5a855fa96453130bbb82a7c865d8615a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Pediatric Airway Management Brian Rogge RN, EMT-P Pediatric Flight Nurse NW Med. Star Spokane County EMS

What is Airway Management? • Opening the airway • Clearing the airway • Securing the airway • After A comes B.

Why? Most pediatric cardiac arrests are secondary to respiratory arrest or airway issue.


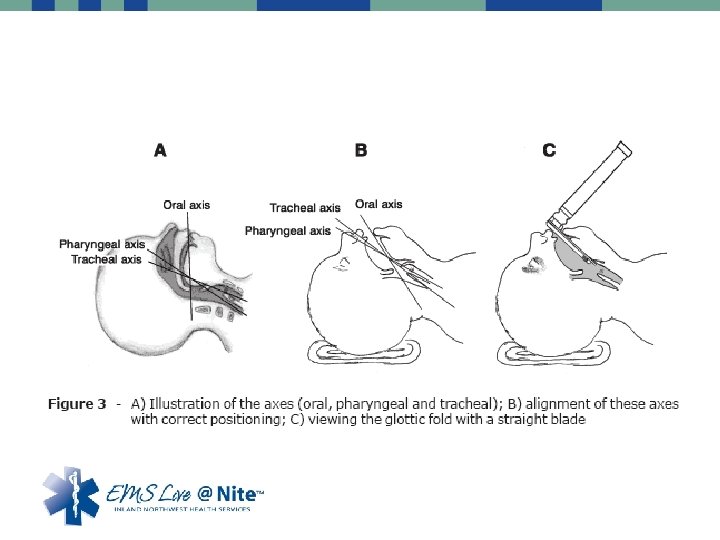
Open the airway • Older Kids (greater than 5 years of age) – More Similar to adults – Head tilt chin lift – Think C-spine (Jaw thrust) • Younger Children – Cervical spine very flexible – Can push posterior pharynx toward tongue and occlude airway – “Sniffing position”
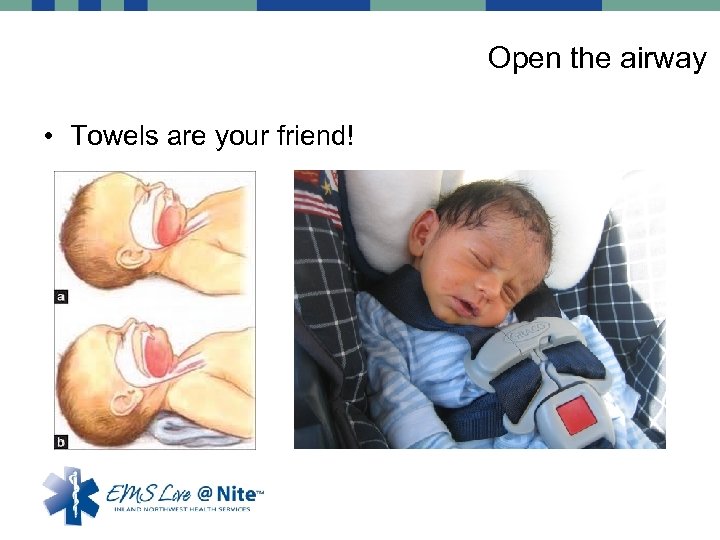
Open the airway • Towels are your friend!
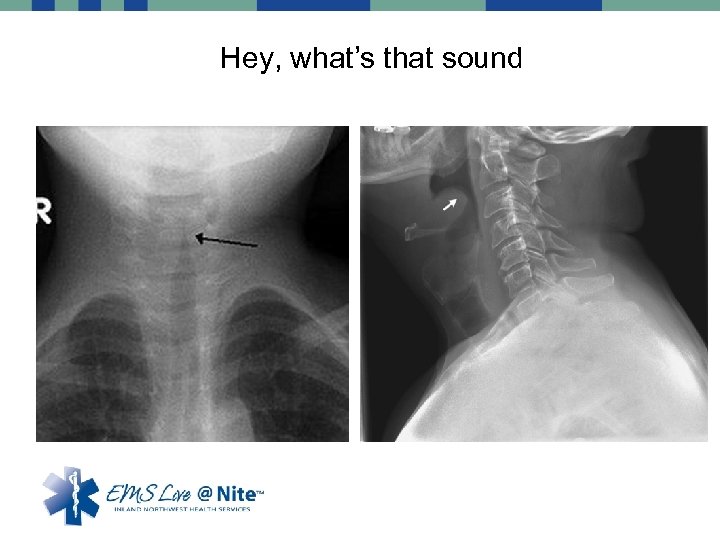
Hey, what’s that sound
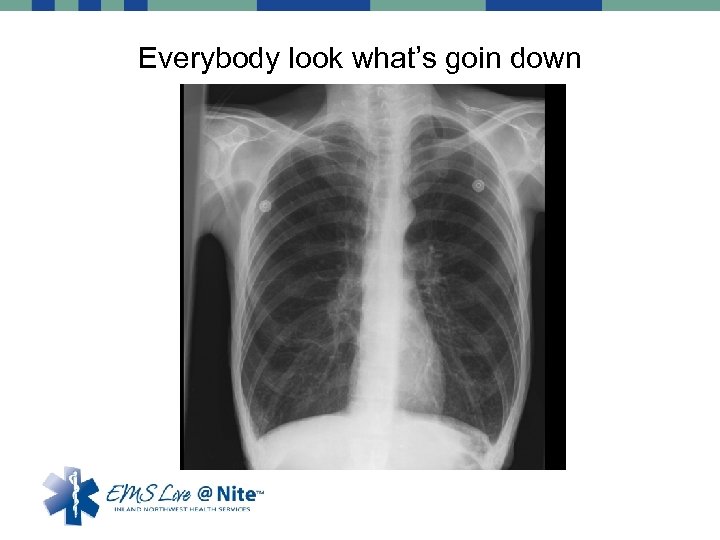
Everybody look what’s goin down

