PS.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Pension system
Pension system
 Introduction Pension prosperity of an old age of citizens is one of actual social and economic problems of the Republic of Kazakhstan. It consequences of change of economic opportunities of Kazakhstan in recent years owing to decrease in rates of economic growth and employment, decrease in birth rate, population aging, and, respectively, increases in a share of persons in it are more senior than able-bodied age. Kazakhstan the first among CIS countries started reforming old solidary system of provision of pensions of citizens with transition to accumulative system. The law "About Provision of Pensions in the Republic of Kazakhstan" adopted on June 20, 1997 began construction in the country of accumulative pension system.
Introduction Pension prosperity of an old age of citizens is one of actual social and economic problems of the Republic of Kazakhstan. It consequences of change of economic opportunities of Kazakhstan in recent years owing to decrease in rates of economic growth and employment, decrease in birth rate, population aging, and, respectively, increases in a share of persons in it are more senior than able-bodied age. Kazakhstan the first among CIS countries started reforming old solidary system of provision of pensions of citizens with transition to accumulative system. The law "About Provision of Pensions in the Republic of Kazakhstan" adopted on June 20, 1997 began construction in the country of accumulative pension system.
 Pension system set of legal, financial and economic and organizational institutes and the norms, having the purpose granting to citizens of material security in the form of pension; or it is set of actions for compensation to citizens of earnings (income). -
Pension system set of legal, financial and economic and organizational institutes and the norms, having the purpose granting to citizens of material security in the form of pension; or it is set of actions for compensation to citizens of earnings (income). -
 Three "whales" of the Kazakhstan system of provision of pensions Provision of pensions in Kazakhstan represents now system from three levels combining at the same time mechanisms of solidary and accumulative systems. The first level is the solidary pension system inherited by Kazakhstan from the USSR after disintegration of the last and founded on "solidarity of generations" in which the state budget at the expense of tax assignments of working part of the population and other receipts becomes a source of pension payments. The amount of pension payments is defined by the seniority. Along with solidary system it is created and the accumulative pension system develops. The second level is an obligatory accumulative pension system with an amount of pension assignments fixed 10 -percent-nym from the monthly income for citizens of Kazakhstan, foreigners and the stateless persons who are constantly living in Kazakhstan. The third level – the accumulative system founded on voluntary and voluntary professional pension contributions.
Three "whales" of the Kazakhstan system of provision of pensions Provision of pensions in Kazakhstan represents now system from three levels combining at the same time mechanisms of solidary and accumulative systems. The first level is the solidary pension system inherited by Kazakhstan from the USSR after disintegration of the last and founded on "solidarity of generations" in which the state budget at the expense of tax assignments of working part of the population and other receipts becomes a source of pension payments. The amount of pension payments is defined by the seniority. Along with solidary system it is created and the accumulative pension system develops. The second level is an obligatory accumulative pension system with an amount of pension assignments fixed 10 -percent-nym from the monthly income for citizens of Kazakhstan, foreigners and the stateless persons who are constantly living in Kazakhstan. The third level – the accumulative system founded on voluntary and voluntary professional pension contributions.
 Systems Basic system Accumulative system Basic pension obligatory contributions; It is paid to all equally irrespective of labor participation. - obligatory assignments with a fixed 10 percent amount of pension assignments from the monthly income. From the seniority To persons at whom the seniority at the time of a retirement, as of January 1, 1998, makes not less than six months. Voluntary contributions: The accumulation based on voluntary and professional pension contributions
Systems Basic system Accumulative system Basic pension obligatory contributions; It is paid to all equally irrespective of labor participation. - obligatory assignments with a fixed 10 percent amount of pension assignments from the monthly income. From the seniority To persons at whom the seniority at the time of a retirement, as of January 1, 1998, makes not less than six months. Voluntary contributions: The accumulation based on voluntary and professional pension contributions
 Advantages and disadvantages of basic system restriction by the maximum size of pension; the pension is paid by the - demographic risks state; (balance violation between stability (security) of people the working population and pensioners conducts to with the low income. increase of social taxes); - legislation change; - difficult system of registration of pension.
Advantages and disadvantages of basic system restriction by the maximum size of pension; the pension is paid by the - demographic risks state; (balance violation between stability (security) of people the working population and pensioners conducts to with the low income. increase of social taxes); - legislation change; - difficult system of registration of pension.
