5cadce976aa573f8ca639be3caef7bbf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 People. Soft. com Case Study Enterprise Information Architecture March 16, 2002 Chiara Fox, People. Soft Peter Merholz, Adaptive Path
People. Soft. com Case Study Enterprise Information Architecture March 16, 2002 Chiara Fox, People. Soft Peter Merholz, Adaptive Path
 What We’ll Talk About I. Project Overview II. The Role of the IA In the Enterprise III. Merging Top-Down and Bottom-Up IA IV. Content Analysis Methodologies 2
What We’ll Talk About I. Project Overview II. The Role of the IA In the Enterprise III. Merging Top-Down and Bottom-Up IA IV. Content Analysis Methodologies 2
 I. Project Overview: The Problem § Three separate web properties with different architectures • People. Soft. com, Customer Connection, and Alliance Connection § No unified user experience and quality varies • Resources are duplicated (sometimes triplicated) • Hard for users to find things cross-site due to differences in IA • Difficult to share content that is the same across sites § Each site has separate technical backend • Sites published with Future. Tense, Lotus Notes, and other relational databases • Three sites, three search engines, no structured content • Two Internet Systems teams to support the different platforms § Need to plan for implementation of People. Soft Portal 3
I. Project Overview: The Problem § Three separate web properties with different architectures • People. Soft. com, Customer Connection, and Alliance Connection § No unified user experience and quality varies • Resources are duplicated (sometimes triplicated) • Hard for users to find things cross-site due to differences in IA • Difficult to share content that is the same across sites § Each site has separate technical backend • Sites published with Future. Tense, Lotus Notes, and other relational databases • Three sites, three search engines, no structured content • Two Internet Systems teams to support the different platforms § Need to plan for implementation of People. Soft Portal 3
