71664e492d76280d0b012ee9a9f27264.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Pengelolan proyek SI Integration & Testing S 2 UG 1
Pengelolan proyek SI Integration & Testing S 2 UG 1
 Integration & Testing • Development/Integration/Testing • Dikebanyakan tempat untuk skedul dan aktivitas bisa tumpang tindih. • Kadang-kadang Integration/Testing pemikiran/berada sebagai satu fase. • Semakin menambah kemampuan • QA team bekerja paralel dengan tim development S 2 UG 2
Integration & Testing • Development/Integration/Testing • Dikebanyakan tempat untuk skedul dan aktivitas bisa tumpang tindih. • Kadang-kadang Integration/Testing pemikiran/berada sebagai satu fase. • Semakin menambah kemampuan • QA team bekerja paralel dengan tim development S 2 UG 2
 Integration Approaches • Top Down • Inti atau meliputi sistem yang diimplementasikan • Kombinasikan kedalam minimal sitem shell. • “Stubs/potongan” yang digunakan untuk mengisi bagian yang tidak lengkap. • Bottom Up • Dimulai dengan modul secara individual dan membangun. • Unit individual (setelah unit testing) dikombinasikan ke sub sistem. • Sub-systems dikombinasikan ke sistem yang lebih besar. S 2 UG 3
Integration Approaches • Top Down • Inti atau meliputi sistem yang diimplementasikan • Kombinasikan kedalam minimal sitem shell. • “Stubs/potongan” yang digunakan untuk mengisi bagian yang tidak lengkap. • Bottom Up • Dimulai dengan modul secara individual dan membangun. • Unit individual (setelah unit testing) dikombinasikan ke sub sistem. • Sub-systems dikombinasikan ke sistem yang lebih besar. S 2 UG 3
 Integration • Siapa yang melakukan testing terintegrasi ? – Bisa tim development dan/atau tim QA • Staffing and budget adalah sasaran utama • Issues • • • Pressure/tekanan Batas tanggal sudah dekat Kesalahan tak terduga (bugs) Motivasi / semangat User menerima perbedaan S 2 UG 4
Integration • Siapa yang melakukan testing terintegrasi ? – Bisa tim development dan/atau tim QA • Staffing and budget adalah sasaran utama • Issues • • • Pressure/tekanan Batas tanggal sudah dekat Kesalahan tak terduga (bugs) Motivasi / semangat User menerima perbedaan S 2 UG 4
 Validation and Verification • Validation – Apa kita telah membuat produk yang benar ? • Verification – Apakah kita telah membuat produk yang benar ? – Testing – Inspection – Static analysis S 2 UG 5
Validation and Verification • Validation – Apa kita telah membuat produk yang benar ? • Verification – Apakah kita telah membuat produk yang benar ? – Testing – Inspection – Static analysis S 2 UG 5
 Quality Assurance/jaminan mutu • QA atau SQA (Software Quality Assurance) • QA yang bagus datang dari proses yang bagus • Kapan SQA dimulai ? – Selama diperlukan • QA adalah jendela terbaik melihat hasil proyek S 2 UG 6
Quality Assurance/jaminan mutu • QA atau SQA (Software Quality Assurance) • QA yang bagus datang dari proses yang bagus • Kapan SQA dimulai ? – Selama diperlukan • QA adalah jendela terbaik melihat hasil proyek S 2 UG 6
 Test Plans (SQAP) • Software Quality Assurance Plan • See example – Menggunakan IEEE 730 standard S 2 UG 7
Test Plans (SQAP) • Software Quality Assurance Plan • See example – Menggunakan IEEE 730 standard S 2 UG 7
 SQAP • Standard sections – Purpose/kegunaan – Reference documents – Management – Documentation – Standards, practices, conventions, metrics • Kualitas pengukuran • Pengujian S 2 UG 8
SQAP • Standard sections – Purpose/kegunaan – Reference documents – Management – Documentation – Standards, practices, conventions, metrics • Kualitas pengukuran • Pengujian S 2 UG 8
