605416096dbe4497b5c97142f38d32d6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

People & the Planet by John Sulston FRS April 2012 A brief review by Richard Vernon 21 st September 2012 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 1

Report background Sir John Sulston FRS was assisted by a working group of 22 experts in the same or related fields. The report was reviewed by an independent panel of 8 experts before being published by the Royal Society in April 2012 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 2

Tips to access ‘People & Planet’ Printed version available from Royal Society has good Contents page but no index, so: Download electronic version from http: //royalsociety. org/uploaded. Files/Royal_So ciety_Content/policy/projects/peopleplanet/2012 -04 -25 -People. Planet. pdf One can then ‘search’ in lieu of index 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 3

Some conventions Least Developed Countries 48 countries mostly in Africa & Asia, with low per capita income & human assets Less Developed Countries Others in Africa & Asia + some in L. America, Caribbean, Pacific Islands. More Developed Countries Europe, N America, Australia, New Zealand & Japan 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 4

3 Key Challenges • raise world’s 1. 3 billion poorest out of extreme poverty • reduce consumption of the most developed and emerging economies • slow global population growth 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 5

1 st Challenge: 1. 3 billion poorest out of extreme poverty In 2000 World leaders commited to Millenium Development Goals 1 st of which was to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Critical to reducing global inequalities Needs increased per capita consumption for this group for improved nutrition & health care Needs reduced family size where currently high p. 7, 13 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 6

2 nd Challenge: reduce consumption by the rest of us Current levels unsustainable Requires radical change of society & current economic models Requires politicians to effect this Requires us to drive change at political level p. 11, Chap 3. 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 7

3 rd Challenge: slow global population growth Policy interventions can impact through investment in: education, especially for females where currently excluded health care including family planning services trade policies to encourage local entreprenurial activities Section 5. 4 – p. 91. . . 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 8
Demographic basics Sulston describes: Total fertility rate (TFR) Demographic transition Replacement fertility Youth dependency ratio Old age dependency ratio Total dependency ratio Demogrpahic dividend Demographic deficit Demographic momentum Demographic inertia See page 17 for a brief explanation of these terms 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 9
Key Demographic components that affect population size & composition Migration (international) Fertility Mortality Demographic Transition shift from high mortality and high fertility to low mortality and low fertility p 15 increase in proportion of old people p. 21 et seq. 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 10
Migration most dynamic population change factor in destination countries increasing: 1990: 156 m 2010: 214 m (+38%) driven mostly by economic change refugees are only c. 8% (2010) (– was 12% in 1990) p. 26, 103 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 11
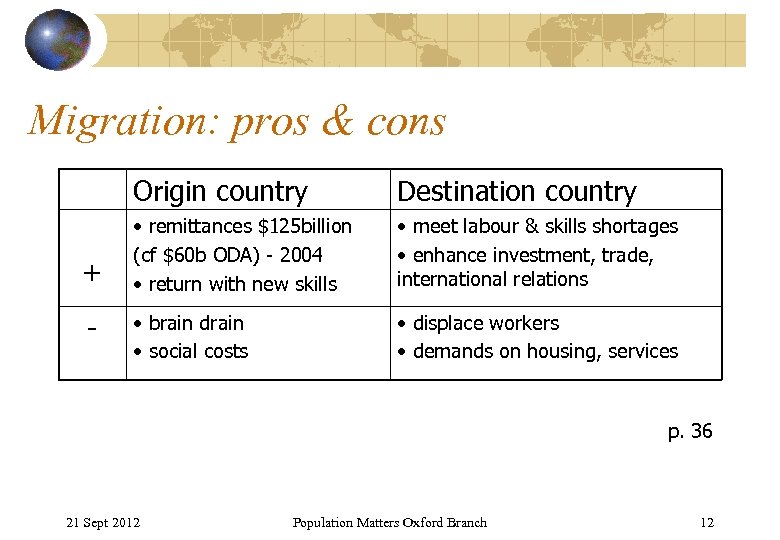
Migration: pros & cons Origin country + - Destination country • remittances $125 billion (cf $60 b ODA) - 2004 • return with new skills • meet labour & skills shortages • enhance investment, trade, international relations • brain drain • social costs • displace workers • demands on housing, services p. 36 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 12

Fertility Source of the greatest effect on future population size ‘More Developed Cntrs’: mostly < 2. 1 Replacement level ‘Least Developed Cntrs’: high fertility rates, > 4. 2, population projected to x 2 in next 40 years Fertility levels declining everywhere but: due to the Demographic Momentum - see next slide, p 16 populations will go on rising for decades p 45 due to large proportion of people of child-bearing age eg Niger p 38 Ghana – see next slide. p. 30. Recommendation 3. 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 13

Fertility: Demographic Momentum 2010: Ghana population c. 20 million fertility rate of 4 births per woman. If by 2020 fertility declines to replacement level Then in 2060: population would stabilise at c. 40 million. 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch p. 21 14

Mortality declined faster than fertility in most Less and Least Developed Countries and especially in infant & child mortality So these are seeing : increase in mothers of child bearing age and greatest population increases p 18, 28 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 15

Other issues raised: Age structure rate of ageing & the number of old people in the population are unprecedented in human history. Globally, over 65 s: 1950 5% 2010 9% 2050 20% big variations between More, Less & Least DCs p. 26 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 16

Other issues raised: Urbanisation the increase in proportion of population living in urban areas a global phenomonen, but much faster in the More Developed Countries Least DCs Less DCs More. DCs 1950 2005 Global 29 % 27 % 46 % 74 % (2050) 49 % (69 %) p 28, 34 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 17

Urbanisation effects + + can reduce material consumption can reduce environmental impact through efficiency delivery of services rapid urbanisation risk of slum conditions needs well planned provision of water supply, waste disposal, power and other services See Recommendation 5 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 18

Other issues: Gross Domestic Product GDP most widely used indicator of a country’s prosperity but a poor indicator of degree to which human needs are met ignores depletion of natural capital: agricultural land, forests, watersheds, fisheries, fresh water etc becomes a driver of consumption instead of saving p. 13, 58, 87 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 19

3 challenges 9 recommendations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. poverty consumption fertility planning urbanisation 6. 7. 8. 9. education research wealth management inter-governmental collaboration p. 9. Chapter 6 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 20

So what can I do? 1. 2. 3. ****** 21 Sept 2012 Population Matters Oxford Branch 21
605416096dbe4497b5c97142f38d32d6.ppt