizations n Sumerian Civilization grew up along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in what is now Kuwait.

Sumerians invented: n n n Cuneiform Wheel Base 60 – using the circle. . . 360 degrees n n n Time – 60 minutes in an hour, 60 seconds in a minute 12 month lunar calendar Brick technology n n n arch ramp ziggurat

Babylon First know written law code n “Rule of Law” n Hammurabi’s Code - 1792 BC n

Code of Hammurabi n 8. If any one steal cattle or sheep, or an ass, or a pig or a goat, if it belong to a god or to the court, the thief shall pay thirtyfold for them; if they belonged to a freed man of the king he shall pay tenfold; if the thief has nothing with which to pay he shall be put to death. n 22. If any one is committing a robbery and is caught, then he shall be put to death. n 25. If fire break out in a house, and some one who comes to put it out cast his eye upon the property of the owner of the house, and take the property of the master of the house, he shall be thrown into that self-same fire. n 129. If a man's wife be surprised with another man, both shall be tied and thrown into the water, but the husband may pardon his wife and the king his slaves. n 137. If a man wish to separate from his wife who has borne him children: then he shall give that wife her dowry, and a part of the fruit of the field, garden, and property, so that she can rear her children. When she has brought up her children, a portion of all that is given to the children, equal as that of one son, shall be given to her. She may then marry the man of her heart.

EGYPT “The Gift of the Nile” n n Hieroglyphics Pyramids Geometry Advances in medicine and surgery Nile River Sahara Desert

Indus River Valley 2500 BC – 1500 BC Harappan culture n Well planned cities n n Grid pattern n Modern plumbing n Built on mud brick platforms n Protected n Larger against seasonal floods cities n Houses n Smaller built of baked brick towns n Houses built of sun-dried mud brick
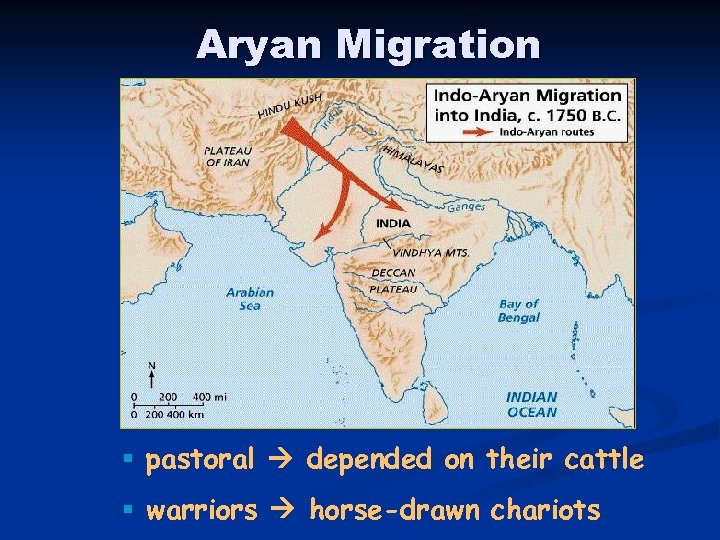
Aryan Migration § pastoral depended on their cattle § warriors horse-drawn chariots
Shang China 1600 BC – 1027 BC n n Yellow River Valley Advanced culture n Religion Astronomy Calendar Medicine n Bronze, jade, stone, bone and ceramic artifacts n n Lack of contact with foreigners led to belief in: n n Strong sense of identity Superiority Center of earth Sole source of civilization

Zhou China 1122 BC – 256 BC n n Bronze, jade, silver, gold Mandate of Heaven n not Veneration of ancestors n n Power to rule came from heaven Power could be removed if ruler just All must honor family responsibilities Period ended with of Warring States Era

Mesoamerica and Andean South America 2900 BC – 1400 BC n Mesoamerica n n n Maize, chili peppers, avocados, beans Pottery Stone bowls Beads Waddle and daub structures No draft animals

Mesoamerica and Andean South America 3500 BC – 1400 BC n Andes n n n Textiles technology Sophisticated government Religion Lacked ceramics Largely without art Most impressive achievement was monumental architecture n n Large platform mounds Sunken circular plazas
60657625fe4b1fbecbae6df0bc92abaf.ppt