 PC Maintenance: Preparing for A+ Certification Chapter 1: Computing Overview
PC Maintenance: Preparing for A+ Certification Chapter 1: Computing Overview
 Chapter 1 Objectives Explain analog versus digital data n Explain input, processing, and output n Understand binary and decimal numbering n Identify key components of a PC n Differentiate between computer types n Understand BIOS, and applications n
Chapter 1 Objectives Explain analog versus digital data n Explain input, processing, and output n Understand binary and decimal numbering n Identify key components of a PC n Differentiate between computer types n Understand BIOS, and applications n
 What All Computers Have in Common Digital Operation n Hardware and Software n User Input n Processing n Output n
What All Computers Have in Common Digital Operation n Hardware and Software n User Input n Processing n Output n
 Analog Continuously variable n No precisely defined values n Often associated with sound (waveforms) n Examples: radio, television broadcasts, telephone n
Analog Continuously variable n No precisely defined values n Often associated with sound (waveforms) n Examples: radio, television broadcasts, telephone n
 Digital Precise values n Numeric data n Quantifiable n Not continuously variable n
Digital Precise values n Numeric data n Quantifiable n Not continuously variable n
 Hardware and Software n Hardware: Physical parts of the computer n n Firmware: a hardware chip with software stored on it n n Examples: Monitor, keyboard, mouse, CPU, disks Examples: BIOS chip, ROM storage of OS in a PDA Software: Programming instructions for the hardware to execute
