bcc7297278c93bf03f3b434304f66349.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Peer Production & Peer Support at the Free Technology Academy Hanneke Potters Adriana Berlanga Lex Bijlsma CSERC 8 -9 April 2011 Heerlen, The Netherlands
Peer Production & Peer Support at the Free Technology Academy Hanneke Potters Adriana Berlanga Lex Bijlsma CSERC 8 -9 April 2011 Heerlen, The Netherlands
 Preparation Ph. D research Hanneke Potters Which Design Principles are suitable to scaffold ‘Peer Production’ for Learning Networks? in order to share knowledge and experiences? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Preparation Ph. D research Hanneke Potters Which Design Principles are suitable to scaffold ‘Peer Production’ for Learning Networks? in order to share knowledge and experiences? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Introduction Ø What is Peer Production? Ø Success story of Peer Production in Free Software en Open Source Software developers Ø Can we transfer the success of the Free en Open Source Software communities towards an Educational Context? Open Educational Communities? Ø Learning Networks and two design principles Ø A case: The Free Technology Academy Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Introduction Ø What is Peer Production? Ø Success story of Peer Production in Free Software en Open Source Software developers Ø Can we transfer the success of the Free en Open Source Software communities towards an Educational Context? Open Educational Communities? Ø Learning Networks and two design principles Ø A case: The Free Technology Academy Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (1) What is Peer Production? • Y. Benkler a new model of economic production in which the creative energy of large numbers of people is coordinated (usually with the aid of the Internet) into large, meaningful projects mostly without traditional hierarchical organization (and often, but not always, without or with decentralized financial compensation). Often used interchangeably with the term social production (source: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Commons-based_peer_production) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(1) What is Peer Production? • Y. Benkler a new model of economic production in which the creative energy of large numbers of people is coordinated (usually with the aid of the Internet) into large, meaningful projects mostly without traditional hierarchical organization (and often, but not always, without or with decentralized financial compensation). Often used interchangeably with the term social production (source: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Commons-based_peer_production) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Economic models: • Intra firm model • Market-base model • Peer Production model no transaction costs and management costs no monetary motives all products are available for all participants • Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Economic models: • Intra firm model • Market-base model • Peer Production model no transaction costs and management costs no monetary motives all products are available for all participants • Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (3) Examples of Peer Production Linux, a computer operating system Slashdot, a news and announcements