 Project Overview: The Team § Consultants – Adaptive Path and Lot 21 • Indi Young, Janice Fraser, Peter Merholz, Marcus Haid § In-house – Web development team • • Chiara Fox, Information Architect Camille Sobalvarro, Manager Design & Information Architecture 11 web producers 10 member migration “posse” 2 thesaurus developer/IA/indexer consultants 3 designers + 2 design consultants 4 usability and metrics specialists 15 technical developers + 3 CMS consultants 4
Project Overview: The Team § Consultants – Adaptive Path and Lot 21 • Indi Young, Janice Fraser, Peter Merholz, Marcus Haid § In-house – Web development team • • Chiara Fox, Information Architect Camille Sobalvarro, Manager Design & Information Architecture 11 web producers 10 member migration “posse” 2 thesaurus developer/IA/indexer consultants 3 designers + 2 design consultants 4 usability and metrics specialists 15 technical developers + 3 CMS consultants 4
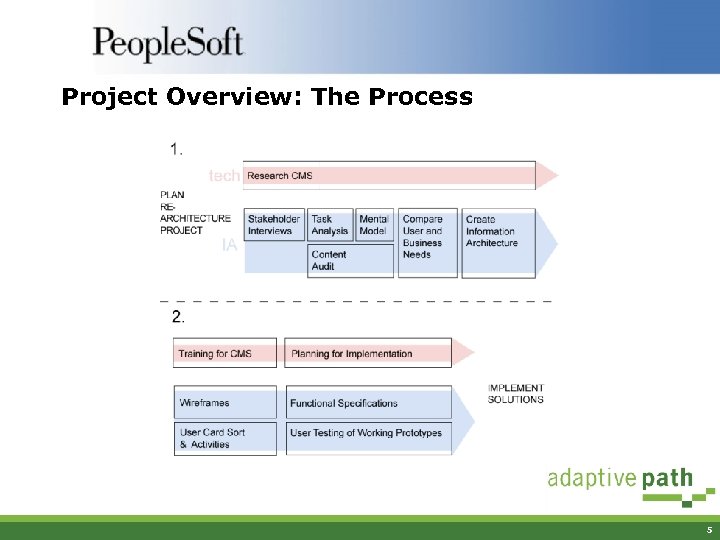 Project Overview: The Process 5
Project Overview: The Process 5
 Project Overview: Implementation Tracks § Visual design and site style guide § Content migration, including ROT removal § Installation and preparation of Interwoven’s Team. Site (templates, workflow, scripting) § Metadata development (schema, vocabularies, indexing) § Training (on using system, creating and using templates, architecture, indexing) § Refining IA at a highly detailed level as content was migrated 6
Project Overview: Implementation Tracks § Visual design and site style guide § Content migration, including ROT removal § Installation and preparation of Interwoven’s Team. Site (templates, workflow, scripting) § Metadata development (schema, vocabularies, indexing) § Training (on using system, creating and using templates, architecture, indexing) § Refining IA at a highly detailed level as content was migrated 6
 7
7
 8
8
 II. The Role of the IA in the Enterprise § § Hub of the entire process Liaison between many teams Migrator training One title, many roles 9
II. The Role of the IA in the Enterprise § § Hub of the entire process Liaison between many teams Migrator training One title, many roles 9
 Role of the IA: Hub of Process § Only team member with detailed knowledge of all content on all sites § Had vision of how sites should function when complete § Understood every aspect of the architecture, wireframes, blueprint, and other specifications 10