 SQAP • Standard sections continued – Reviews and Audits • Process and specific reviews – Requirements Review (SRR) – Test Plan Review – Code reviews – Risk Management • Terikat dengan QA untuk keseluruhan perencanaan resiko managemen – Problem Reporting dan koreksi – Tools, Techniques, Methodologies – Koleksi dan penyimpanan record S 2 UG 9
SQAP • Standard sections continued – Reviews and Audits • Process and specific reviews – Requirements Review (SRR) – Test Plan Review – Code reviews – Risk Management • Terikat dengan QA untuk keseluruhan perencanaan resiko managemen – Problem Reporting dan koreksi – Tools, Techniques, Methodologies – Koleksi dan penyimpanan record S 2 UG 9
 Software Quality • Traceability/pelacakan • Kesanggupan untuk melacak hubungan antara pekerjaan yang dihasilkan • Formal Reviews • Dilakukan pada akhir setiap lifecycle phase • SRR (System Requirements Review ), CDR(Clinical Data Repositories ), etc. S 2 UG 10
Software Quality • Traceability/pelacakan • Kesanggupan untuk melacak hubungan antara pekerjaan yang dihasilkan • Formal Reviews • Dilakukan pada akhir setiap lifecycle phase • SRR (System Requirements Review ), CDR(Clinical Data Repositories ), etc. S 2 UG 10
 Testing • Berlatih program komputer dengan mengantisipasi banyak input • Membandingkan hasil sebenarnya kemudian hasil yang diharapkan • Testing adalah sebuah bentuk dari sampling • Tidak dapat benar-benar membuktikan adanya kecacatan • Semaua software mempunyai periode bug. • Testing bukan debugging. S 2 UG 11
Testing • Berlatih program komputer dengan mengantisipasi banyak input • Membandingkan hasil sebenarnya kemudian hasil yang diharapkan • Testing adalah sebuah bentuk dari sampling • Tidak dapat benar-benar membuktikan adanya kecacatan • Semaua software mempunyai periode bug. • Testing bukan debugging. S 2 UG 11
 Test Cases • Key elements of a test plan • May include scripts, data, checklists • May map to a Requirements Coverage Matrix • A traceability tool S 2 UG 12
Test Cases • Key elements of a test plan • May include scripts, data, checklists • May map to a Requirements Coverage Matrix • A traceability tool S 2 UG 12
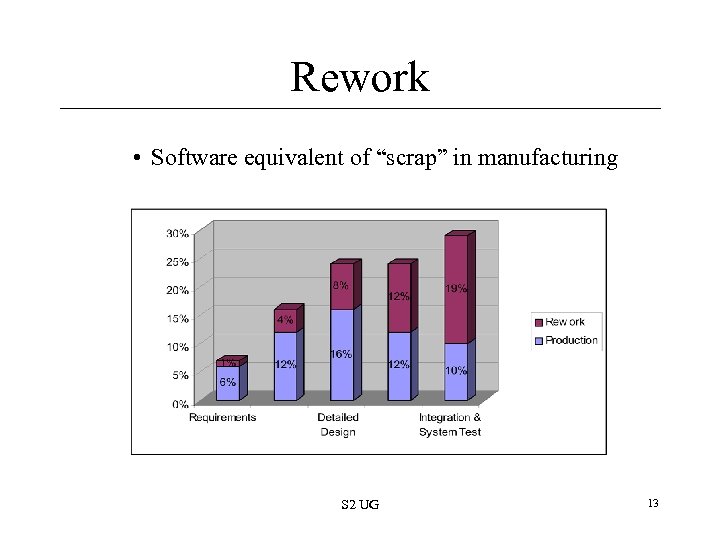 Rework • Software equivalent of “scrap” in manufacturing S 2 UG 13
Rework • Software equivalent of “scrap” in manufacturing S 2 UG 13
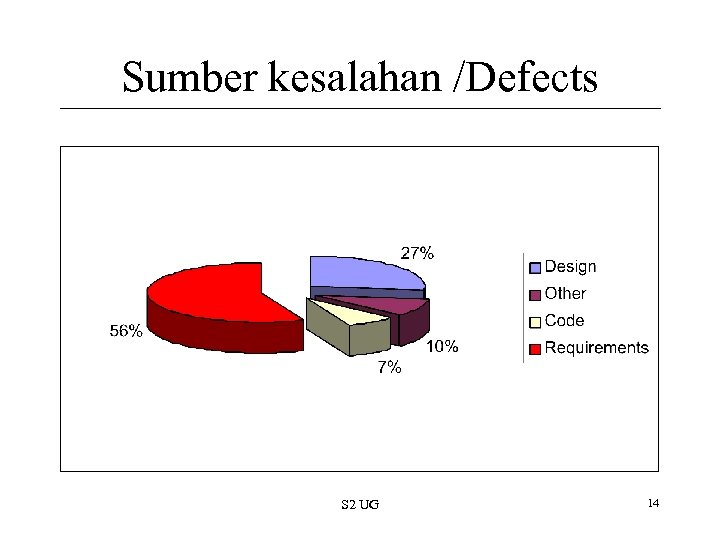 Sumber kesalahan /Defects S 2 UG 14
Sumber kesalahan /Defects S 2 UG 14
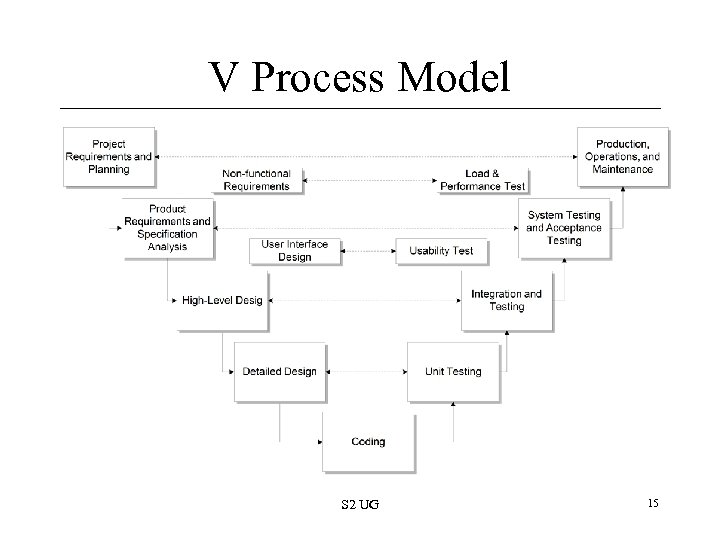 V Process Model S 2 UG 15
V Process Model S 2 UG 15
 Project Testing Flow • • Unit Testing Integration Testing System Testing User Acceptance Testing S 2 UG 16
Project Testing Flow • • Unit Testing Integration Testing System Testing User Acceptance Testing S 2 UG 16
 Black-Box Testing • Functional Testing • Program is a “black-box” – Not concerned with how it works but what it does – Focus on inputs & outputs • Test cases are based on SRS (specs) S 2 UG 17
Black-Box Testing • Functional Testing • Program is a “black-box” – Not concerned with how it works but what it does – Focus on inputs & outputs • Test cases are based on SRS (specs) S 2 UG 17
 White-Box Testing • Accounts for the structure of the program • Coverage – Pernyataan eksekusi – Mengikuti sampai bentuk code S 2 UG 18
White-Box Testing • Accounts for the structure of the program • Coverage – Pernyataan eksekusi – Mengikuti sampai bentuk code S 2 UG 18