website Wikipedia, an online encyclopedia Distributed Proofreaders, which proof reads public domain etexts for publication on Project Gutenberg SETI@home, a project which searches for extra terrestrial life Kuro 5 hin, a discussion site for technology and culture Clickworkers, a citizen science program Sourceforge, a software development organization Rep. Rap Project, a project to create an open-source self-copying 3 D printer. Pirate Bay, a shared index of bittorrents (under legal scrutiny in Sweden as of February 2009) Open. Street. Map, a free map of the world Appropedia, a project for development of Open Source Appropriate Technology Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(3) Examples of Peer Production Linux, a computer operating system Slashdot, a news and announcements website Wikipedia, an online encyclopedia Distributed Proofreaders, which proof reads public domain etexts for publication on Project Gutenberg SETI@home, a project which searches for extra terrestrial life Kuro 5 hin, a discussion site for technology and culture Clickworkers, a citizen science program Sourceforge, a software development organization Rep. Rap Project, a project to create an open-source self-copying 3 D printer. Pirate Bay, a shared index of bittorrents (under legal scrutiny in Sweden as of February 2009) Open. Street. Map, a free map of the world Appropedia, a project for development of Open Source Appropriate Technology Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Peer Production at Free Software ( FS) Open Source Software (OSS) communities Characteristics of FS and OSS communities Ø Ø Ø Ø Free availability of source code Distributed ownership and control Continual influx of new people High tolerance for mistakes by the community members Selection based on elegance Cost are relatively low and the benefits of het members also Entry cost for a community and the transition costs are very low Not hierarchically organized Van Wendel et al ( 2003) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Peer Production at Free Software ( FS) Open Source Software (OSS) communities Characteristics of FS and OSS communities Ø Ø Ø Ø Free availability of source code Distributed ownership and control Continual influx of new people High tolerance for mistakes by the community members Selection based on elegance Cost are relatively low and the benefits of het members also Entry cost for a community and the transition costs are very low Not hierarchically organized Van Wendel et al ( 2003) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (1) Motivation factors of the FS and OSS community members Ø Ø Ø Art and beauty Reputation Ego boosting Job as vocation Share Identity and beliefs system User driven innovation factor Steven Weber (2004), the success of Open Source Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(1) Motivation factors of the FS and OSS community members Ø Ø Ø Art and beauty Reputation Ego boosting Job as vocation Share Identity and beliefs system User driven innovation factor Steven Weber (2004), the success of Open Source Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (2) Motivation factors of the FS and OSS community members Ø Having fun- flow Ø User need Ø Improving programming skills Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(2) Motivation factors of the FS and OSS community members Ø Having fun- flow Ø User need Ø Improving programming skills Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (1) Peer Production in a Educational Context Can we transfer the success of the Free en Open Software communities towards Learning Networks in a Educational context? With use of Open Educational Resources? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(1) Peer Production in a Educational Context Can we transfer the success of the Free en Open Software communities towards Learning Networks in a Educational context? With use of Open Educational Resources? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Open Educational Resources are… Hylén(2005) defines OER initiatives as 1) open courseware and content; 2) open software tools (e. g. learning management systems); 3) open material for e-learning capacity building of faculty staff; 4) repositories of learning objects (LO); and 5) free educational courses Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Open Educational Resources are… Hylén(2005) defines OER initiatives as 1) open courseware and content; 2) open software tools (e. g. learning management systems); 3) open material for e-learning capacity building of faculty staff; 4) repositories of learning objects (LO); and 5) free educational courses Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Open Educational Resources are according a report of UNESCO at 2002 also. . • • Visiting lecturers and experts Twinning arrangements, providing for international exchanges of students and academic staff Imported courseware in a variety of media Externally developed sponsored programmes Inter-institutional programmes developed collaboratively Publications Information resources of the Internet Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Open Educational Resources are according a report of UNESCO at 2002 also. . • • Visiting lecturers and experts Twinning arrangements, providing for international exchanges of students and academic staff Imported courseware in a variety of media Externally developed sponsored programmes Inter-institutional programmes developed collaboratively Publications Information resources of the Internet Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (2) Examples of OERs in an Educational Context Open. Er Wikiwijs Ed. Share Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(2) Examples of OERs in an Educational Context Open. Er Wikiwijs Ed. Share Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
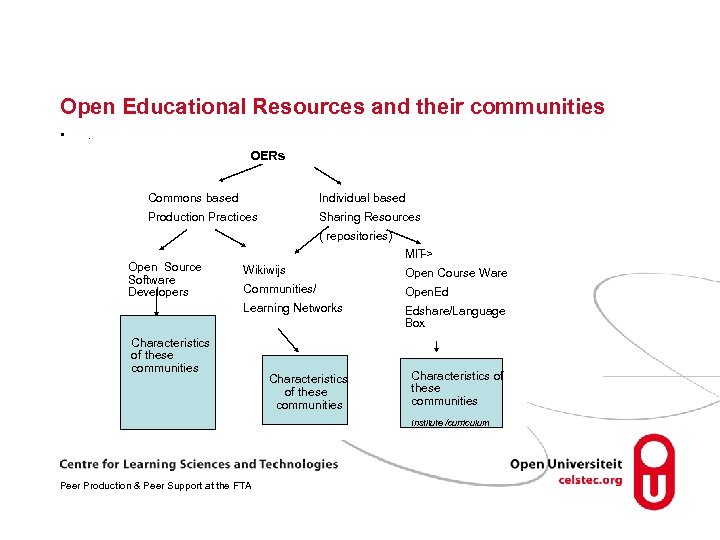 Open Educational Resources and their communities • . OERs Commons based Individual based Production Practices Sharing Resources ( repositories) Open Source Software Developers MIT -> Wikiwijs Open Course Ware Communities/ Open. Ed Learning Networks Edshare/Language Box Characteristics of these communities Institute /curriculum Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Open Educational Resources and their communities • . OERs Commons based Individual based Production Practices Sharing Resources ( repositories) Open Source Software Developers MIT -> Wikiwijs Open Course Ware Communities/ Open. Ed Learning Networks Edshare/Language Box Characteristics of these communities Institute /curriculum Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