Role of the IA: Hub of Process § Only team member with detailed knowledge of all content on all sites § Had vision of how sites should function when complete § Understood every aspect of the architecture, wireframes, blueprint, and other specifications 10
 Role of the IA: Liaison Between Many Teams § Consultants • Information architecture, CMS implementation, graphic design § Internet Systems § In-house designers § Other departments within People. Soft, such as product marketing 11
Role of the IA: Liaison Between Many Teams § Consultants • Information architecture, CMS implementation, graphic design § Internet Systems § In-house designers § Other departments within People. Soft, such as product marketing 11
 Role of the IA: Migrator Training § § Understand new architecture How content fits into wireframes Use of CMS templates “Ask Dr. IA” newsletter 12
Role of the IA: Migrator Training § § Understand new architecture How content fits into wireframes Use of CMS templates “Ask Dr. IA” newsletter 12
 Role of the IA: One Title, Many Roles § § § § Project manager XML coder Vocabulary editor Content migrator Copyeditor Directory creator CMS system architecture designer 13
Role of the IA: One Title, Many Roles § § § § Project manager XML coder Vocabulary editor Content migrator Copyeditor Directory creator CMS system architecture designer 13
 III. Merging Top-Down and Bottom-Up IA Two primary approaches to developing the new information architecture § Top-Down • Driven by user research • Develop mental models of audience types • Derive main site organization from this understanding of approaches to the task § Bottom-Up • • Foundation for designing architecture Building product module pages Metadata development Site and product indexes 14
III. Merging Top-Down and Bottom-Up IA Two primary approaches to developing the new information architecture § Top-Down • Driven by user research • Develop mental models of audience types • Derive main site organization from this understanding of approaches to the task § Bottom-Up • • Foundation for designing architecture Building product module pages Metadata development Site and product indexes 14
