2515a5921bf13fff0e92cba48f106e18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Performance Analysis of Two. Dimensional Scheduling Algorithms in IEEE 802. 16 Wi. MAX™ Supervised by: Dr. Michael Segal Mr. Itzik Kitroser Shani Levy Meshi Peer Communication Systems Engineering Department Ben - Gurion University, Israel 1
Performance Analysis of Two. Dimensional Scheduling Algorithms in IEEE 802. 16 Wi. MAX™ Supervised by: Dr. Michael Segal Mr. Itzik Kitroser Shani Levy Meshi Peer Communication Systems Engineering Department Ben - Gurion University, Israel 1
 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 2
Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 2
 Main Goals n n n Design and implementation of an environment suitable for performance analysis of two dimensional scheduling algorithms for wireless networks based on the IEEE 802. 16 standard. Implementation of a simulation environment under NS-2 network simulator. Run and research the implementation with various parameters to investigate network traffic and load to optimize the system. 3
Main Goals n n n Design and implementation of an environment suitable for performance analysis of two dimensional scheduling algorithms for wireless networks based on the IEEE 802. 16 standard. Implementation of a simulation environment under NS-2 network simulator. Run and research the implementation with various parameters to investigate network traffic and load to optimize the system. 3
 Project Steps Studying: n 802. 16 IEEE standard and relevant articles. n NS 2 simulator and it’s tools, using LINUX OS. n Examine existing implementations to work with. Implementation: n Implementing the Ranging and BW request algorithm. n Try to optimize the ranging process in terms of efficient, while reducing the required number of codes/ranging slots. Results: n Create graphs from the results and try to get optimize results under different conditions. 4
