Pediatric Visual Diagnosis Ilana Greenstone MD Division of








































20162-pediatric_visual_diagnosis.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 Pediatric Visual Diagnosis Ilana Greenstone MD Division of Emergency Medicine Montreal Children’s Hospital McGill University Health Center
Pediatric Visual Diagnosis Ilana Greenstone MD Division of Emergency Medicine Montreal Children’s Hospital McGill University Health Center
 Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
 Terminology Macules, Papules, Nodules Patches and Plaques Vesicles, Pustules, Bullae Colour Erosions – when bullae rupture Ulcerations and excoriations
Terminology Macules, Papules, Nodules Patches and Plaques Vesicles, Pustules, Bullae Colour Erosions – when bullae rupture Ulcerations and excoriations




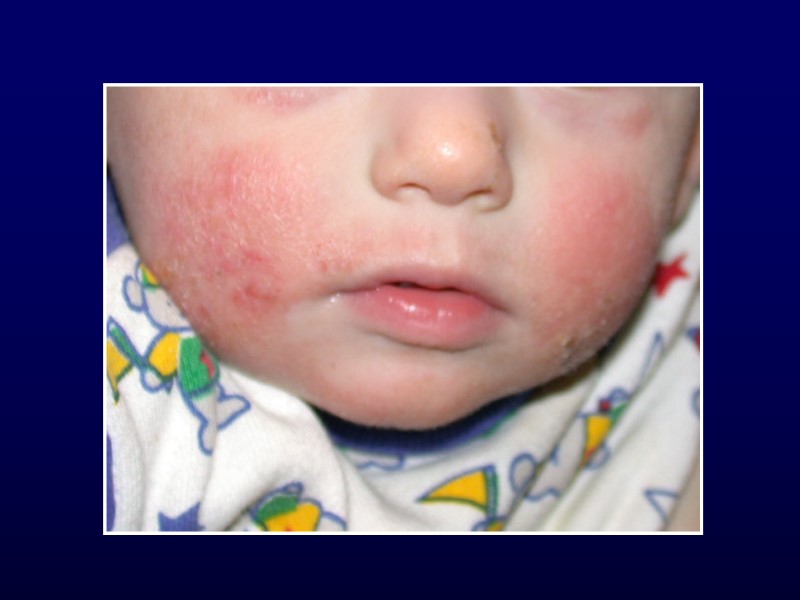
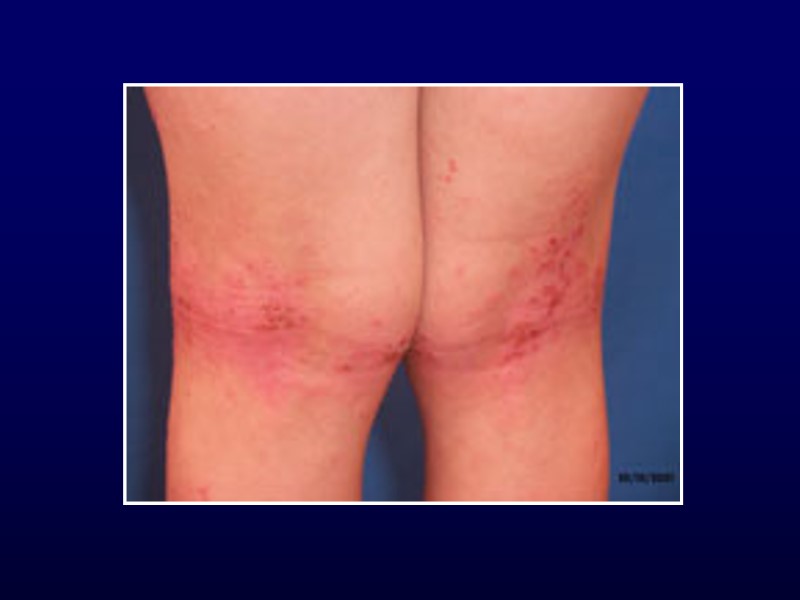
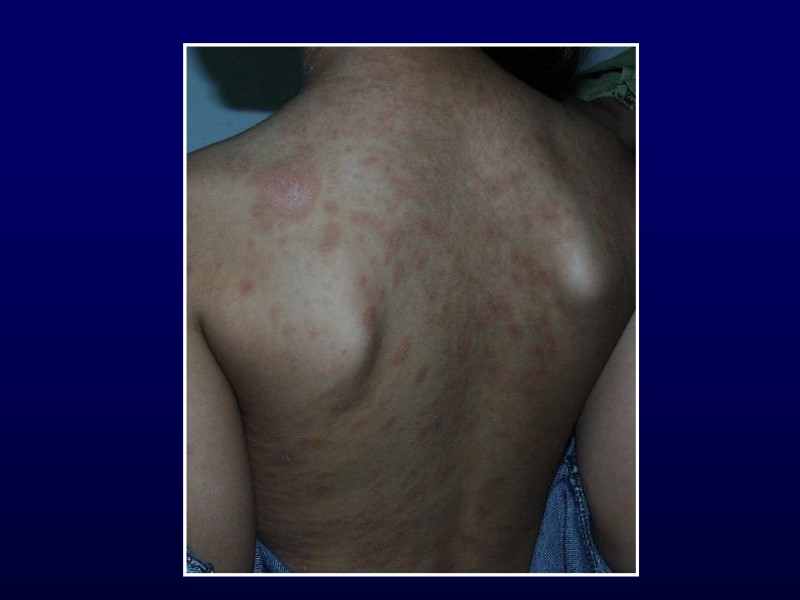
 Atopic Dermatitis 3-5% of children 6 mo to 10 yr Described in 1935 Ill-defined, red, pruritic, papules/plaques Diaper area spared Acute: erythema, scaly, vesicles, crusts Chronic: scaly, lichenified, pigment changes
Atopic Dermatitis 3-5% of children 6 mo to 10 yr Described in 1935 Ill-defined, red, pruritic, papules/plaques Diaper area spared Acute: erythema, scaly, vesicles, crusts Chronic: scaly, lichenified, pigment changes

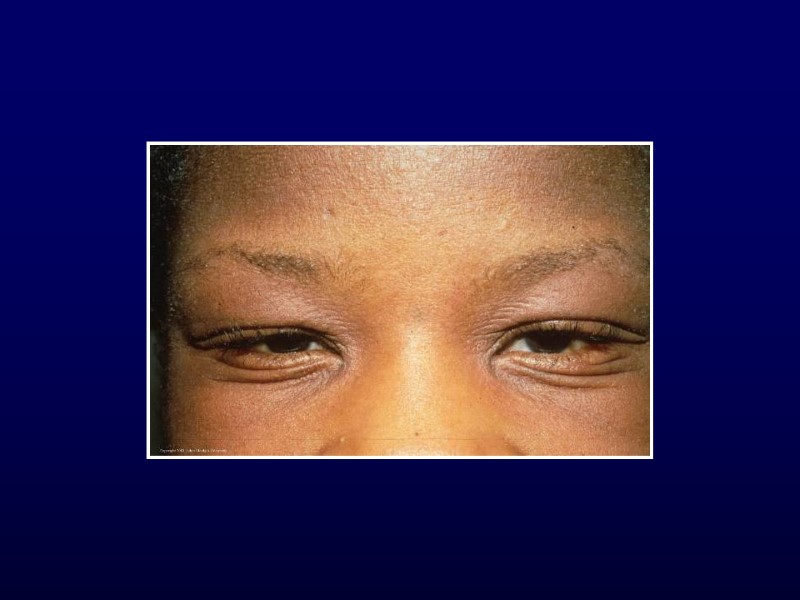
 Atopic Dermatitis Hints to diagnosis Generalized dry skin Accentuation of skin markings on palms and soles Dennie-Morgan lines Fissures at base of earlobe Allergic history
Atopic Dermatitis Hints to diagnosis Generalized dry skin Accentuation of skin markings on palms and soles Dennie-Morgan lines Fissures at base of earlobe Allergic history




 Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Moisturize Baths only Anti-histamine Topical steroids to red and rough areas Prevex HC Desacort Immune modulators
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Moisturize Baths only Anti-histamine Topical steroids to red and rough areas Prevex HC Desacort Immune modulators

 Superinfected Eczema Red and crusty Usually S. aureus Cephalexin 40 mg/kg/day divided TID for 10 days More potent topical steroid Topical antibiotic – Fucidin Anti-histamine Refer to Dermatology
Superinfected Eczema Red and crusty Usually S. aureus Cephalexin 40 mg/kg/day divided TID for 10 days More potent topical steroid Topical antibiotic – Fucidin Anti-histamine Refer to Dermatology




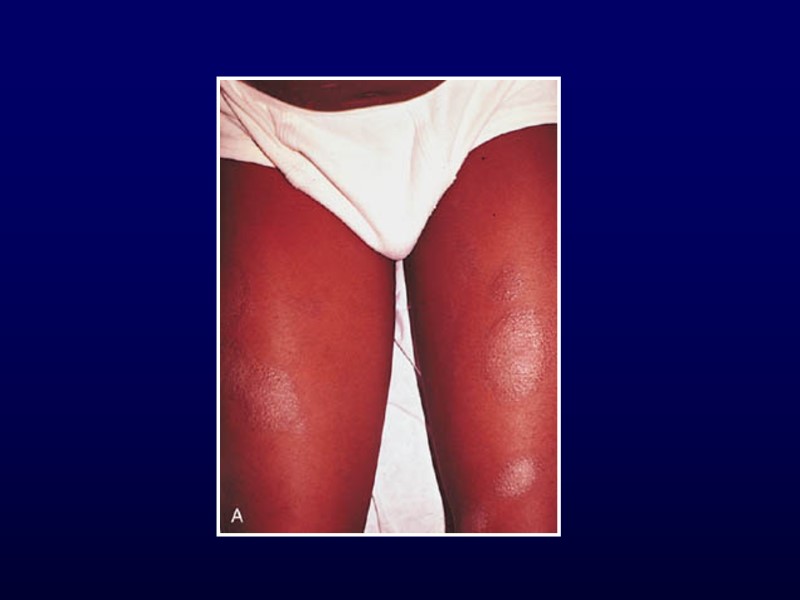
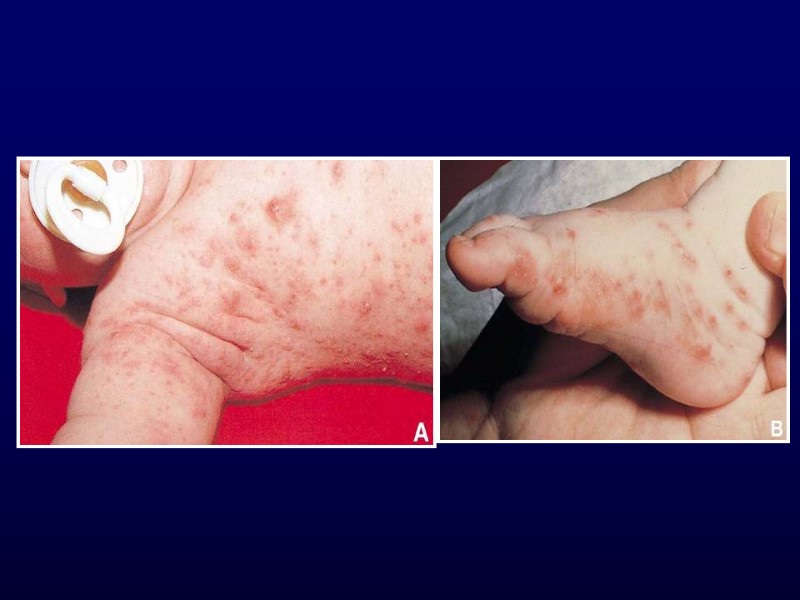
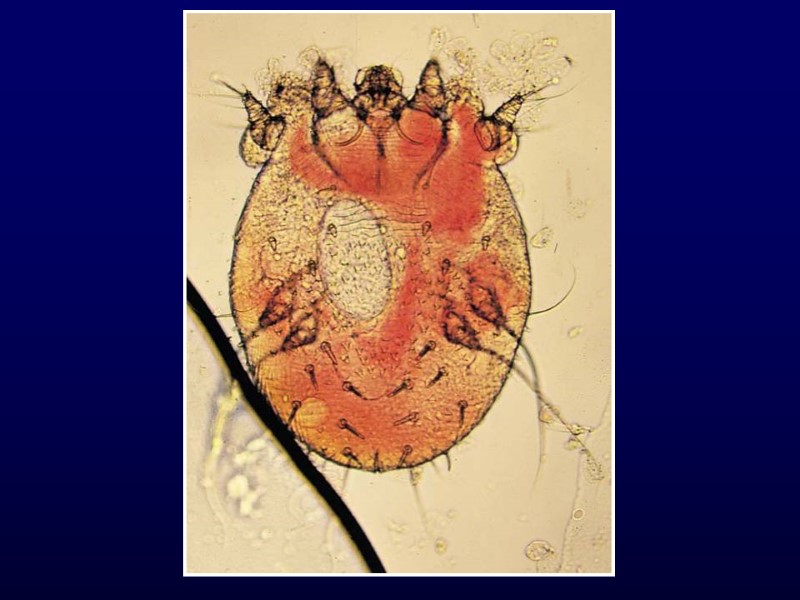
 Scabies Intense pruritus Diffuse, papular rash Between fingers, flexor aspects of wrists, anterior axillary folds, waist, navel May be vesicular in children < 2 years Head, neck, palms, soles Hypersensitivity reaction to protein of parasite
Scabies Intense pruritus Diffuse, papular rash Between fingers, flexor aspects of wrists, anterior axillary folds, waist, navel May be vesicular in children < 2 years Head, neck, palms, soles Hypersensitivity reaction to protein of parasite
 Scabies Treatment 5% permethrin cream for infants, young children, pregnant and nursing mother Kwellada-P or Nix Cover entire body from neck down Include head and neck for infants Wash after 8-14 hours Can use Lindane for older children
Scabies Treatment 5% permethrin cream for infants, young children, pregnant and nursing mother Kwellada-P or Nix Cover entire body from neck down Include head and neck for infants Wash after 8-14 hours Can use Lindane for older children


