349d8b64249b717420505009ff7aa258.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65

PERFORMANCE METRICS | IAN HUNG | BOBBIN LO | | YAN MA | LOUIS SZETO | Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
PERFORMANCE METRICS DEFINITION The standard measurement for describing performance Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MEASURING ELECTRONIC SHOPPING EFFECTIVENESS Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MOTIVATION • Designing an online store with effective customer interfaces has a critical influence on traffic and sales Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

ELECTRONIC SHOPPING • Electronic marketplace (EM) becoming a major part of commerce in the coming decade • In 1995, cyberspace sales of $1 B in US • Total US retail industry of $1 trillion • 2000 projection of $7 B-$117 B Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

ELECTRONIC SHOPPING cont • Changes how business is conducted – – – Business strategy Technical infrastructure Government policies EM demographics How technology is used Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

ELECTRONIC SHOPPING cont • Differences in EM and traditional store – Service desk → help button – Layout → pull-down menus, product indices, search engines • Very important: User Interface (UI) • Should not assume customers know-it-all • UI affects productivity in general Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

TRAFFIC AND SALE FACTORS • 6 factors affecting traffic and sales 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Merchandise Service Promotion Convenience Checkout Store navigation Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

1/6. MERCHANDISE • • Customers prefer wide range of products 5% of stores had 500+ items 62% of stores had < 50 items Range of products causes 17% variance in traffic, but no affect on sales • Physical properties cannot be sampled Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
1/6. MERCHANDISE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

1/6. MERCHANDISE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
1/6. MERCHANDISE cont • < 8% screen area contained images • Large images: Slow • Small images: Poor quality Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
1/6. MERCHANDISE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

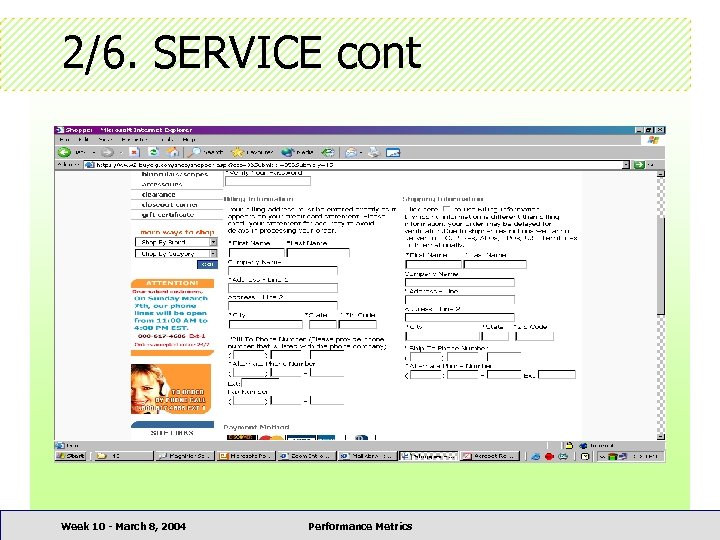
2/6. SERVICE • • • Provide company profile + history Quick responsiveness to inquiries Anytime, anywhere, any language Useful FAQs Credit, debit, and payment policies Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
2/6. SERVICE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
2/6. SERVICE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
2/6. SERVICE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