Project Steps Studying: n 802. 16 IEEE standard and relevant articles. n NS 2 simulator and it’s tools, using LINUX OS. n Examine existing implementations to work with. Implementation: n Implementing the Ranging and BW request algorithm. n Try to optimize the ranging process in terms of efficient, while reducing the required number of codes/ranging slots. Results: n Create graphs from the results and try to get optimize results under different conditions. 4
 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 5
Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 5
 What is Wi. MAX? n n Wi. MAX - World Interoperability for Microwave Access. The next generation of Wi. Fi (IEEE 802. 11), Based on the IEEE 802. 16 standard. Expected to enable true broadband speeds over wireless networks at a cost point to enable mass market adoption. A wireless networking technology that will connect you to the Internet at faster speeds and from much longer ranges than current wireless technology allows. 6
What is Wi. MAX? n n Wi. MAX - World Interoperability for Microwave Access. The next generation of Wi. Fi (IEEE 802. 11), Based on the IEEE 802. 16 standard. Expected to enable true broadband speeds over wireless networks at a cost point to enable mass market adoption. A wireless networking technology that will connect you to the Internet at faster speeds and from much longer ranges than current wireless technology allows. 6
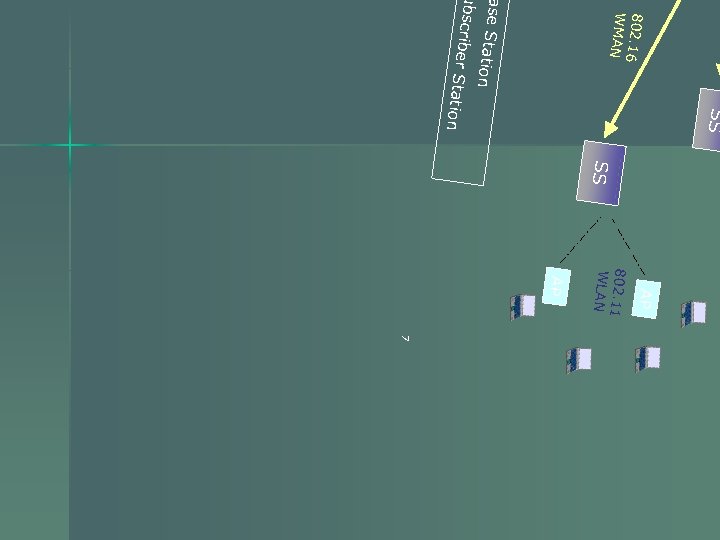 802. 16 WMAN SS tion ase Sta tion ub scriber Sta SS AP 802. 11 WLAN AP 7 7
802. 16 WMAN SS tion ase Sta tion ub scriber Sta SS AP 802. 11 WLAN AP 7 7
 OFDMA – Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access n n OFDM subdivides the bandwidth into multiple frequency sub-carriers. OFDMA is a multiple-access scheme for OFDM. It provides Multiplexing operation of data streams from multiple users. Resources are available in the time domain by means of OFDMA symbols and in the frequency domain by means of sub-carriers. 8
OFDMA – Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access n n OFDM subdivides the bandwidth into multiple frequency sub-carriers. OFDMA is a multiple-access scheme for OFDM. It provides Multiplexing operation of data streams from multiple users. Resources are available in the time domain by means of OFDMA symbols and in the frequency domain by means of sub-carriers. 8