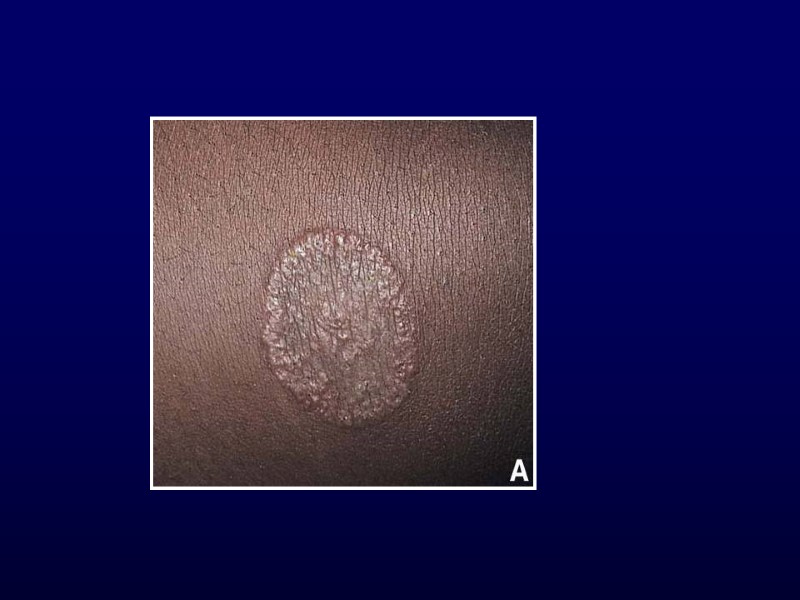
 Tinea corporis Ringworm Face, trunk or limbs Pruritic, circular, slightly erythematous Well-demarcated with scaly, vesicular or pustular border Id reaction Mistaken for atopic, seborrheic or contact dermatitis Treament: Terbinafine (Lamisil)
Tinea corporis Ringworm Face, trunk or limbs Pruritic, circular, slightly erythematous Well-demarcated with scaly, vesicular or pustular border Id reaction Mistaken for atopic, seborrheic or contact dermatitis Treament: Terbinafine (Lamisil)

 Pityriasis Rosea Begins with herald patch Large, isolated oval lesion with central clearing More lesions 5-10 days later Christmas tree distribution Treatment: anti-histamines
Pityriasis Rosea Begins with herald patch Large, isolated oval lesion with central clearing More lesions 5-10 days later Christmas tree distribution Treatment: anti-histamines
 Eczema Differential Diagnosis Atopic dermatitis Scabies Tinea corporis Pityriasis rosea If vesicular, check for HSV1, HSV2, VZV Beware of superinfection Think of immune deficiency if difficult to treat
Eczema Differential Diagnosis Atopic dermatitis Scabies Tinea corporis Pityriasis rosea If vesicular, check for HSV1, HSV2, VZV Beware of superinfection Think of immune deficiency if difficult to treat


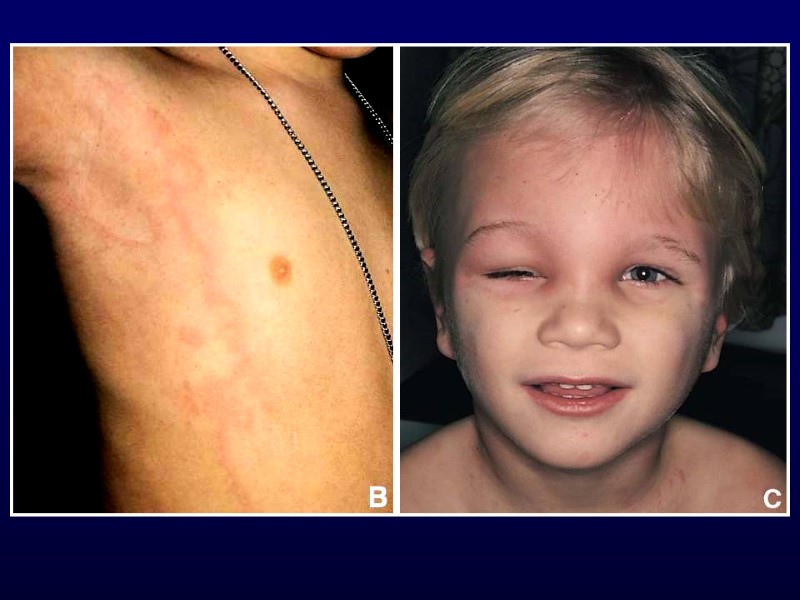
 Urticaria Transient, well-demarcated wheels Pruritic Part of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction May leave central clearing Triggers are numerous
Urticaria Transient, well-demarcated wheels Pruritic Part of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction May leave central clearing Triggers are numerous




