PenetrationTesting_QAreer.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 26

Penetration Testing Roman Denisenko, 20 February 2013

Agenda • Theoretical part: – – What is Security Testing? Classification. When? Who? For what purposes? Workflow of penetration testing of web application. Common vulnerabilities. • Toolkit of penetration testers: – Review and classification of necessary tools. • Practical part.

Security testing(by final goal): • • • Vulnerability Assessment. Penetration testing. Code Review. Vulnerability Scan. Security review.

Security testing(by impact level): • Application level. • Network level. • Physical level.


When should we perform ST? 1. Within development cycle. 2. As additional service after deployment.

Who should perform? 1. Ordinary testers. 2. Specialist of Security expertise. 3. Developers.
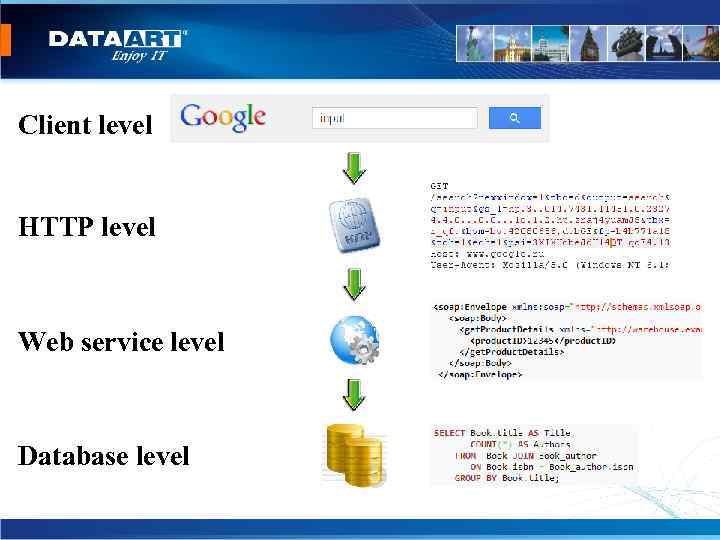
Client level HTTP level Web service level Database level
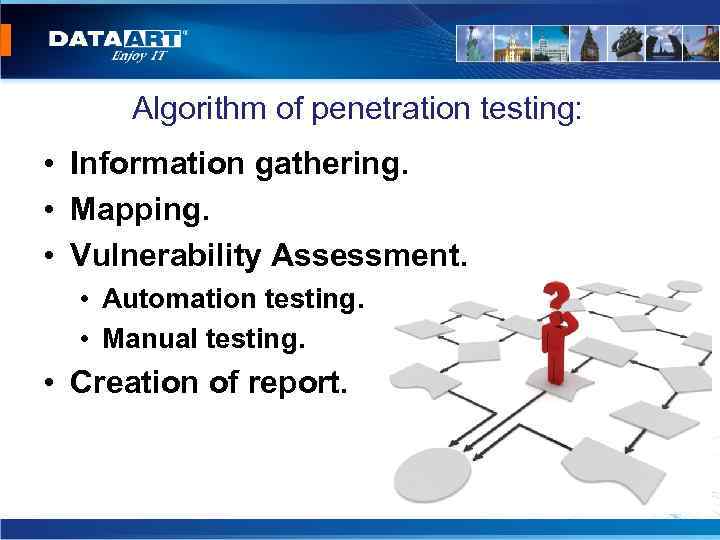
Algorithm of penetration testing: • Information gathering. • Mapping. • Vulnerability Assessment. • Automation testing. • Manual testing. • Creation of report.
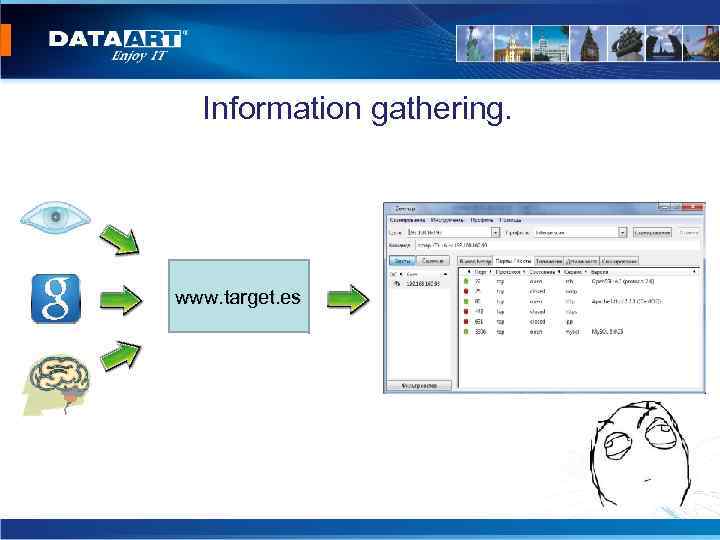
Information gathering. www. target. es
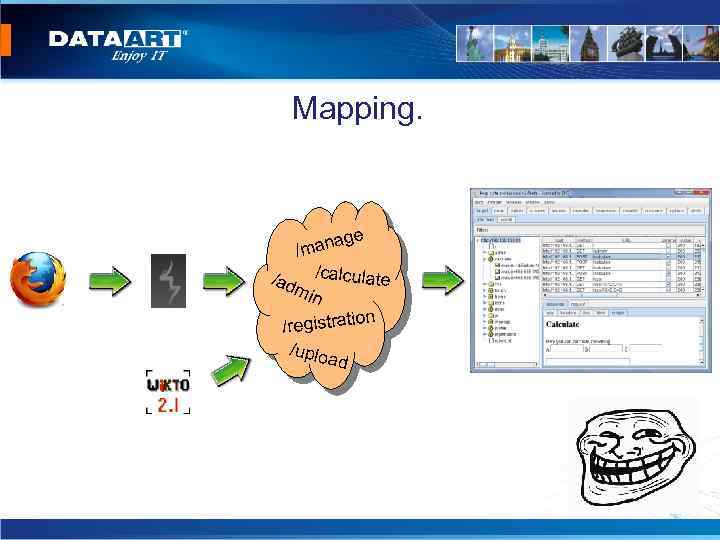
Mapping. age man / /ad /calculate min n /registratio /uplo ad
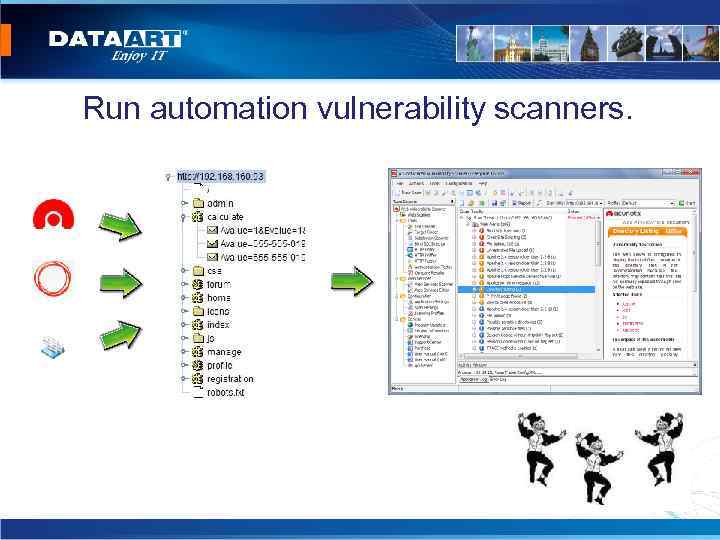
Run automation vulnerability scanners.
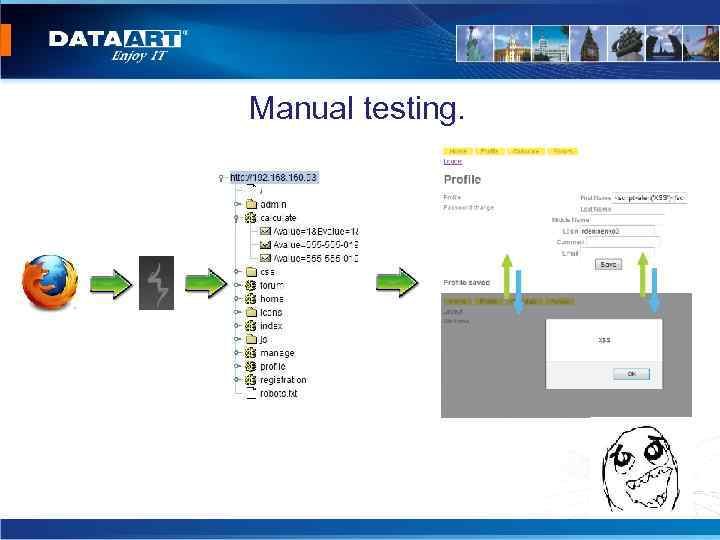
Manual testing.
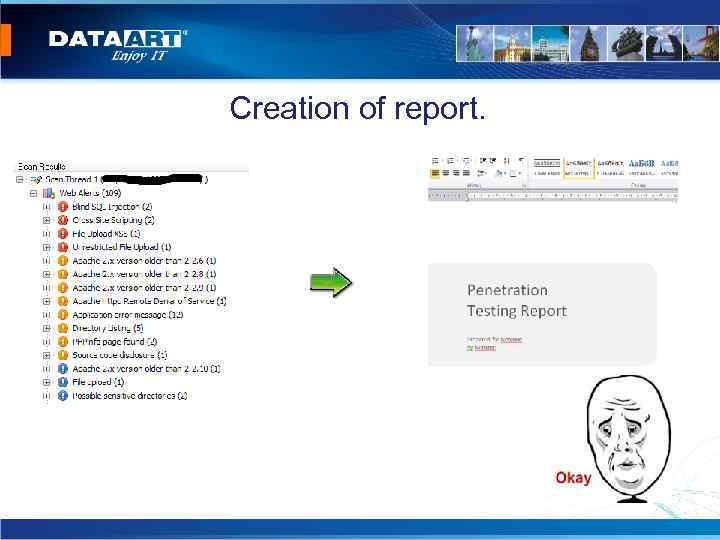
Creation of report.

