5f289e2bdd35378b50ff78c58ad5c0f6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 PENGENALAN TEKNIK TELEKOMUNIKASI Modul : 07 Transmisi Faculty of Electrical Engineering BANDUNG, 2015 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
PENGENALAN TEKNIK TELEKOMUNIKASI Modul : 07 Transmisi Faculty of Electrical Engineering BANDUNG, 2015 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
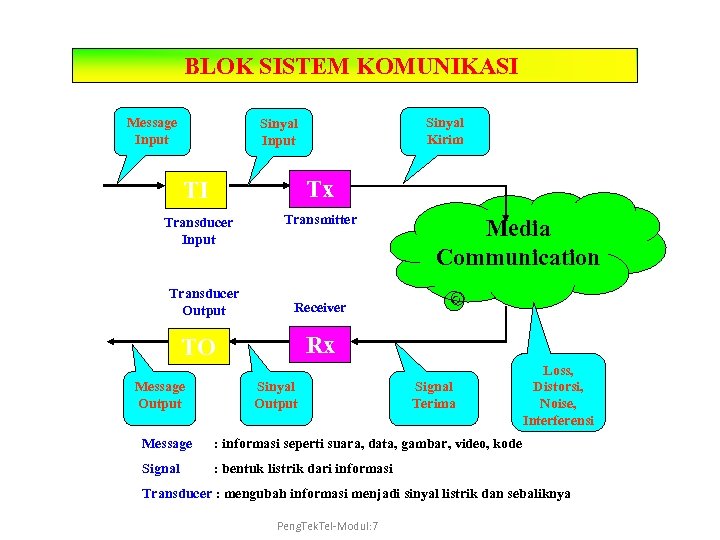 BLOK SISTEM KOMUNIKASI Message Input Sinyal Kirim Sinyal Input TI Tx Transducer Input Transmitter Transducer Output Receiver Rx TO Message Output Media Communication Sinyal Output Signal Terima Message : informasi seperti suara, data, gambar, video, kode Signal Loss, Distorsi, Noise, Interferensi : bentuk listrik dari informasi Transducer : mengubah informasi menjadi sinyal listrik dan sebaliknya Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
BLOK SISTEM KOMUNIKASI Message Input Sinyal Kirim Sinyal Input TI Tx Transducer Input Transmitter Transducer Output Receiver Rx TO Message Output Media Communication Sinyal Output Signal Terima Message : informasi seperti suara, data, gambar, video, kode Signal Loss, Distorsi, Noise, Interferensi : bentuk listrik dari informasi Transducer : mengubah informasi menjadi sinyal listrik dan sebaliknya Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 BLOK SISTEM KOMUNIKASI RADIO ANALOG Baseband from Multiplex Baseband Equipment IF Equipment Limiter Modulator Analog Up. Converter Local Oscillator PA Waveguide Filter ANTENNA Local Oscillator Base band to Demultiplex Baseband Equipment Demodulat or Analog IF Filter & Amplifier Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 Down Converter Waveguide Filter
BLOK SISTEM KOMUNIKASI RADIO ANALOG Baseband from Multiplex Baseband Equipment IF Equipment Limiter Modulator Analog Up. Converter Local Oscillator PA Waveguide Filter ANTENNA Local Oscillator Base band to Demultiplex Baseband Equipment Demodulat or Analog IF Filter & Amplifier Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 Down Converter Waveguide Filter
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