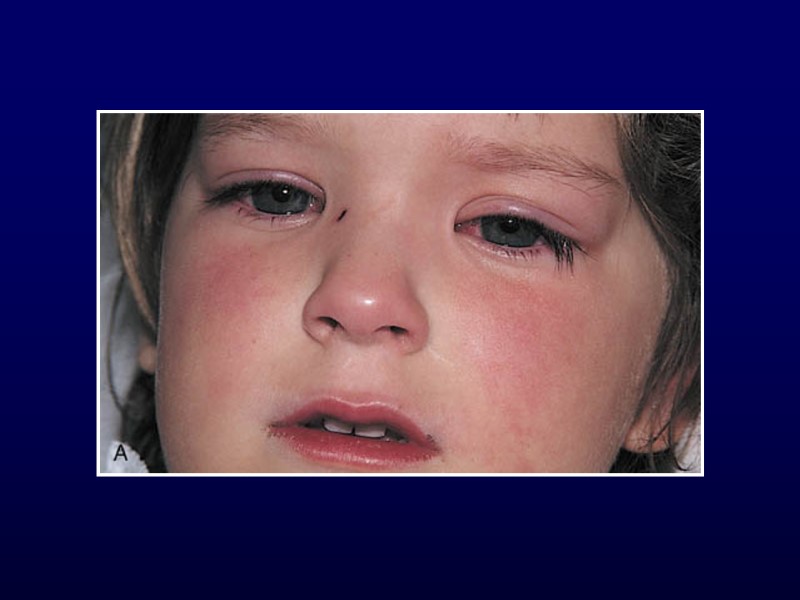
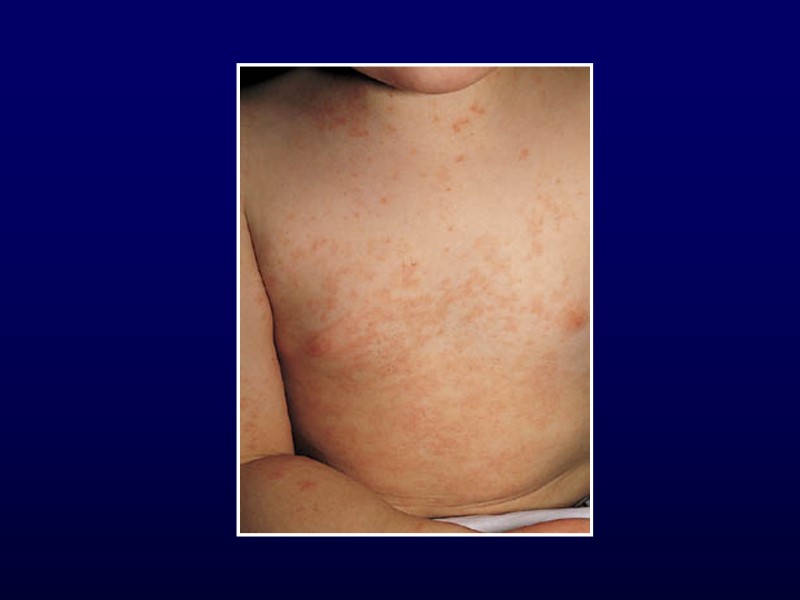
 Kawasaki Disease Diagnostic Criteria Fever for 5 or more days Presence of 4 of the following: Bilateral conjunctival injection Changes in the oropharyngeal mucous membranes Changes of the peripheral extremities Rash Cervical adenopathy Illness can’t be explained by other disease
Kawasaki Disease Diagnostic Criteria Fever for 5 or more days Presence of 4 of the following: Bilateral conjunctival injection Changes in the oropharyngeal mucous membranes Changes of the peripheral extremities Rash Cervical adenopathy Illness can’t be explained by other disease
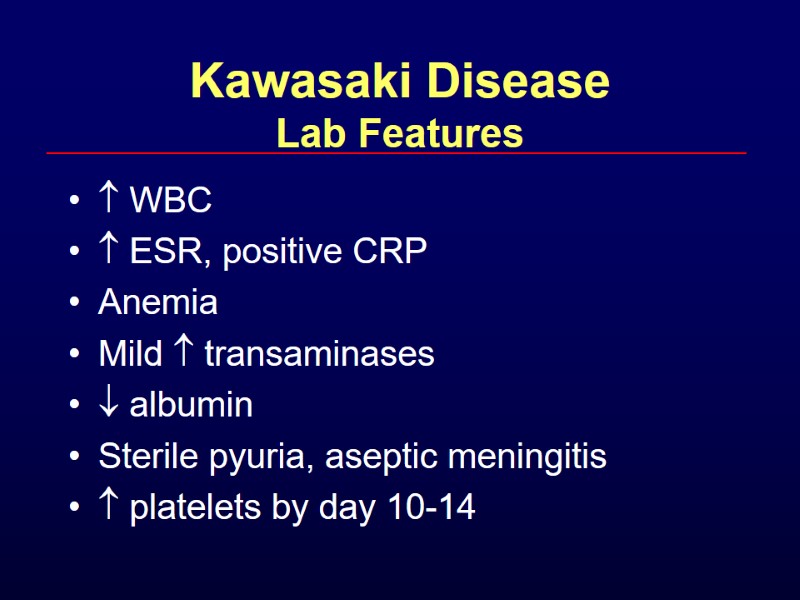
 Kawasaki Disease Lab Features WBC ESR, positive CRP Anemia Mild transaminases albumin Sterile pyuria, aseptic meningitis platelets by day 10-14
Kawasaki Disease Lab Features WBC ESR, positive CRP Anemia Mild transaminases albumin Sterile pyuria, aseptic meningitis platelets by day 10-14
 Kawasaki Disease Differential Diagnosis Measles Scarlet fever Drug reactions Viral exanthems Toxic Shock Syndrome Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Systemic Onset Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Staph scalded skin syndrome
Kawasaki Disease Differential Diagnosis Measles Scarlet fever Drug reactions Viral exanthems Toxic Shock Syndrome Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Systemic Onset Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Staph scalded skin syndrome
 Kawasaki Disease Difficulties with Diagnosis Clinical diagnosis No single test Diagnosis of exclusion Atypical KD Do not fulfill all criteria More common in < 1 year and > 8 years
Kawasaki Disease Difficulties with Diagnosis Clinical diagnosis No single test Diagnosis of exclusion Atypical KD Do not fulfill all criteria More common in < 1 year and > 8 years
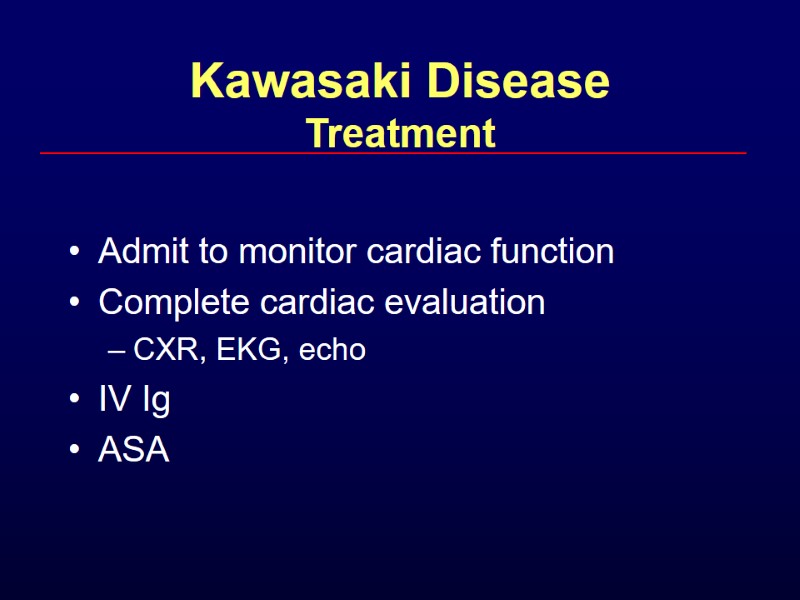
 Kawasaki Disease Treatment Admit to monitor cardiac function Complete cardiac evaluation CXR, EKG, echo IV Ig ASA
Kawasaki Disease Treatment Admit to monitor cardiac function Complete cardiac evaluation CXR, EKG, echo IV Ig ASA
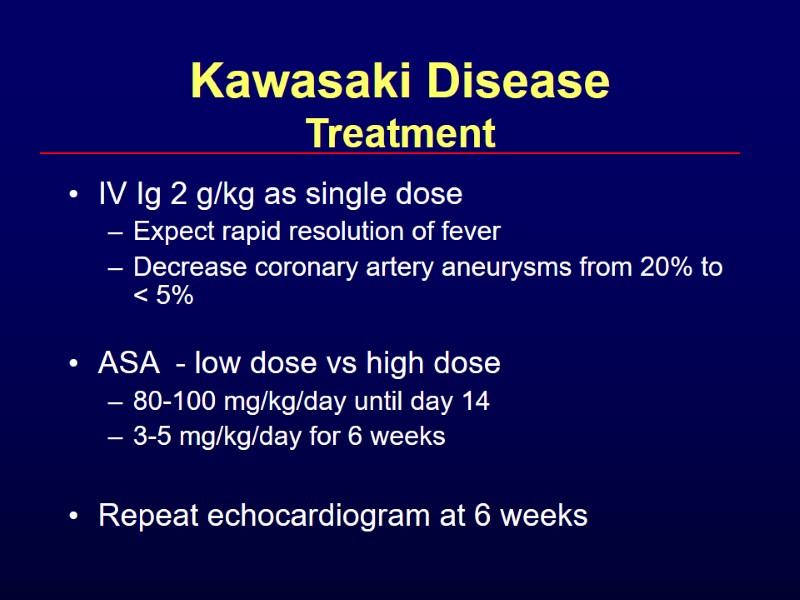
 Kawasaki Disease Treatment IV Ig 2 g/kg as single dose Expect rapid resolution of fever Decrease coronary artery aneurysms from 20% to < 5% ASA - low dose vs high dose 80-100 mg/kg/day until day 14 3-5 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks Repeat echocardiogram at 6 weeks
Kawasaki Disease Treatment IV Ig 2 g/kg as single dose Expect rapid resolution of fever Decrease coronary artery aneurysms from 20% to < 5% ASA - low dose vs high dose 80-100 mg/kg/day until day 14 3-5 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks Repeat echocardiogram at 6 weeks



