Pediatrics_oncology.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Pediatrics oncology Dr. OWIS KHATER
Pediatrics oncology Dr. OWIS KHATER
 n n n The most common neonatal tumor is neuroblastoma The most common infant tumor is neuroblastoma The most common childhood tumor is acute lymphoblasic leukaemia (ALL) The most common solid tumor in childhood is brain tumors The 2 nd most common tumor in childhood is brain tumors
n n n The most common neonatal tumor is neuroblastoma The most common infant tumor is neuroblastoma The most common childhood tumor is acute lymphoblasic leukaemia (ALL) The most common solid tumor in childhood is brain tumors The 2 nd most common tumor in childhood is brain tumors
 Leukaemia n n ALL accounts for about 80% of leukaemia in children The remainder are acute myeloid leukaemia(AML) , acute non lymphocytic leukaemia (ANLL) Chronic myeloid leukaaemia is rare (CML) Presentation with. . malaise , pallor , infection , abnormal bruising , hepatosplenomegaly , lymphadenopathy and bone pain
Leukaemia n n ALL accounts for about 80% of leukaemia in children The remainder are acute myeloid leukaemia(AML) , acute non lymphocytic leukaemia (ANLL) Chronic myeloid leukaaemia is rare (CML) Presentation with. . malaise , pallor , infection , abnormal bruising , hepatosplenomegaly , lymphadenopathy and bone pain
 n n n n CBC. . Not all patient have abnormal blood count. . (anemia , thrombocytopenia and circulating blast cells Bone marrow biopsy is essential to confirm the diagnosis The most common type is T-cell type The worst prognosis with B-cell and pre B-cell type Relapse occur in CNS , testis and bone marrow DIC occur with AML M 3 type Gingival hypertrophy with AML M 4 type AML M 7 is the worst prognosis except with Down syndrome >>>GOOD PROGNOSIS
n n n n CBC. . Not all patient have abnormal blood count. . (anemia , thrombocytopenia and circulating blast cells Bone marrow biopsy is essential to confirm the diagnosis The most common type is T-cell type The worst prognosis with B-cell and pre B-cell type Relapse occur in CNS , testis and bone marrow DIC occur with AML M 3 type Gingival hypertrophy with AML M 4 type AML M 7 is the worst prognosis except with Down syndrome >>>GOOD PROGNOSIS
 poor Prognosis in ALL n n n n Age <1 year or > 10 Male Black WBC count at presentation >50000 B-cell or pre B-cell Slow response to initial therapy Hypodiploidy Philadelphia chromosom n n n n Translocation (8, 14) or (1, 19) Hepatosplenomegaly Lymphadenopathy CNS involvement Increase LDH Decrease steroid receptors and Ig PAS stain is negative
poor Prognosis in ALL n n n n Age <1 year or > 10 Male Black WBC count at presentation >50000 B-cell or pre B-cell Slow response to initial therapy Hypodiploidy Philadelphia chromosom n n n n Translocation (8, 14) or (1, 19) Hepatosplenomegaly Lymphadenopathy CNS involvement Increase LDH Decrease steroid receptors and Ig PAS stain is negative
 Predisposing disease to leukaemia Syndromes. . n Down (in the 1 st three years of life AML is more common and with better prognosis ) n Turner n Kleinfilter n neurofibromatosis type 1
Predisposing disease to leukaemia Syndromes. . n Down (in the 1 st three years of life AML is more common and with better prognosis ) n Turner n Kleinfilter n neurofibromatosis type 1
 Non Hodgkin lymphoma n More common in male than female n Age of presentation 7 -10 years n Extranodal n Types ( T , B , Large and follicular cells n T cell type more common in the chest and it is the most common type n B cell type is the worst type and present in the abdominal cavity