 Unit Testing • Module Testing • Type of white-box testing – Kadang-kadang diperlakukan seperti black-box • Siapa yang melakukan Unit Testing? • Developers • Unit tests are written in code – Same language as the module – a. k. a. “Test drivers” • Kapan melakukan Unit Testing? • Selama development • Sebagai modul individual dibuat komplit S 2 UG 19
Unit Testing • Module Testing • Type of white-box testing – Kadang-kadang diperlakukan seperti black-box • Siapa yang melakukan Unit Testing? • Developers • Unit tests are written in code – Same language as the module – a. k. a. “Test drivers” • Kapan melakukan Unit Testing? • Selama development • Sebagai modul individual dibuat komplit S 2 UG 19
 Unit Testing • Individual tests can be grouped – “deretan Test” S 2 UG 20
Unit Testing • Individual tests can be grouped – “deretan Test” S 2 UG 20
 Integration Testing • Testing interface diantara komponen • Langkah pertama setelah testing unit • Komponen bisa bekerja sendiri tetapi ketika berjalan bersama bisa rusak • Kerusakan bisa muncul di satu modul tetapi bisa menjelma dalam bentuk lain • Black-box tests S 2 UG 21
Integration Testing • Testing interface diantara komponen • Langkah pertama setelah testing unit • Komponen bisa bekerja sendiri tetapi ketika berjalan bersama bisa rusak • Kerusakan bisa muncul di satu modul tetapi bisa menjelma dalam bentuk lain • Black-box tests S 2 UG 21
 System Testing • Test sistem menyeluruh • Tipe testing semacam black box S 2 UG 22
System Testing • Test sistem menyeluruh • Tipe testing semacam black box S 2 UG 22
 User Acceptance Testing • • Peristiwa terakhir didalam phase testing test & sign-off konsumen terakhir Kadang-kadang synonymous dengan beta tests Based on “Acceptance Criteria” – Kondisi software harus cocok dengan yang diminta customer agar sistem diterima – Idealnya didefinisikan sebelum kontrak ditandatangani – Menggunakan kondisi yang dapat dihitung dan dapat diukur S 2 UG 23
User Acceptance Testing • • Peristiwa terakhir didalam phase testing test & sign-off konsumen terakhir Kadang-kadang synonymous dengan beta tests Based on “Acceptance Criteria” – Kondisi software harus cocok dengan yang diminta customer agar sistem diterima – Idealnya didefinisikan sebelum kontrak ditandatangani – Menggunakan kondisi yang dapat dihitung dan dapat diukur S 2 UG 23
 Kemunduran / Regression Testing – running kembali testing setelah fix atau ada perubahan dibuat ke software atau lingkungan – contoh: QA mendapati kerusakan, developer fixes, QA melakukan test untuk verify – Tool automatik sangat membantu S 2 UG 24
Kemunduran / Regression Testing – running kembali testing setelah fix atau ada perubahan dibuat ke software atau lingkungan – contoh: QA mendapati kerusakan, developer fixes, QA melakukan test untuk verify – Tool automatik sangat membantu S 2 UG 24
 Compatibility Testing – Testing against other “platforms” • Ex: Testing against multiple browsers • Does it work under Netscape/IE, Windows/Mac S 2 UG 25
Compatibility Testing – Testing against other “platforms” • Ex: Testing against multiple browsers • Does it work under Netscape/IE, Windows/Mac S 2 UG 25
 External Testing Milestones • Alpha 1 st, Beta 2 nd • Testing by users outside the organization • Dikerjakan oleh user • Alpha release • Diberikan ke pengguna yang terbatas • Product tidak menggambarkan secara lengkap • Beta release • Customer testing dan evaluasi • Lebih menonjol • Lebih baik setelah doftware stabil S 2 UG 26