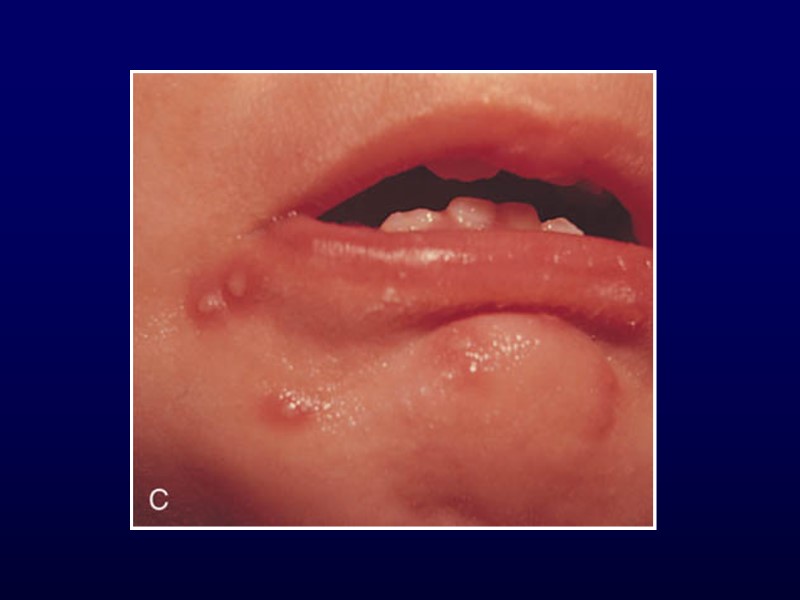
 Coxsackie Virus Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Painful, shallow, yellow ulcers surrounded by red halos Found on buccal mucosa, tongue, soft palate, uvula and anterior tonsillar pillars Oral lesions without the exanthem = herpangina Exanthem involves palmar, plantar and interdigital surfaces of the hands and feet +/- buttocks
Coxsackie Virus Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Painful, shallow, yellow ulcers surrounded by red halos Found on buccal mucosa, tongue, soft palate, uvula and anterior tonsillar pillars Oral lesions without the exanthem = herpangina Exanthem involves palmar, plantar and interdigital surfaces of the hands and feet +/- buttocks

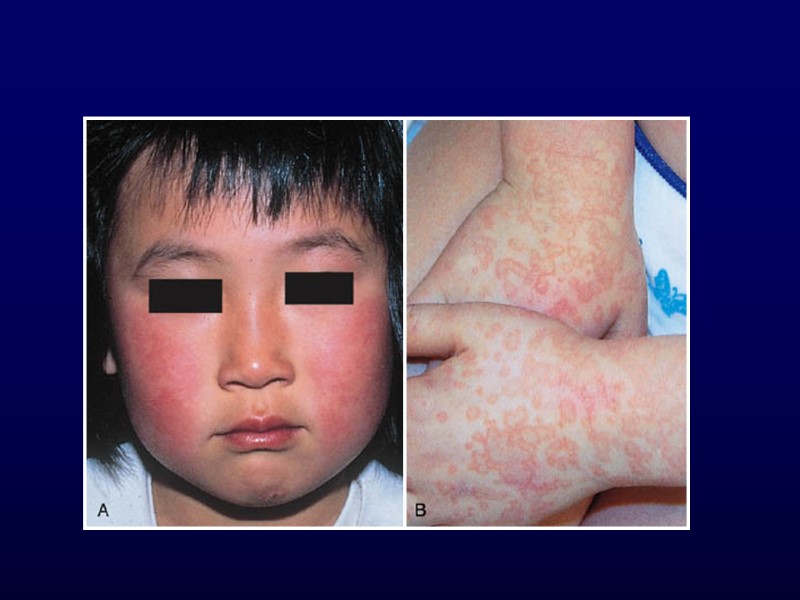
 Erythema Infectiosum Fifth Disease Parvovirus B19 Mostly preschool age Recognized by exanthem Contagious before rash Resolution between 3 and 7 days
Erythema Infectiosum Fifth Disease Parvovirus B19 Mostly preschool age Recognized by exanthem Contagious before rash Resolution between 3 and 7 days

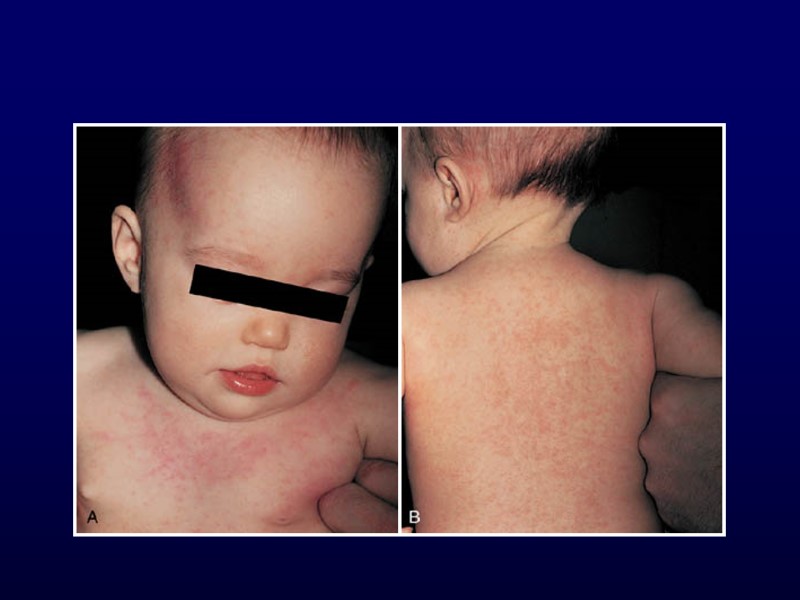
 Roseola 6 to 36 months Human herpesvirus 6 High fever without source and irritability for 3 days Rash develops as fever decreases
Roseola 6 to 36 months Human herpesvirus 6 High fever without source and irritability for 3 days Rash develops as fever decreases


