1eccf4f26463d953cdf7594dcdd4b636.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Payout Policy in the st 21 Century Alon Brav Duke University, Durham, NC USA John R. Graham Duke University, Durham, NC USA Campbell R. Harvey Duke University, Durham, NC USA National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, MA USA Roni Michaely Cornell University, Ithaca, NY USA IDC, Israel 1
Payout Policy in the st 21 Century Alon Brav Duke University, Durham, NC USA John R. Graham Duke University, Durham, NC USA Campbell R. Harvey Duke University, Durham, NC USA National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, MA USA Roni Michaely Cornell University, Ithaca, NY USA IDC, Israel 1
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Introduction • In 1956, John Lintner laid the foundation for the modern understanding of dividend policy • He conducted detailed interviews with 28 companies • His research helped set the agenda for theoretical and empirical research on dividend policy • Much has changed in the last 50 years. – Possibly different payout policy goals – Repurchases – More insights from theory that may help direct the spotlight in the right direction • We revisit this path-breaking study at the beginning of the 21 st century 2
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Introduction • In 1956, John Lintner laid the foundation for the modern understanding of dividend policy • He conducted detailed interviews with 28 companies • His research helped set the agenda for theoretical and empirical research on dividend policy • Much has changed in the last 50 years. – Possibly different payout policy goals – Repurchases – More insights from theory that may help direct the spotlight in the right direction • We revisit this path-breaking study at the beginning of the 21 st century 2
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Introduction • We survey 384 financial executives with an instrument that focuses on both dividends and repurchases – 256 public, 128 private – Most presented results are based on the public firms • We conduct one-on-one interviews with 23 CFOs or Treasurers of prominent corporations – Interviews last between 40 minutes and two hours 3
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Introduction • We survey 384 financial executives with an instrument that focuses on both dividends and repurchases – 256 public, 128 private – Most presented results are based on the public firms • We conduct one-on-one interviews with 23 CFOs or Treasurers of prominent corporations – Interviews last between 40 minutes and two hours 3
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Methodology Survey and Interview Design • Draft survey instrument “refereed” by both finance researchers and experts in survey design • Interviewed structured to adhere to best scientific practices of interviews, e. g. Sudman and Bradburn (1983) 4
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Methodology Survey and Interview Design • Draft survey instrument “refereed” by both finance researchers and experts in survey design • Interviewed structured to adhere to best scientific practices of interviews, e. g. Sudman and Bradburn (1983) 4
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Methodology Survey Delivery • Survey CFOs, Treasurers, Finance VPs • Primarily members of Financial Executives International • Two $500 random winners • Three surveys – – FEI CFO Forum (April 23, 2002, Co. Springs CO) Dave Ikenberry NFCF (May 1, 2002, Houston TX) Mass emailing to 2200 FEI members Overall ~16% response rate 5