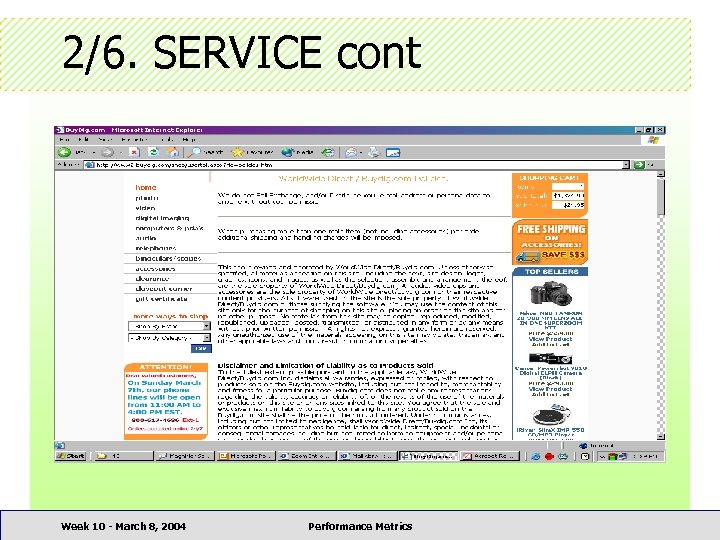
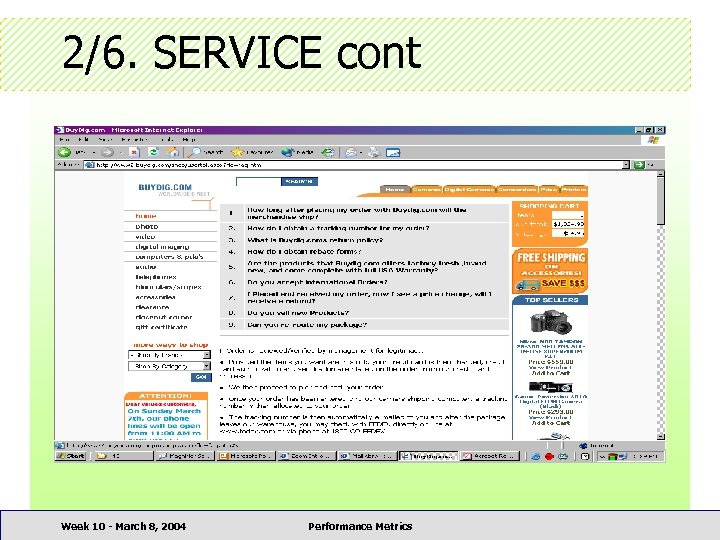
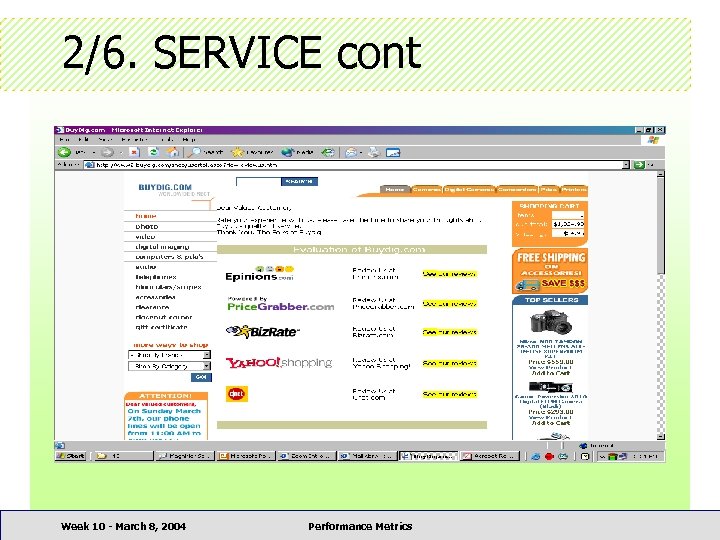
2/6. SERVICE cont • • < 33% provide company profile + history 80% had < 10 lines of such information 95% did not have links to related products 25% had help for product selection < 9% had FAQ section 47% did not have interactive email 80% of stores had 1+ complaints Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
2/6. SERVICE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

2/6. SERVICE cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

2/6. SERVICE cont • FAQ section increases traffic • Feedback + help section increases sales • Delays in answering complaints a PR disaster Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

3/6. PROMOTION • 1 hr promotion → 4%↑ in variance of sales and 1. 4%↑ in variance of traffic • Promotion = sales, advertising, appetizer features • 6% of stores offer ‘What’s New’ section • 76% did not offer incentives • Related links an important part of promotion Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