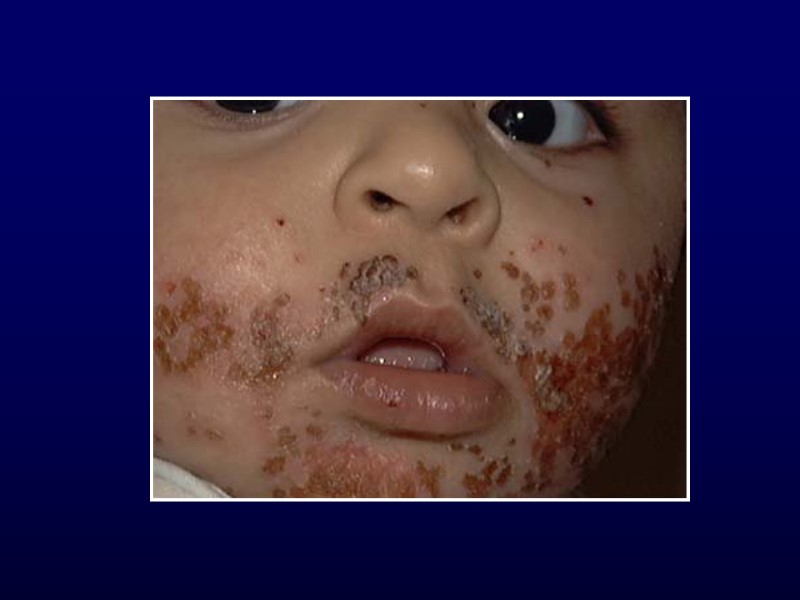
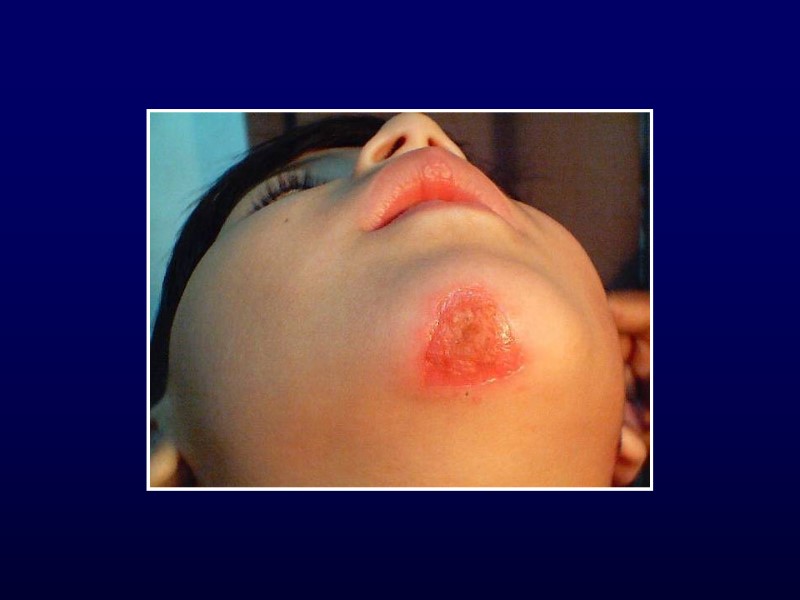
 Impetigo Mostly face, extremities, hands and neck Localized unless underlying skin disease Strep or Staph Honey-coloured crust Treatment: topical and systemic antibiotics
Impetigo Mostly face, extremities, hands and neck Localized unless underlying skin disease Strep or Staph Honey-coloured crust Treatment: topical and systemic antibiotics


 Herpes Simplex Gingivostomatitis most common 1º infection in children Fever, irritability, cervical nodes Small yellow ulcerations with red halos on mucous membranes Involvement more diffuse – easy to differentiate from herpangina and exudative tonsillitis Treatment: supportive
Herpes Simplex Gingivostomatitis most common 1º infection in children Fever, irritability, cervical nodes Small yellow ulcerations with red halos on mucous membranes Involvement more diffuse – easy to differentiate from herpangina and exudative tonsillitis Treatment: supportive

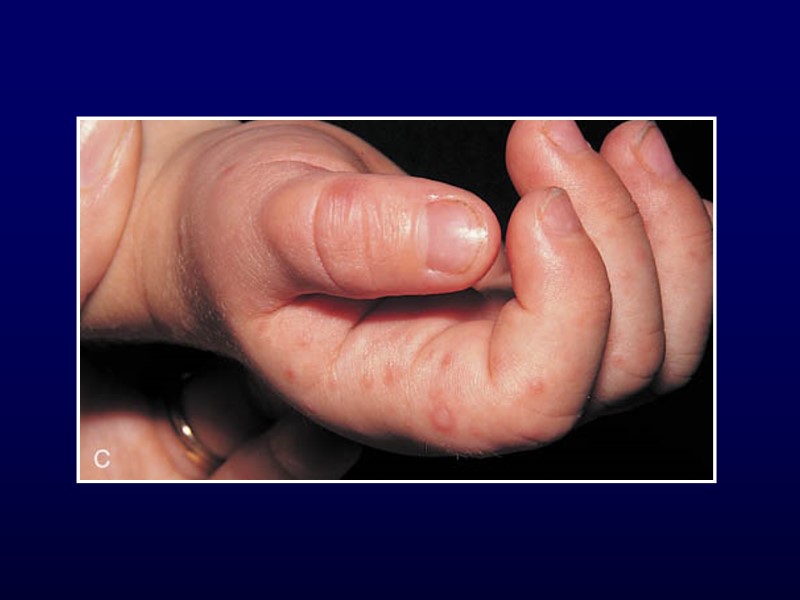
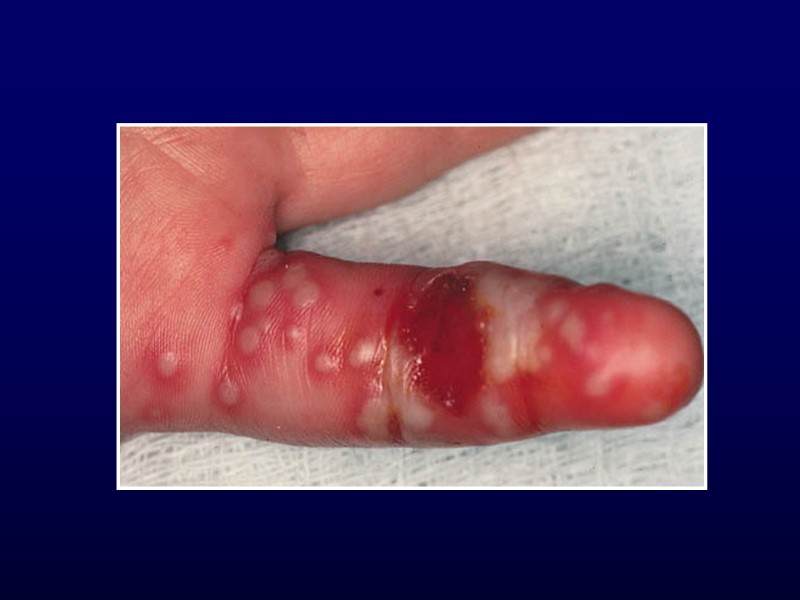
 Herpetic Whitlow Lesions on thumb usually 2° to autoinoculation Group, thick-walled vesicles on erythematous base Painful Tend to coalesce, ulcerate and then crust May require topical or oral acyclovir
Herpetic Whitlow Lesions on thumb usually 2° to autoinoculation Group, thick-walled vesicles on erythematous base Painful Tend to coalesce, ulcerate and then crust May require topical or oral acyclovir