 Advantages and disadvantages of accumulative system - direct dependence of the size of pension on level of the income of the investor; - state guarantee; - inheritance of pension accumulation; - increase in the sum of pension accumulation at the expense of the investment income; - possibility of management of the pension accumulation by means of system of multiportfolios. influence of stock markets on the size of the investment income; - not developed system of voluntary pension assignments; - the OPV minimum size (at some categories of investors).
Advantages and disadvantages of accumulative system - direct dependence of the size of pension on level of the income of the investor; - state guarantee; - inheritance of pension accumulation; - increase in the sum of pension accumulation at the expense of the investment income; - possibility of management of the pension accumulation by means of system of multiportfolios. influence of stock markets on the size of the investment income; - not developed system of voluntary pension assignments; - the OPV minimum size (at some categories of investors).
 Pension fund Ø it is set of the assets brought by future pensioners, on the basis of the contract, the profits intended for receiving, and the subsequent distribution of the investment income between investors. v For management of assets, the pension fund can attract the special companies (KUPA), or is independent. v For this purpose the license for investment management of pension assets is required. v Result of activity of fund : the investment income which increases the sum of initial investments. Thus, at a retirement, the investor receives except the accumulation, money from the fund income.
Pension fund Ø it is set of the assets brought by future pensioners, on the basis of the contract, the profits intended for receiving, and the subsequent distribution of the investment income between investors. v For management of assets, the pension fund can attract the special companies (KUPA), or is independent. v For this purpose the license for investment management of pension assets is required. v Result of activity of fund : the investment income which increases the sum of initial investments. Thus, at a retirement, the investor receives except the accumulation, money from the fund income.
 Main functions of the Pension fund: 1. collecting and accumulation of insurance premiums, financing of expenses; 2. capitalization of means, attraction in it voluntary contributions of physical and legal entities; 3. joint control with tax authorities behind receipt of insurance bringing and behind the correct and their rational expenditure; 4. the organization of the state databank on all categories of payers of contributions; 5. interstate and international cooperation concerning provision of pensions, development of contracts and agreements concerning pensions and grants; 6. research work in the field of the state pension insurance; 7. carrying out explanatory work among the population and legal entities concerning pension insurance.
Main functions of the Pension fund: 1. collecting and accumulation of insurance premiums, financing of expenses; 2. capitalization of means, attraction in it voluntary contributions of physical and legal entities; 3. joint control with tax authorities behind receipt of insurance bringing and behind the correct and their rational expenditure; 4. the organization of the state databank on all categories of payers of contributions; 5. interstate and international cooperation concerning provision of pensions, development of contracts and agreements concerning pensions and grants; 6. research work in the field of the state pension insurance; 7. carrying out explanatory work among the population and legal entities concerning pension insurance.
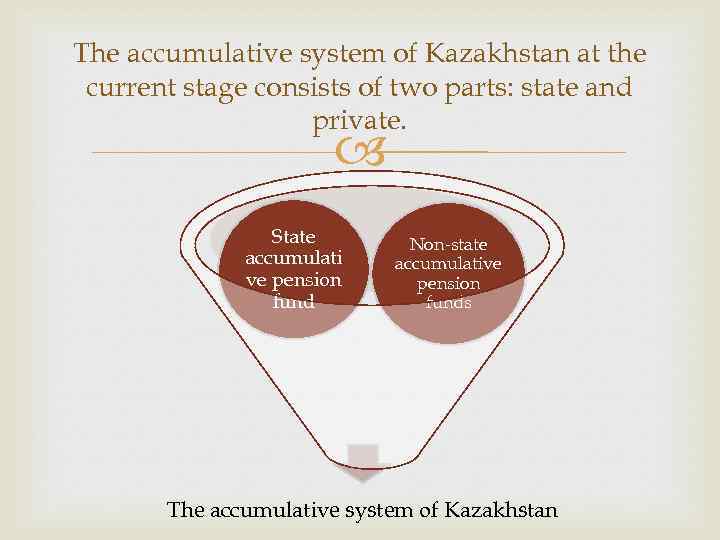 The accumulative system of Kazakhstan at the current stage consists of two parts: state and private. State accumulati ve pension fund Non-state accumulative pension funds The accumulative system of Kazakhstan
The accumulative system of Kazakhstan at the current stage consists of two parts: state and private. State accumulati ve pension fund Non-state accumulative pension funds The accumulative system of Kazakhstan
 the State accumulative pension fund -– makes collecting only obligatory pension expels of investors and carries out pension payments to recipients in an order established by the Government of RK. After a certain period of time privatization, i. e. actually all pension system is planned will be concentrated in the private sector.
the State accumulative pension fund -– makes collecting only obligatory pension expels of investors and carries out pension payments to recipients in an order established by the Government of RK. After a certain period of time privatization, i. e. actually all pension system is planned will be concentrated in the private sector.