3/6. PROMOTION cont • Advertising – – Banners: top/ bottom of page Spotlight: the logo prior to entrance Features: first thing you see Positions: some ads are never read Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
3/6. PROMOTION cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

4/6. CONVENIENCE • • • Layout, organization, ease of use Help function should assist convenience 12% had help sections Status indicators Short text, informative headlines (multilayered), use of white-space, colors Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

5/6. CHECKOUT • • Long checkout lose customers Repetitive entry of information Ideal: universal checkout interface Shopping cart scheme – Remove items at will – w/o moving everything at a time • Shipping date, out-of-stock info Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
5/6. CHECKOUT cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

6/6. STORE NAVIGATION • Contribution to ease of navigation: – Product search – Sitemaps – Products indices – Site organization and design, – Links to related products Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
6/6. STORE NAVIGATION cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

6/6. STORE NAVIGATION cont • • • 4% of stores have site index 6% had product search engines 22% offered browsing buttons Product list ↑ sales by 61%, ↑ traffic 7% More description, pictures, and less click to purchase increase sales • Link to master index (site map) • Groupings, cross-store searches Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
WEB INFORMATION SYSTEMS • Search engines are important, especially for large sites • Navigation path of user unknown • Every page must have navigation tools Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MARKETING & MERCHANDISING METRICS Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MOTIVATION • Internet has become the channel for sales and customer service • Max return on investment – Understand the effectiveness of their sites – Make appropriate action • Two main perspectives for analyzing the effectiveness of the sites – Marketing – Merchandising Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MARKETING • Definition – Defined as the activities used to acquire customers to an online store and retain them • Techniques – Use of banner ads, email campaigns Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MARKETING METRICS • Traditionally – Clickthrough rate: the percentage of viewers who click on a banner ad – Conversion rate: the percentage of visitors who purchase from the store • Recently – Ad banner return on investment (ROI) Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MERCHANDISING • Definition – Activities involved in acquiring particular products and making them available at the places, times, and prices and in the quantity to enable a retailer store to reach its goal, it also include how and where to display products, and which products to advertise and promote • Responsibilities – Product assortment and product display, including promotions, cross-selling and up-selling Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
MERCHANDISING METRICS • Traditionally – Web page hit counts • Provide a broad indication of visitor interest – Conversion rate • Indicates the percentage of visitors who purchase form the store • Useful for evaluating the overall effectiveness of the store • Cannot understand the possible factors within the store that may affect the sales performance • Recently – Micro-conversion rates • Provide detailed insight into the success of different web merchandising, product assortment, and site design strategies Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

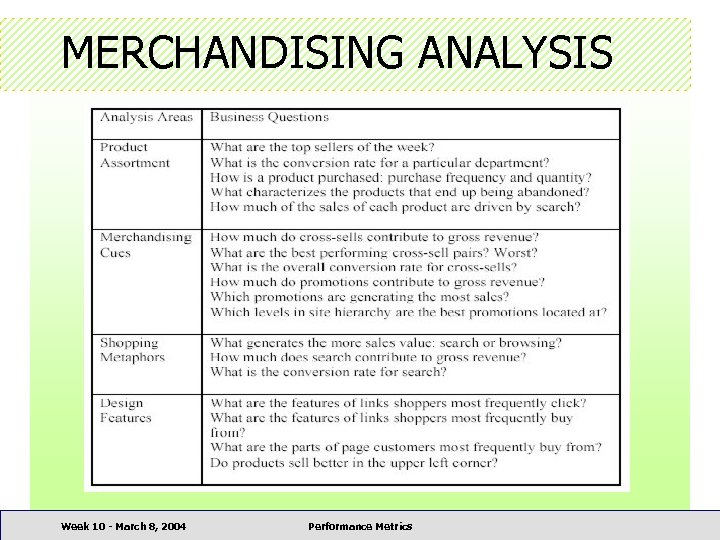
MERCHANDISING ANALYSIS 1. Product assortment – Deals with whether the products in an online store appeal to the visitors – Merchant can adjust brands, quality, selection, inventory or price to optimize sales Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MERCHANDISING ANALYSIS 2. Merchandising cues – Different ways web merchants present their products to motivate purchase in online stores • Cross-sells – Refers the visitor to a web page marketing an item complementary in function to the item marketed on the current web page • Up-sells – Refers visitor to a web page presenting a similar but more upscale item • Recommendations – Highlights product pages that are likely to be of interest to the shopper based on knowledge of the shopper and the behavior of a larger population • Promotions – Refers a visitor to a product page for informing, persuading and/or reminding the shoppers about a product and/or other aspects of the site Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MERCHANDISING ANALYSIS 3. Shopping metaphor – Different ways that shoppers use to find products of interest 4. Web design features – Different ways how hyperlinks group together Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
MERCHANDISING ANALYSIS Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