External Testing Milestones • Alpha 1 st, Beta 2 nd • Testing by users outside the organization • Dikerjakan oleh user • Alpha release • Diberikan ke pengguna yang terbatas • Product tidak menggambarkan secara lengkap • Beta release • Customer testing dan evaluasi • Lebih menonjol • Lebih baik setelah doftware stabil S 2 UG 26
 External Testing Milestones • Value of Beta Testing • Testing didunia nyata • Menjadi sebuah software yang diminati • Nilai pasar • Beta testers must be “recruited” • From: Existing base, marketing, tech support, site • Memerlukan peran manajer beta • Semaua harus diskedule manajer produksi S 2 UG 27
External Testing Milestones • Value of Beta Testing • Testing didunia nyata • Menjadi sebuah software yang diminati • Nilai pasar • Beta testers must be “recruited” • From: Existing base, marketing, tech support, site • Memerlukan peran manajer beta • Semaua harus diskedule manajer produksi S 2 UG 27
 External Testing Milestones • Release Candidate (RC) • Dikirim ke pabrik jika testing sukses • Release to Manufacturing (RTM) • Production release formally mengirim ke pabrik • Mencoba mencapai sebuah periode yang stabil sebelum ke peristiwa yang penting – Team focus on quality, integration, stability S 2 UG 28
External Testing Milestones • Release Candidate (RC) • Dikirim ke pabrik jika testing sukses • Release to Manufacturing (RTM) • Production release formally mengirim ke pabrik • Mencoba mencapai sebuah periode yang stabil sebelum ke peristiwa yang penting – Team focus on quality, integration, stability S 2 UG 28
 Test Scripts • Two meanings • 1. Set instruksi step by step bertujuan untuk memimpin test personal sampai selesai – List semua aksi dan response yang diharapkan • 2. Automated test script (program) S 2 UG 29
Test Scripts • Two meanings • 1. Set instruksi step by step bertujuan untuk memimpin test personal sampai selesai – List semua aksi dan response yang diharapkan • 2. Automated test script (program) S 2 UG 29
 Static Testing • Reviews • artifacts penting dapat direview • Proposal, contract, schedule, requirements, code, data model, test plans – Peer Reviews • Methodical examination of software work products by peers untuk mengidentifikasi kerusakan dan perubahan yang perlu • Goal: menghilangkan kerusakan lebih awal dan secara efisien • Dipalning oleh PM, performed in meetings, documented S 2 UG 30
Static Testing • Reviews • artifacts penting dapat direview • Proposal, contract, schedule, requirements, code, data model, test plans – Peer Reviews • Methodical examination of software work products by peers untuk mengidentifikasi kerusakan dan perubahan yang perlu • Goal: menghilangkan kerusakan lebih awal dan secara efisien • Dipalning oleh PM, performed in meetings, documented S 2 UG 30
 Automated Testing • Human testers = inefficient • Pros • • • Lowers overall cost of testing Tools can run unattended Tools run through ‘suites’ faster than people Great for regression and compatibility tests Tests create a body of knowledge Can reduce QA staff size • Cons • But not everything can be automated • Learning curve or expertise in tools • Cost of high-end tools $5 -80 K (low-end are still cheap) S 2 UG 31
Automated Testing • Human testers = inefficient • Pros • • • Lowers overall cost of testing Tools can run unattended Tools run through ‘suites’ faster than people Great for regression and compatibility tests Tests create a body of knowledge Can reduce QA staff size • Cons • But not everything can be automated • Learning curve or expertise in tools • Cost of high-end tools $5 -80 K (low-end are still cheap) S 2 UG 31