Non Hodgkin lymphoma n More common in male than female n Age of presentation 7 -10 years n Extranodal n Types ( T , B , Large and follicular cells n T cell type more common in the chest and it is the most common type n B cell type is the worst type and present in the abdominal cavity
 Hogkin lymphoma n More common in adult n Good prognosis n Types. 1. lymphocytic predominant 2. lymphocytic depleted (the worst) 3. mixed cellularity 4. nodular sclerosis (the most common)
Hogkin lymphoma n More common in adult n Good prognosis n Types. 1. lymphocytic predominant 2. lymphocytic depleted (the worst) 3. mixed cellularity 4. nodular sclerosis (the most common)
 Wilm tumor n n n n Age of onset. . 3 years or more Male affected as female 80% presented as abdominal mass Hematuria in 20% and hypertension and polycythemia Usually unilateral and does not cross the midline Surgery is the main treatment then chemo and radiotherapy Chromosom affected 11
Wilm tumor n n n n Age of onset. . 3 years or more Male affected as female 80% presented as abdominal mass Hematuria in 20% and hypertension and polycythemia Usually unilateral and does not cross the midline Surgery is the main treatment then chemo and radiotherapy Chromosom affected 11
 Diseases associated with Wilms n Beakwith-weidman syndrome n WAGAR n Neurofibromatosis n Urogenital anomalies n Denys-Drash syndrome n May associated with aniridia n Calcification egg-shell like n Metastasis into the lungs
Diseases associated with Wilms n Beakwith-weidman syndrome n WAGAR n Neurofibromatosis n Urogenital anomalies n Denys-Drash syndrome n May associated with aniridia n Calcification egg-shell like n Metastasis into the lungs
 Neuroblastoma n Age of presentation <2 years n Male affected more than female n Most common presentation is abdominal mass which cross the midline n Eye manifestation. . heterochromia , opsiclonus , racoon eyes and proptosis n Blue berry muffin lesion n 1 st line of treatment is chemotherapy
Neuroblastoma n Age of presentation <2 years n Male affected more than female n Most common presentation is abdominal mass which cross the midline n Eye manifestation. . heterochromia , opsiclonus , racoon eyes and proptosis n Blue berry muffin lesion n 1 st line of treatment is chemotherapy
 Disease associated with neuroblastoma n n n n Hirschsprung disease Fetal alcohol syndrome Beckwith-weidman syndrome Good prognosis…. (less than 1 year of age , thoracic or mediastinal ) Poor prognosis…(age >2 year and abdominal mass ) Calcification. . stippled Metastasis to the bone
Disease associated with neuroblastoma n n n n Hirschsprung disease Fetal alcohol syndrome Beckwith-weidman syndrome Good prognosis…. (less than 1 year of age , thoracic or mediastinal ) Poor prognosis…(age >2 year and abdominal mass ) Calcification. . stippled Metastasis to the bone
 Ewing sarcoma n n n n n Involved diaphysis More in the femur and pelvis>painful mass with soft tissue extension More common in male Osteolytic lesions (osteoclast activity ) White more than black Age. . adolescent and young children High ESR , high LDH, lymphopenia>poor prognosis Onion like lesion in the x-ray Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the main treatment Metastasis to the lungs
Ewing sarcoma n n n n n Involved diaphysis More in the femur and pelvis>painful mass with soft tissue extension More common in male Osteolytic lesions (osteoclast activity ) White more than black Age. . adolescent and young children High ESR , high LDH, lymphopenia>poor prognosis Onion like lesion in the x-ray Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the main treatment Metastasis to the lungs
