001f0c16c1e70cf53b3aa40db2b1959e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 PERILAKU KONSUMEN Kode PTE-42 PERTEMUAN ENAM: SIKAP ONSUMEN Rini Dwiastuti & Riyanti 2008
PERILAKU KONSUMEN Kode PTE-42 PERTEMUAN ENAM: SIKAP ONSUMEN Rini Dwiastuti & Riyanti 2008
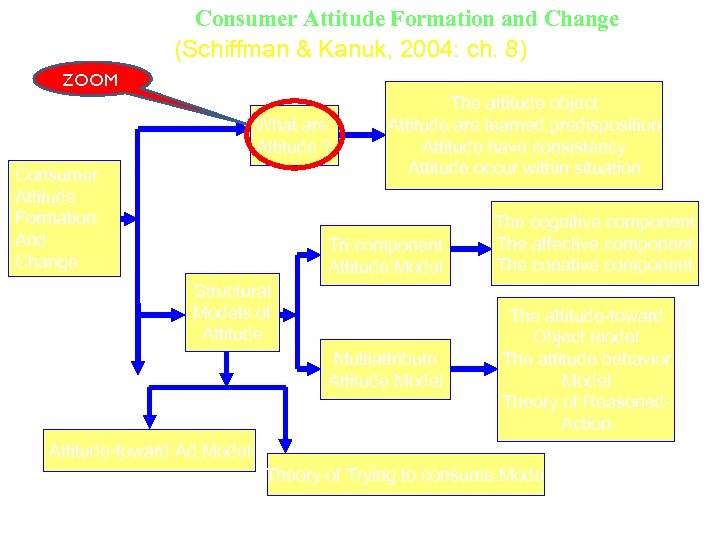 Consumer Attitude Formation and Change (Schiffman & Kanuk, 2004: ch. 8) ZOOM (1) What are Attitude ? Consumer Attitude Formation And Change The attitude object Attitude are learned predisposition Attitude have consistency Attitude occur within situation Tri component Attitude Model (2) Structural Models of Attitude Multiattribute Attitude Model The cognitive component The affective component The conative component The attitude-toward Object model The attitude behavior Model Theory of Reasoned. Action Attitude-toward Ad Model Theory of Trying to consume Model
Consumer Attitude Formation and Change (Schiffman & Kanuk, 2004: ch. 8) ZOOM (1) What are Attitude ? Consumer Attitude Formation And Change The attitude object Attitude are learned predisposition Attitude have consistency Attitude occur within situation Tri component Attitude Model (2) Structural Models of Attitude Multiattribute Attitude Model The cognitive component The affective component The conative component The attitude-toward Object model The attitude behavior Model Theory of Reasoned. Action Attitude-toward Ad Model Theory of Trying to consume Model
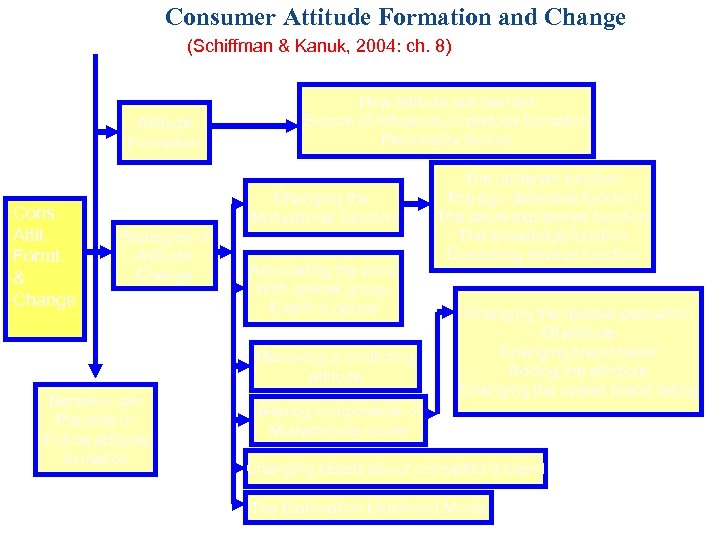 Consumer Attitude Formation and Change (Schiffman & Kanuk, 2004: ch. 8) (3) Attitude Formation Cons. Attit. Formt. & Change (4) Strategies of Attitude Change How attitude are learned Source of influence on attitude formation Personality factors Changing the Motivational function Associating the prod. With special group, Event or cause Resolving 2 conflicting attitude Behavior can (5) Precede or Follow attitude formation The utilitarian function The ego defensive function The value-expressive function The knowledge function Combining several function Changing the relative evaluation Of attitude Changing brand belief Adding the attribute Changing the overall brand rating Altering components of Multiattribute model Changing beliefs about competitor’s brand The Elaboration Likelihood Model