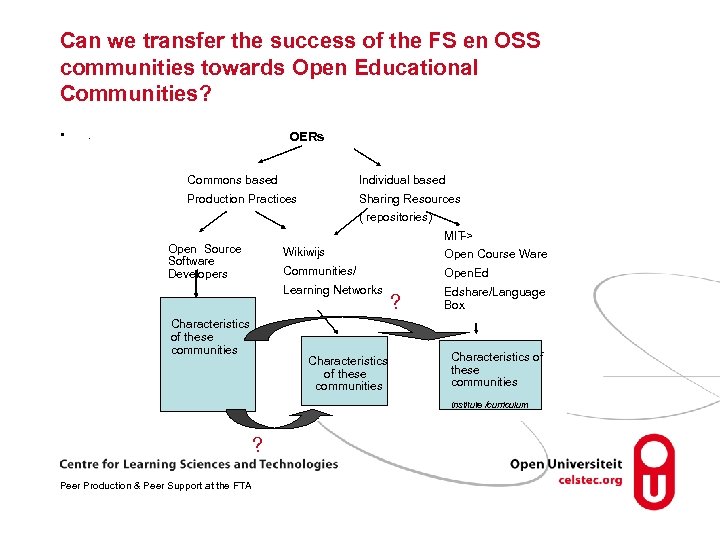 Can we transfer the success of the FS en OSS communities towards Open Educational Communities? • . OERs Commons based Individual based Production Practices Sharing Resources ( repositories) MIT -> Open Source Software Developers Wikiwijs Open Course Ware Communities/ Open. Ed Learning Networks Characteristics of these communities ? Edshare/Language Box Characteristics of these communities Institute /curriculum ? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Can we transfer the success of the FS en OSS communities towards Open Educational Communities? • . OERs Commons based Individual based Production Practices Sharing Resources ( repositories) MIT -> Open Source Software Developers Wikiwijs Open Course Ware Communities/ Open. Ed Learning Networks Characteristics of these communities ? Edshare/Language Box Characteristics of these communities Institute /curriculum ? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Expectations Designers and Users of Repositories are different Most of the OERs examples are using repositories of Learning objects (LO) Identified problems at Institutions: • The users often already use an Virtual Learning environment, but het OER is often not integrated with the VLE • The users found it difficult tagging their material. • The users don’t felt ownership: remote -> local • Quality issue • Personal copyright -> institution copyright Source: Margaryan and Littlejohn 2008 & Davis et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Expectations Designers and Users of Repositories are different Most of the OERs examples are using repositories of Learning objects (LO) Identified problems at Institutions: • The users often already use an Virtual Learning environment, but het OER is often not integrated with the VLE • The users found it difficult tagging their material. • The users don’t felt ownership: remote -> local • Quality issue • Personal copyright -> institution copyright Source: Margaryan and Littlejohn 2008 & Davis et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Peer Production and OERs Once a VLE with OERs is designed, that does not mean that the users are also willing to use it and come to activities like working together , exchange and make new material. A Learning Network should be formed to bridge this gap. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Peer Production and OERs Once a VLE with OERs is designed, that does not mean that the users are also willing to use it and come to activities like working together , exchange and make new material. A Learning Network should be formed to bridge this gap. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (1) Learning Networks A Learning Network is an online social network that is specifically designed to support learning. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(1) Learning Networks A Learning Network is an online social network that is specifically designed to support learning. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (2) Learning Networks are specific to a certain domain of knowledge and consists of: Ø Learning Network participants: people with the intent to learn and the willingness to share their knowledge in the specified domain. Ø Resources: collections of learning activities that are created and shared in order to exchange knowledge and experience. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(2) Learning Networks are specific to a certain domain of knowledge and consists of: Ø Learning Network participants: people with the intent to learn and the willingness to share their knowledge in the specified domain. Ø Resources: collections of learning activities that are created and shared in order to exchange knowledge and experience. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 (3) Learning Networks Various factors influence the success of a Learning Network: Ø Ø Ø Strength and weakness of the ties of the participants Trust and Trustworthiness relations among participants Motivation of the participants Continuity of the network Ease or difficulty to make connections inside the network Heterogeneity of the participants. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
(3) Learning Networks Various factors influence the success of a Learning Network: Ø Ø Ø Strength and weakness of the ties of the participants Trust and Trustworthiness relations among participants Motivation of the participants Continuity of the network Ease or difficulty to make connections inside the network Heterogeneity of the participants. Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Two Design Principles 1. Ad Hoc –Transient Communities model Source: Van Rosmalen et al. 2006 2. TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness Rusman et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Two Design Principles 1. Ad Hoc –Transient Communities model Source: Van Rosmalen et al. 2006 2. TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness Rusman et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 1. Ad Hoc -Transient Communities model (1) 1. The model invokes peer learners to give support when a learner has a content-related question Tutor competency rating system Content competency portfolio Tutor availability agenda Tutor eligibility- similarity competence level 2. Temporary a Transient community (wiki) has been formed until the question has been answered Source: Van Rosmalen et al. 2006 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
1. Ad Hoc -Transient Communities model (1) 1. The model invokes peer learners to give support when a learner has a content-related question Tutor competency rating system Content competency portfolio Tutor availability agenda Tutor eligibility- similarity competence level 2. Temporary a Transient community (wiki) has been formed until the question has been answered Source: Van Rosmalen et al. 2006 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
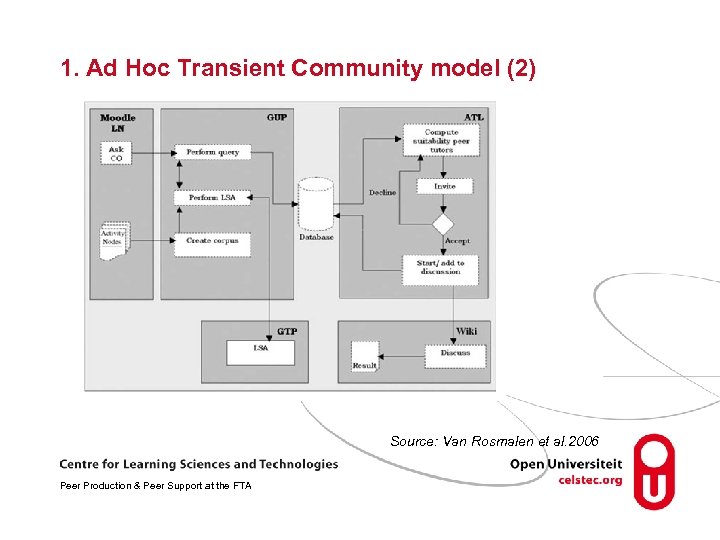 1. Ad Hoc Transient Community model (2) Source: Van Rosmalen et al. 2006 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
1. Ad Hoc Transient Community model (2) Source: Van Rosmalen et al. 2006 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness • Interpersonal trust: a positive psycho-logical state (cognitive and emotional) of a trustor (person who can trust/distrust) towards a trustee (person who can be trusted/distrusted) comprising of trustor’s positive expectations of the intentions and future behaviour of the trustee, leading to a willingness to display trusting behaviour in a specific context. Source: Rusman et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness • Interpersonal trust: a positive psycho-logical state (cognitive and emotional) of a trustor (person who can trust/distrust) towards a trustee (person who can be trusted/distrusted) comprising of trustor’s positive expectations of the intentions and future behaviour of the trustee, leading to a willingness to display trusting behaviour in a specific context. Source: Rusman et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
