99af524c00ac71e34a1aea0fd7bc8372.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 People and Terms YOU need to know!
People and Terms YOU need to know!
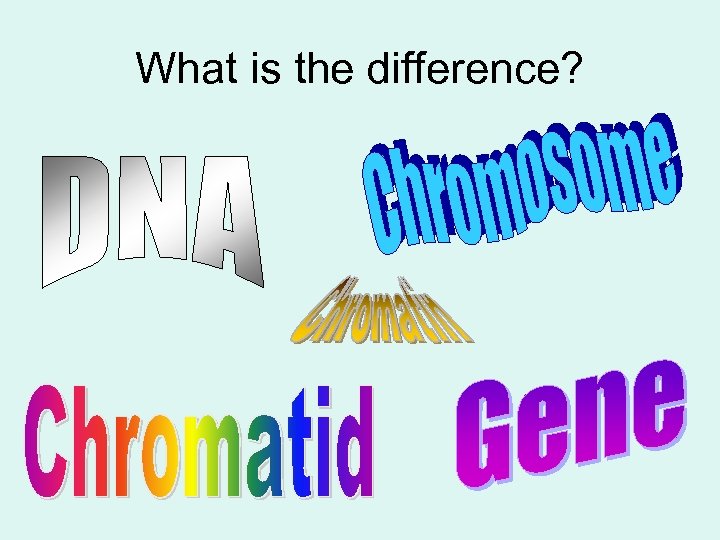 What is the difference?
What is the difference?
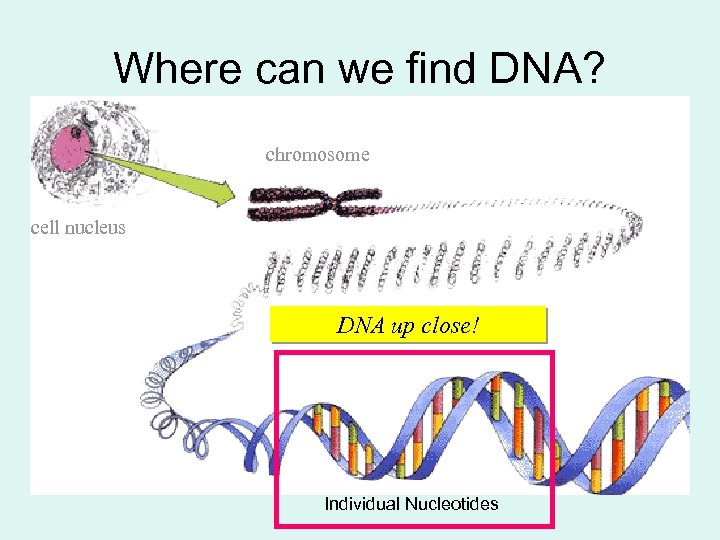 Where can we find DNA? chromosome cell nucleus Double stranded DNA molecule DNA up close! Individual Nucleotides
Where can we find DNA? chromosome cell nucleus Double stranded DNA molecule DNA up close! Individual Nucleotides
 Messages from the inside? • DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the genetic information of all living organisms stored in units called genes • A gene is a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein – These proteins make up our traits!!!
Messages from the inside? • DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the genetic information of all living organisms stored in units called genes • A gene is a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein – These proteins make up our traits!!!