Hardware and Software n Hardware: Physical parts of the computer n n Firmware: a hardware chip with software stored on it n n Examples: Monitor, keyboard, mouse, CPU, disks Examples: BIOS chip, ROM storage of OS in a PDA Software: Programming instructions for the hardware to execute
 Binary Numbering Two digits: 0 and 1 n Native format for CPU processing of data n
Binary Numbering Two digits: 0 and 1 n Native format for CPU processing of data n
 Decimal Numbering Ten digits: 0 to 9 n Standard numbering system for humans n
Decimal Numbering Ten digits: 0 to 9 n Standard numbering system for humans n
 Hexadecimal Numbering Sixteen digits: 0 to 9 and A to F n Used for memory addresses n
Hexadecimal Numbering Sixteen digits: 0 to 9 and A to F n Used for memory addresses n
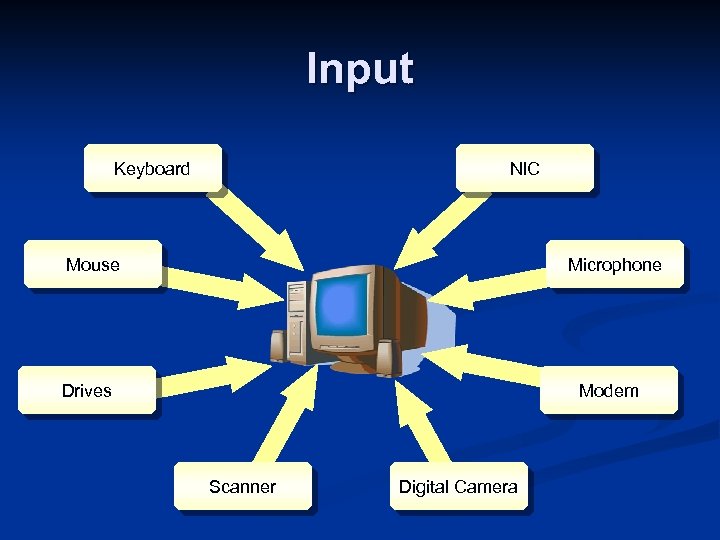 Input Keyboard NIC Mouse Microphone Drives Modem Scanner Digital Camera
Input Keyboard NIC Mouse Microphone Drives Modem Scanner Digital Camera
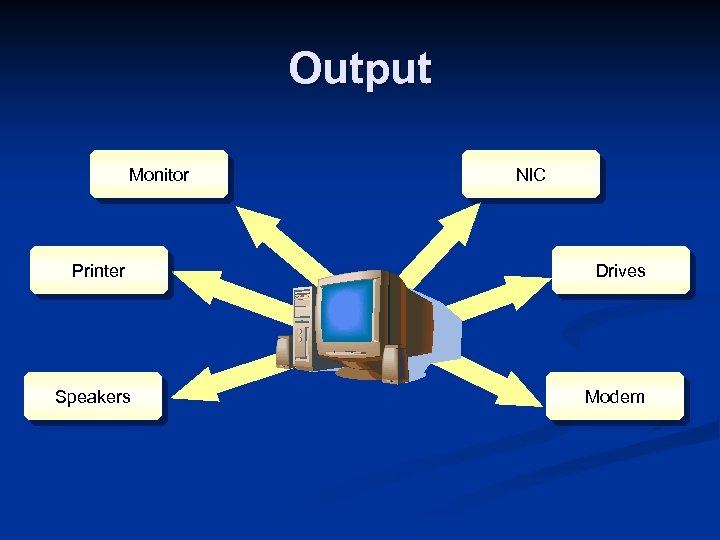 Output Monitor Printer Speakers NIC Drives Modem
Output Monitor Printer Speakers NIC Drives Modem
 PC Exterior: Front CD drive Floppy drive Hard disk light Power button
PC Exterior: Front CD drive Floppy drive Hard disk light Power button
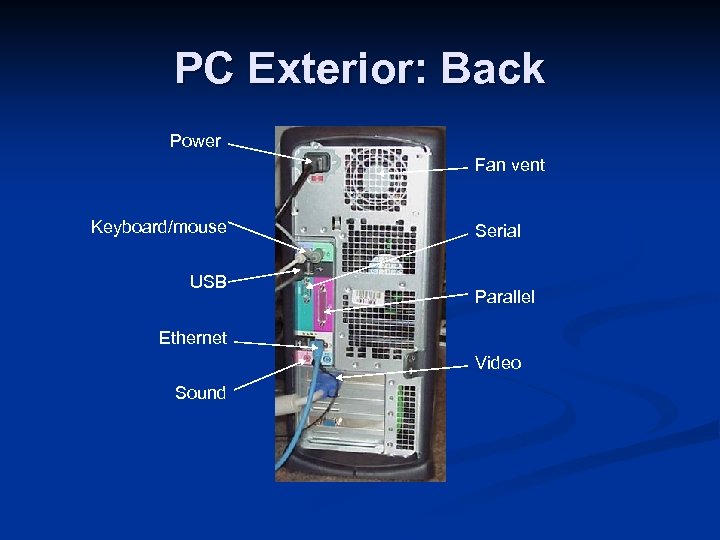 PC Exterior: Back Power Fan vent Keyboard/mouse USB Serial Parallel Ethernet Video Sound
PC Exterior: Back Power Fan vent Keyboard/mouse USB Serial Parallel Ethernet Video Sound