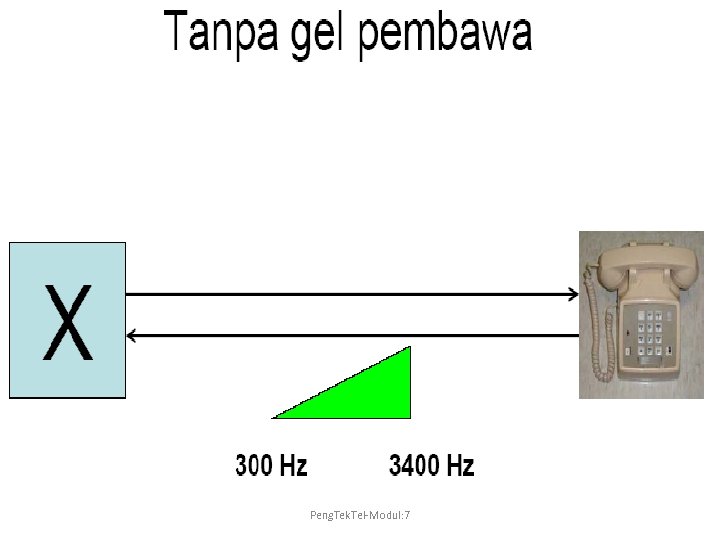 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
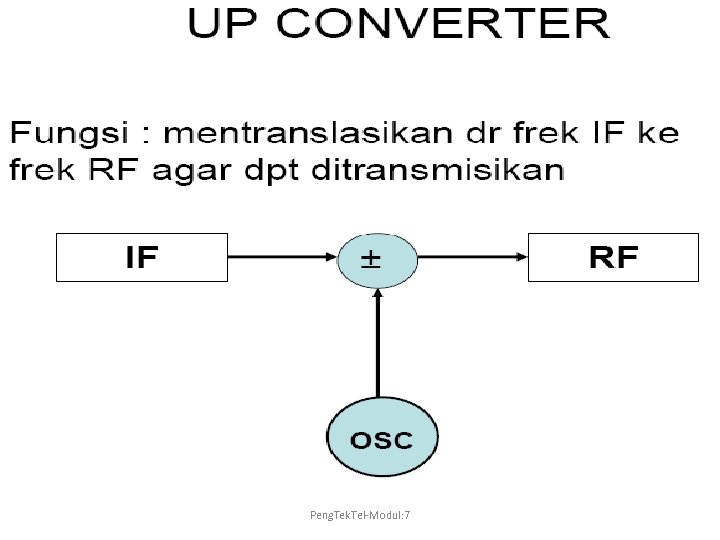 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
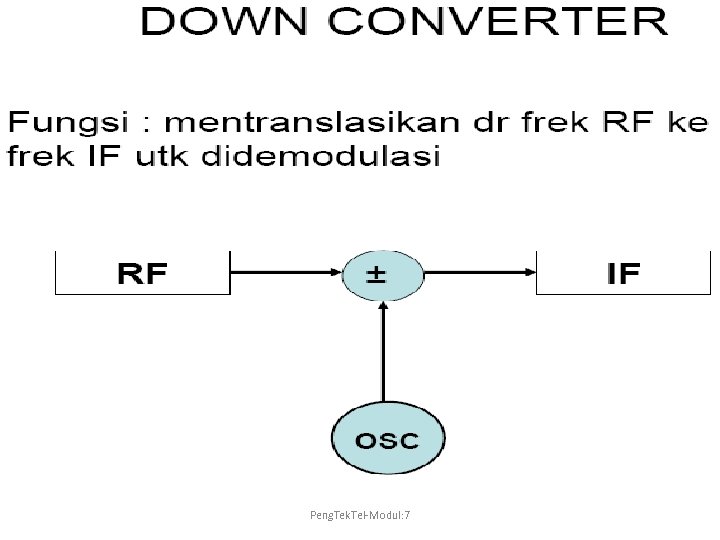 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Modulasi / Demodulasi Modulasi adalah proses menumpangkan sinyal informasi kedalam gelombang pembawa & Demodulasi adalah proses mengambil kembali sinyal informasi yang ditumpangkan & Teknik Modulasi / Demodulasi dilakukan dengan mengubah parameter gelombang pembawa, antara lain : & Amplitudo & Frekwensi & Phasa & Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Modulasi / Demodulasi Modulasi adalah proses menumpangkan sinyal informasi kedalam gelombang pembawa & Demodulasi adalah proses mengambil kembali sinyal informasi yang ditumpangkan & Teknik Modulasi / Demodulasi dilakukan dengan mengubah parameter gelombang pembawa, antara lain : & Amplitudo & Frekwensi & Phasa & Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
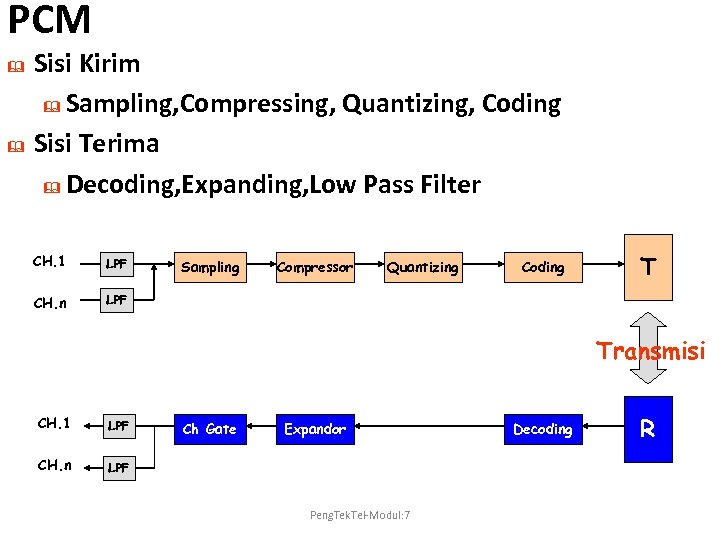 PCM & & Sisi Kirim & Sampling, Compressing, Quantizing, Coding Sisi Terima & Decoding, Expanding, Low Pass Filter CH. 1 LPF CH. n T LPF Sampling Compressor Quantizing Coding Transmisi CH. 1 LPF CH. n LPF Ch Gate Expandor Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 Decoding R
PCM & & Sisi Kirim & Sampling, Compressing, Quantizing, Coding Sisi Terima & Decoding, Expanding, Low Pass Filter CH. 1 LPF CH. n T LPF Sampling Compressor Quantizing Coding Transmisi CH. 1 LPF CH. n LPF Ch Gate Expandor Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 Decoding R
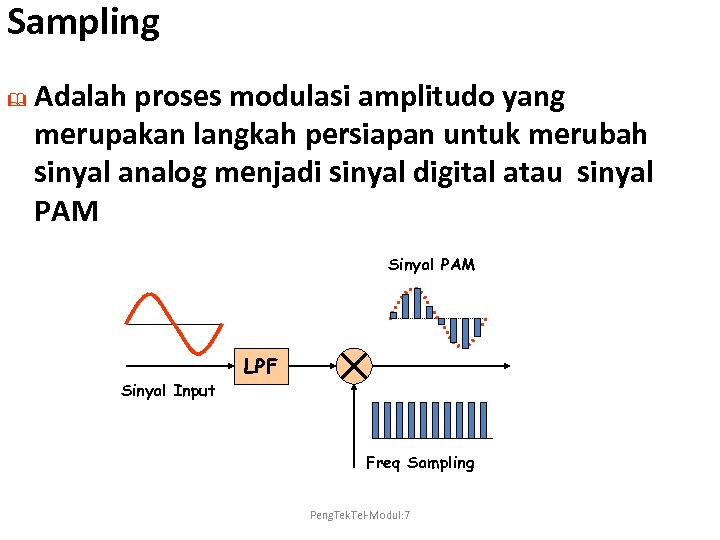 Sampling & Adalah proses modulasi amplitudo yang merupakan langkah persiapan untuk merubah sinyal analog menjadi sinyal digital atau sinyal PAM Sinyal Input LPF Freq Sampling Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Sampling & Adalah proses modulasi amplitudo yang merupakan langkah persiapan untuk merubah sinyal analog menjadi sinyal digital atau sinyal PAM Sinyal Input LPF Freq Sampling Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Quantizing Adalah proses awal untuk