 Cross Correlation The number of orthogonal codes that can be transmitted in each combination of Symbol and Subchannel. n Raised from Energy reasons. n Depends on the environment conditions (weather, high buildings). n 9
Cross Correlation The number of orthogonal codes that can be transmitted in each combination of Symbol and Subchannel. n Raised from Energy reasons. n Depends on the environment conditions (weather, high buildings). n 9
 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 10
Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 10
 Ranging n n n Ranging is the process to acquire up-link synchronization, control the power between SS and BS and perform the bandwidth request to BS. There are 3 main steps in the ranging process: 4 Initial and periodic ranging are supported to synchronize the SS’s with the BS at the initial network entry. 4 BW Request allows SS to ask for BW allocation. If a Station is already transmitting it can send a BW request message on a data packet as Piggyback. 11
Ranging n n n Ranging is the process to acquire up-link synchronization, control the power between SS and BS and perform the bandwidth request to BS. There are 3 main steps in the ranging process: 4 Initial and periodic ranging are supported to synchronize the SS’s with the BS at the initial network entry. 4 BW Request allows SS to ask for BW allocation. If a Station is already transmitting it can send a BW request message on a data packet as Piggyback. 11
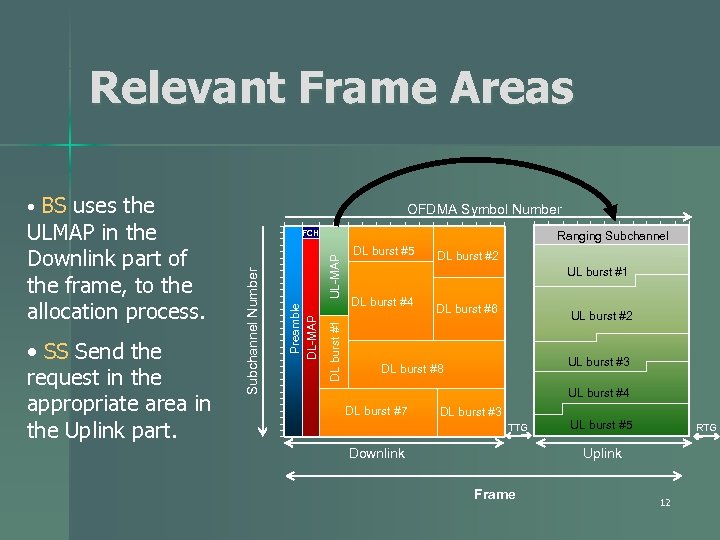 Relevant Frame Areas • BS uses the UL-MAP Ranging Subchannel DL burst #1 Preamble DL-MAP • SS Send the request in the appropriate area in the Uplink part. FCH Subchannel Number ULMAP in the Downlink part of the frame, to the allocation process. OFDMA Symbol Number DL burst #5 DL burst #2 UL burst #1 DL burst #4 DL burst #6 UL burst #2 UL burst #3 DL burst #8 UL burst #4 DL burst #7 DL burst #3 TTG Downlink UL burst #5 RTG Uplink Frame 12