Common vulnerabilities.
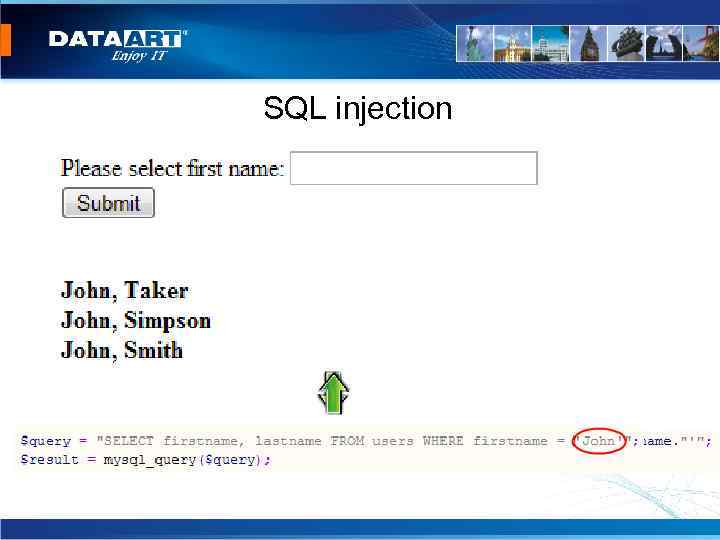
SQL injection
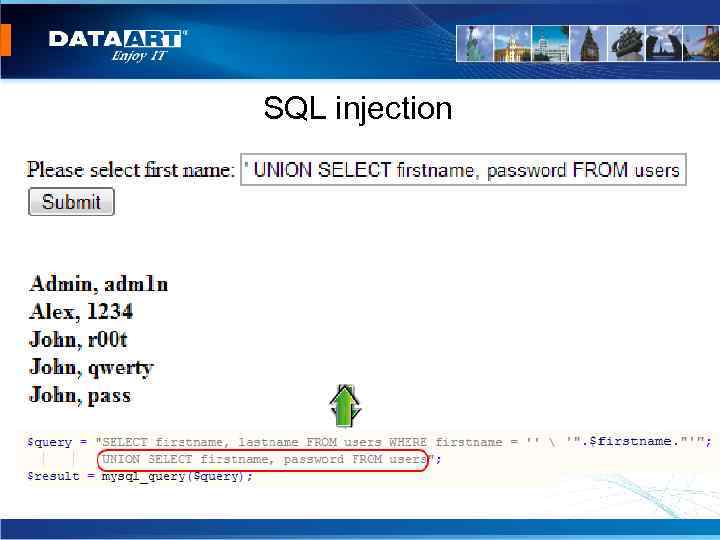
SQL injection
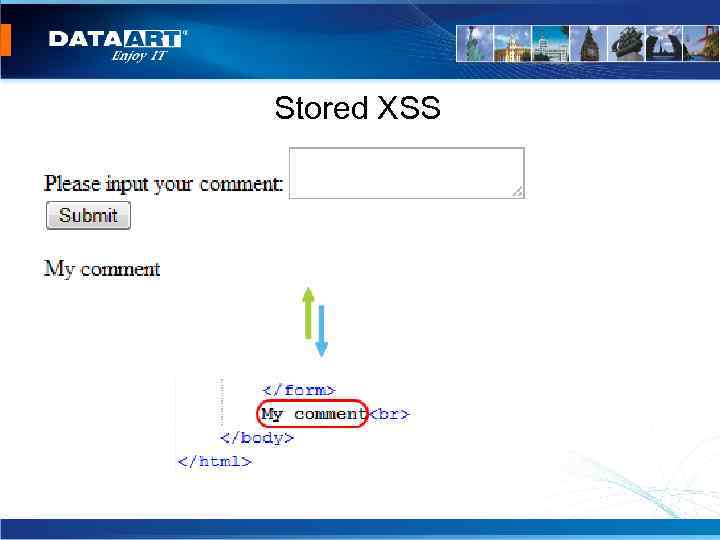
Stored XSS
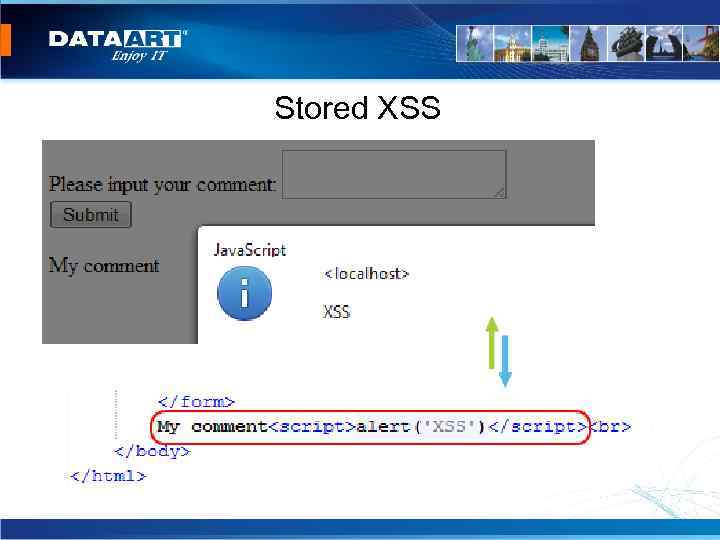
Stored XSS
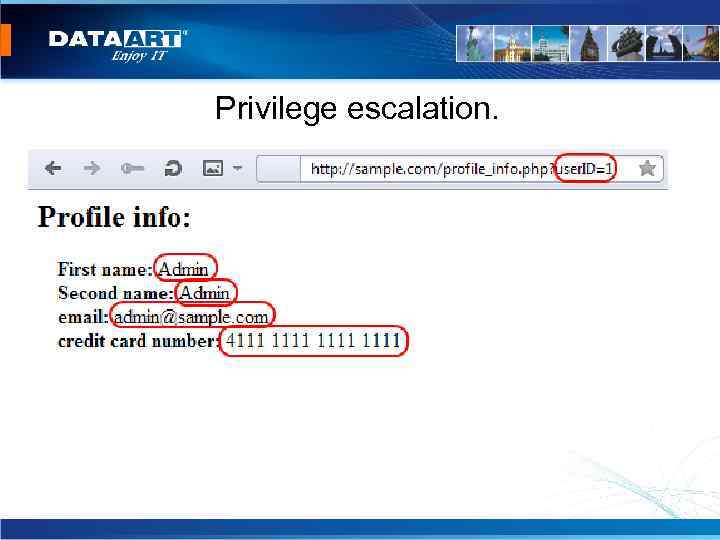