merubah sinyal PAM menjadi susunan digit, dimana sinyal hasil sampling dihargakan pada tegangan pembanding terdekat & Quantisasi Uniform & Quantisasi Non-Uniform & Sinyal PAM Ter-Kuantisasi Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Quantizing Adalah proses awal untuk merubah sinyal PAM menjadi susunan digit, dimana sinyal hasil sampling dihargakan pada tegangan pembanding terdekat & Quantisasi Uniform & Quantisasi Non-Uniform & Sinyal PAM Ter-Kuantisasi Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Coding & & & Pada tahapan ini semua sinyal yang sudah dikuantisasi diubah menjadi kode 8 bit SABCWXYZ S = Polaritas sinyal PAM ABC = Nomor Segmen dalam 0 s/d 7 (biner) WXYZ = Nomor interval 0 s/d 15 (Biner) Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Coding & & & Pada tahapan ini semua sinyal yang sudah dikuantisasi diubah menjadi kode 8 bit SABCWXYZ S = Polaritas sinyal PAM ABC = Nomor Segmen dalam 0 s/d 7 (biner) WXYZ = Nomor interval 0 s/d 15 (Biner) Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Multiplexing & & Adalah proses penggabungan beberapa saluran atau kanal pembicaraan (VBW) menjadi satu kedalam bentuk sinyal lain, untuk disalurkan secara bersamaan tanpa saling mengganggu Jenis-jenis Multiplexer & FDM (Frequency Division Multiplex) & TDM (Time Division Multiplex) Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Multiplexing & & Adalah proses penggabungan beberapa saluran atau kanal pembicaraan (VBW) menjadi satu kedalam bentuk sinyal lain, untuk disalurkan secara bersamaan tanpa saling mengganggu Jenis-jenis Multiplexer & FDM (Frequency Division Multiplex) & TDM (Time Division Multiplex) Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Multiplexing • Multiplexing is sending more than one signal on a carrier. • There are two standard types of multiplexing. – Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM): the medium carries a number of signals, which have different frequencies; the signals are carried simultaneously. – Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM): different signals are transmitted over the same medium but they do so at different times – they take turns. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Multiplexing • Multiplexing is sending more than one signal on a carrier. • There are two standard types of multiplexing. – Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM): the medium carries a number of signals, which have different frequencies; the signals are carried simultaneously. – Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM): different signals are transmitted over the same medium but they do so at different times – they take turns. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Multiplexing • There are several data inputs and one of them is routed to the output (possibly the shared communication channel). – Like selecting a television channel (although that example is FDM). • In addition to data inputs, there must be select inputs. – The select inputs determine which data input gets through. • How many select pins are needed? – Depends on number of data inputs. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Multiplexing • There are several data inputs and one of them is routed to the output (possibly the shared communication channel). – Like selecting a television channel (although that example is FDM). • In addition to data inputs, there must be select inputs. – The select inputs determine which data input gets through. • How many select pins are needed? – Depends on number of data inputs. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
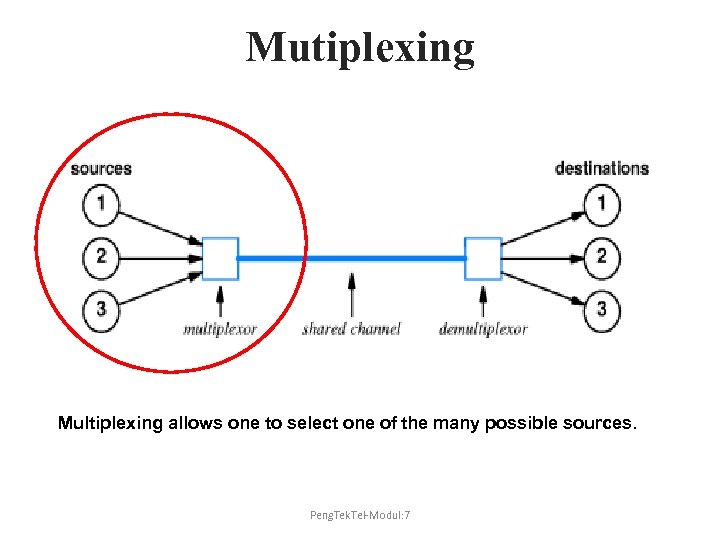 Mutiplexing Multiplexing allows one to select one of the many possible sources. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Mutiplexing Multiplexing allows one to select one of the many possible sources. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
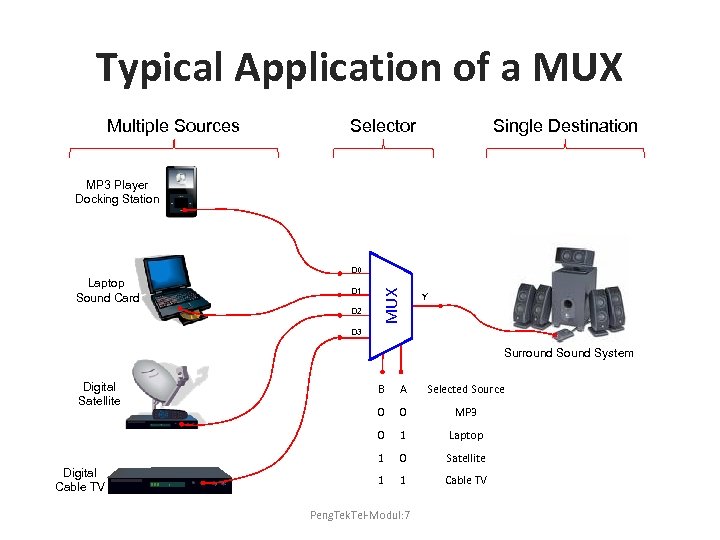 Typical Application of a MUX Multiple Sources Selector Single Destination MP 3 Player Docking Station D 1 D 2 MUX D 0 Laptop Sound Card Y D 3 Surround System Digital Satellite A Selected Source 0 0 MP 3 0 1 Laptop 1 Digital Cable TV B 0 Satellite 1 1 Cable TV Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Typical Application of a MUX Multiple Sources Selector Single Destination MP 3 Player Docking Station D 1 D 2 MUX D 0 Laptop Sound Card Y D 3 Surround System Digital Satellite A Selected Source 0 0 MP 3 0 1 Laptop 1 Digital Cable TV B 0 Satellite 1 1 Cable TV Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