Relevant Frame Areas • BS uses the UL-MAP Ranging Subchannel DL burst #1 Preamble DL-MAP • SS Send the request in the appropriate area in the Uplink part. FCH Subchannel Number ULMAP in the Downlink part of the frame, to the allocation process. OFDMA Symbol Number DL burst #5 DL burst #2 UL burst #1 DL burst #4 DL burst #6 UL burst #2 UL burst #3 DL burst #8 UL burst #4 DL burst #7 DL burst #3 TTG Downlink UL burst #5 RTG Uplink Frame 12
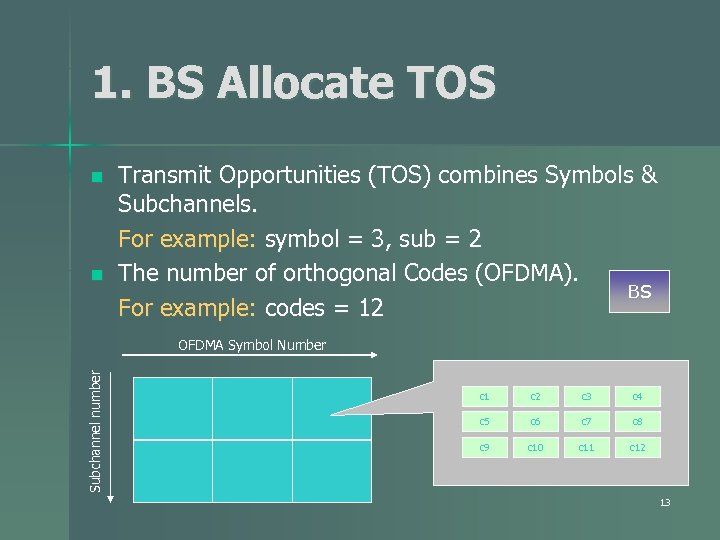 1. BS Allocate TOS n n Transmit Opportunities (TOS) combines Symbols & Subchannels. For example: symbol = 3, sub = 2 The number of orthogonal Codes (OFDMA). BS For example: codes = 12 Subchannel number OFDMA Symbol Number c 1 c 2 c 3 c 4 c 5 c 6 c 7 c 8 c 9 c 10 c 11 c 12 13
1. BS Allocate TOS n n Transmit Opportunities (TOS) combines Symbols & Subchannels. For example: symbol = 3, sub = 2 The number of orthogonal Codes (OFDMA). BS For example: codes = 12 Subchannel number OFDMA Symbol Number c 1 c 2 c 3 c 4 c 5 c 6 c 7 c 8 c 9 c 10 c 11 c 12 13
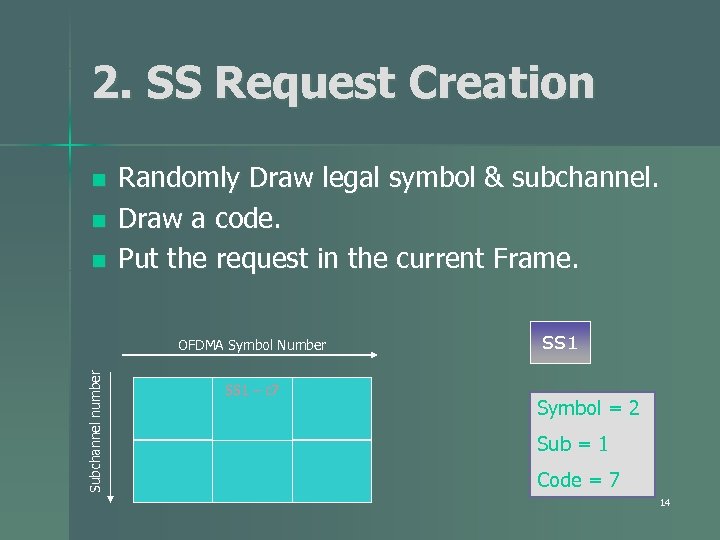 2. SS Request Creation n Randomly Draw legal symbol & subchannel. Draw a code. Put the request in the current Frame. Subchannel number OFDMA Symbol Number SS 1 – c 7 SS 1 Symbol = 2 Sub = 1 Code = 7 14
2. SS Request Creation n Randomly Draw legal symbol & subchannel. Draw a code. Put the request in the current Frame. Subchannel number OFDMA Symbol Number SS 1 – c 7 SS 1 Symbol = 2 Sub = 1 Code = 7 14
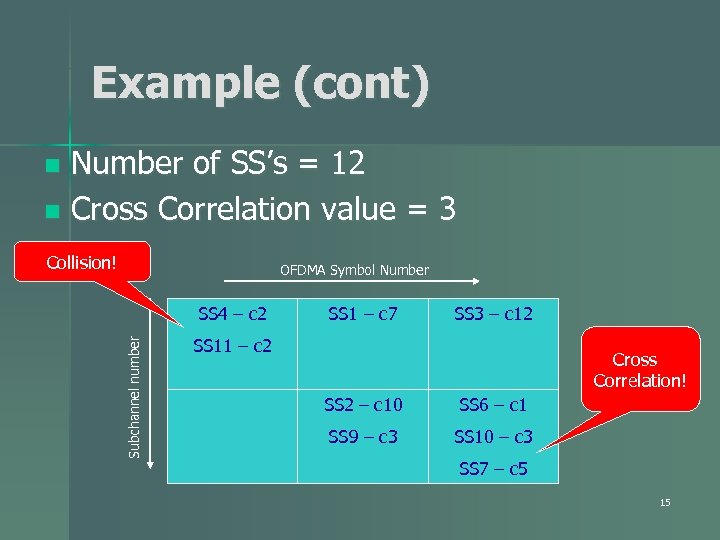 Example (cont) Number of SS’s = 12 n Cross Correlation value = 3 n Collision! OFDMA Symbol Number Subchannel number SS 4 – c 2 SS 1 – c 7 SS 3 – c 12 SS 11 – c 2 Cross Correlation! SS 2 – c 10 SS 6 – c 1 SS 9 – c 3 SS 10 – c 3 SS 7 – c 5 15
Example (cont) Number of SS’s = 12 n Cross Correlation value = 3 n Collision! OFDMA Symbol Number Subchannel number SS 4 – c 2 SS 1 – c 7 SS 3 – c 12 SS 11 – c 2 Cross Correlation! SS 2 – c 10 SS 6 – c 1 SS 9 – c 3 SS 10 – c 3 SS 7 – c 5 15
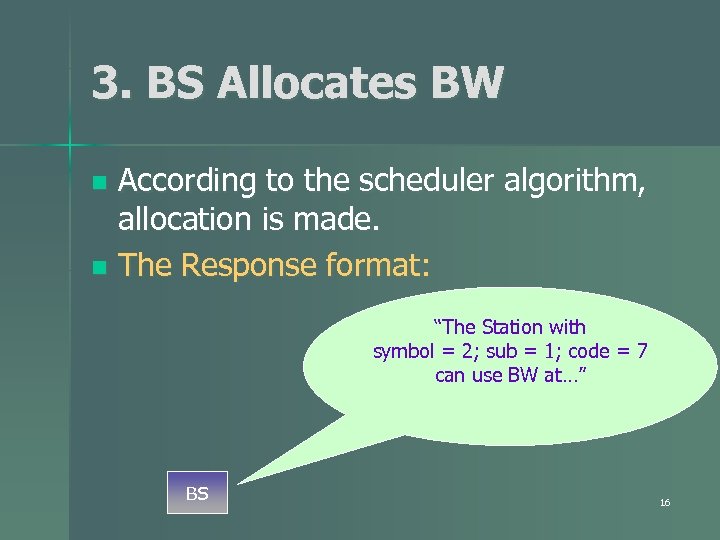 3. BS Allocates BW According to the scheduler algorithm, allocation is made. n The Response format: n “The Station with symbol = 2; sub = 1; code = 7 can use BW at…” BS 16