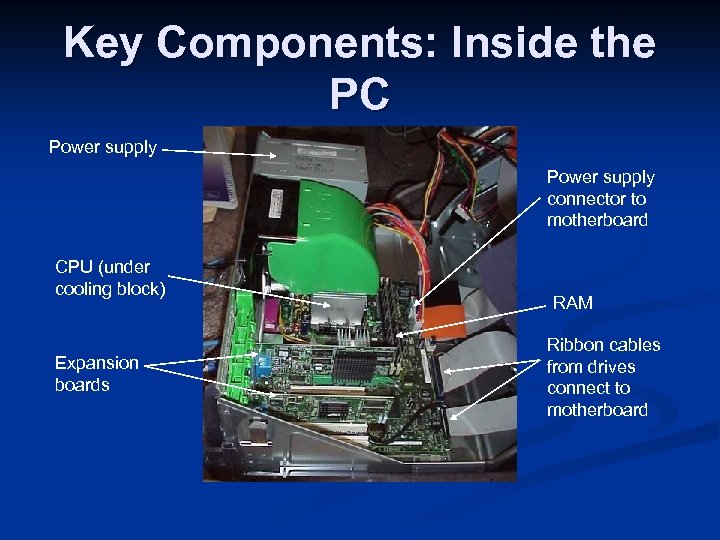 Key Components: Inside the PC Power supply connector to motherboard CPU (under cooling block) Expansion boards RAM Ribbon cables from drives connect to motherboard
Key Components: Inside the PC Power supply connector to motherboard CPU (under cooling block) Expansion boards RAM Ribbon cables from drives connect to motherboard
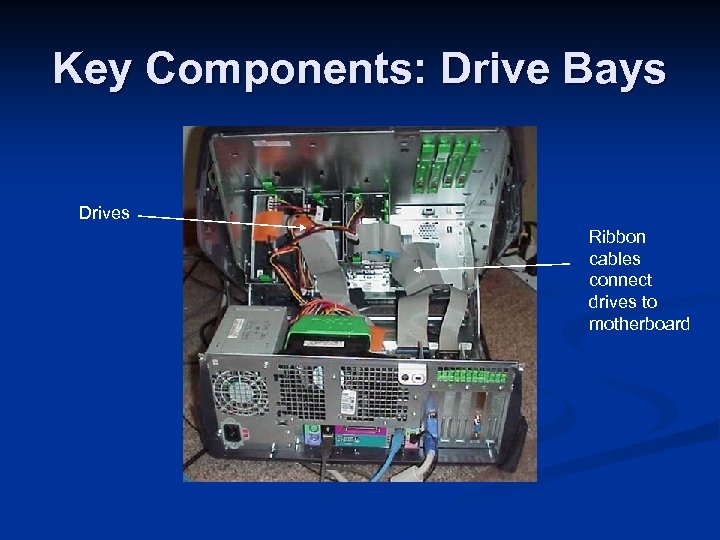 Key Components: Drive Bays Drives Ribbon cables connect drives to motherboard
Key Components: Drive Bays Drives Ribbon cables connect drives to motherboard
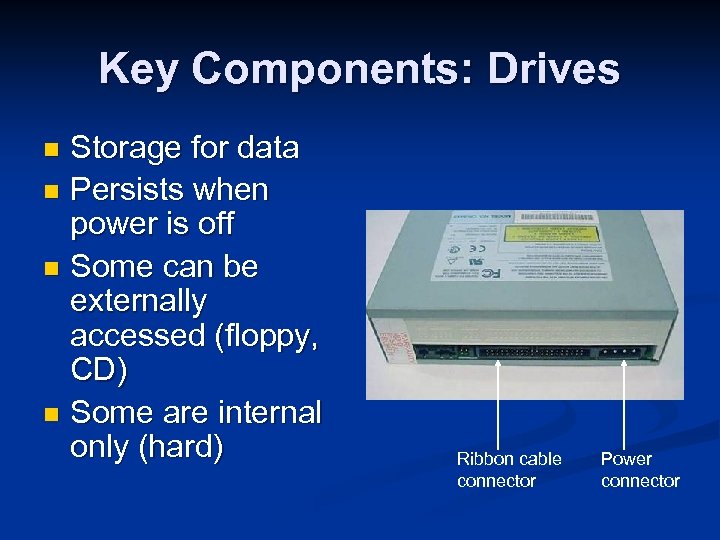 Key Components: Drives Storage for data n Persists when power is off n Some can be externally accessed (floppy, CD) n Some are internal only (hard) n Ribbon cable connector Power connector
Key Components: Drives Storage for data n Persists when power is off n Some can be externally accessed (floppy, CD) n Some are internal only (hard) n Ribbon cable connector Power connector
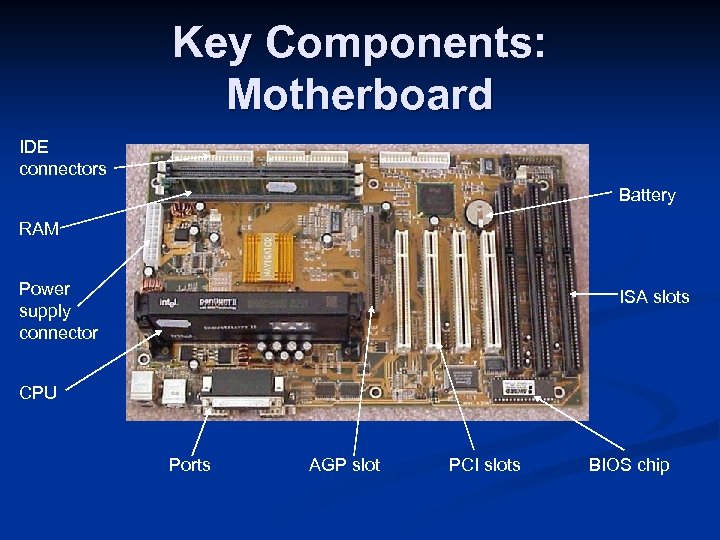 Key Components: Motherboard IDE connectors Battery RAM Power supply connector ISA slots CPU Ports AGP slot PCI slots BIOS chip
Key Components: Motherboard IDE connectors Battery RAM Power supply connector ISA slots CPU Ports AGP slot PCI slots BIOS chip
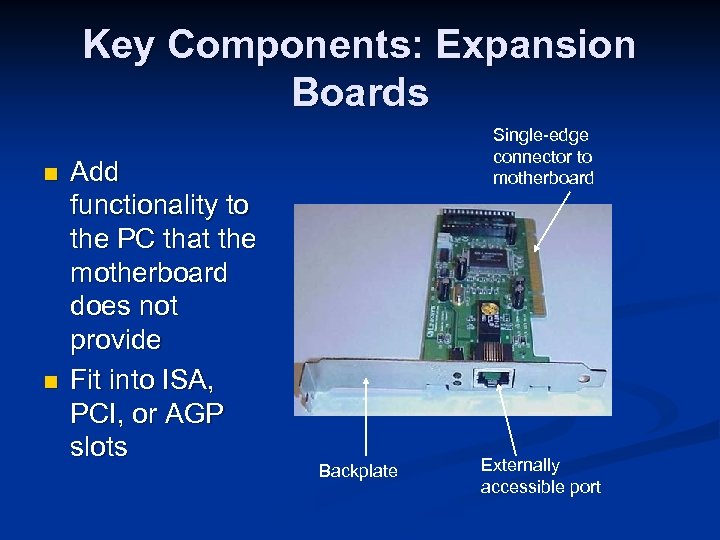 Key Components: Expansion Boards n n Add functionality to the PC that the motherboard does not provide Fit into ISA, PCI, or AGP slots Single-edge connector to motherboard Backplate Externally accessible port