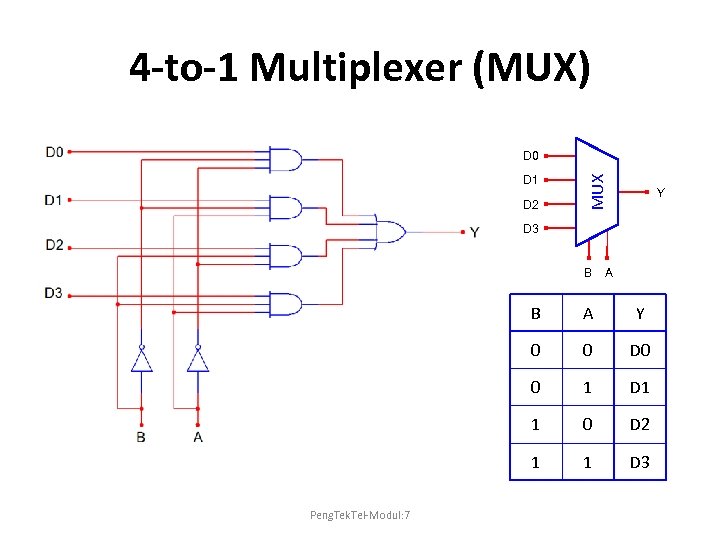 4 -to-1 Multiplexer (MUX) D 1 D 2 MUX D 0 Y D 3 B A B Y 0 0 D 0 0 1 D 1 1 0 D 2 1 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 A 1 D 3
4 -to-1 Multiplexer (MUX) D 1 D 2 MUX D 0 Y D 3 B A B Y 0 0 D 0 0 1 D 1 1 0 D 2 1 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 A 1 D 3
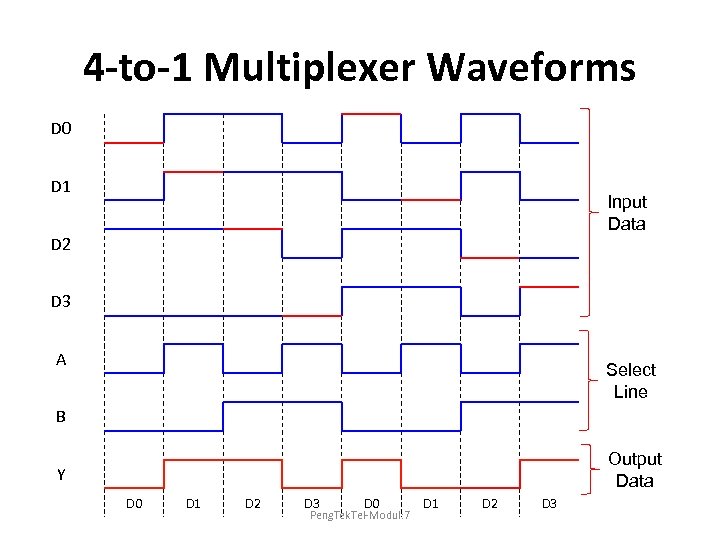 4 -to-1 Multiplexer Waveforms D 0 D 1 Input Data D 2 D 3 A Select Line B Output Data Y D 0 D 1 D 2 D 3 D 0 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 D 1 D 2 D 3
4 -to-1 Multiplexer Waveforms D 0 D 1 Input Data D 2 D 3 A Select Line B Output Data Y D 0 D 1 D 2 D 3 D 0 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 D 1 D 2 D 3
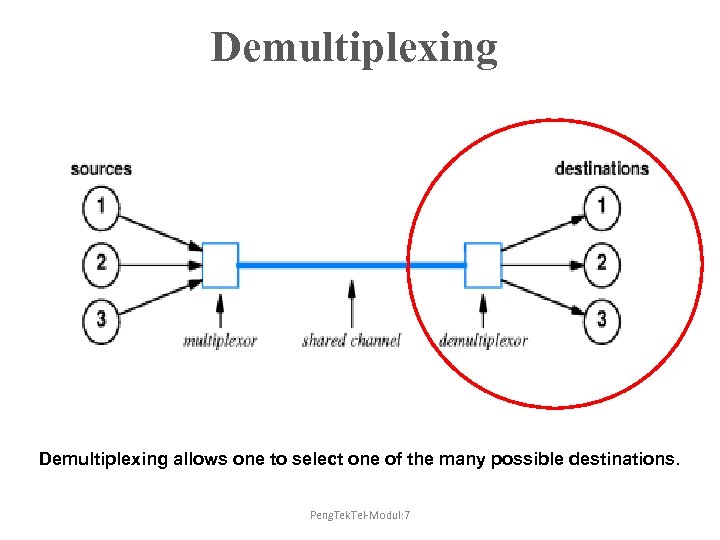 Demultiplexing allows one to select one of the many possible destinations. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Demultiplexing allows one to select one of the many possible destinations. Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
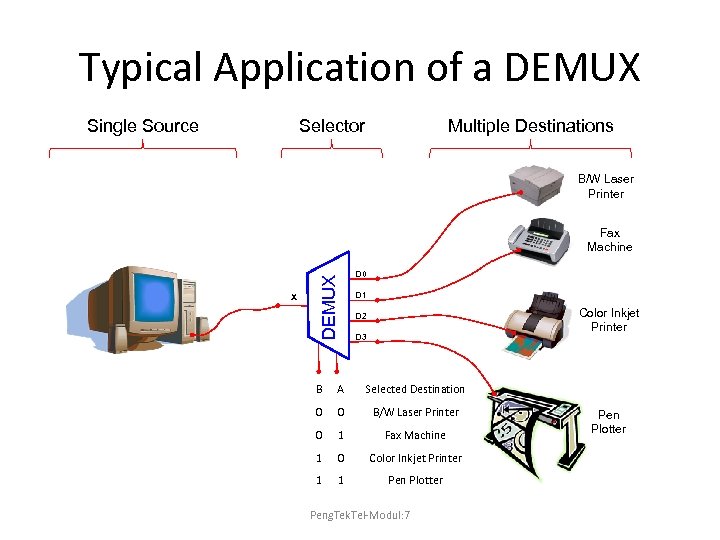 Typical Application of a DEMUX Selector Single Source Multiple Destinations B/W Laser Printer X DEMUX Fax Machine D 0 D 1 Color Inkjet Printer D 2 D 3 B A Selected Destination 0 0 B/W Laser Printer 0 1 Fax Machine 1 0 Color Inkjet Printer 1 1 Pen Plotter Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 Pen Plotter
Typical Application of a DEMUX Selector Single Source Multiple Destinations B/W Laser Printer X DEMUX Fax Machine D 0 D 1 Color Inkjet Printer D 2 D 3 B A Selected Destination 0 0 B/W Laser Printer 0 1 Fax Machine 1 0 Color Inkjet Printer 1 1 Pen Plotter Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 Pen Plotter
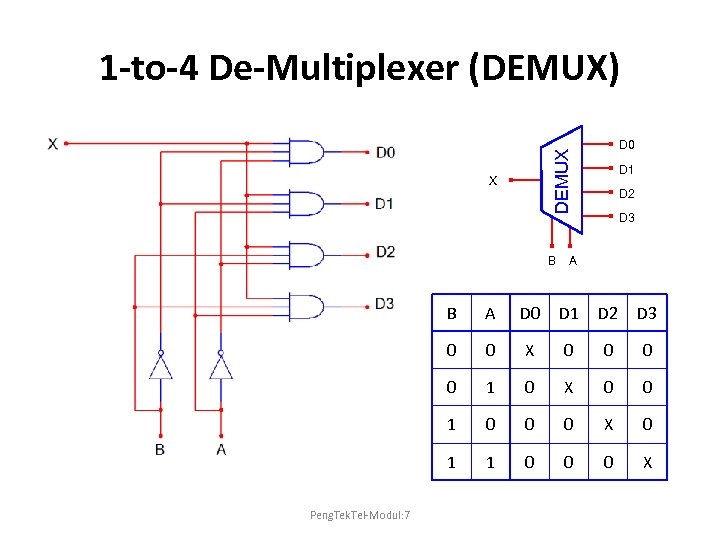 1 -to-4 De-Multiplexer (DEMUX) DEMUX D 0 X B D 1 D 2 D 3 A B D 0 D 1 D 2 D 3 0 0 X 0 0 1 0 0 0 X 0 1 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 A 1 0 0 0 X
