031e0aaf6ac167af7d62cea9f054140e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

PDSA Cycles Kyrie Shomaker, MD February 3, 2009
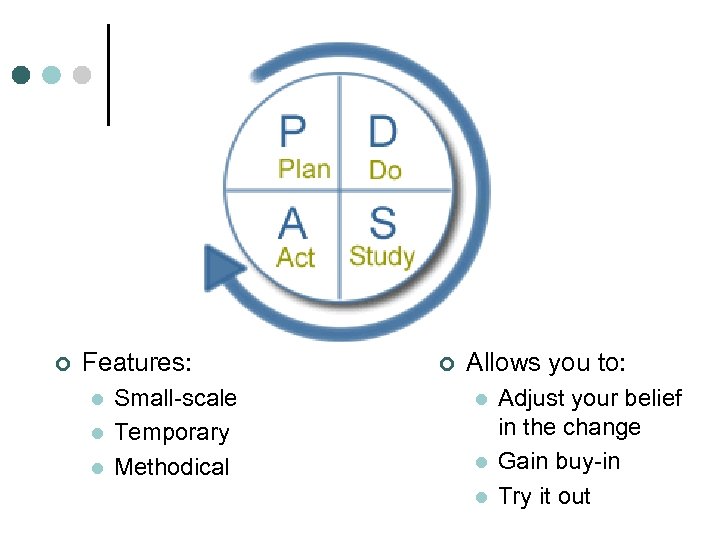
¢ Features: l l l Small-scale Temporary Methodical ¢ Allows you to: l l l Adjust your belief in the change Gain buy-in Try it out
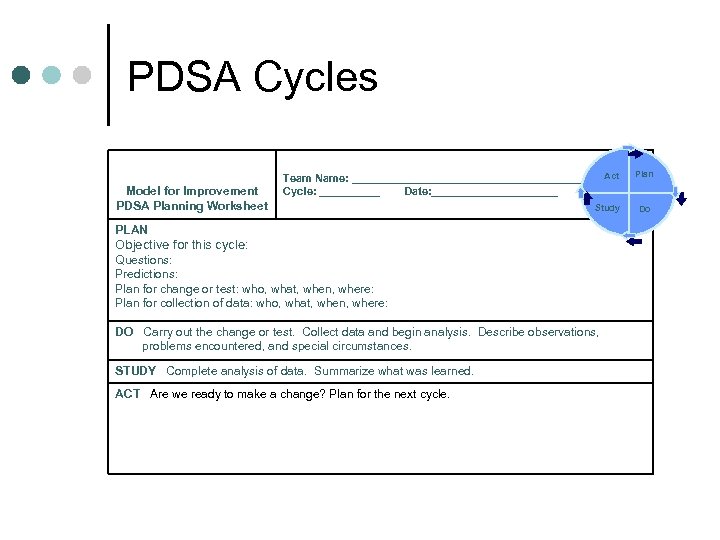
PDSA Cycles Model for Improvement PDSA Planning Worksheet Act Team Name: _____________________ Cycle: ______ Date: ____________ Study PLAN Objective for this cycle: Questions: Predictions: Plan for change or test: who, what, when, where: Plan for collection of data: who, what, when, where: DO Carry out the change or test. Collect data and begin analysis. Describe observations, problems encountered, and special circumstances. STUDY Complete analysis of data. Summarize what was learned. ACT Are we ready to make a change? Plan for the next cycle. Plan Do