Privilege escalation.
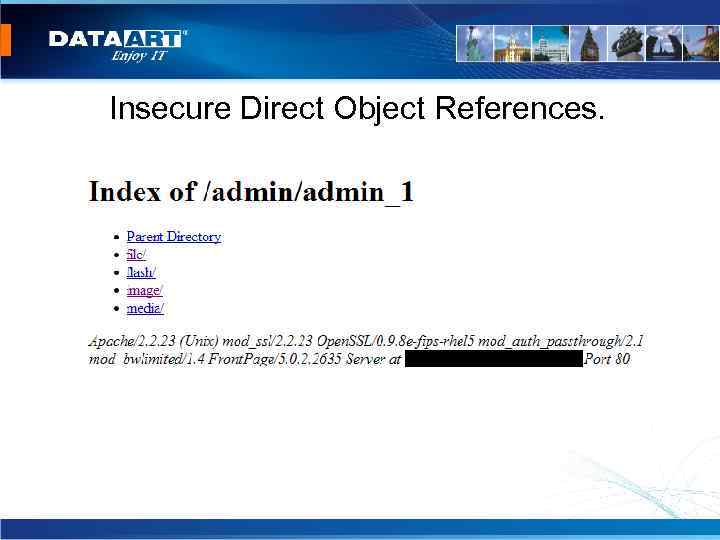
Insecure Direct Object References.
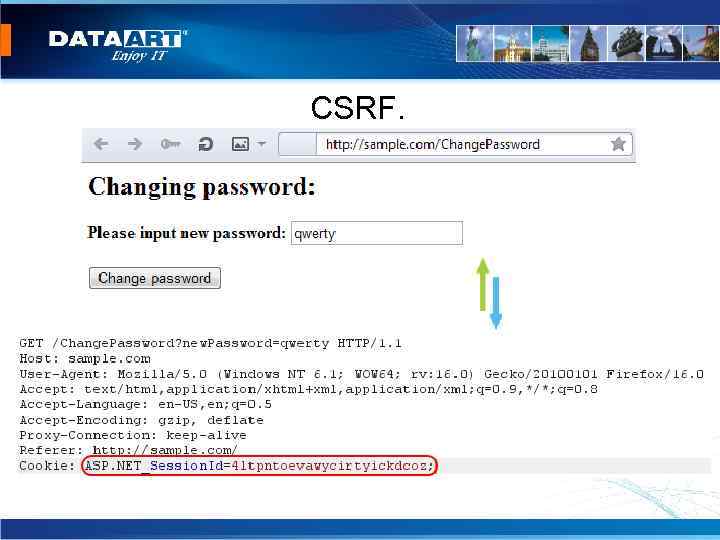
CSRF.
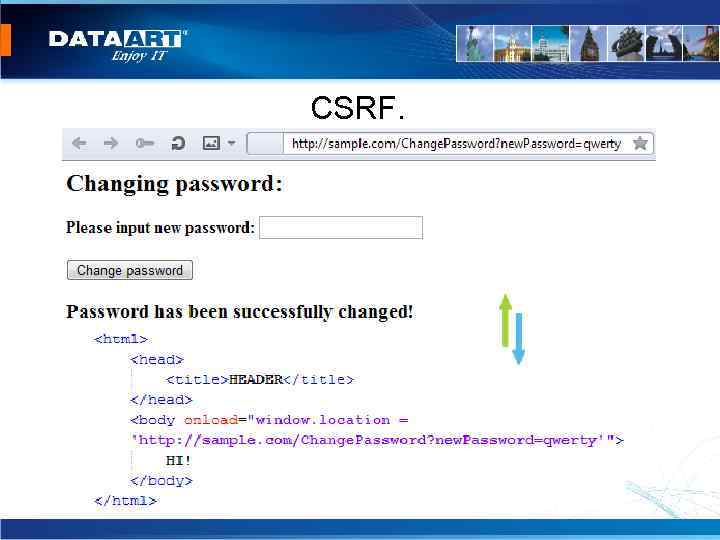
CSRF.

Necessary toolkit. • Gathering tools. – nmap. – nikto • Automation vulnerabilities scanners. – – Acunetix Nexuss Web. Inspect w 3 af • Sniffing tools. – Wireshark – Fiddler. • Manual testing tools. – Burp. Suite – Sqlmap

Penetration testing of the test site. . .
Contacts: : Roman. Denisenko@dataart. com : roman__denisenko
PenetrationTesting_QAreer.pptx