 Top-Down IA: User Interviews § 19 subjects • 6 potential customers, 7 current customers, 6 alliance partners • Four slices – C-level, Director, Manager, Implementer § Hour-long task analysis interviews, probing how the person was involved in the process of purchasing enterprise-level software 15
Top-Down IA: User Interviews § 19 subjects • 6 potential customers, 7 current customers, 6 alliance partners • Four slices – C-level, Director, Manager, Implementer § Hour-long task analysis interviews, probing how the person was involved in the process of purchasing enterprise-level software 15
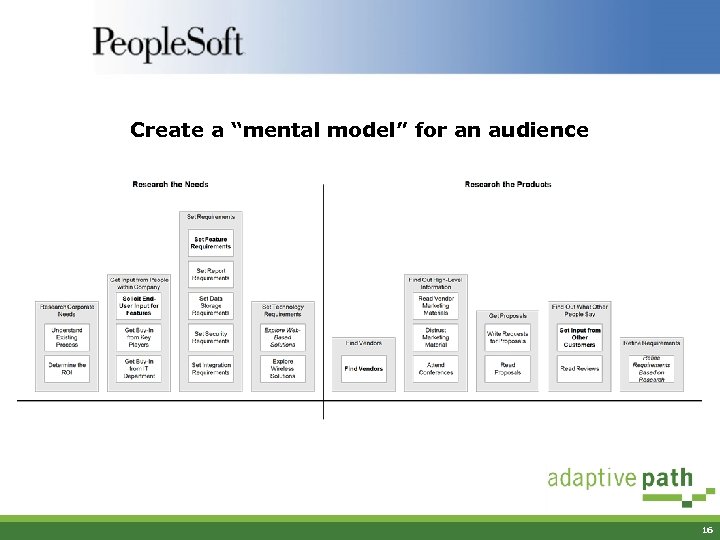 Create a “mental model” for an audience 16
Create a “mental model” for an audience 16
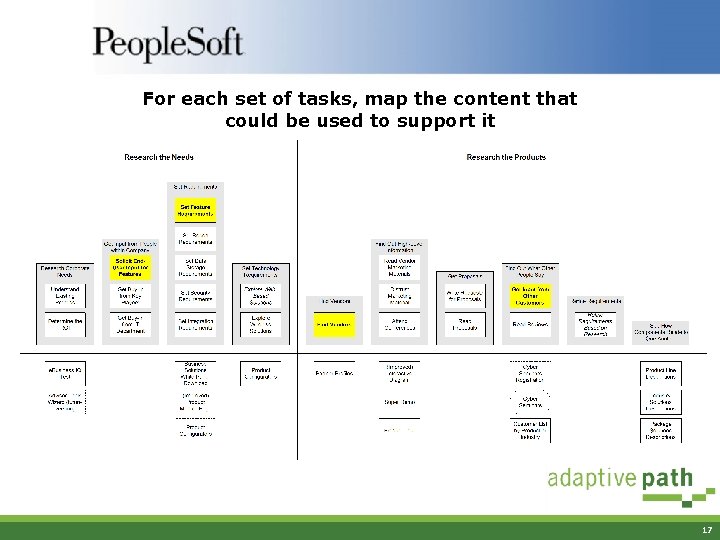 For each set of tasks, map the content that could be used to support it 17
For each set of tasks, map the content that could be used to support it 17
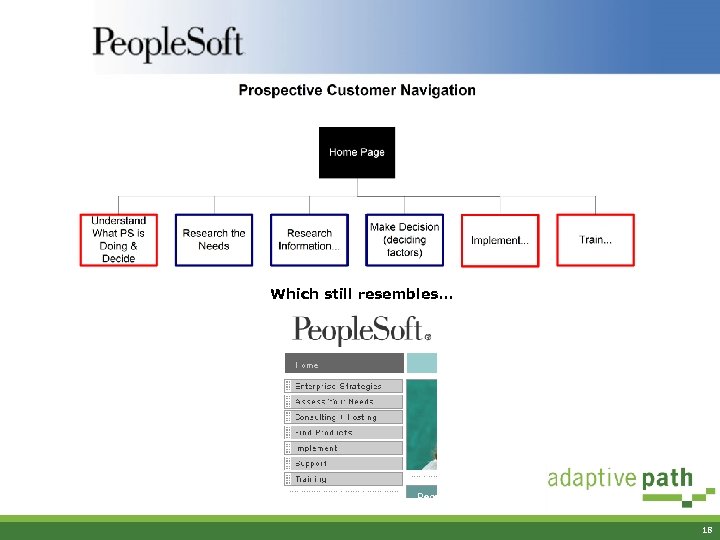 Which still resembles… 18
Which still resembles… 18
 Bottom-Up IA: Forms the Foundation § Closely linked with the content analysis § Focused on: • Understanding and describing the content • Finding the patterns and groupings • Matching content with user needs § Results are leveraged in different ways 19
Bottom-Up IA: Forms the Foundation § Closely linked with the content analysis § Focused on: • Understanding and describing the content • Finding the patterns and groupings • Matching content with user needs § Results are leveraged in different ways 19
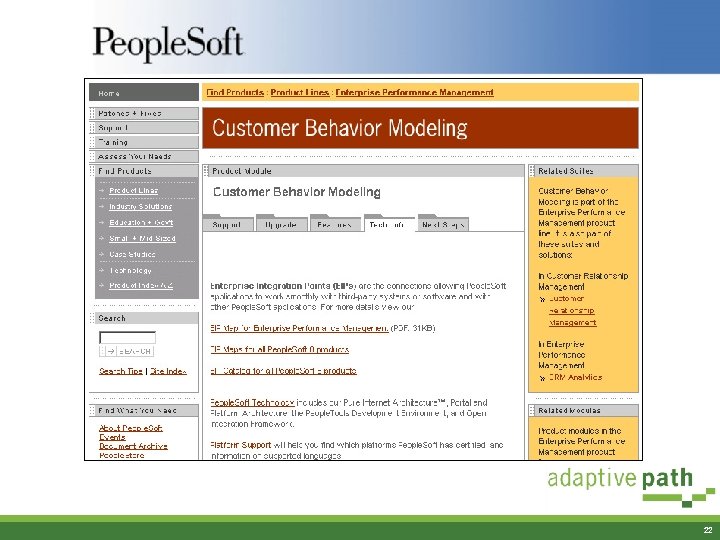
 Bottom-Up IA: Building Product Module Pages § Went through the site and pulled together all information related to products • Support • Upgrades • Marketing § Used sticky notes to gather the items into logical groups § Logical groups became the tabs on the module pages 20
Bottom-Up IA: Building Product Module Pages § Went through the site and pulled together all information related to products • Support • Upgrades • Marketing § Used sticky notes to gather the items into logical groups § Logical groups became the tabs on the module pages 20