Example 1

Example 1 ¢ Overall aim: l ¢ Most pressing problem: l ¢ To use non-work time more efficiently Too many trips to the store and nothing for dinner Ideas for change: 1) Buy more stuff l 2) Make a weekly dinner menu l
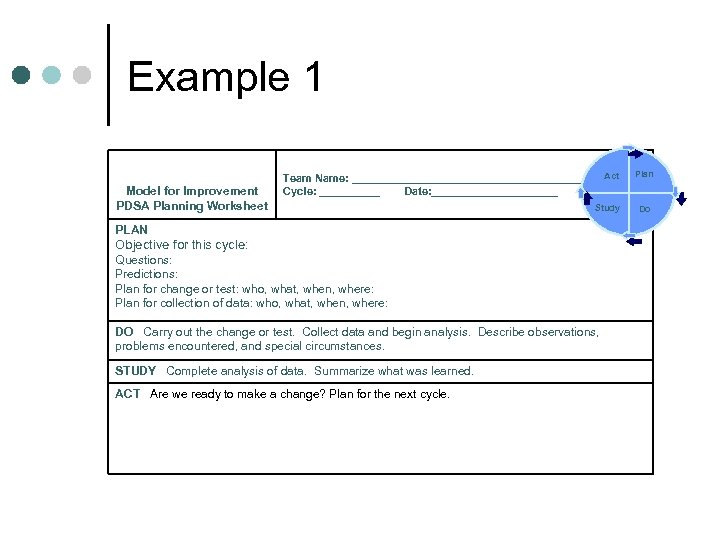
Example 1 Model for Improvement PDSA Planning Worksheet Act Team Name: _____________________ Cycle: ______ Date: ____________ Study PLAN Objective for this cycle: Questions: Predictions: Plan for change or test: who, what, when, where: Plan for collection of data: who, what, when, where: DO Carry out the change or test. Collect data and begin analysis. Describe observations, problems encountered, and special circumstances. STUDY Complete analysis of data. Summarize what was learned. ACT Are we ready to make a change? Plan for the next cycle. Plan Do
PDSA Ramps e& c ata D A P S D n ide v A P S D E Theories, hunches, & best practices A S P D A P S D t Le ng rni a i nd a m e rov p n me Breakthrough Results
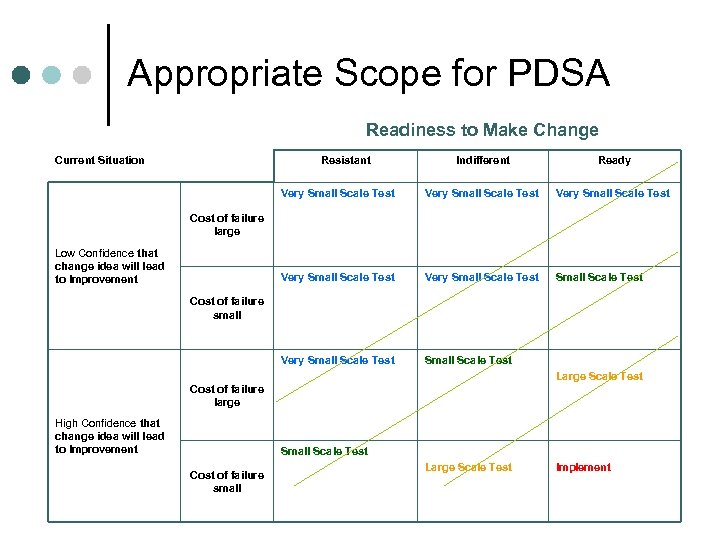
Appropriate Scope for PDSA Readiness to Make Change Current Situation Resistant Indifferent Ready Very Small Scale Test Very Small Scale Test Cost of failure large Low Confidence that change idea will lead to Improvement Cost of failure small Large Scale Test Cost of failure large High Confidence that change idea will lead to Improvement Small Scale Test Cost of failure small Large Scale Test Implement
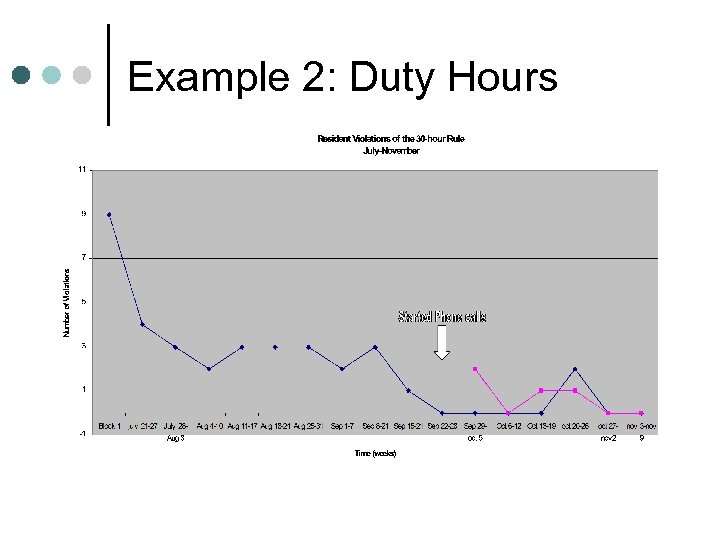
Example 2: Duty Hours
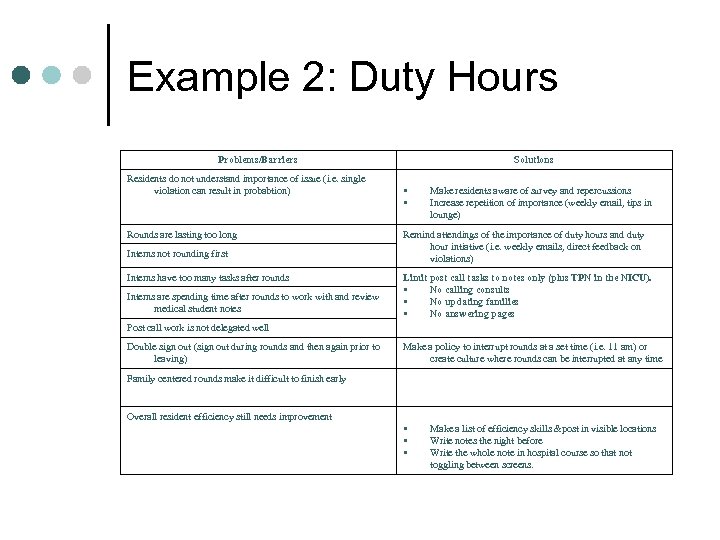
Example 2: Duty Hours Problems/Barriers Residents do not understand importance of issue (i. e. single violation can result in probabtion) Rounds are lasting too long Interns not rounding first Interns have too many tasks after rounds Interns are spending time after rounds to work with and review medical student notes Solutions Make residents aware of survey and repercussions Increase repetition of importance (weekly email, tips in lounge) Remind attendings of the importance of duty hours and duty hour intiative (i. e. weekly emails, direct feedback on violations) Limit post call tasks to notes only (plus TPN in the NICU). No calling consults No updating families No answering pages Post call work is not delegated well Double sign out (sign out during rounds and then again prior to leaving) Make a policy to interrupt rounds at a set time (i. e. 11 am) or create culture where rounds can be interrupted at any time Family centered rounds make it difficult to finish early Overall resident efficiency still needs improvement Make a list of efficiency skills &post in visible locations Write notes the night before Write the whole note in hospital course so that not toggling between screens.
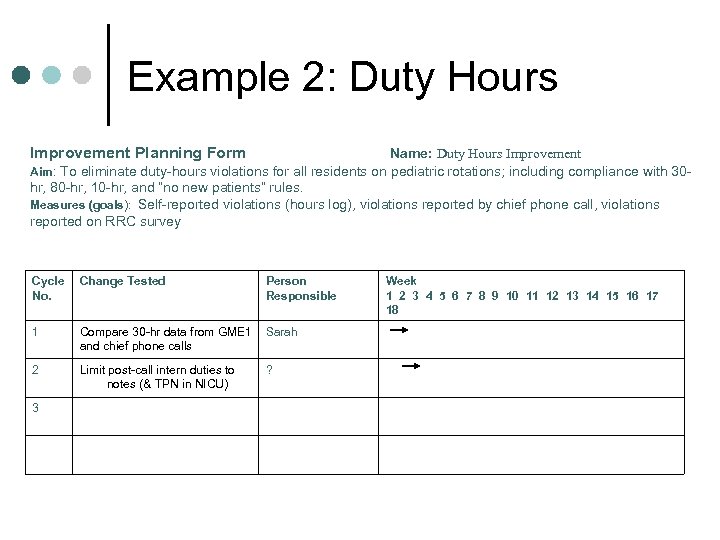
Example 2: Duty Hours Improvement Planning Form Name: Duty Hours Improvement Aim: To eliminate duty-hours violations for all residents on pediatric rotations; including compliance with 30 hr, 80 -hr, 10 -hr, and “no new patients” rules. Measures (goals): Self-reported violations (hours log), violations reported by chief phone call, violations reported on RRC survey Cycle No. Change Tested Person Responsible 1 Compare 30 -hr data from GME 1 and chief phone calls Sarah 2 Limit post-call intern duties to notes (& TPN in NICU) ? 3 Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18