Consumer Attitude Formation and Change (Schiffman & Kanuk, 2004: ch. 8) (3) Attitude Formation Cons. Attit. Formt. & Change (4) Strategies of Attitude Change How attitude are learned Source of influence on attitude formation Personality factors Changing the Motivational function Associating the prod. With special group, Event or cause Resolving 2 conflicting attitude Behavior can (5) Precede or Follow attitude formation The utilitarian function The ego defensive function The value-expressive function The knowledge function Combining several function Changing the relative evaluation Of attitude Changing brand belief Adding the attribute Changing the overall brand rating Altering components of Multiattribute model Changing beliefs about competitor’s brand The Elaboration Likelihood Model
 Sub-Pokok Bahasan: 1. Pengertian sikap 2. Model Struktural Perilaku: a. Tri component Attitude Model b. Multiattribute Attitude Model c. Attitude-toward Ad Model d. Theory of Trying to consume Model 3. Bentukan Sikap 4. Strategi mengubah sikap
Sub-Pokok Bahasan: 1. Pengertian sikap 2. Model Struktural Perilaku: a. Tri component Attitude Model b. Multiattribute Attitude Model c. Attitude-toward Ad Model d. Theory of Trying to consume Model 3. Bentukan Sikap 4. Strategi mengubah sikap
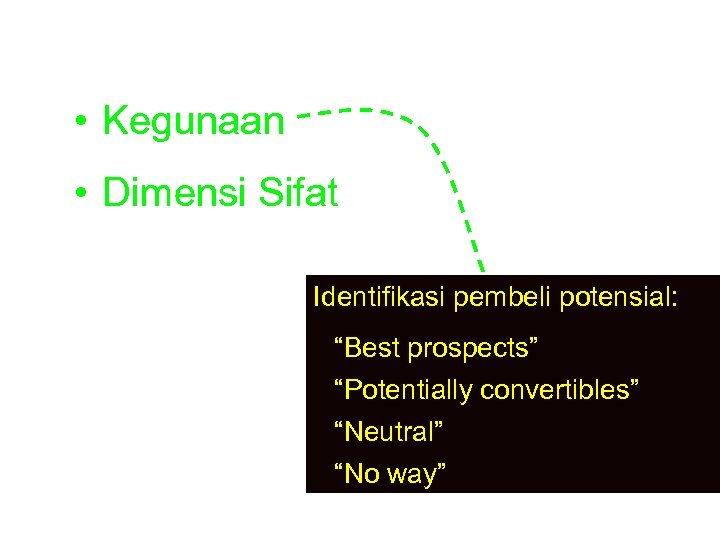 1. Pengertian sikap • Kegunaan • Dimensi Sifat Identifikasi pembeli potensial: “Best prospects” “Potentially convertibles” “Neutral” “No way”
1. Pengertian sikap • Kegunaan • Dimensi Sifat Identifikasi pembeli potensial: “Best prospects” “Potentially convertibles” “Neutral” “No way”
 “Best prospects” segmen yg mengindikasikan sikap sangat baik thdp kesempatan membeli produk dlm waktu segera “Potentially convertibles” segmen yg mengindikasikan sikap baik thdp kesempatan membeli produk beberapa waktu y. a. d, namun tdk dlm jk waktu dekat. “Neutral” anggota masy dg sikap tdk ada rasa suka maupun tidak membeli produk “No way” anggota masy dg sikap tidak membeli produk
“Best prospects” segmen yg mengindikasikan sikap sangat baik thdp kesempatan membeli produk dlm waktu segera “Potentially convertibles” segmen yg mengindikasikan sikap baik thdp kesempatan membeli produk beberapa waktu y. a. d, namun tdk dlm jk waktu dekat. “Neutral” anggota masy dg sikap tdk ada rasa suka maupun tidak membeli produk “No way” anggota masy dg sikap tidak membeli produk
 What Are Attitude ? Consumer researcher assess attitude by asking questions or making inferences from behavior. Attitude are not directly observable but must be infered from what people say or what they do. Consistency of purchases, recommendations to others, top ranking, beliefs, evaluations, and intentions are related to attitudes. In consumer behavior context, an attitude is a learned predisposition to behavior in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way with respect to a given object.