MARKETING VS MERCHANDISING Web Marketing • Uses banner ads and referral sites • Clickthrough rates, ad banner ROI • Controlled in external sites Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Web Merchandising • Hyperlinks and image links within the store • Micro-conversion rates • Controlled internally Performance Metrics

PROBLEM • Tracking and measuring – Classifying each hyperlink by its merchandising purposes – Tracking and measuring traffic on the hyperlinks and analyzing their effectiveness – Attributing the profit of the hyperlinks to their merchandising cue type, shopping metaphor, and design features Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
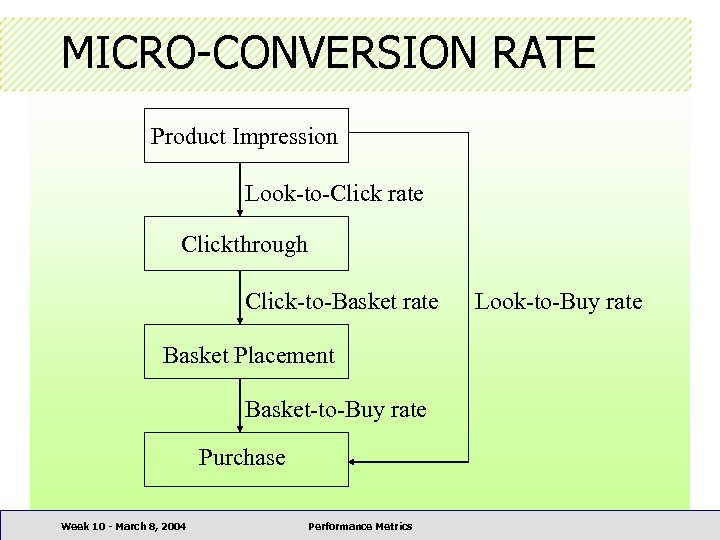
MICRO-CONVERSION RATE Product Impression Look-to-Click rate Clickthrough Click-to-Basket rate Basket Placement Basket-to-Buy rate Purchase Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics Look-to-Buy rate
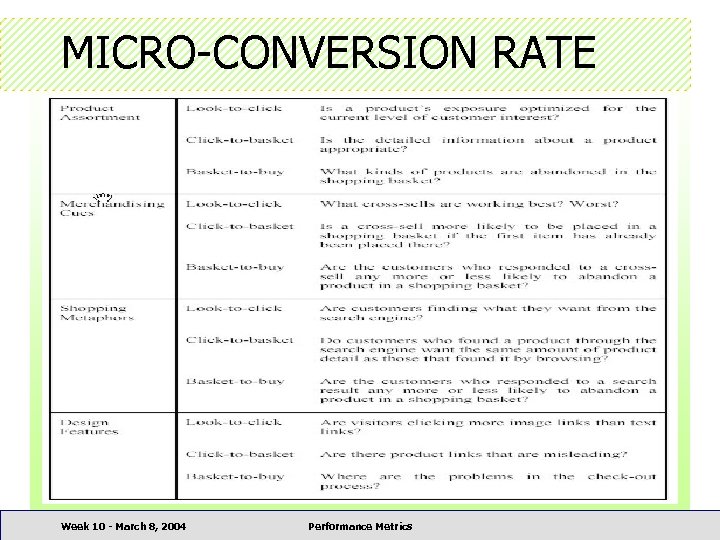
MICRO-CONVERSION RATE Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
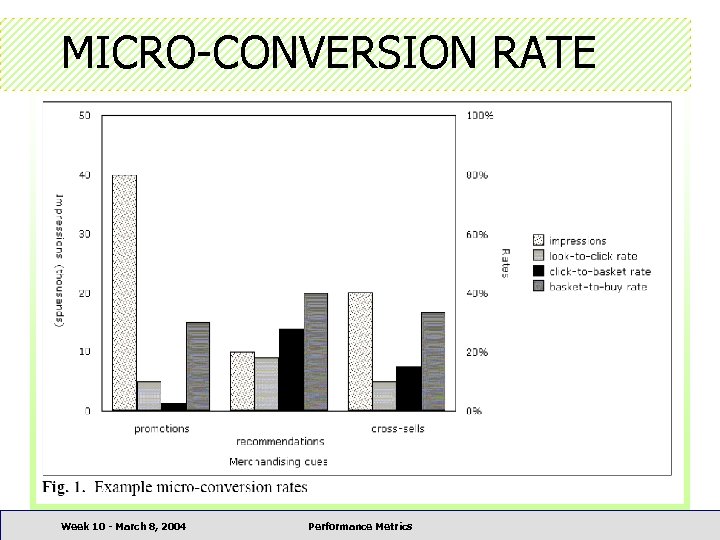
MICRO-CONVERSION RATE Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
MICRO-CONVERSION RATE • Micro-conversion rate can be calculated for – – – individual individual merchandising cue types products shopping metaphor types design features banner ads • Mini-Conclusion – All the individual hyperlinks pointing to product pages in various forms and purposes can be analyzed Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
PARALLEL COORDINATES & STARFIELD VISUALIZATION Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF WEB MERCHANDISING 1. To visualize the effectiveness: – Traffic data, from web server logs – Sales data, from the database of associated commerce server 2. To visualize a complete set of microconversion: – Product impression data: • From content meta-data tags or • Dynamically parser the content of a web page Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF WEB MERCHANDISING cont 3. To examine merchandising purpose: – Implementation time data: • Static hyperlink labels • Tagged hyperlinks and dynamically parsed Overall: – Data preparation is easier for dynamic online stores – Dynamic URLs can be easily identified Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