Key Points ¢ For initial cycles, Use the smallest scale possible (“cycle of one” is best!) l Failed cycles are good learning opportunities when small l ¢ For implementation cycles, l Test under many different conditions (busy days, different staff, things naysayers worry about)

Activity ¢ Given an aim and a list of brainstormed ideas, have each group come up with an initial PDSA cycle to test a selected change

Make your own PDSA ¢ Aim l ¢ Problem l ¢ To free up more beds in the Children’s Hospital by increasing throughput. Even when the discharge date is known in advance, patients often do not vacate their room until afternoon, creating delays in the work-up and management of incoming patients. Ideas for change: l l l l l Complete the brief summary and any other necessary paperwork the night before Schedule a ride for the patient in the morning Round on the patients to be discharged first (beginning at 9 am) Round on the patients to be discharged earlier (i. e. before morning conference) Have the night team discharge the patient Tell the charge nurse the night before that the patient is to be discharged Communicate the discharge goals to the family/nurses in writing (i. e. the “discharge board”) Communicate the discharge goals to the nurses with an anticipate discharge order (i. e. “anticipate discharge when…”) Move the patients out of their rooms to a waiting area once they are discharged so the rooms can be cleaned and used again Other ideas?
031e0aaf6ac167af7d62cea9f054140e.ppt