ee742dfff66ccf1c0a809785663435bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Pedagogical Grammar Prof. Penny Ur Teaching ‘Present Simple’ Presented by: Khalaily Lena 1/6/2011
Pedagogical Grammar Prof. Penny Ur Teaching ‘Present Simple’ Presented by: Khalaily Lena 1/6/2011
 Present Simple Use 1) Facts. ex. Cats like milk. Water boils at 100 Celsius. 2) Habits (repeated actions /daily routines). ex. She always drinks milk in the morning. I come to school everyday. She visits her friend once a month.
Present Simple Use 1) Facts. ex. Cats like milk. Water boils at 100 Celsius. 2) Habits (repeated actions /daily routines). ex. She always drinks milk in the morning. I come to school everyday. She visits her friend once a month.
 3) Events ex. The movie tells the story of a poor girl. . Birds fly to hot countries. 4) States ex: I know the answer. Alice likes bananas.
3) Events ex. The movie tells the story of a poor girl. . Birds fly to hot countries. 4) States ex: I know the answer. Alice likes bananas.
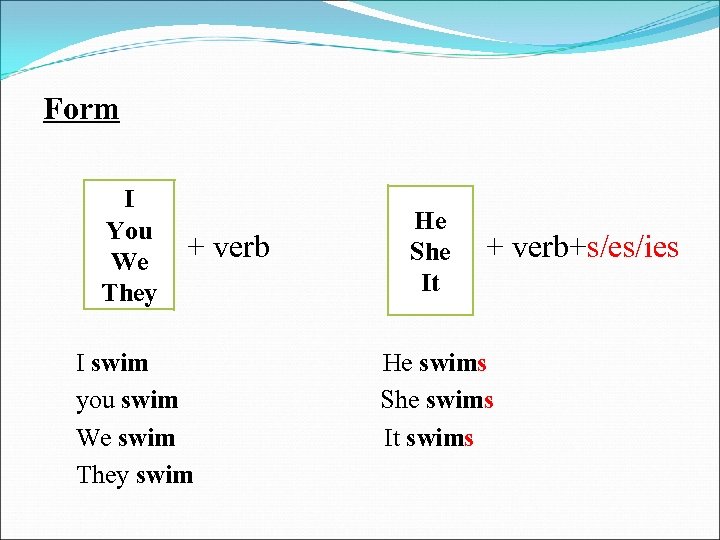 Form I You We They + verb I swim you swim We swim They swim He She It + verb+s/es/ies He swims She swims It swims
Form I You We They + verb I swim you swim We swim They swim He She It + verb+s/es/ies He swims She swims It swims
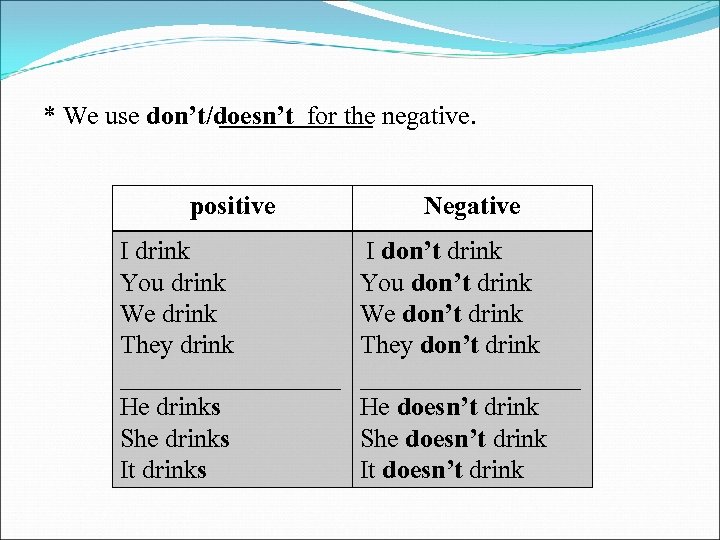 * We use don’t/doesn’t for the negative. positive Negative I drink You drink We drink They drink _________ He drinks She drinks It drinks I don’t drink You don’t drink We don’t drink They don’t drink _________ He doesn’t drink She doesn’t drink It doesn’t drink
* We use don’t/doesn’t for the negative. positive Negative I drink You drink We drink They drink _________ He drinks She drinks It drinks I don’t drink You don’t drink We don’t drink They don’t drink _________ He doesn’t drink She doesn’t drink It doesn’t drink
 Spelling rules 1)We add es to the verb when it ends with s miss crash catch mix go sh misses crashes catches mixes goes ch x z o
Spelling rules 1)We add es to the verb when it ends with s miss crash catch mix go sh misses crashes catches mixes goes ch x z o
 2) When the verb ends with y and there is a consonant before, we drop it and add ies fly cry flies cries UT 3) When the verb ends with y and there is a vowel before, we will not drop the y and add just s plays buys
2) When the verb ends with y and there is a consonant before, we drop it and add ies fly cry flies cries UT 3) When the verb ends with y and there is a vowel before, we will not drop the y and add just s plays buys
 we pronounce the ‘s’ like ‘z’ except Tip after the sounds k, f, p, t Time expressions Sometimes, often, never, always , usually every day/week/month/year once a week/month/year twice a week/month/year