3. BS Allocates BW According to the scheduler algorithm, allocation is made. n The Response format: n “The Station with symbol = 2; sub = 1; code = 7 can use BW at…” BS 16
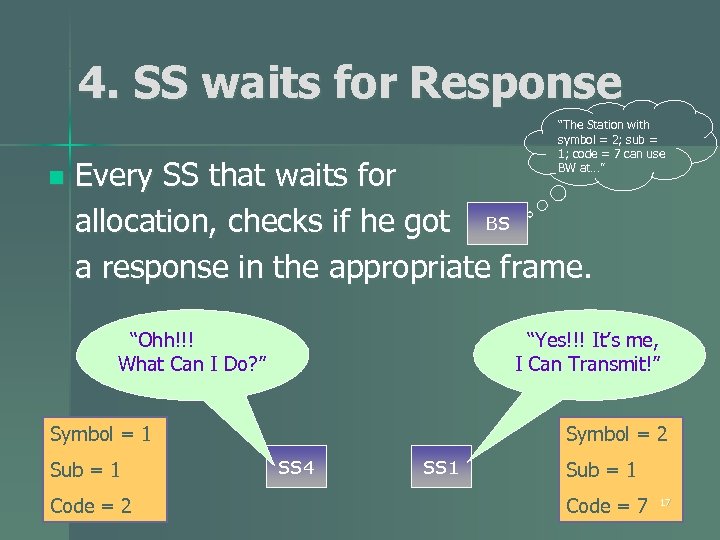 4. SS waits for Response n “The Station with symbol = 2; sub = 1; code = 7 can use BW at…” Every SS that waits for allocation, checks if he got BS a response in the appropriate frame. “Ohh!!! What Can I Do? ” “Yes!!! It’s me, I Can Transmit!” Symbol = 1 Sub = 1 Code = 2 Symbol = 2 SS 4 SS 1 Sub = 1 Code = 7 17
4. SS waits for Response n “The Station with symbol = 2; sub = 1; code = 7 can use BW at…” Every SS that waits for allocation, checks if he got BS a response in the appropriate frame. “Ohh!!! What Can I Do? ” “Yes!!! It’s me, I Can Transmit!” Symbol = 1 Sub = 1 Code = 2 Symbol = 2 SS 4 SS 1 Sub = 1 Code = 7 17
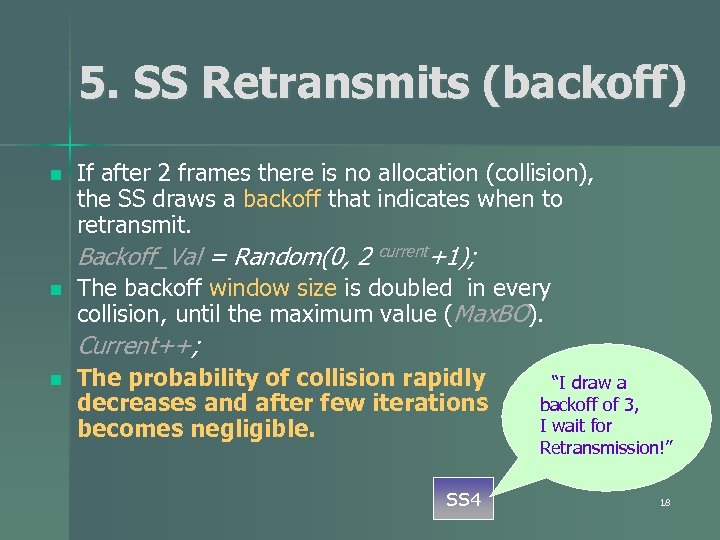 5. SS Retransmits (backoff) n If after 2 frames there is no allocation (collision), the SS draws a backoff that indicates when to retransmit. Backoff_Val = Random(0, 2 n current+1); The backoff window size is doubled in every collision, until the maximum value (Max. BO). Current++; n The probability of collision rapidly decreases and after few iterations becomes negligible. SS 4 “I draw a backoff of 3, I wait for Retransmission!” 18
5. SS Retransmits (backoff) n If after 2 frames there is no allocation (collision), the SS draws a backoff that indicates when to retransmit. Backoff_Val = Random(0, 2 n current+1); The backoff window size is doubled in every collision, until the maximum value (Max. BO). Current++; n The probability of collision rapidly decreases and after few iterations becomes negligible. SS 4 “I draw a backoff of 3, I wait for Retransmission!” 18
 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 19
Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Project’s goals and steps Background Ranging & BW Request Summary 19
 Expected Results n n n – stations w – TOs c – codes α – cross correlation value 20
Expected Results n n n – stations w – TOs c – codes α – cross correlation value 20
 Questions 21
Questions 21