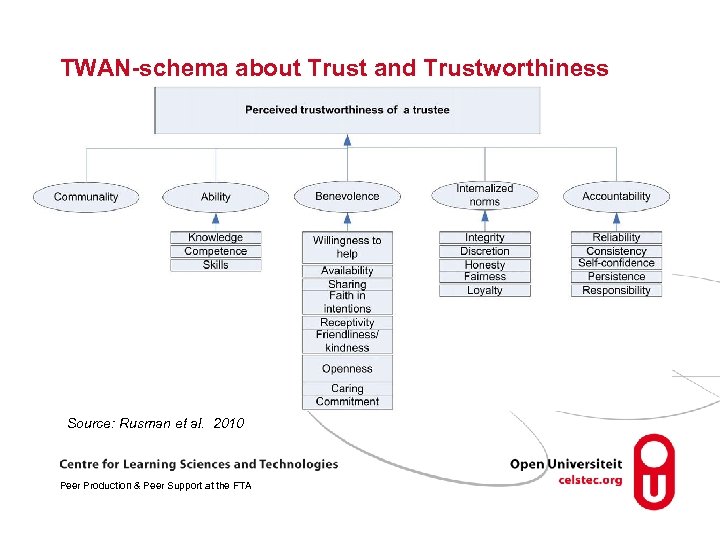 TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness Source: Rusman et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness Source: Rusman et al. 2010 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
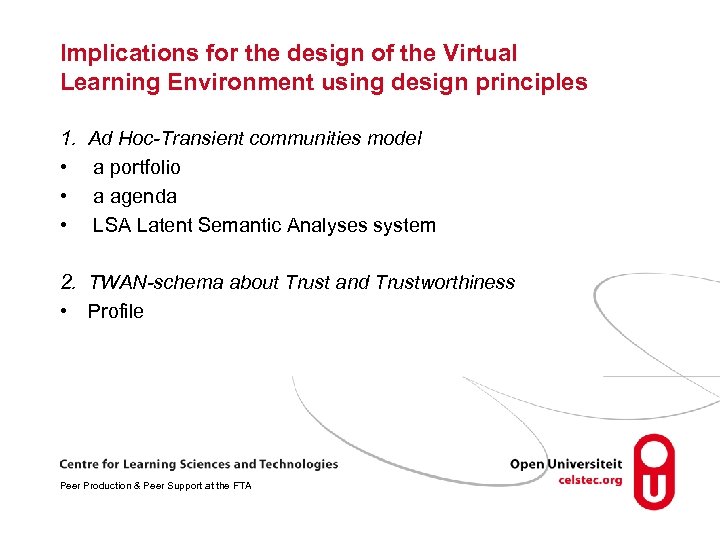 Implications for the design of the Virtual Learning Environment using design principles 1. • • • Ad Hoc-Transient communities model a portfolio a agenda LSA Latent Semantic Analyses system 2. TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness • Profile Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Implications for the design of the Virtual Learning Environment using design principles 1. • • • Ad Hoc-Transient communities model a portfolio a agenda LSA Latent Semantic Analyses system 2. TWAN-schema about Trust and Trustworthiness • Profile Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Free Technology Academy ( FTA) a case-study The Free Technology Academy is a programme of masterlevel courses on Free Software and Open Standards that publishes all of its materials as Open Educational Resources open courseware and content Inter-institutional programmes developed collaboratively Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Free Technology Academy ( FTA) a case-study The Free Technology Academy is a programme of masterlevel courses on Free Software and Open Standards that publishes all of its materials as Open Educational Resources open courseware and content Inter-institutional programmes developed collaboratively Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
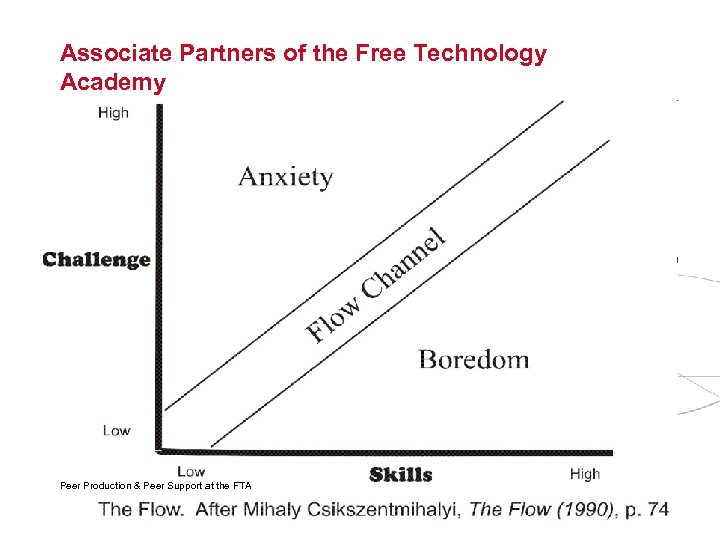 Associate Partners of the Free Technology Academy Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Associate Partners of the Free Technology Academy Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 The Educational Methodology • • • The Virtual Campus (Virtual Learning Environment) built in Moodle is for everybody open ( only registration). Course modules are Free downloadable Virtual classrooms are only accessible by students whom are enrolled in the courses ( and pay for services like support by tutors and peers) Everybody who wants to start a project about FS and OSS or initiative is welcome to do so ECTS –accreditation Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
The Educational Methodology • • • The Virtual Campus (Virtual Learning Environment) built in Moodle is for everybody open ( only registration). Course modules are Free downloadable Virtual classrooms are only accessible by students whom are enrolled in the courses ( and pay for services like support by tutors and peers) Everybody who wants to start a project about FS and OSS or initiative is welcome to do so ECTS –accreditation Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
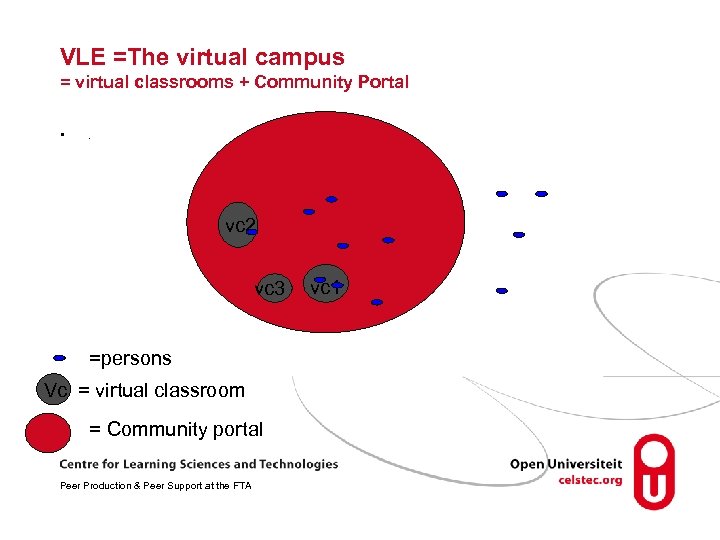 VLE =The virtual campus = virtual classrooms + Community Portal • . vc 2 vc 3 =persons Vc = virtual classroom = Community portal Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA vc 1