 Non-state accumulative pension funds (with authorized capital not less than 180 million tenges) - the legal entities organized in the form of joint-stock company of opened or closed type. According to the Law "About Provision of Pensions in RK" of NNPF are the central link in pension system. ü organize work with investors ü sign pension contracts ü keep the individual accounting of pension contributions and charges of the investment income
Non-state accumulative pension funds (with authorized capital not less than 180 million tenges) - the legal entities organized in the form of joint-stock company of opened or closed type. According to the Law "About Provision of Pensions in RK" of NNPF are the central link in pension system. ü organize work with investors ü sign pension contracts ü keep the individual accounting of pension contributions and charges of the investment income
 Dynamics of change of pension payment, investment income and pension accumulation 3500 3000 2500 2000 pension payment 1500 investment income 1000 pension accumulation 500 0 2 / 1 0
Dynamics of change of pension payment, investment income and pension accumulation 3500 3000 2500 2000 pension payment 1500 investment income 1000 pension accumulation 500 0 2 / 1 0
 Modernization of pension system is urged to increase efficiency and transparency of system as a whole, to provide social justice for all categories of citizens.
Modernization of pension system is urged to increase efficiency and transparency of system as a whole, to provide social justice for all categories of citizens.
 Modernization of pension system Modernization purposes: to provide compliance of pension payments to earlier gained income and a growing standard of living; to achieve financial stability of pension system.
Modernization of pension system Modernization purposes: to provide compliance of pension payments to earlier gained income and a growing standard of living; to achieve financial stability of pension system.
 Modernization of pension system Modernization functions: Uniform Accumulative Pension Fund (UAPF) creation Increase of efficiency of accumulative pension system; involvement of new investors in accumulative pension system; change of system of the minimum guarantees of provision of pensions; transition from voluntary to obligatory professional system of provision of pensions of citizens,
Modernization of pension system Modernization functions: Uniform Accumulative Pension Fund (UAPF) creation Increase of efficiency of accumulative pension system; involvement of new investors in accumulative pension system; change of system of the minimum guarantees of provision of pensions; transition from voluntary to obligatory professional system of provision of pensions of citizens,
 Responsible institutes: Protection of the The Ministry of Labour and Social population of RK - development of the main directions of improvement of pension system, the mechanism of their realization, the analysis of results; The RK National bank - management and investment of pension assets, control of realization of investment strategy and activity of the companies operating pension assets; Council at the President of RK (representatives of the government, NB RK, participants of the financial market and independent experts) - development of recommendations about a choice of effective tools for investment of pension assets.
Responsible institutes: Protection of the The Ministry of Labour and Social population of RK - development of the main directions of improvement of pension system, the mechanism of their realization, the analysis of results; The RK National bank - management and investment of pension assets, control of realization of investment strategy and activity of the companies operating pension assets; Council at the President of RK (representatives of the government, NB RK, participants of the financial market and independent experts) - development of recommendations about a choice of effective tools for investment of pension assets.
 Conclusion In those countries where already there accumulative pension systems, pension assets play considerable social and economic, and at times and a political role in society. Assets of pension funds have huge investment value for economic development of the countries as they are an important component of internal investment resources.
Conclusion In those countries where already there accumulative pension systems, pension assets play considerable social and economic, and at times and a political role in society. Assets of pension funds have huge investment value for economic development of the countries as they are an important component of internal investment resources.
 Value of state regulation of pension system for society becomes more and more essential. About 21 billion dollars makes the volume of pension accumulation of inhabitants of the country today. Kazakhstan citizens store the savings in 11 accumulative pension funds. And to the middle of 2013 in the country will create uniform accumulative fund.
Value of state regulation of pension system for society becomes more and more essential. About 21 billion dollars makes the volume of pension accumulation of inhabitants of the country today. Kazakhstan citizens store the savings in 11 accumulative pension funds. And to the middle of 2013 in the country will create uniform accumulative fund.
 Thank you 4 your attention
Thank you 4 your attention