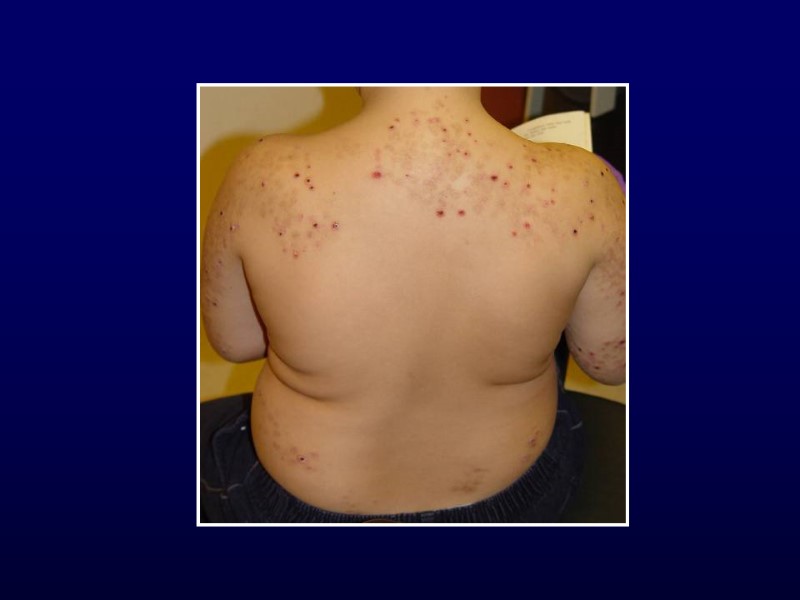
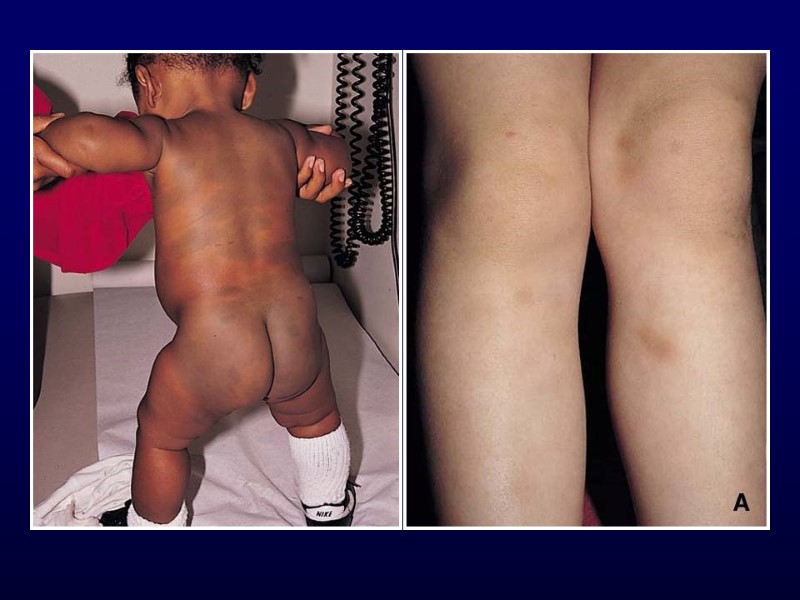
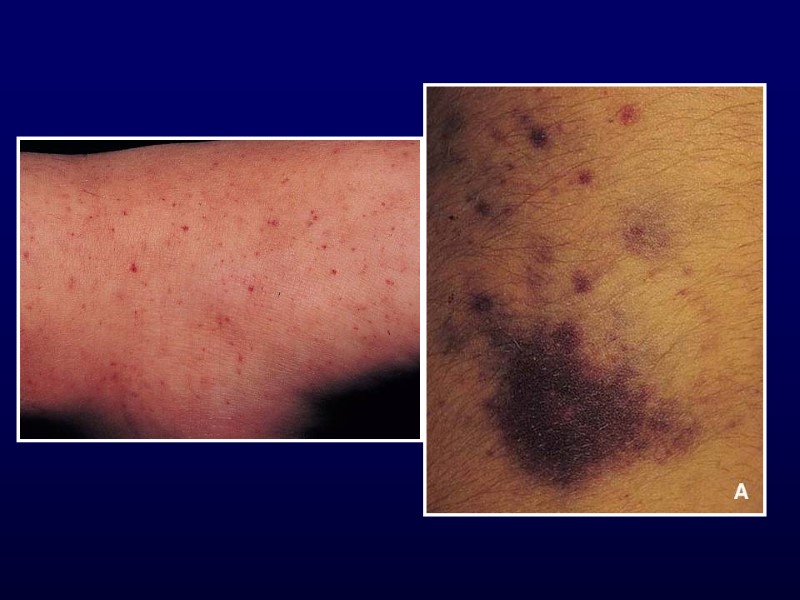
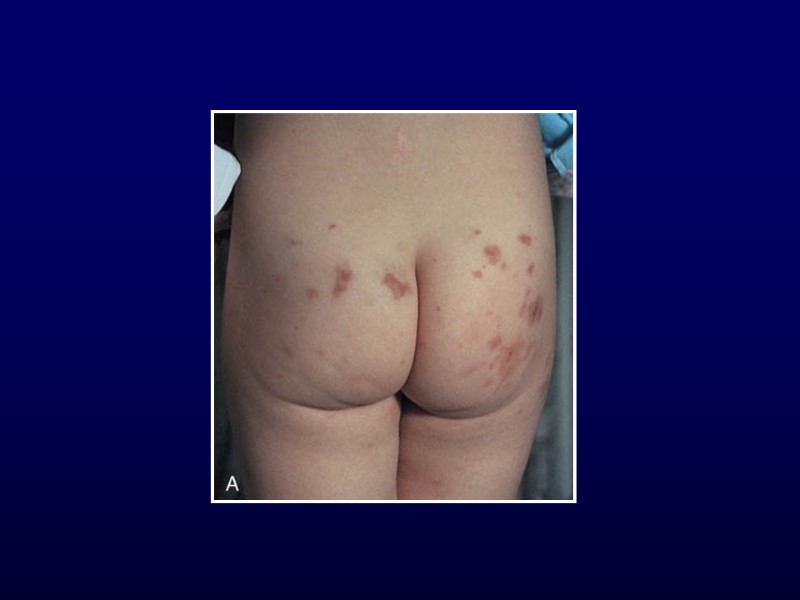
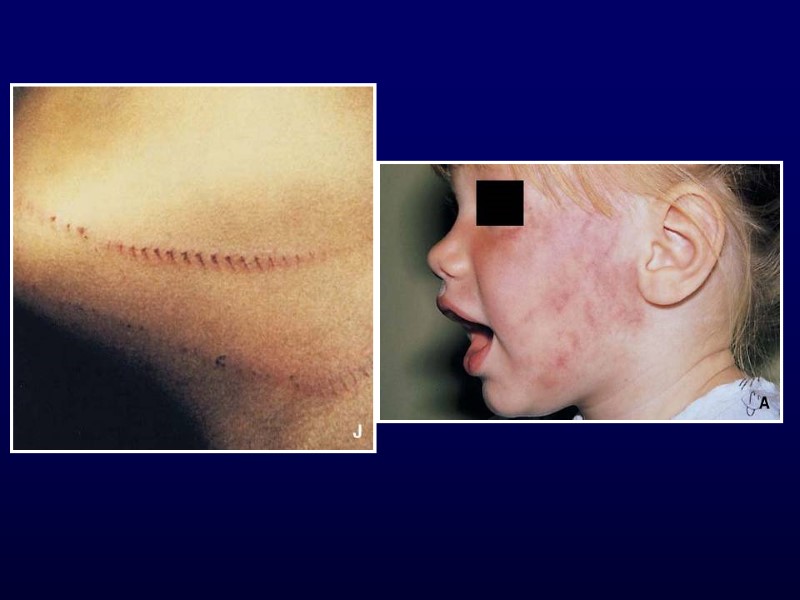
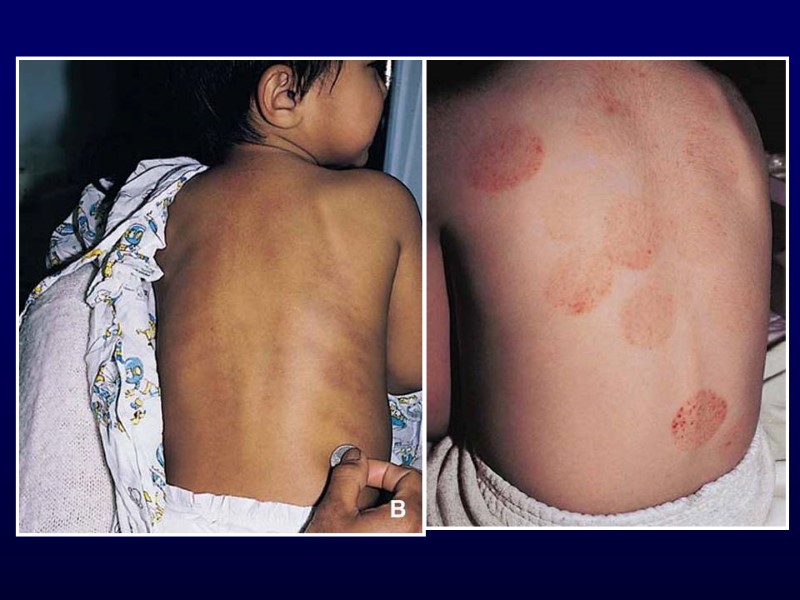
 Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Clinical features Palpable purpura of extremities Arthralgia or non-migratory arthritis No permanent deformities Mostly ankles and knees Abdominal pain May develop intussusception Renal involvement Hematuria, hypertension, renal failure
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Clinical features Palpable purpura of extremities Arthralgia or non-migratory arthritis No permanent deformities Mostly ankles and knees Abdominal pain May develop intussusception Renal involvement Hematuria, hypertension, renal failure
 HSP Management Supportive NSAIDs may control the pain and do not increase the risk of bleeding Steroids – controversial Efficacy not proven re: abdo pain No effect on purpura, duration of the illness or the frequency of recurrences Unclear of protective effect on renal disease
HSP Management Supportive NSAIDs may control the pain and do not increase the risk of bleeding Steroids – controversial Efficacy not proven re: abdo pain No effect on purpura, duration of the illness or the frequency of recurrences Unclear of protective effect on renal disease
 HSP Indications for admission R/O intussusception Severe GI bleed Severe renal disease Need for renal biopsy Hypertension Pulmonary hemorrhage
HSP Indications for admission R/O intussusception Severe GI bleed Severe renal disease Need for renal biopsy Hypertension Pulmonary hemorrhage