we pronounce the ‘s’ like ‘z’ except Tip after the sounds k, f, p, t Time expressions Sometimes, often, never, always , usually every day/week/month/year once a week/month/year twice a week/month/year
 Procedure *The teacher starts talking about , habits, routines and daily activities. *He gives his own examples and then ask the pupils for their examples. What do they do usually, every morning, every day week, every month, once a year? ex. *I brush my teeth every morning. *I visit my friend once a month.
Procedure *The teacher starts talking about , habits, routines and daily activities. *He gives his own examples and then ask the pupils for their examples. What do they do usually, every morning, every day week, every month, once a year? ex. *I brush my teeth every morning. *I visit my friend once a month.
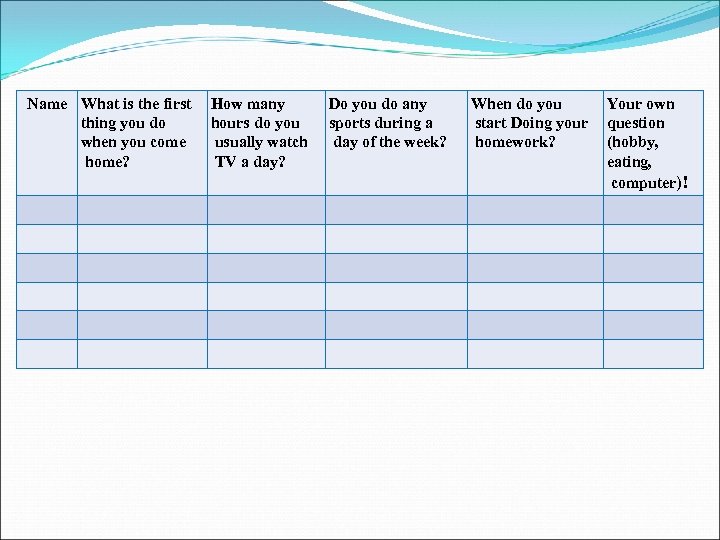 Name What is the first thing you do when you come home? How many hours do you usually watch TV a day? Do you do any sports during a day of the week? When do you start Doing your homework? Your own question (hobby, eating, computer)!
Name What is the first thing you do when you come home? How many hours do you usually watch TV a day? Do you do any sports during a day of the week? When do you start Doing your homework? Your own question (hobby, eating, computer)!
 *It’s very important to write full sentences. *The teacher asks the students to sit in groups. *The group members go over the information they collected together. They try to find at least five interesting sentences and facts about different pupils in the class. *One student will present these sentences to the whole class. It’s very important to use the names of the students so that the pupils who are presenting will use third person.
*It’s very important to write full sentences. *The teacher asks the students to sit in groups. *The group members go over the information they collected together. They try to find at least five interesting sentences and facts about different pupils in the class. *One student will present these sentences to the whole class. It’s very important to use the names of the students so that the pupils who are presenting will use third person.
 Underlying Theory Norris, J. M. & Ortega, L (2001) concluded that explicit instruction of grammar is crucial in the classroom and it is considered more effective than implicit instruction on its own. Ellis (2002) thinks that exposure and sufficient quantity of the correct form through meaningful and communicative activities is desirable. He said that explicit teaching is useful because it encourages noticing.