1 -to-4 De-Multiplexer (DEMUX) DEMUX D 0 X B D 1 D 2 D 3 A B D 0 D 1 D 2 D 3 0 0 X 0 0 1 0 0 0 X 0 1 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 A 1 0 0 0 X
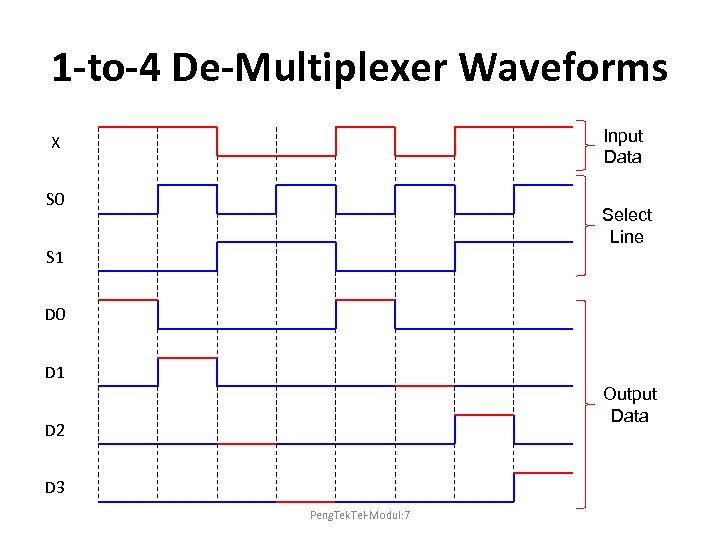 1 -to-4 De-Multiplexer Waveforms Input Data X S 0 Select Line S 1 D 0 D 1 Output Data D 2 D 3 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
1 -to-4 De-Multiplexer Waveforms Input Data X S 0 Select Line S 1 D 0 D 1 Output Data D 2 D 3 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Multiplexing Techniques q Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Ø Each signal is allocated a different frequency band Ø Usually used with analog signals Ø Modulation equipment is needed to move each signal to the required frequency band (channel) Ø Multiple carriers are used, each is called sub-carrier Ø Multiplexing equipment is needed to combine the modulated signals q Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Ø Usually used with digital signal is carrying digital data Ø Data from various sources are carried in repetitive frames Ø Each frame consists of of a set of time slots Ø Each source is assigned one or more time slots per frame Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Multiplexing Techniques q Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Ø Each signal is allocated a different frequency band Ø Usually used with analog signals Ø Modulation equipment is needed to move each signal to the required frequency band (channel) Ø Multiple carriers are used, each is called sub-carrier Ø Multiplexing equipment is needed to combine the modulated signals q Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Ø Usually used with digital signal is carrying digital data Ø Data from various sources are carried in repetitive frames Ø Each frame consists of of a set of time slots Ø Each source is assigned one or more time slots per frame Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
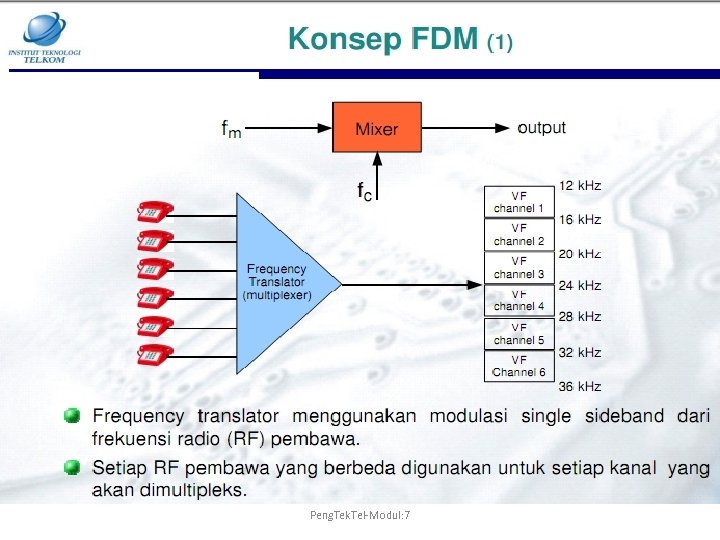 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
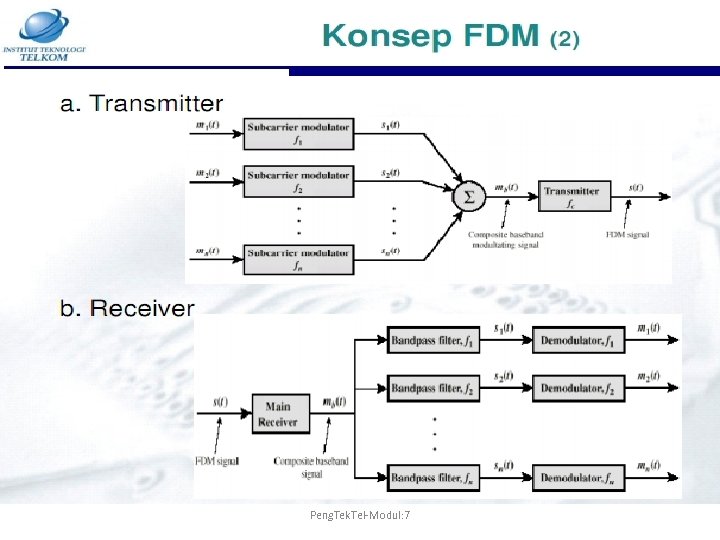 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