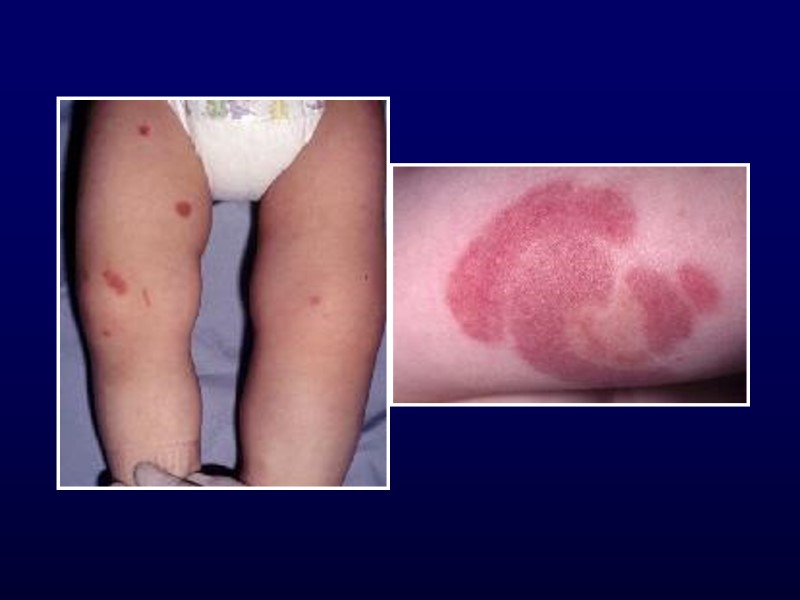
 Acute Hemorrhagic Edema of Infancy 4-24 months Recent URI or antibiotics Non-toxic Resolves in 1-3 weeks small- vessel, leukocytoclastic vasculitis Annular or targetoid pupura and edema on face and extremities
Acute Hemorrhagic Edema of Infancy 4-24 months Recent URI or antibiotics Non-toxic Resolves in 1-3 weeks small- vessel, leukocytoclastic vasculitis Annular or targetoid pupura and edema on face and extremities




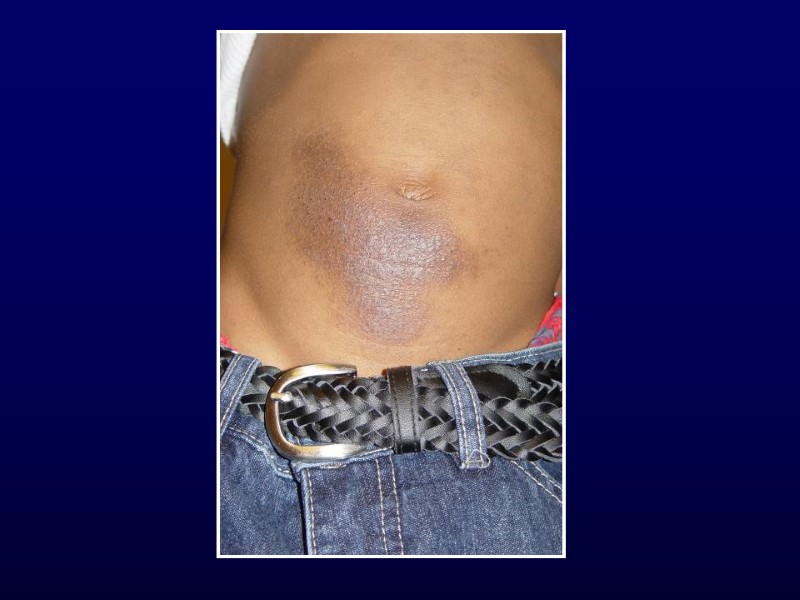
 Conclusions Not all that itches is eczema Treatment is often supportive for viral exanthems Remember rashes as a sign of systemic illness Careful history and physical essential for evaluation of bruises
Conclusions Not all that itches is eczema Treatment is often supportive for viral exanthems Remember rashes as a sign of systemic illness Careful history and physical essential for evaluation of bruises