 Test Tools • • Capture & Playback Coverage Analysis Performance Testing Test Case Management S 2 UG 32
Test Tools • • Capture & Playback Coverage Analysis Performance Testing Test Case Management S 2 UG 32
 Load & Stress Testing • Mendorong sistem keluar dari kapasitas terbatas • Sering mengerjakan lewat scrip otomatis • By the QA team • Near end of functional tests • Dapat menunjukkan – – Hidden functional issues Maximum system capacity Unacceptable data or service loss Determine if “Performance Requirements” met • Remember, these are part of “non-functional” requirements S 2 UG 33
Load & Stress Testing • Mendorong sistem keluar dari kapasitas terbatas • Sering mengerjakan lewat scrip otomatis • By the QA team • Near end of functional tests • Dapat menunjukkan – – Hidden functional issues Maximum system capacity Unacceptable data or service loss Determine if “Performance Requirements” met • Remember, these are part of “non-functional” requirements S 2 UG 33
 Load & Stress Testing • Metrics – Minimal acceptable response time – Minimal acceptable number of concurrent users – Minimal acceptable downtime S 2 UG 34
Load & Stress Testing • Metrics – Minimal acceptable response time – Minimal acceptable number of concurrent users – Minimal acceptable downtime S 2 UG 34
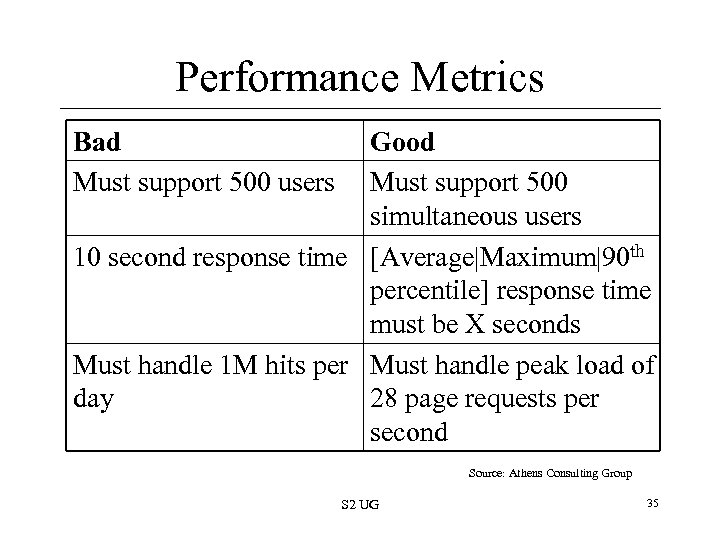 Performance Metrics Bad Must support 500 users Good Must support 500 simultaneous users 10 second response time [Average|Maximum|90 th percentile] response time must be X seconds Must handle 1 M hits per Must handle peak load of day 28 page requests per second Source: Athens Consulting Group S 2 UG 35
Performance Metrics Bad Must support 500 users Good Must support 500 simultaneous users 10 second response time [Average|Maximum|90 th percentile] response time must be X seconds Must handle 1 M hits per Must handle peak load of day 28 page requests per second Source: Athens Consulting Group S 2 UG 35
 Other Testing • Installation Testing – Very important if not a Web-based system – Can lead to high support costs and customer dissatisfaction • Usability Testing – Verification of user satisfaction • Navigability • User-friendliness • Ability to accomplish primary tasks S 2 UG 36
Other Testing • Installation Testing – Very important if not a Web-based system – Can lead to high support costs and customer dissatisfaction • Usability Testing – Verification of user satisfaction • Navigability • User-friendliness • Ability to accomplish primary tasks S 2 UG 36
 Miscellaneous • Pareto Analysis – The 80 -20 rule • 80% of defects from 20% of code – Identifying the problem modules • Phase Containment – Testing at the end of each phase – Prevent problems moving phase-to-phase • Burn-in – Allowing system to run “longer” period of time – Variation of stress testing S 2 UG 37
Miscellaneous • Pareto Analysis – The 80 -20 rule • 80% of defects from 20% of code – Identifying the problem modules • Phase Containment – Testing at the end of each phase – Prevent problems moving phase-to-phase • Burn-in – Allowing system to run “longer” period of time – Variation of stress testing S 2 UG 37
 Miscellaneous • “Code Freeze” – When developers stop writing new code and only do bug fixes – Occurs at a varying point in integration/testing • Tester-to-Coder Ratio – It depends – Often 1: 3 or 1: 4 – QA staff size grows: QA Mgr and/or lead early S 2 UG 38