What Are Attitude ? Consumer researcher assess attitude by asking questions or making inferences from behavior. Attitude are not directly observable but must be infered from what people say or what they do. Consistency of purchases, recommendations to others, top ranking, beliefs, evaluations, and intentions are related to attitudes. In consumer behavior context, an attitude is a learned predisposition to behavior in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way with respect to a given object.
 What Are Attitude ? (cont. ) “Object” : product, product category, brand, service, possessions, product use, causes or issues, people, advertisement, price, medium, Internet site, or retailer object specific. Are learned, that attitudes relevant to purchase behavior are formed as a result or direct experience with the product, WOM inf. acquired from others, or exposure to mass-media ads, the Internet and various forms of direct marketing as a result of consumer learning attitudes are not synonymous with behavior.
What Are Attitude ? (cont. ) “Object” : product, product category, brand, service, possessions, product use, causes or issues, people, advertisement, price, medium, Internet site, or retailer object specific. Are learned, that attitudes relevant to purchase behavior are formed as a result or direct experience with the product, WOM inf. acquired from others, or exposure to mass-media ads, the Internet and various forms of direct marketing as a result of consumer learning attitudes are not synonymous with behavior.
 What Are Attitude ? (cont. ) Consistent with the behavior they reflect : when consumers are free to act as they wish, we anticipate that their actions will be consistent with their attitude. Occur within a situation : events or cincumstances that, at a particular point of time, influence the relationship between attitude and behavior individuals can have a variety of attitude toward a particular behavior, each corresponding to a particular situations influence consumer attitude.
What Are Attitude ? (cont. ) Consistent with the behavior they reflect : when consumers are free to act as they wish, we anticipate that their actions will be consistent with their attitude. Occur within a situation : events or cincumstances that, at a particular point of time, influence the relationship between attitude and behavior individuals can have a variety of attitude toward a particular behavior, each corresponding to a particular situations influence consumer attitude.
 Dimensi/sifat Sikap: § Favorability kesukaan § Intencity kehebatan § Confidence kepercayaan § Stability kemantapan Note: Sikap dpt beragam dlm bentuk dr apakah yg didasarkan pd manfaat yg dirasakan atau sifat kesenangan*)
Dimensi/sifat Sikap: § Favorability kesukaan § Intencity kehebatan § Confidence kepercayaan § Stability kemantapan Note: Sikap dpt beragam dlm bentuk dr apakah yg didasarkan pd manfaat yg dirasakan atau sifat kesenangan*)
 Note (lanjutan): § Beberapa produk, sikap tgt kemanfaatan yg dirasakan manfaat fungsional merek § Produk yg lain, sikap tgt pd sifat kesenangan yg dihasilkan taman, musik, bioskop dll.
Note (lanjutan): § Beberapa produk, sikap tgt kemanfaatan yg dirasakan manfaat fungsional merek § Produk yg lain, sikap tgt pd sifat kesenangan yg dihasilkan taman, musik, bioskop dll.
 2. STRUCTURAL MODELS OF ATTITUDE 1. Tricomponent Attitude Model, attitude consist of 3 major components : (a) a cognitive component (b) an affective component (c) a conative component • Peter dan Olson (1999) • Schiffmen dan Kanuk (1994) • Solomon (1999)
2. STRUCTURAL MODELS OF ATTITUDE 1. Tricomponent Attitude Model, attitude consist of 3 major components : (a) a cognitive component (b) an affective component (c) a conative component • Peter dan Olson (1999) • Schiffmen dan Kanuk (1994) • Solomon (1999)