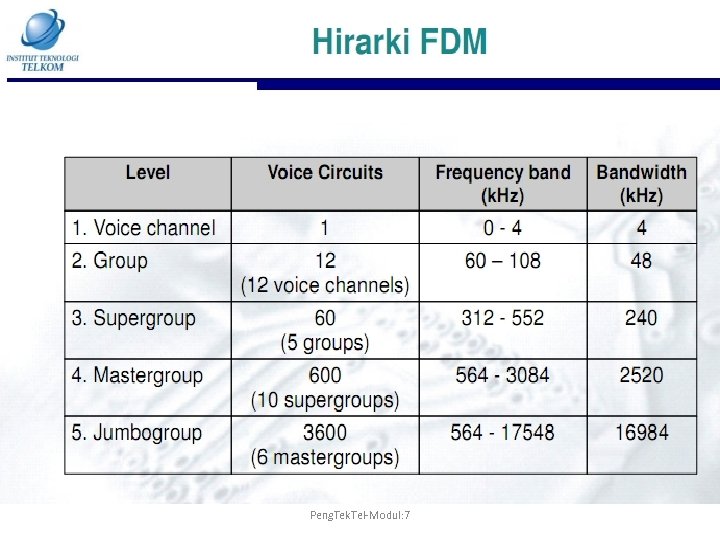 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
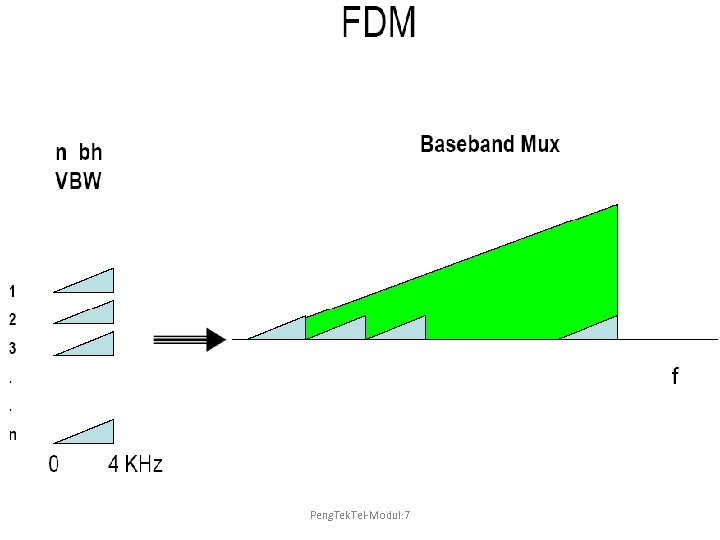
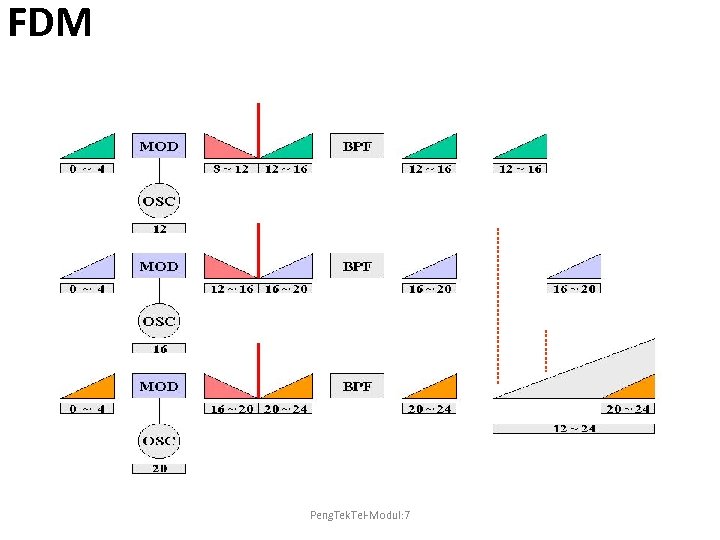 FDM Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
FDM Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
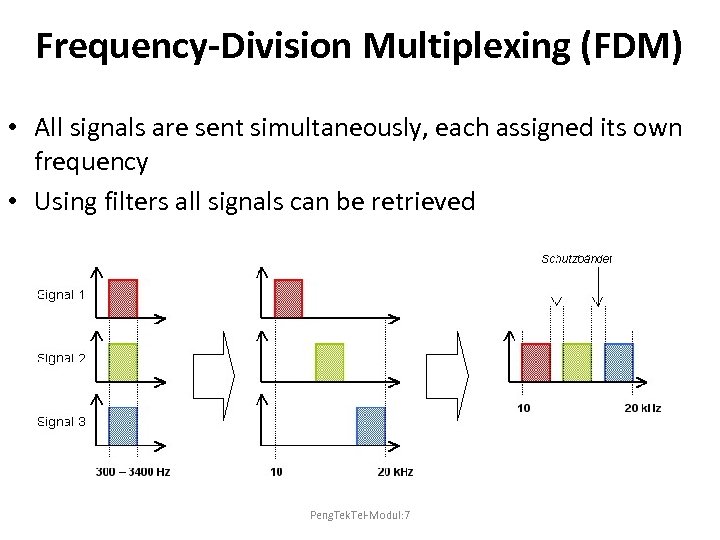 Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) • All signals are sent simultaneously, each assigned its own frequency • Using filters all signals can be retrieved Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) • All signals are sent simultaneously, each assigned its own frequency • Using filters all signals can be retrieved Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
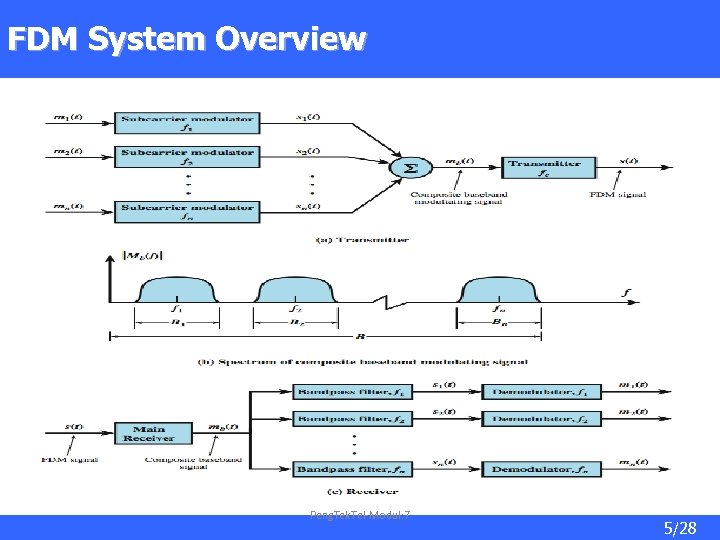 FDM System Overview Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 5/28
FDM System Overview Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 5/28
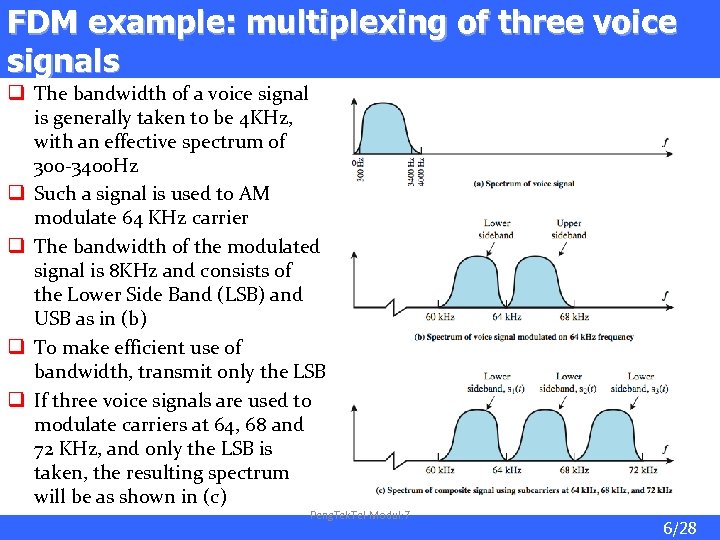 FDM example: multiplexing of three voice signals q The bandwidth of a voice signal is generally taken to be 4 KHz, with an effective spectrum of 300 -3400 Hz q Such a signal is used to AM modulate 64 KHz carrier q The bandwidth of the modulated signal is 8 KHz and consists of the Lower Side Band (LSB) and USB as in (b) q To make efficient use of bandwidth, transmit only the LSB q If three voice signals are used to modulate carriers at 64, 68 and 72 KHz, and only the LSB is taken, the resulting spectrum will be as shown in (c) Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 6/28
FDM example: multiplexing of three voice signals q The bandwidth of a voice signal is generally taken to be 4 KHz, with an effective spectrum of 300 -3400 Hz q Such a signal is used to AM modulate 64 KHz carrier q The bandwidth of the modulated signal is 8 KHz and consists of the Lower Side Band (LSB) and USB as in (b) q To make efficient use of bandwidth, transmit only the LSB q If three voice signals are used to modulate carriers at 64, 68 and 72 KHz, and only the LSB is taken, the resulting spectrum will be as shown in (c) Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7 6/28