 What about those alleles we learned about last time? • Our traits (genes) are inherited by our ancestors, but how do those traits tell our bodies to look the way we look? It’s a code! (Like the Braille activity we did!) = CODE
What about those alleles we learned about last time? • Our traits (genes) are inherited by our ancestors, but how do those traits tell our bodies to look the way we look? It’s a code! (Like the Braille activity we did!) = CODE
 Rosalind Franklin • Took x-ray of what is now known as the DNA double helix • Shared the Nobel Prize for aiding in discovery of the double helix of DNA
Rosalind Franklin • Took x-ray of what is now known as the DNA double helix • Shared the Nobel Prize for aiding in discovery of the double helix of DNA
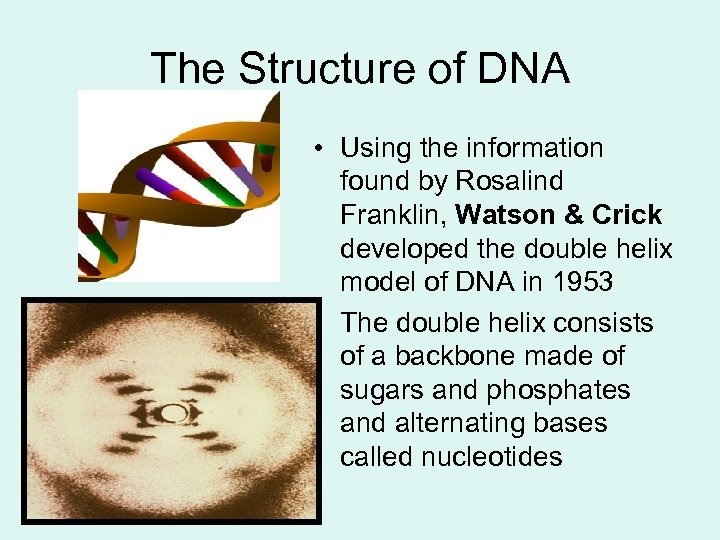 The Structure of DNA • Using the information found by Rosalind Franklin, Watson & Crick developed the double helix model of DNA in 1953 • The double helix consists of a backbone made of sugars and phosphates and alternating bases called nucleotides