 21
21
 22
22
 Bottom-up IA: Metadata Development § 12 attribute schema developed based upon patterns found and functionality we wanted § 10 controlled vocabularies developed of varying complexity § Individual thesauri were developed for the products, services, and subject attributes § Semi-automatic indexing tool used to tag content, as well as manual tagging 23
Bottom-up IA: Metadata Development § 12 attribute schema developed based upon patterns found and functionality we wanted § 10 controlled vocabularies developed of varying complexity § Individual thesauri were developed for the products, services, and subject attributes § Semi-automatic indexing tool used to tag content, as well as manual tagging 23
![FINANCIALS [Financial Analytics] FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT [Financial Analytics] Analytic Forecasting {Financial Analytic Forecasting} {Financial FINANCIALS [Financial Analytics] FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT [Financial Analytics] Analytic Forecasting {Financial Analytic Forecasting} {Financial](https://present5.com/presentation/5cadce976aa573f8ca639be3caef7bbf/image-24.jpg) FINANCIALS [Financial Analytics] FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT [Financial Analytics] Analytic Forecasting {Financial Analytic Forecasting} {Financial Forecasting} Asset Liability Management {Liability Management} Asset Management {Managing Assets} Balanced Scorecard Billing {Bills} Budgeting {Budgets} CFO Portal {Portal for CFO} {Chief Financial Officer Portal} {Portal for Chief Financial Officer} Contracts {Contracting} Deduction Management {Deductions} {Managing Deduction} e. Bill Payment {e-Bill Payment} {Bill Payment} Expenses Financial Insight [Financial Analytics] General Ledger {G/L} Payables {Accounts Payable} {A/P} Projects Purchasing Receivables {Accounts Receivable} {A/R} MARKETPAY [Market. Place] TREASURY MANAGEMENT Deal Management {Managing Deals} {Management of Deals} Risk Management {Risk} {Managing Risk} {Management of Risk} 24