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
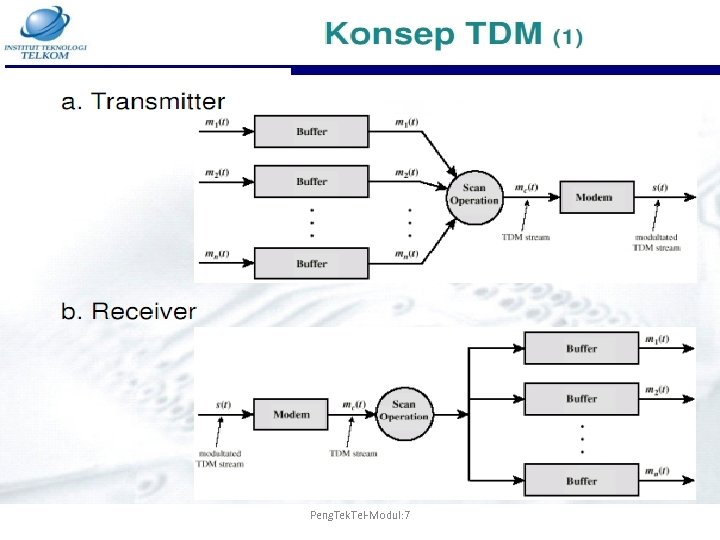 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
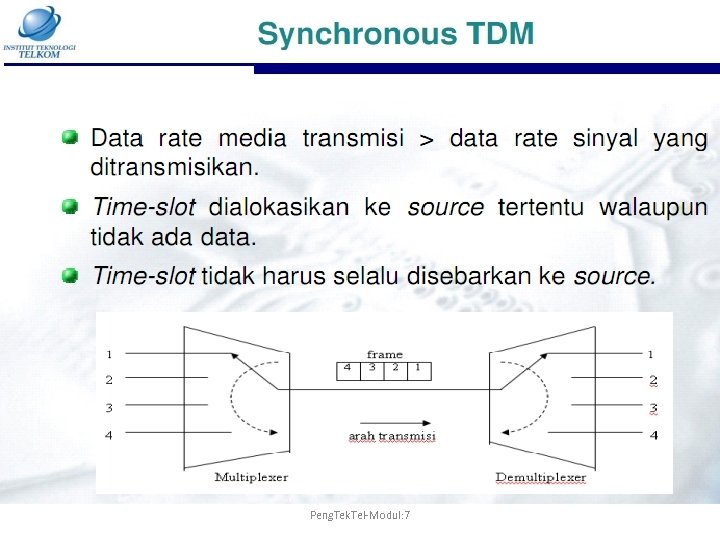 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
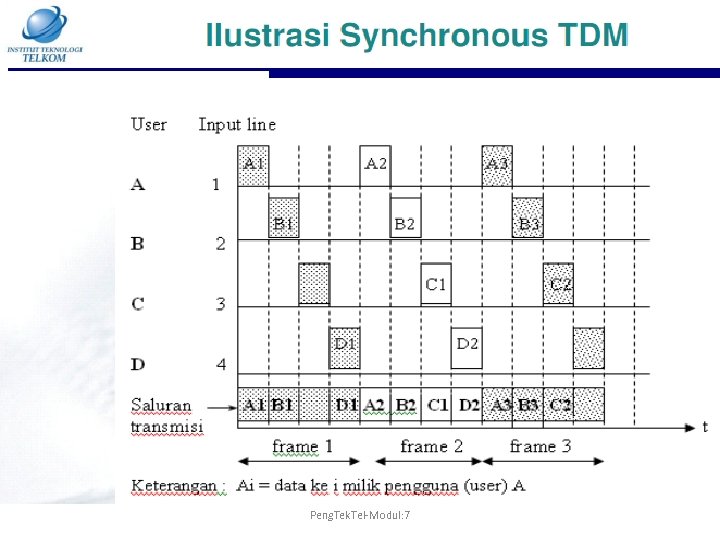 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
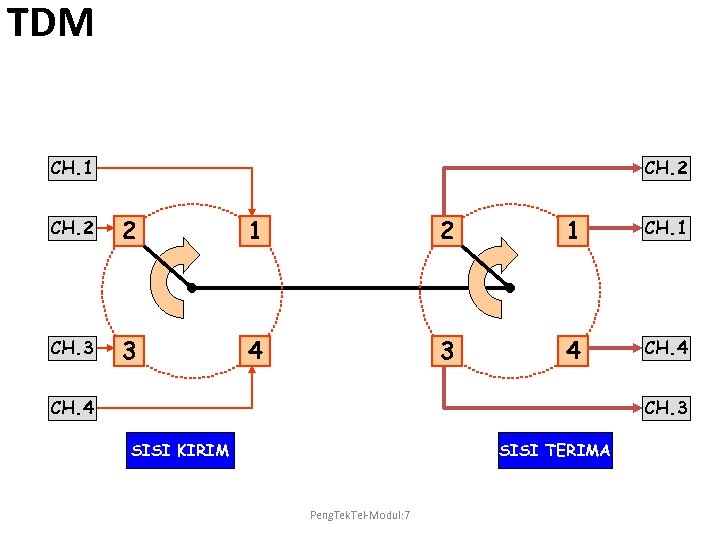 TDM CH. 1 CH. 2 2 1 CH. 3 3 4 CH. 3 SISI KIRIM SISI TERIMA Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
TDM CH. 1 CH. 2 2 1 CH. 3 3 4 CH. 3 SISI KIRIM SISI TERIMA Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
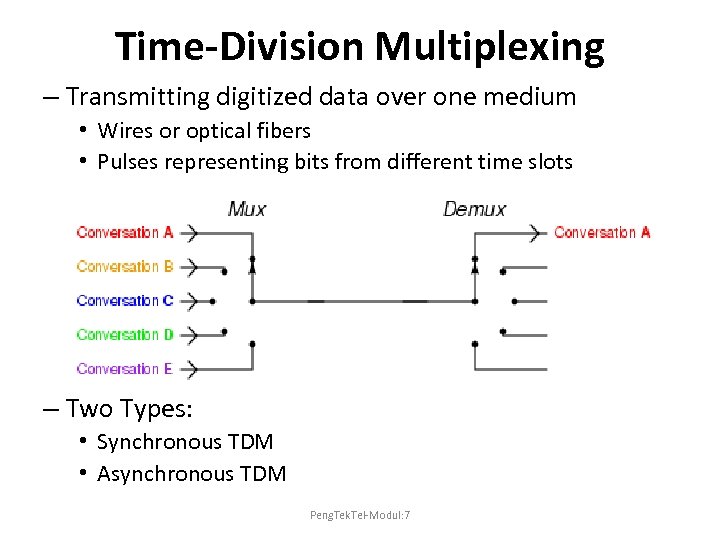 Time-Division Multiplexing – Transmitting digitized data over one medium • Wires or optical fibers • Pulses representing bits from different time slots – Two Types: • Synchronous TDM • Asynchronous TDM Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Time-Division Multiplexing – Transmitting digitized data over one medium • Wires or optical fibers • Pulses representing bits from different time slots – Two Types: • Synchronous TDM • Asynchronous TDM Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
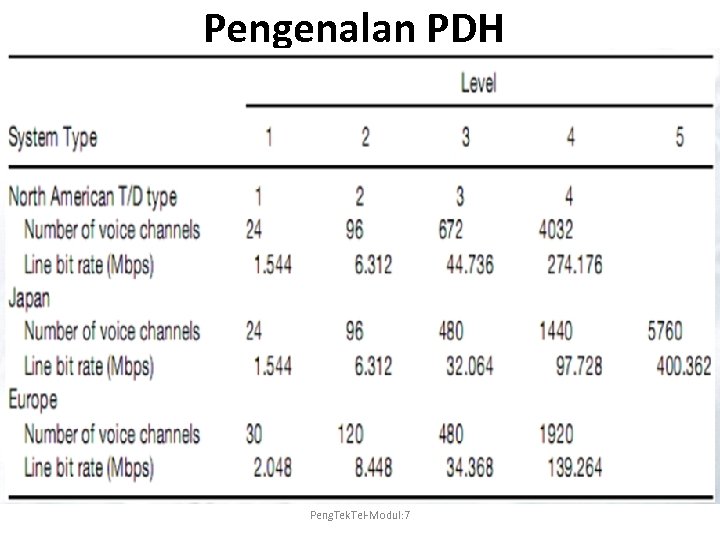 Pengenalan PDH Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Pengenalan PDH Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
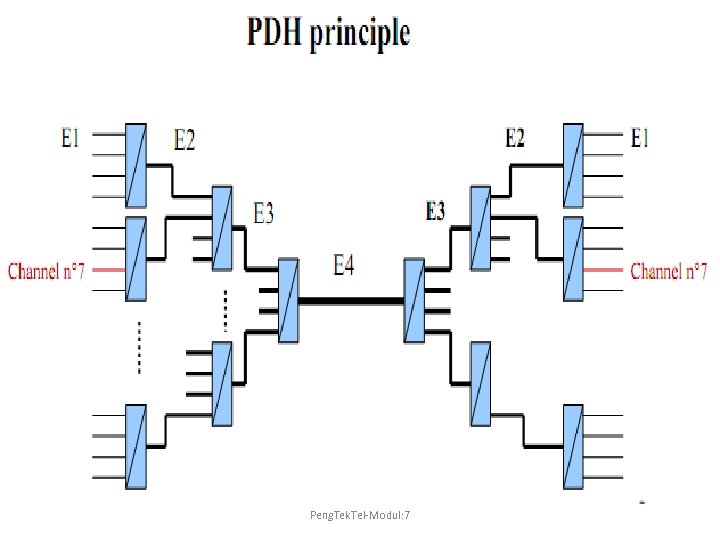 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
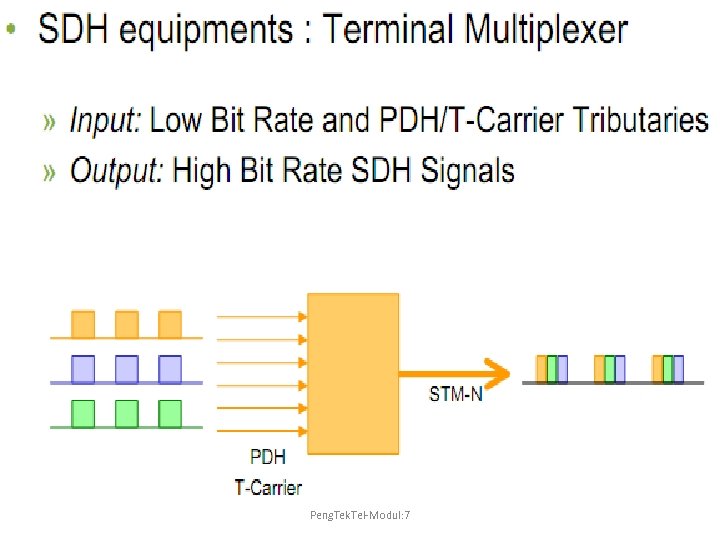 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Pengenalan SDH Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Pengenalan SDH Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
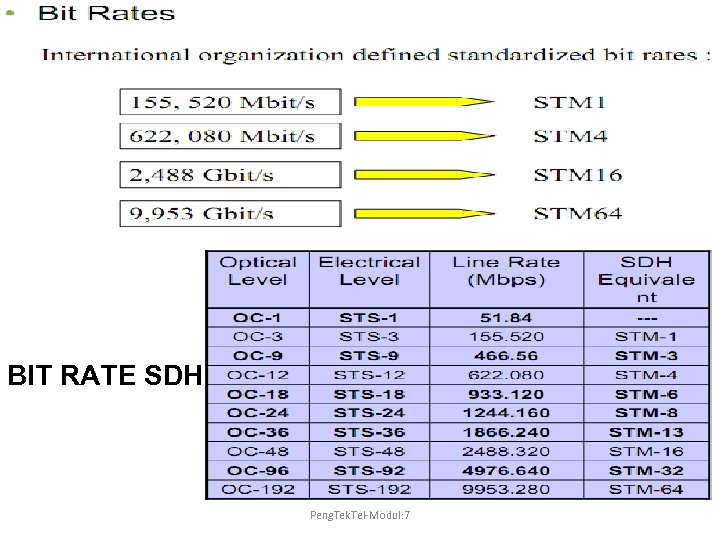 BIT RATE SDH Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
BIT RATE SDH Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
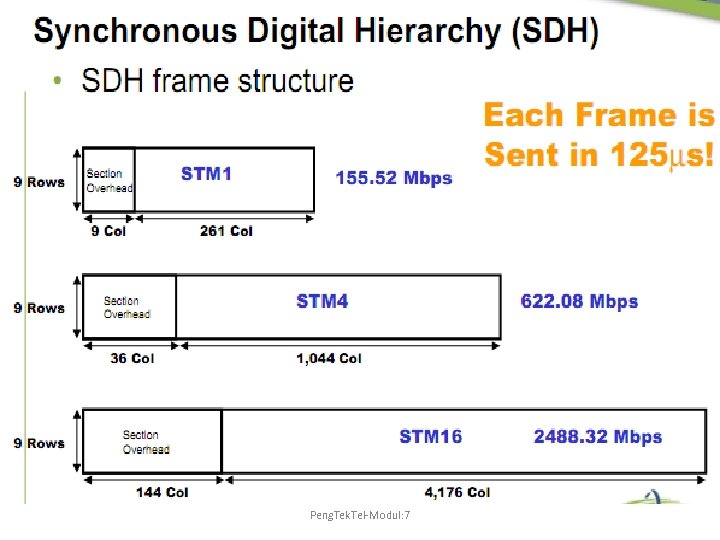 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
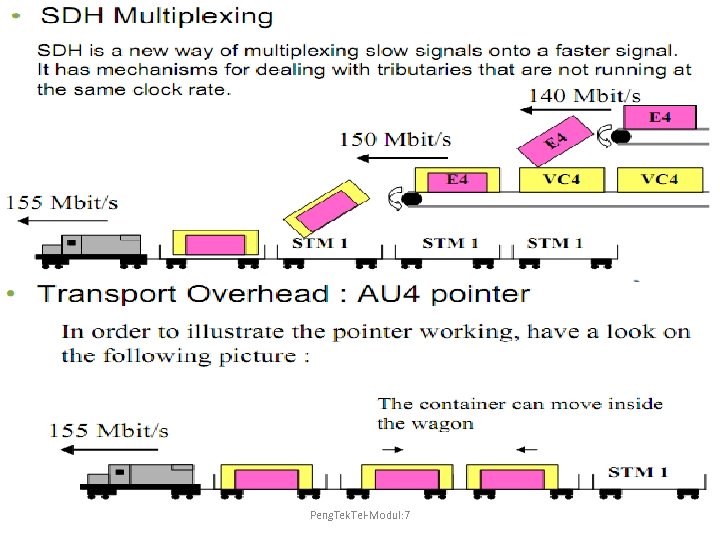 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
 Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7
Peng. Tek. Tel-Modul: 7