The Structure of DNA • Using the information found by Rosalind Franklin, Watson & Crick developed the double helix model of DNA in 1953 • The double helix consists of a backbone made of sugars and phosphates and alternating bases called nucleotides
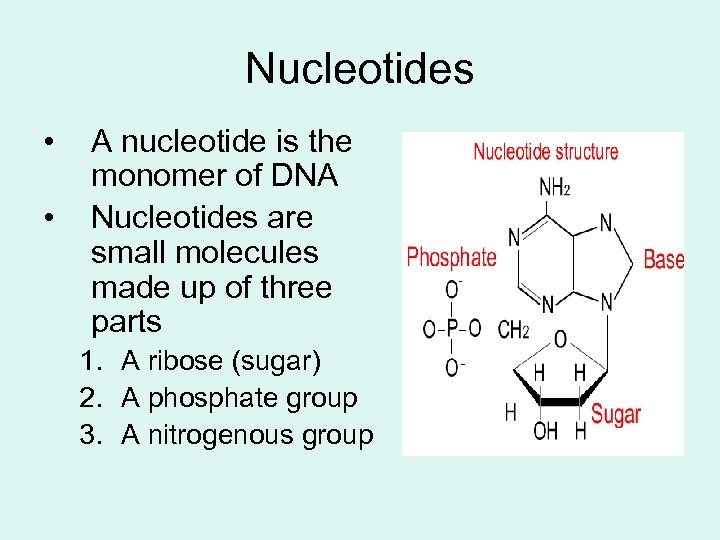 Nucleotides • • A nucleotide is the monomer of DNA Nucleotides are small molecules made up of three parts 1. A ribose (sugar) 2. A phosphate group 3. A nitrogenous group
Nucleotides • • A nucleotide is the monomer of DNA Nucleotides are small molecules made up of three parts 1. A ribose (sugar) 2. A phosphate group 3. A nitrogenous group
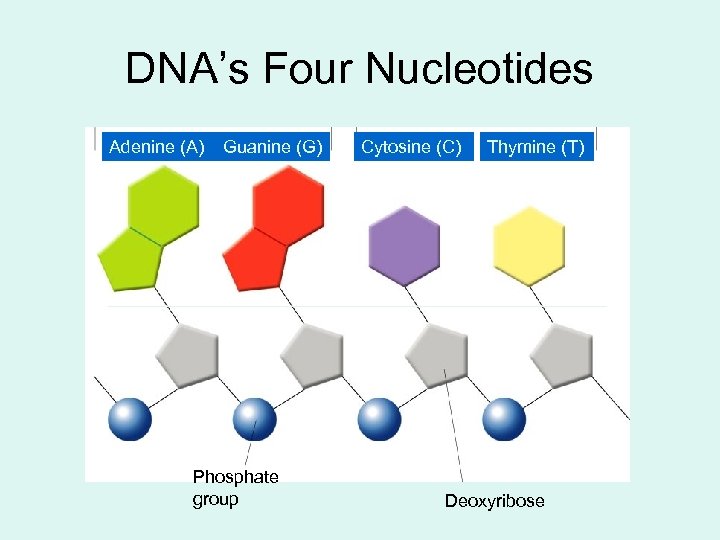 DNA’s Four Nucleotides Adenine (A) Guanine (G) Phosphate group Cytosine (C) Thymine (T) Deoxyribose
DNA’s Four Nucleotides Adenine (A) Guanine (G) Phosphate group Cytosine (C) Thymine (T) Deoxyribose