CLICKSTREAM DATA • Displays the progression of sessions in terms of micro-conversions among shopping steps • To understand where the store loses customers • To compare shopping behavior • To understand the effectiveness of different merchandising tactics Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
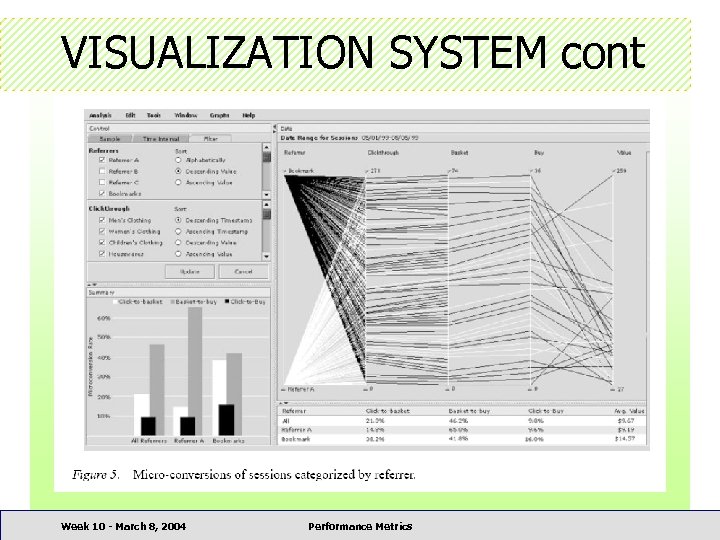
PARALLEL COORDINATE • Displays multivariate data sets to identify the relationship among the variates • Used to visualize clickstream • The sequential steps of look, click and buy represented by a series of parallel axes Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
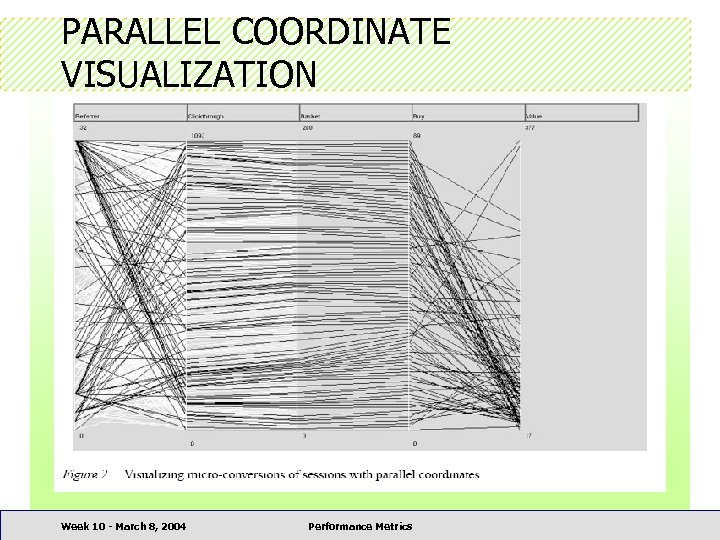
PARALLEL COORDINATE VISUALIZATION Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