Key Components: Expansion Boards n n Add functionality to the PC that the motherboard does not provide Fit into ISA, PCI, or AGP slots Single-edge connector to motherboard Backplate Externally accessible port
 Notebook PCs Built-in LCD screen Built-in pointing device Can run on AC or battery PCMCIA slots instead of ISA/PCI
Notebook PCs Built-in LCD screen Built-in pointing device Can run on AC or battery PCMCIA slots instead of ISA/PCI
 Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Hand-held computer n Limited amount of RAM n Limited in functionality n Write, tap with stylus on touchsensitive screen n
Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Hand-held computer n Limited amount of RAM n Limited in functionality n Write, tap with stylus on touchsensitive screen n
 Basic Input Output System (BIOS) Startup instructions for low-level hardware n Typically on a chip on the motherboard n Does not change readily; requires special utility n
Basic Input Output System (BIOS) Startup instructions for low-level hardware n Typically on a chip on the motherboard n Does not change readily; requires special utility n
 Operating System Interacts with human user n Manages communication with software n Runs applications n Controls input and output n
Operating System Interacts with human user n Manages communication with software n Runs applications n Controls input and output n
 Applications Perform useful human tasks n Run on top of an operating system n Are written for a specific OS n Examples: Word, Quicken, games n
Applications Perform useful human tasks n Run on top of an operating system n Are written for a specific OS n Examples: Word, Quicken, games n