Is airway open? • Are they now spontaneously breathing • Do you need to clear the airway? • Can you assist if they are not breathing – Chest Rise – Feel the bag • Again do you need to clear the airway? – This is a question you will need to ask over and over (how long is this transport? )

Clearing the airway • NO BLIND FINGER SWEEPS! – Infant back blows and chest thrusts (5 each) – Pediatric heimlich on witness choking until unresponsive • Suctioning the airway – Not just for something to do – May cause harm • Trauma • Bradycardia

Clearing the airway • Positioning – Drainage • Semi-fowlers • Rescue position • Older children position of comfort – Remember other issues such as trauma

Securing the airway • Check your protocols!!!! – Not every agency has intubation within their protocols – Can be very challenging due to frequency and pitfalls • Do you need to phone a friend? – Rendezvous with ALS or Air Service? – Medical Control (this is where closest appropriate facility may be challenging)

Securing the airway • Know your equipment!!! • Oral pharyngeal airways • Nasal Pharyngeal airway

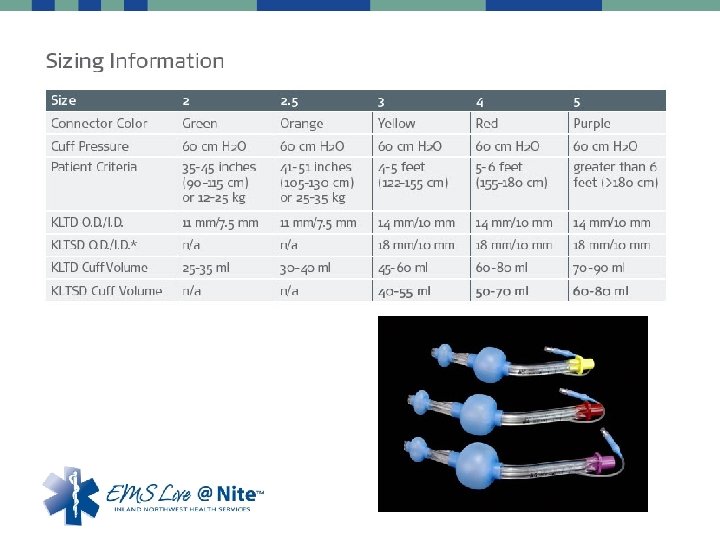
Securing the airway • More definitive airways • • Combitubes King Airways Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Endotracheal tubes – Uncuffed – Cuffed