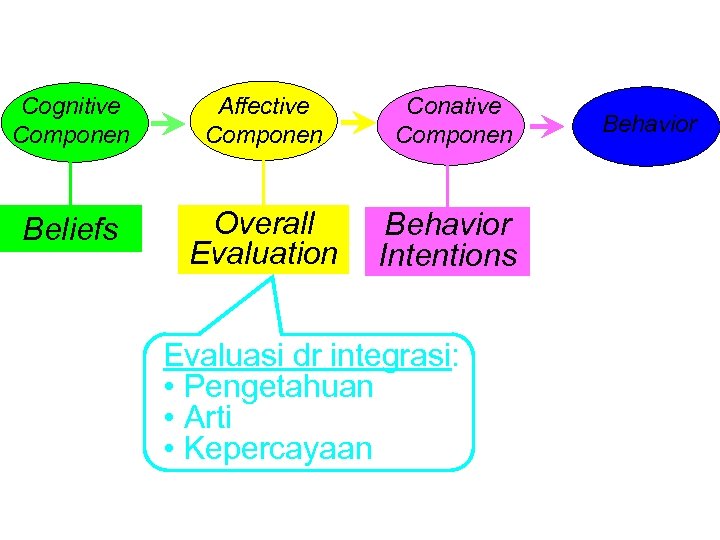 Cognitive Componen Affective Componen Conative Componen Beliefs Overall Evaluation Behavior Intentions Evaluasi dr integrasi: • Pengetahuan • Arti • Kepercayaan Behavior
Cognitive Componen Affective Componen Conative Componen Beliefs Overall Evaluation Behavior Intentions Evaluasi dr integrasi: • Pengetahuan • Arti • Kepercayaan Behavior
 Contoh Alternatif mengukur Beliefs, Attitudes, dan Intentions Mengukur Beliefs 1. How likely is it that Pepsi tastes sweet? very likely …. . : …. very unlikely 2. How would you rate that sweetness of Pepsi’s tastes? very sweet …. . : …. very bitter
Contoh Alternatif mengukur Beliefs, Attitudes, dan Intentions Mengukur Beliefs 1. How likely is it that Pepsi tastes sweet? very likely …. . : …. very unlikely 2. How would you rate that sweetness of Pepsi’s tastes? very sweet …. . : …. very bitter
 3. Indicate how strongly you agree with the following statement: “Pepsi’s has a sweet tastes” a. Strongly agree b. Somewhat agree c. Slightly agree d. Neither agree nor disagree e. Slightly disagree f. Somewhat disagree g. Strongly disagree Note: Lihat sifat sikap pd slide no. 9
3. Indicate how strongly you agree with the following statement: “Pepsi’s has a sweet tastes” a. Strongly agree b. Somewhat agree c. Slightly agree d. Neither agree nor disagree e. Slightly disagree f. Somewhat disagree g. Strongly disagree Note: Lihat sifat sikap pd slide no. 9
 Mengukur Attitudes 1. How much do you like Pepsi? like very much … : … : . . dislike very much 2. How favorable is your overall opinion of Pepsi? very favorable … : … : . . very unfavorable 3. Pepsi is good … : … : . . Bad appealing … : … : . . Unappealing pleasant … : … : . . unpleasant
Mengukur Attitudes 1. How much do you like Pepsi? like very much … : … : . . dislike very much 2. How favorable is your overall opinion of Pepsi? very favorable … : … : . . very unfavorable 3. Pepsi is good … : … : . . Bad appealing … : … : . . Unappealing pleasant … : … : . . unpleasant
 3. Indicate how strongly you agree with the following statement: “I really like Pepsi” a. Strongly agree b. Somewhat agree c. Slightly agree d. Neither agree nor disagree e. Slightly disagree f. Somewhat disagree g. Strongly disagree Note: Bandingkan dg mengukur belief pd slide no. 13 – 14
3. Indicate how strongly you agree with the following statement: “I really like Pepsi” a. Strongly agree b. Somewhat agree c. Slightly agree d. Neither agree nor disagree e. Slightly disagree f. Somewhat disagree g. Strongly disagree Note: Bandingkan dg mengukur belief pd slide no. 13 – 14
 Mengukur Intention 1. Do you intend to by Pepsi? definitely intend buy. . : . definitely intend buy 2. How likely is it that you buy Pepsi? very likely …. . : …. very unlikely 3. What is the probability that you will buy Pepsi? 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% … … … 100%
Mengukur Intention 1. Do you intend to by Pepsi? definitely intend buy. . : . definitely intend buy 2. How likely is it that you buy Pepsi? very likely …. . : …. very unlikely 3. What is the probability that you will buy Pepsi? 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% … … … 100%
 3. Indicate how strongly you agree with the following statement: “I intend to buy Pepsi” a. Strongly agree b. Somewhat agree c. Slightly agree d. Neither agree nor disagree e. Slightly disagree f. Somewhat disagree g. Strongly disagree
3. Indicate how strongly you agree with the following statement: “I intend to buy Pepsi” a. Strongly agree b. Somewhat agree c. Slightly agree d. Neither agree nor disagree e. Slightly disagree f. Somewhat disagree g. Strongly disagree