Miscellaneous • “Code Freeze” – When developers stop writing new code and only do bug fixes – Occurs at a varying point in integration/testing • Tester-to-Coder Ratio – It depends – Often 1: 3 or 1: 4 – QA staff size grows: QA Mgr and/or lead early S 2 UG 38
 Stopping Testing • • • When do you stop? Rarely are all defects “closed” by release Shoot for all Critical/High/Medium defects Often, occurs when time runs out Final Sign-off (see also UAT) • By: customers, engineering, product mgmt. , S 2 UG 39
Stopping Testing • • • When do you stop? Rarely are all defects “closed” by release Shoot for all Critical/High/Medium defects Often, occurs when time runs out Final Sign-off (see also UAT) • By: customers, engineering, product mgmt. , S 2 UG 39
 Test Metrics • Load: Max. acceptable response time, min. # of simultaneous users • Disaster: Max. allowable downtime • Compatibility: Min/Max. browsers & OS’s supported • Usability: Min. approval rating from focus groups • Functional: Requirements coverage; 100% pass rate for automated test suites S 2 UG 40
Test Metrics • Load: Max. acceptable response time, min. # of simultaneous users • Disaster: Max. allowable downtime • Compatibility: Min/Max. browsers & OS’s supported • Usability: Min. approval rating from focus groups • Functional: Requirements coverage; 100% pass rate for automated test suites S 2 UG 40
 Defect Metrics • These are very important to the PM • Number of outstanding defects – Ranked by severity • Critical, High, Medium, Low • Showstoppers • Opened vs. closed S 2 UG 41
Defect Metrics • These are very important to the PM • Number of outstanding defects – Ranked by severity • Critical, High, Medium, Low • Showstoppers • Opened vs. closed S 2 UG 41
 Defect Tracking • Get tools to do this for you – Bugzilla, Test. Track Pro, Rational Clear. Case – Some good ones are free or low-cost • Make sure all necessary team members have access (meaning nearly all) • Have regular ‘defect review meetings’ – Can be weekly early in test, daily in crunch • Who can enter defects into the tracking system? – Lots of people: QA staff, developers, analysts, managers, (sometimes) users, PM S 2 UG 42
Defect Tracking • Get tools to do this for you – Bugzilla, Test. Track Pro, Rational Clear. Case – Some good ones are free or low-cost • Make sure all necessary team members have access (meaning nearly all) • Have regular ‘defect review meetings’ – Can be weekly early in test, daily in crunch • Who can enter defects into the tracking system? – Lots of people: QA staff, developers, analysts, managers, (sometimes) users, PM S 2 UG 42
 Defect Tracking • Fields – State: open, closed, pending – Date created, updated, closed – Description of problem – Release/version number – Person submitting – Priority: low, medium, high, critical – Comments: by QA, developer, other S 2 UG 43
Defect Tracking • Fields – State: open, closed, pending – Date created, updated, closed – Description of problem – Release/version number – Person submitting – Priority: low, medium, high, critical – Comments: by QA, developer, other S 2 UG 43
 Defect Metrics • Open Rates – How many new bugs over a period of time • Close Rates – How many closed over that same period – Ex: 10 bugs/day • Change Rate – Number of times the same issue updated • Fix Failed Counts – Fixes that didn’t really fix (still open) – One measure of “vibration” in project S 2 UG 44