STARFIELD VISUALIZATION • Displays product-oriented information helpful to understand the product assortment aspects of the store Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
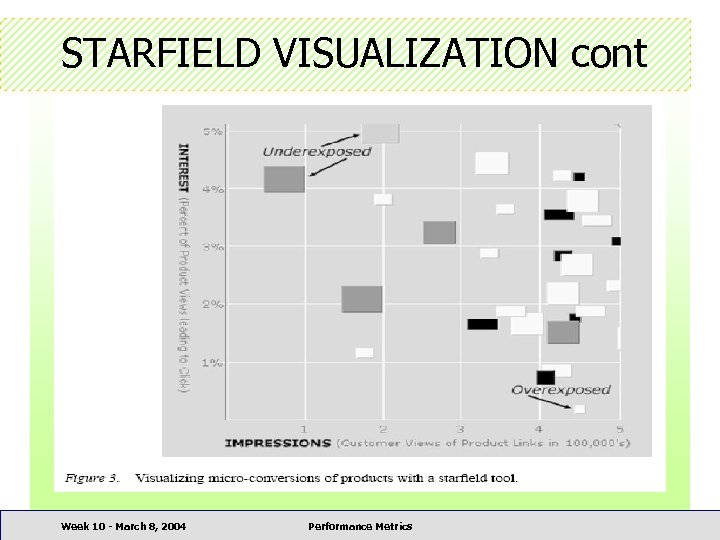
STARFIELD VISUALIZATION cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
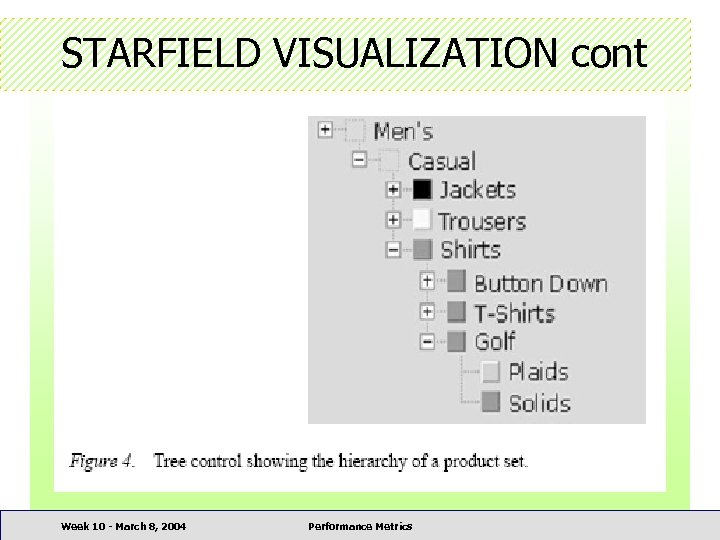
STARFIELD VISUALIZATION cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
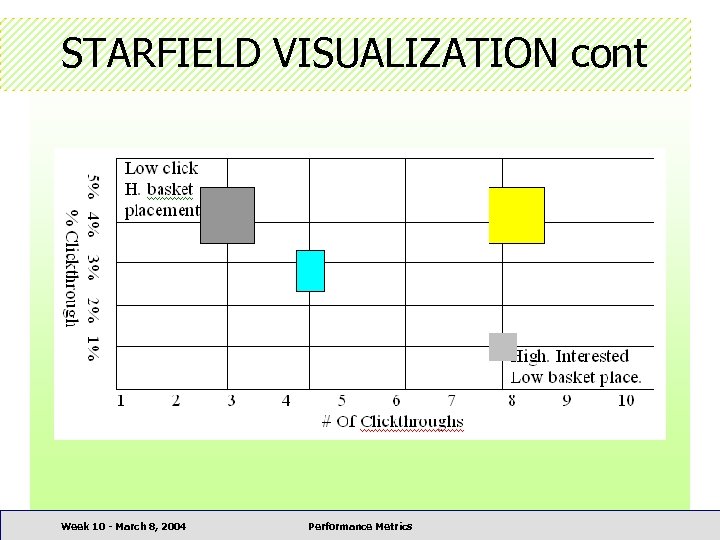
STARFIELD VISUALIZATION cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
VISUALIZATION SYSTEM IN PRACTICE Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
VISUALIZATION SYSTEM • Background – Interactive visualization system implemented as part of the E-Commerce Intelligence project at IBM T. J. Watson Research Center • Purpose – Help users explore and interpret web usage data to maximize merchandising effectiveness • Features – Visualization of parallel coordinates, starfield graphs, color-coding, filtering, zooming, data sampling, dynamic querying, and summary data Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
VISUALIZATION SYSTEM cont Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
VISUALIZATION WEAKNESSES • Does not identify the exact merchandising attribute leading to a sale or exit • Does not track the session time at each sequence of the clickstream • Assumes users traverse the site in a linear fashion Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