FINANCIALS [Financial Analytics] FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT [Financial Analytics] Analytic Forecasting {Financial Analytic Forecasting} {Financial Forecasting} Asset Liability Management {Liability Management} Asset Management {Managing Assets} Balanced Scorecard Billing {Bills} Budgeting {Budgets} CFO Portal {Portal for CFO} {Chief Financial Officer Portal} {Portal for Chief Financial Officer} Contracts {Contracting} Deduction Management {Deductions} {Managing Deduction} e. Bill Payment {e-Bill Payment} {Bill Payment} Expenses Financial Insight [Financial Analytics] General Ledger {G/L} Payables {Accounts Payable} {A/P} Projects Purchasing Receivables {Accounts Receivable} {A/R} MARKETPAY [Market. Place] TREASURY MANAGEMENT Deal Management {Managing Deals} {Management of Deals} Risk Management {Risk} {Managing Risk} {Management of Risk} 24
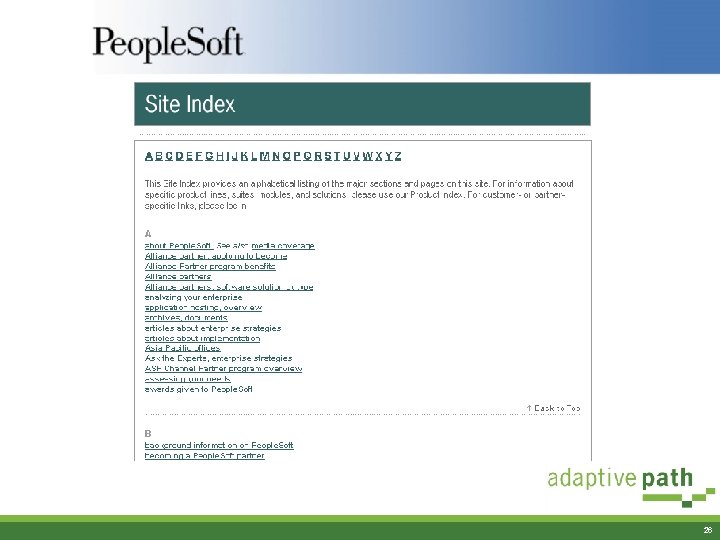
 Bottom-up IA: Site Index & Product Index § Alternative to the primary navigation for getting to content § Indexed just like a back of the book index § Product index based upon the product vocabulary § Australian Indexers Society award for Web Indexes 25
Bottom-up IA: Site Index & Product Index § Alternative to the primary navigation for getting to content § Indexed just like a back of the book index § Product index based upon the product vocabulary § Australian Indexers Society award for Web Indexes 25
 26
26
 IV. Content Analysis Methodologies Many methodologies of content analysis were employed § § Content inventory Unified content map Product matrix Classification scheme analysis 27
IV. Content Analysis Methodologies Many methodologies of content analysis were employed § § Content inventory Unified content map Product matrix Classification scheme analysis 27
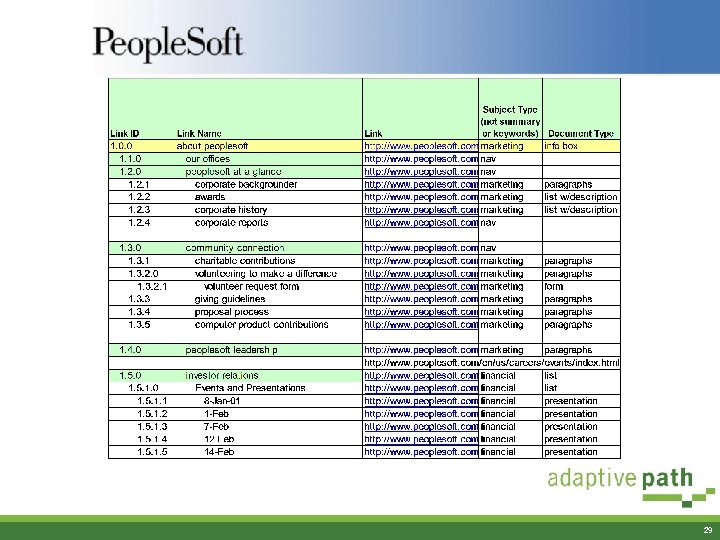
 Content Analysis: Content Inventory § Clicked through thousands of pages across the three properties (8, 000 lines in the Excel spreadsheet) § Automated attempts insufficient—manual attention required § Tagged each piece of content with metadata, preparing it for both IA and CMS migration • Content types • Where it lives • Link Ids • Etc. 28