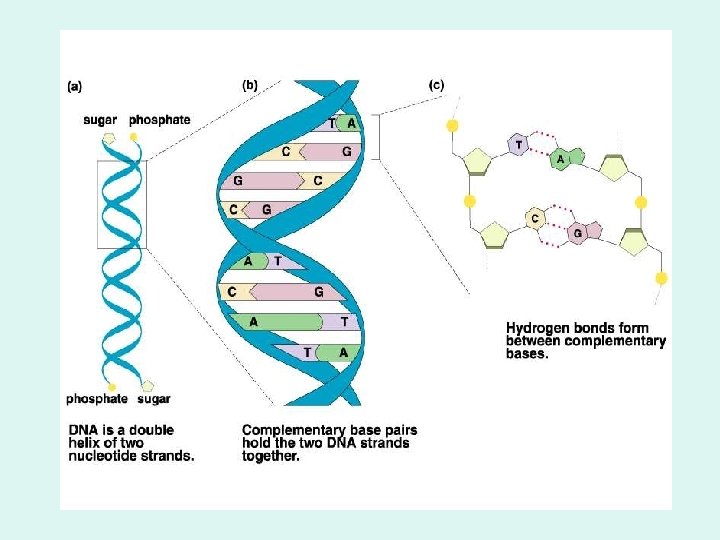
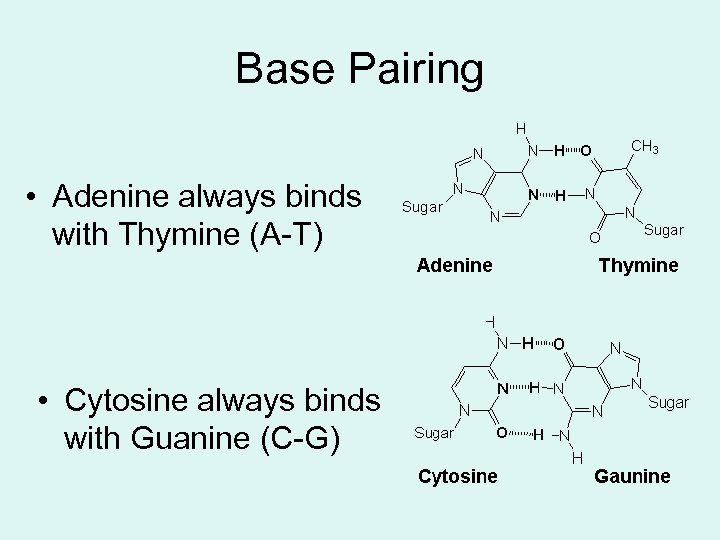 Base Pairing • Adenine always binds with Thymine (A-T) • Cytosine always binds with Guanine (C-G)
Base Pairing • Adenine always binds with Thymine (A-T) • Cytosine always binds with Guanine (C-G)
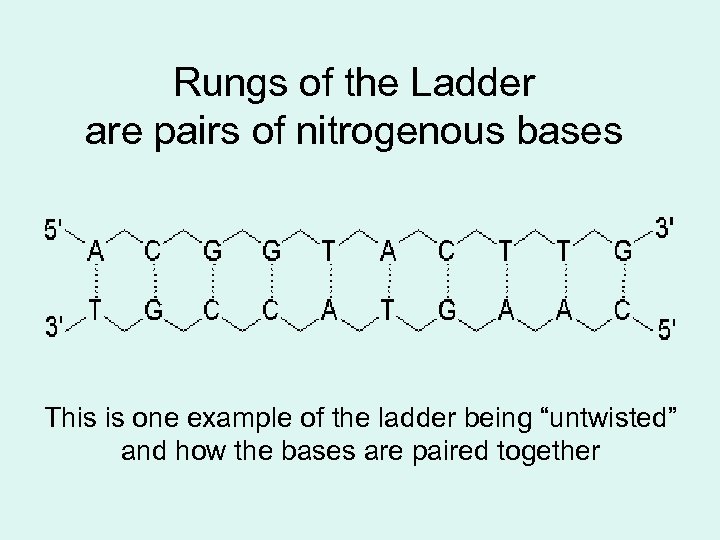 Rungs of the Ladder are pairs of nitrogenous bases This is one example of the ladder being “untwisted” and how the bases are paired together
Rungs of the Ladder are pairs of nitrogenous bases This is one example of the ladder being “untwisted” and how the bases are paired together
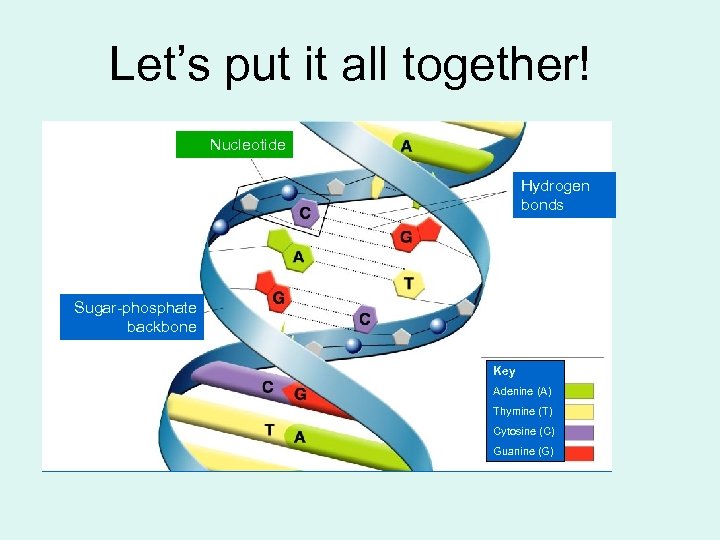 Let’s put it all together! Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Sugar-phosphate backbone Key Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G)
Let’s put it all together! Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Sugar-phosphate backbone Key Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G)