Defect Metrics • Open Rates – How many new bugs over a period of time • Close Rates – How many closed over that same period – Ex: 10 bugs/day • Change Rate – Number of times the same issue updated • Fix Failed Counts – Fixes that didn’t really fix (still open) – One measure of “vibration” in project S 2 UG 44
 Defect Rates • Microsoft Study – 10 -20/KLOC during test – 0. 5/KLOC after release S 2 UG 45
Defect Rates • Microsoft Study – 10 -20/KLOC during test – 0. 5/KLOC after release S 2 UG 45
 Test Environments • You need to test somewhere. Where? • Typically separate hardware/network environment(s) S 2 UG 46
Test Environments • You need to test somewhere. Where? • Typically separate hardware/network environment(s) S 2 UG 46
 Hardware Environments • • Development QA Staging (optional) Production S 2 UG 47
Hardware Environments • • Development QA Staging (optional) Production S 2 UG 47
 Hardware Environments • Typical environments – Development • Where programmers work • Unit tests happen here – Test • For integration, system, and regression testing – Stage • For burn-in and load testing – Production • Final deployment environment(s) S 2 UG 48
Hardware Environments • Typical environments – Development • Where programmers work • Unit tests happen here – Test • For integration, system, and regression testing – Stage • For burn-in and load testing – Production • Final deployment environment(s) S 2 UG 48
 Web Site Testing • Unique factors – – Distributed (N-tiers, can be many) Very high availability needs Uses public network (Internet) Large number of platforms (browsers + OS) • 5 causes of most site failures (Jupiter, 1999) – – – Internal network performance External network performance Hardware performance Unforeseeable traffic spikes Web application performance S 2 UG 49
Web Site Testing • Unique factors – – Distributed (N-tiers, can be many) Very high availability needs Uses public network (Internet) Large number of platforms (browsers + OS) • 5 causes of most site failures (Jupiter, 1999) – – – Internal network performance External network performance Hardware performance Unforeseeable traffic spikes Web application performance S 2 UG 49
 Web Site Testing • Commercial Tools: Load Test & Site Management – Mercury Interactive • Site. Scope, Site. Seer – Segue • Commercial Subscription Services – Keynote Systems • Monitoring Tools • Availability: More “Nines” = More $’s • Must balance QA & availability costs vs. benefits S 2 UG 50
Web Site Testing • Commercial Tools: Load Test & Site Management – Mercury Interactive • Site. Scope, Site. Seer – Segue • Commercial Subscription Services – Keynote Systems • Monitoring Tools • Availability: More “Nines” = More $’s • Must balance QA & availability costs vs. benefits S 2 UG 50
 QA Roles • QA Manager • Hires QA team; creates test plans; selects tools; manages team • Salary: $50 -80 K/yr, $50 -100/hr • Test Developer/Test Engineer • Performs functional tests; develops automated scripts • Salary: $35 -70 K/yr, $40 -100/hr • System Administrator • Supports QA functions but not official QA team member • Copy Editor/Documentation Writer • Supports QA; also not part of official team S 2 UG 51
QA Roles • QA Manager • Hires QA team; creates test plans; selects tools; manages team • Salary: $50 -80 K/yr, $50 -100/hr • Test Developer/Test Engineer • Performs functional tests; develops automated scripts • Salary: $35 -70 K/yr, $40 -100/hr • System Administrator • Supports QA functions but not official QA team member • Copy Editor/Documentation Writer • Supports QA; also not part of official team S 2 UG 51