Content Analysis: Content Inventory § Clicked through thousands of pages across the three properties (8, 000 lines in the Excel spreadsheet) § Automated attempts insufficient—manual attention required § Tagged each piece of content with metadata, preparing it for both IA and CMS migration • Content types • Where it lives • Link Ids • Etc. 28
 29
29
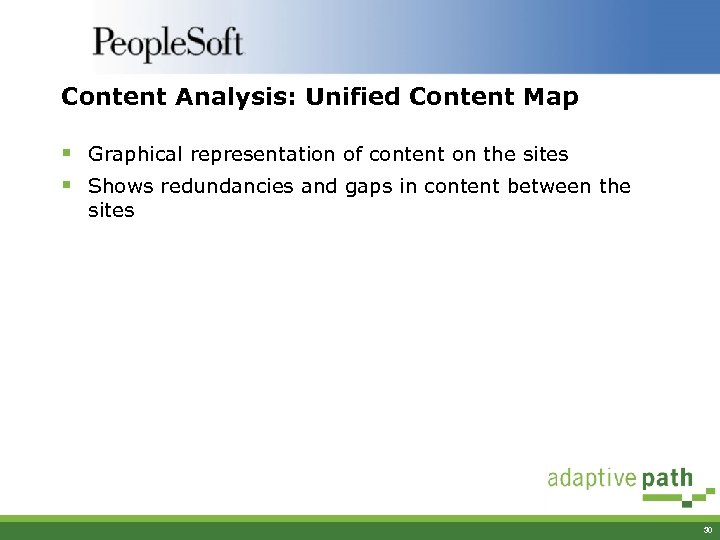 Content Analysis: Unified Content Map § Graphical representation of content on the sites § Shows redundancies and gaps in content between the sites 30
Content Analysis: Unified Content Map § Graphical representation of content on the sites § Shows redundancies and gaps in content between the sites 30
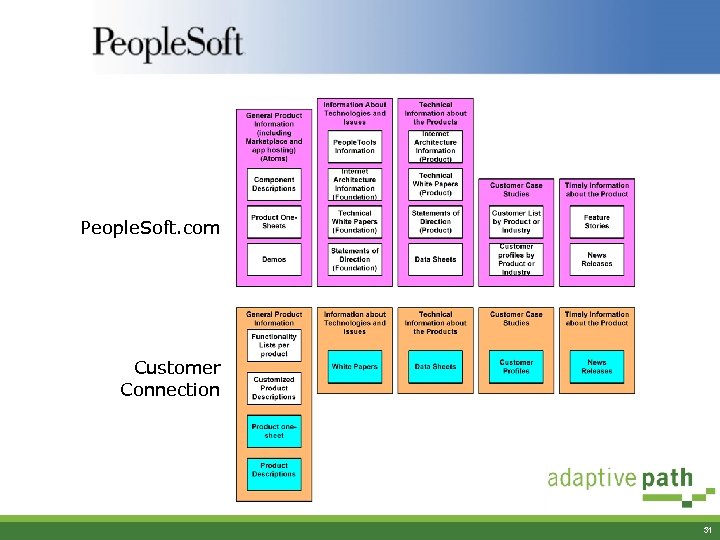 People. Soft. com Customer Connection 31
People. Soft. com Customer Connection 31
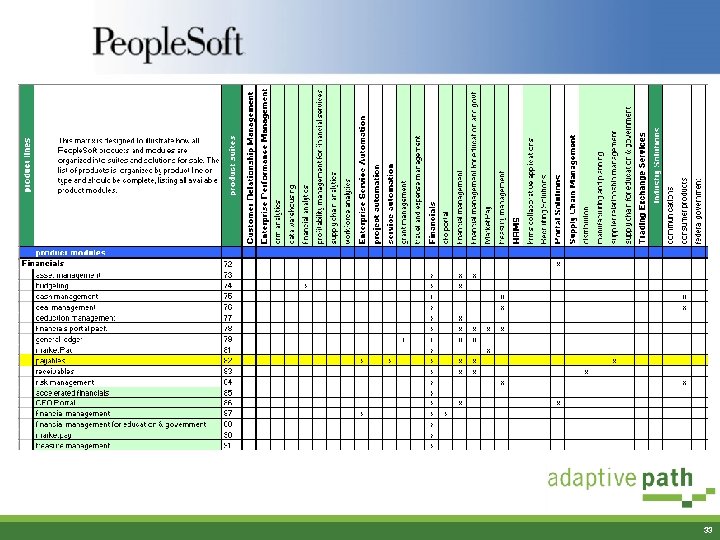
 Content Analysis: Product Matrix § § Began as a way to understand how products fit together Illustrates the atom –> molecule –> crystal model Forms the basis of the product hierarchy Now used in other departments to understand how products are structured 32
Content Analysis: Product Matrix § § Began as a way to understand how products fit together Illustrates the atom –> molecule –> crystal model Forms the basis of the product hierarchy Now used in other departments to understand how products are structured 32
 33
33
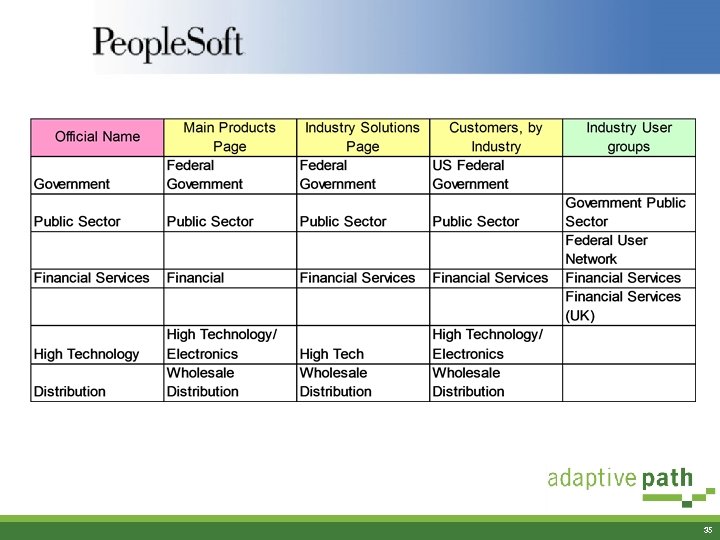
 Content Analysis: Classification Scheme Analysis § Done early in project § Compare terms used across the different sites § Great for building a case for the project by showing inconsistencies § Used to discover alternate terms for vocabularies 34
Content Analysis: Classification Scheme Analysis § Done early in project § Compare terms used across the different sites § Great for building a case for the project by showing inconsistencies § Used to discover alternate terms for vocabularies 34
 35
35
 Thank You Chiara Fox Peter Merholz Information Architect, People. Soft Partner, Adaptive Path chiara_fox@peoplesoft. com peterme@adaptivepath. com http: //www. chiarafox. com http: //www. peterme. com 36
Thank You Chiara Fox Peter Merholz Information Architect, People. Soft Partner, Adaptive Path chiara_fox@peoplesoft. com peterme@adaptivepath. com http: //www. chiarafox. com http: //www. peterme. com 36