VISUALIZATION IMPROVEMENTS • Enhance shopping step data – Each session is currently identified by a unique timestamp corresponding to a data point on the parallel axis – Does not indicate volume or time spent on each step • Extend User Actions – Apply visualization technique to different web paradigms (Online Auction) – Require a different set of sequential steps with parallel coordinates (Click-to-Bid) Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
VISUALIZATION IMPROVEMENTS • Explore other visualization methods – Mosaic graphs • “Richer” session categorizing variables – Besides referrers, host names, etc. . , include shopping metaphors, merchandising cues, design features, and customer profile information • Challenging to quantify/classify variables – Relationships among category variables may be studied for their impact on store performance • Validation – More empirical studies over longer time range needed – Provide optimal set of visualizations to understand merchandising effectiveness with minimal effort Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
OTHER PERFORMANCE METRICS • Web Server Log Analysis – Lack integration with knowledge of site layout – Generally does not relate Web usage data with their meaning in commerce • Datamining – Supplement visualization results – Predictive Modeling • Derived rewards stored in online customer profile for personalized product promotions – Collaborative Filtering • Dynamic merchandising mechanism for unregistered users (Amazon. com) Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics

QUESTIONS Week 10 - March 8, 2004 Performance Metrics
349d8b64249b717420505009ff7aa258.ppt