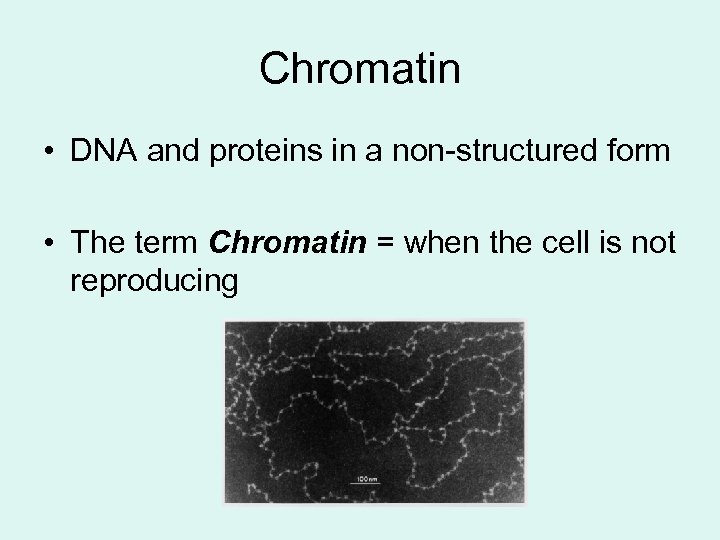 Chromatin • DNA and proteins in a non-structured form • The term Chromatin = when the cell is not reproducing
Chromatin • DNA and proteins in a non-structured form • The term Chromatin = when the cell is not reproducing
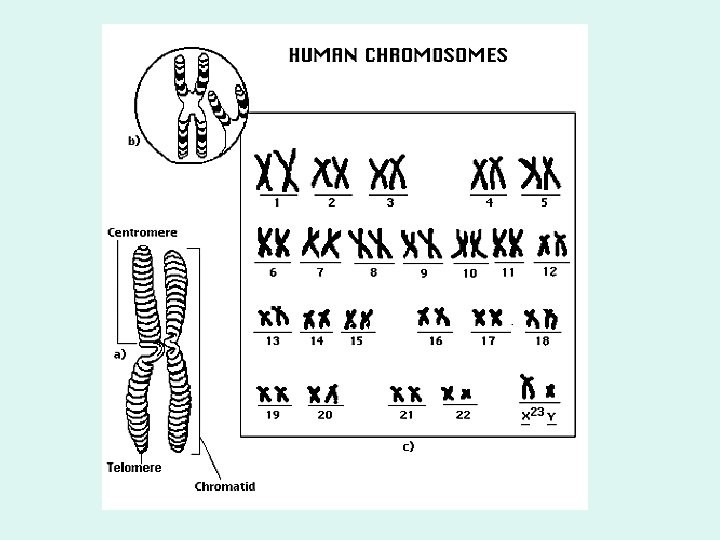
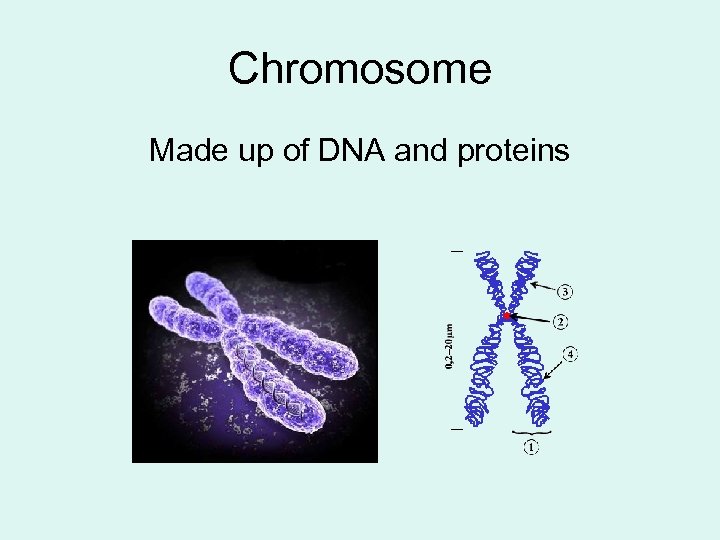 Chromosome Made up of DNA and proteins
Chromosome Made up of DNA and proteins
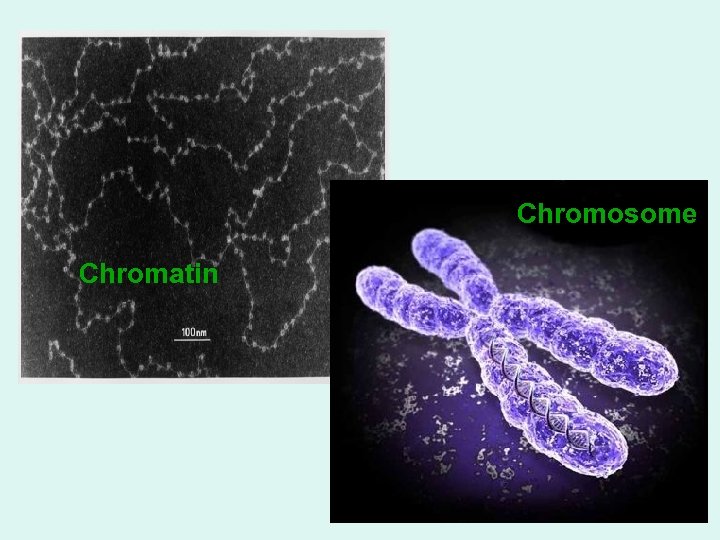 Chromosome Chromatin
Chromosome Chromatin
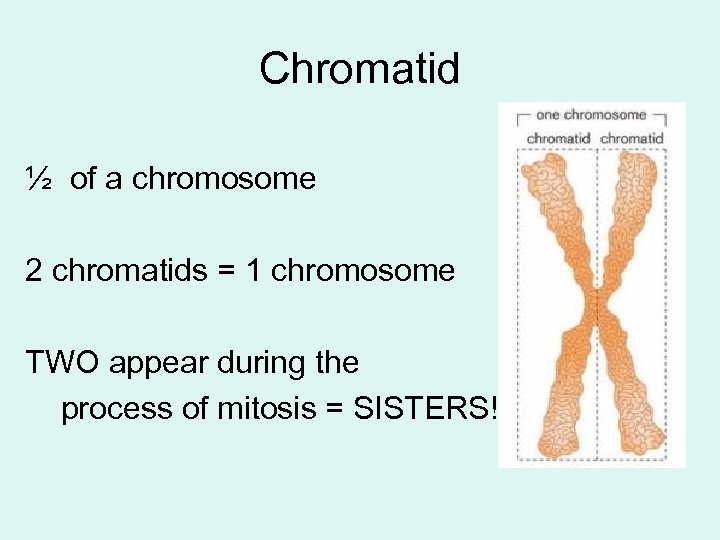 Chromatid ½ of a chromosome 2 chromatids = 1 chromosome TWO appear during the process of mitosis = SISTERS!
Chromatid ½ of a chromosome 2 chromatids = 1 chromosome TWO appear during the process of mitosis = SISTERS!
 DNA Contains hereditary information Found in chromosomes
DNA Contains hereditary information Found in chromosomes
 Gene “Instructions” Many genes within DNA Why we are who we are!