 Osteogenic sarcoma n n n n n Involved epiphysis and metaphysis Male affected more than female Age of presentation. . adolescent Around the shoulder and the knees Presented with painful mass after trauma and pathological fracture Osteobalstic activity Sun-burst appearance in x-ray Chemotherapy is the main treatment ( no radiotherapy ) Normal ESR and high ALP Poor prognosis( age <10 y, more than 15 cm , high LDH, symptoms <2 months and humerus or axial skeleton )
Osteogenic sarcoma n n n n n Involved epiphysis and metaphysis Male affected more than female Age of presentation. . adolescent Around the shoulder and the knees Presented with painful mass after trauma and pathological fracture Osteobalstic activity Sun-burst appearance in x-ray Chemotherapy is the main treatment ( no radiotherapy ) Normal ESR and high ALP Poor prognosis( age <10 y, more than 15 cm , high LDH, symptoms <2 months and humerus or axial skeleton )
 Rhabdomyosarcoma n n n The most common soft tissue tumor Most common at skeletal muscles The most important prognostic factor is the extension of the disease at time of diagnosis Age. . 2 -6 years and at adolescent Types. . 1. alveolar >>most serious 2. embryonal>>most common Treatment. . surgery , chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Rhabdomyosarcoma n n n The most common soft tissue tumor Most common at skeletal muscles The most important prognostic factor is the extension of the disease at time of diagnosis Age. . 2 -6 years and at adolescent Types. . 1. alveolar >>most serious 2. embryonal>>most common Treatment. . surgery , chemotherapy and radiotherapy
 Retinoblastoma 60% unilateral and non-hereditary 30% bilateral and non-hereditary 15% bilateral and hereditary Bilateral 40% <1 year , 20%>1 year Hereditary is bilateral and multifocal Non hereditary is unilateral and unifocal Never do biopsy(orbital US , CT or MRI) Presentation. . strabismus , leukochorea , hyphema , orbital inflammation ) n It is painless unless glaucoma is present n Treatment. . enucleation for unilateral and chemotherapy for bilateral tumor …prognosis is good n n n n
Retinoblastoma 60% unilateral and non-hereditary 30% bilateral and non-hereditary 15% bilateral and hereditary Bilateral 40% <1 year , 20%>1 year Hereditary is bilateral and multifocal Non hereditary is unilateral and unifocal Never do biopsy(orbital US , CT or MRI) Presentation. . strabismus , leukochorea , hyphema , orbital inflammation ) n It is painless unless glaucoma is present n Treatment. . enucleation for unilateral and chemotherapy for bilateral tumor …prognosis is good n n n n
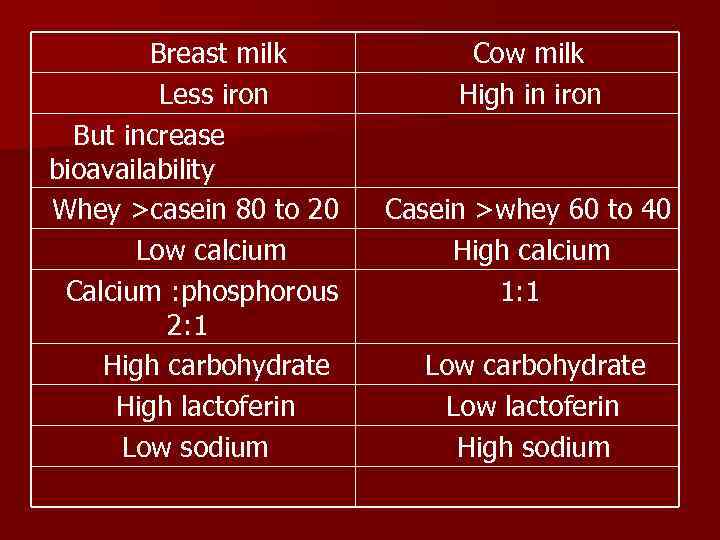 Breast milk Less iron But increase bioavailability Whey >casein 80 to 20 Low calcium Calcium : phosphorous 2: 1 High carbohydrate High lactoferin Low sodium Cow milk High in iron Casein >whey 60 to 40 High calcium 1: 1 Low carbohydrate Low lactoferin High sodium
Breast milk Less iron But increase bioavailability Whey >casein 80 to 20 Low calcium Calcium : phosphorous 2: 1 High carbohydrate High lactoferin Low sodium Cow milk High in iron Casein >whey 60 to 40 High calcium 1: 1 Low carbohydrate Low lactoferin High sodium
 Contraindication of breast feeding n HIV n Active TB n Active glomerulonephritis n Active psychosis n CMV Infection n Hepatitis B( until the infant vaccinated and given Ig )
Contraindication of breast feeding n HIV n Active TB n Active glomerulonephritis n Active psychosis n CMV Infection n Hepatitis B( until the infant vaccinated and given Ig )