VLE =The virtual campus = virtual classrooms + Community Portal • . vc 2 vc 3 =persons Vc = virtual classroom = Community portal Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA vc 1
 The Virtual Classroom (only for enrolled participants) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
The Virtual Classroom (only for enrolled participants) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 The Community Portal (open for everybody) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
The Community Portal (open for everybody) Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
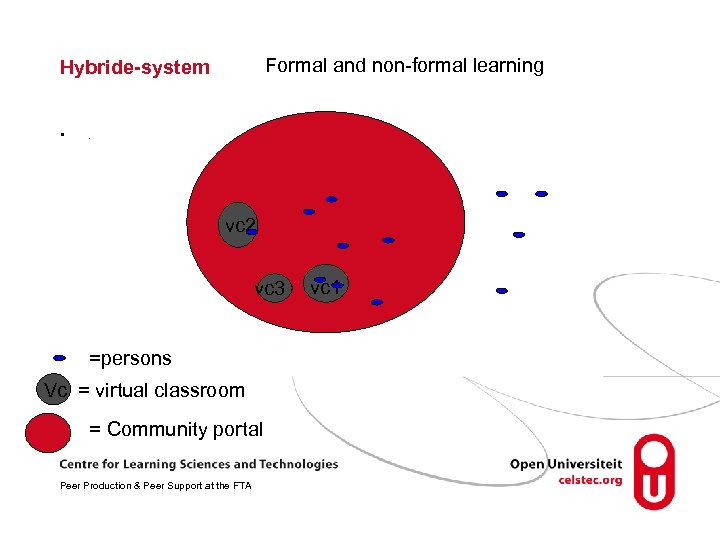 Formal and non-formal learning Hybride-system • . vc 2 vc 3 =persons Vc = virtual classroom = Community portal Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA vc 1
Formal and non-formal learning Hybride-system • . vc 2 vc 3 =persons Vc = virtual classroom = Community portal Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA vc 1
 Research Questions: a case study: Free Technology Academy 1. How can the production of course materials be economically sustainable? 2. How can we scaffold Peer Production in the virtual campus? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Research Questions: a case study: Free Technology Academy 1. How can the production of course materials be economically sustainable? 2. How can we scaffold Peer Production in the virtual campus? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 Peers are… 1. Everybody who is in the virtual campus 1. Via an annotation tool- feedback on course modules 2. Associate Partners of FTA -> building a Master Programme 3. All persons whom are involved in the virtual campus, volunteers, paid students, partners user generated content Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Peers are… 1. Everybody who is in the virtual campus 1. Via an annotation tool- feedback on course modules 2. Associate Partners of FTA -> building a Master Programme 3. All persons whom are involved in the virtual campus, volunteers, paid students, partners user generated content Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
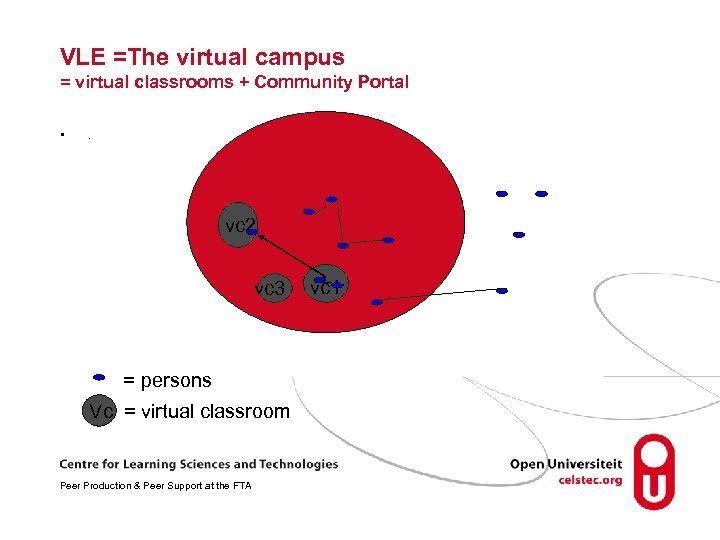 VLE =The virtual campus = virtual classrooms + Community Portal • . vc 2 vc 3 = persons Vc = virtual classroom Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA vc 1
VLE =The virtual campus = virtual classrooms + Community Portal • . vc 2 vc 3 = persons Vc = virtual classroom Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA vc 1
 Questions !? Formal and informal learning is that a problem for peer production? Which Design Principles are suitable to scaffold ‘Peer Production’ for Learning Networks? Can you give more examples or suggestions of design principles and tools? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
Questions !? Formal and informal learning is that a problem for peer production? Which Design Principles are suitable to scaffold ‘Peer Production’ for Learning Networks? Can you give more examples or suggestions of design principles and tools? Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION Hanneke Potters E-mail: pottershanneke@gmail. com Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION Hanneke Potters E-mail: pottershanneke@gmail. com Peer Production & Peer Support at the FTA