Gene “Instructions” Many genes within DNA Why we are who we are!
 What does homologous mean? Homo = the same Hetero = different
What does homologous mean? Homo = the same Hetero = different
 Homologous The same!! We get ½ our chromosomes from … and ½ our chromosomes from
Homologous The same!! We get ½ our chromosomes from … and ½ our chromosomes from
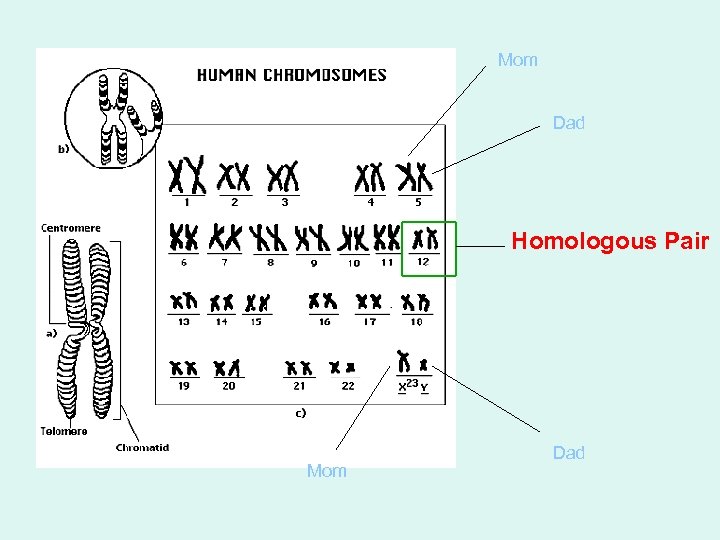 Mom Dad Homologous Pair Mom Dad
Mom Dad Homologous Pair Mom Dad
 Haploid vs. Diploid
Haploid vs. Diploid
 Haploid *Total number of homologous pairs of chromosomes in a cell* What is the haploid number of human cells?
Haploid *Total number of homologous pairs of chromosomes in a cell* What is the haploid number of human cells?
 Diploid Total number of chromosomes in a cell What is the diploid number of human cells?
Diploid Total number of chromosomes in a cell What is the diploid number of human cells?
 Haploid vs. Diploid The reference to haploid cells is 1 N The reference to diploid cells is 2 N If N = 23 for humans (haploid) Then 2 N ( 2 x 23 ) = 46 (diploid) Get it? ?
Haploid vs. Diploid The reference to haploid cells is 1 N The reference to diploid cells is 2 N If N = 23 for humans (haploid) Then 2 N ( 2 x 23 ) = 46 (diploid) Get it? ?
 Sex chromosomes vs. Autosomes • Sex chromosomes = this is what determines our sex (duh!) • Autosomes = all the other chromosomes
Sex chromosomes vs. Autosomes • Sex chromosomes = this is what determines our sex (duh!) • Autosomes = all the other chromosomes
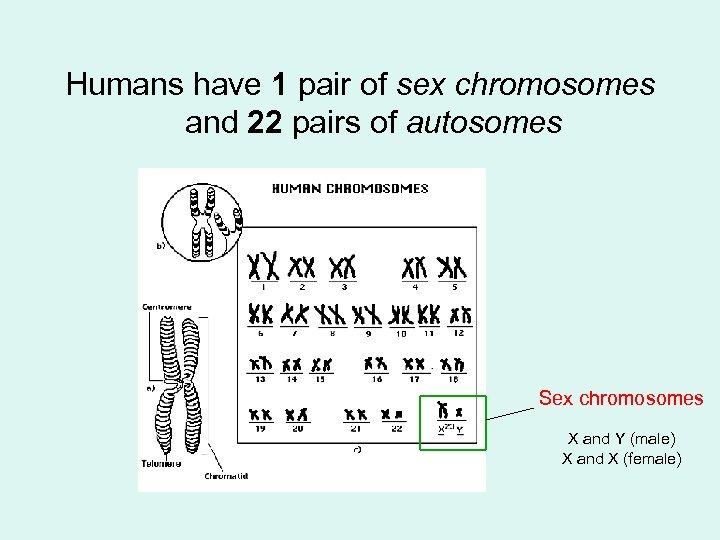 Humans have 1 pair of sex chromosomes and 22 pairs of autosomes Sex chromosomes X and Y (male) X and X (female)
Humans have 1 pair of sex chromosomes and 22 pairs of autosomes Sex chromosomes X and Y (male) X and X (female)