So finally done…. . with A • Move on to “B”reathing • Rate • Rhythm • Quality • Sustainability and Trending – Reassessment

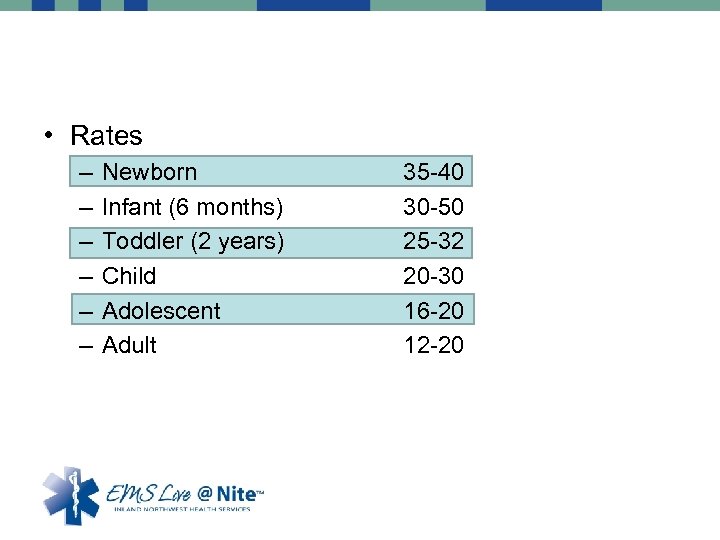
• Rates – – – Newborn Infant (6 months) Toddler (2 years) Child Adolescent Adult 35 -40 30 -50 25 -32 20 -30 16 -20 12 -20

Breathing • Is yours affective? – – Chest rise Color Improvement If not, change what you need

Questions? Brian Rogge roggebe 3@nwmedstar. org

POST-TEST 1. You can occlude the airway in a pediatric patient by: A) Hyperextending the neck B) Hyperflexing the neck C) Both A & B are correct D) None of the above 2. Pediatric tongue is relatively larger than the adult tongue A) True B) False 3. Wheezing and Stridor are signs of what respiratory problems: A) Wheezing is from problems in the upper airway, stridor is from lower airway (lungs) B) Wheezing and stridor are different names for the same thing C) Wheezing is from problems in the lower airway (lungs), stridor is from upper airway D) They are different, but treated the same way so it doesn’t matter 4. Pediatric cardiac arrest is usually caused from: A) Primary cardiac arrest (sudden cardiac arrhythmia) B) Primary respiratory problem (respiratory issue which leads to cardiac arrest) 5. There are many EMS agencies in which Pediatric intubation are not within their protocols: A) True B) False

SECRET QUESTION The narrowest part of the pediatric airway is: A) Right behind the tongue B) Right above the vocal cords C) At the vocal cords when they are open D) At the cricoid cartilage

Special thanks to Sheila Crow Stitchin’ Dreams Embroidery wcsocrow@yahoo. com For providing our Secret Question prize

Questions? Contact: Samantha Roberts 509 -242 -4264 1 -866 -630 -4033 robertss@inhs. org Fax: 509 -232 -8344

Updates Please EMS Live@Nite presentation, all certificates will be printed by participants or their agency. The certificate template will be available through the health training website at the same location as all presentation downloads. It will be posted the day after each monthly presentation.


5a855fa96453130bbb82a7c865d8615a.ppt