Underlying Theory Norris, J. M. & Ortega, L (2001) concluded that explicit instruction of grammar is crucial in the classroom and it is considered more effective than implicit instruction on its own. Ellis (2002) thinks that exposure and sufficient quantity of the correct form through meaningful and communicative activities is desirable. He said that explicit teaching is useful because it encourages noticing.
 Focus on form(Long, 1991, Long & Robinson, 1998) The Teacher should keep a totally communicative classroom till he encounters a form that he wants to highlight or because students came up with it. The teacher can discuss the form or only present it, give examples and practice it. This means that this include explicit teaching. Teachers just try to combine communicative activities with some grammar teaching.
Focus on form(Long, 1991, Long & Robinson, 1998) The Teacher should keep a totally communicative classroom till he encounters a form that he wants to highlight or because students came up with it. The teacher can discuss the form or only present it, give examples and practice it. This means that this include explicit teaching. Teachers just try to combine communicative activities with some grammar teaching.
 Task-based instruction(Skehan, P. 1997) *The teacher gives the pupils tasks to complete in the classroom. This helps the pupils to be engaged in a naturalistic acquisitional mechanisms and stretch the underlying interlanguage system. *Tasks within the TBI model do not focus on a particular linguistic feature, they are totally communicative and meaning based.
Task-based instruction(Skehan, P. 1997) *The teacher gives the pupils tasks to complete in the classroom. This helps the pupils to be engaged in a naturalistic acquisitional mechanisms and stretch the underlying interlanguage system. *Tasks within the TBI model do not focus on a particular linguistic feature, they are totally communicative and meaning based.
 Task-based + focus on form 1) The lesson will be based on a communicative task that will involve a written or a spoken text. 2) Occasionally time is devoted to clarification of grammatical forms, and possibly even practice activities. 3) Most of the lesson time and effort is devoted to the task and its meaning -focused outcomes.
Task-based + focus on form 1) The lesson will be based on a communicative task that will involve a written or a spoken text. 2) Occasionally time is devoted to clarification of grammatical forms, and possibly even practice activities. 3) Most of the lesson time and effort is devoted to the task and its meaning -focused outcomes.
 Conclusions -Deciding on a particular practical method for teaching any grammatical feature isn’t an easy job! - Context and many other pedagogical factors should be taken into consideration by the teachers. - There are many insights but there is no best way for grammar teaching. All depends on the teacher’s preferences and professional judgment.
Conclusions -Deciding on a particular practical method for teaching any grammatical feature isn’t an easy job! - Context and many other pedagogical factors should be taken into consideration by the teachers. - There are many insights but there is no best way for grammar teaching. All depends on the teacher’s preferences and professional judgment.
 Bibliography Ellis, R. (2001). Grammar teaching - Practice or consciousness-raising? . In Richards, J. C. & Renandya, W. A. (Eds. ). Methodology in Language Teaching (pp. 167 -174). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Long, M. H. & Robinson, P. (1998). Focus on form: Theory, research and practice. In C. Doughty & Williams. (Eds. ), Focus on form in Classroom Second Language Acquisition (pp. 15 -41). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Swan, M. (2005). Practical English Usage (Third Edition). Oxford: Oxford University Press. Skehan, P. (1997). A Cognitive Approach to Language Learning. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Ur, P. 1988. Grammar Practice Activities. Cambridge: Cambridge University
Bibliography Ellis, R. (2001). Grammar teaching - Practice or consciousness-raising? . In Richards, J. C. & Renandya, W. A. (Eds. ). Methodology in Language Teaching (pp. 167 -174). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Long, M. H. & Robinson, P. (1998). Focus on form: Theory, research and practice. In C. Doughty & Williams. (Eds. ), Focus on form in Classroom Second Language Acquisition (pp. 15 -41). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Swan, M. (2005). Practical English Usage (Third Edition). Oxford: Oxford University Press. Skehan, P. (1997). A Cognitive Approach to Language Learning. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Ur, P. 1988. Grammar Practice Activities. Cambridge: Cambridge University
 Thanks for listening Lena Khalaily
Thanks for listening Lena Khalaily