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Methodology Survey Delivery • Survey CFOs, Treasurers, Finance VPs • Primarily members of Financial Executives International • Two $500 random winners • Three surveys – – FEI CFO Forum (April 23, 2002, Co. Springs CO) Dave Ikenberry NFCF (May 1, 2002, Houston TX) Mass emailing to 2200 FEI members Overall ~16% response rate 5
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy How are payout decisions made? Goals of Treasury department: • Fund investment – M&M • Liquidity and possible contingencies • Payout decisions are second-order Except. . . • DO NOT CUT DIVIDENDS ranks equal to or above all of these items 6
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy How are payout decisions made? Goals of Treasury department: • Fund investment – M&M • Liquidity and possible contingencies • Payout decisions are second-order Except. . . • DO NOT CUT DIVIDENDS ranks equal to or above all of these items 6
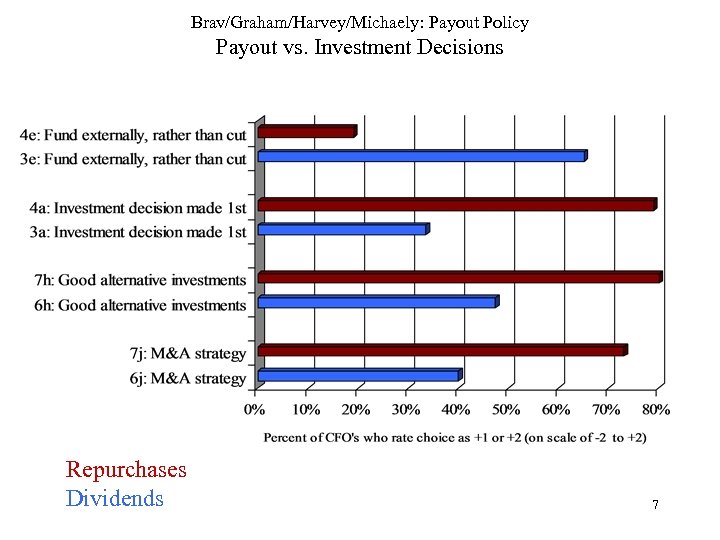 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout vs. Investment Decisions Repurchases Dividends 7
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout vs. Investment Decisions Repurchases Dividends 7
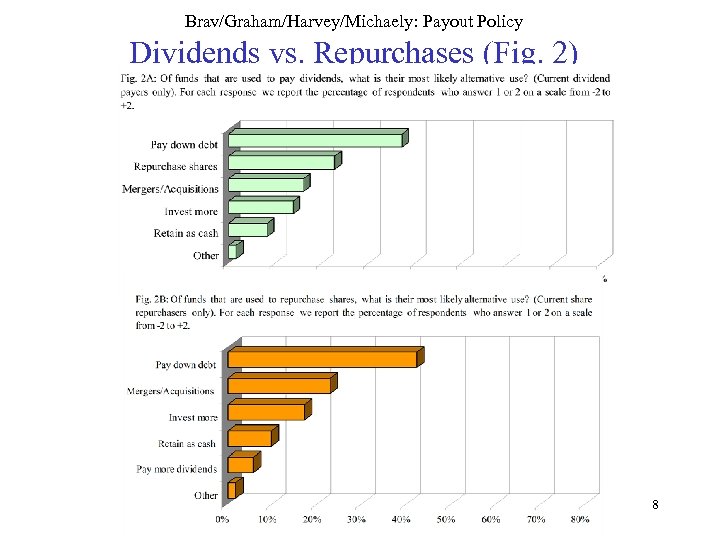 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Dividends vs. Repurchases (Fig. 2) 8
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Dividends vs. Repurchases (Fig. 2) 8
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Complements or Substitutes? • Level of dividend fixed • Substitute repurchases for change in dividends – One way substitution • Would use even more repurchases if they were free of constraint of dividend history 9
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Complements or Substitutes? • Level of dividend fixed • Substitute repurchases for change in dividends – One way substitution • Would use even more repurchases if they were free of constraint of dividend history 9
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Lintner (1956) Three main points • Target payout ratio (dividend/earnings) • Dividend policy set conservatively – “partial adjustment” to target payout – smooth through time – sticky (history important) • Level given, focus on changes – tied to long-run sustainable earnings – do not increase now if you might have to cut later • No repurchases 10
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Lintner (1956) Three main points • Target payout ratio (dividend/earnings) • Dividend policy set conservatively – “partial adjustment” to target payout – smooth through time – sticky (history important) • Level given, focus on changes – tied to long-run sustainable earnings – do not increase now if you might have to cut later • No repurchases 10
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Compare to Lintner (1956) Dividend policy still “conservative”? • Yes • Perceived big penalty for cut, small reward for increase – So, smooth, to avoid future cuts • Path dependence of dividend policy • BUT – stealth dividend cut if possible – holding dividend constant OK 11
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Compare to Lintner (1956) Dividend policy still “conservative”? • Yes • Perceived big penalty for cut, small reward for increase – So, smooth, to avoid future cuts • Path dependence of dividend policy • BUT – stealth dividend cut if possible – holding dividend constant OK 11
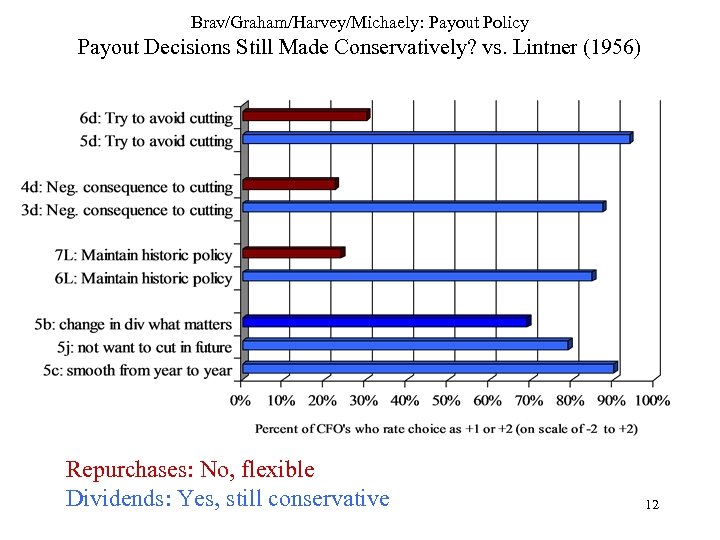 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout Decisions Still Made Conservatively? vs. Lintner (1956) Repurchases: No, flexible Dividends: Yes, still conservative 12
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout Decisions Still Made Conservatively? vs. Lintner (1956) Repurchases: No, flexible Dividends: Yes, still conservative 12
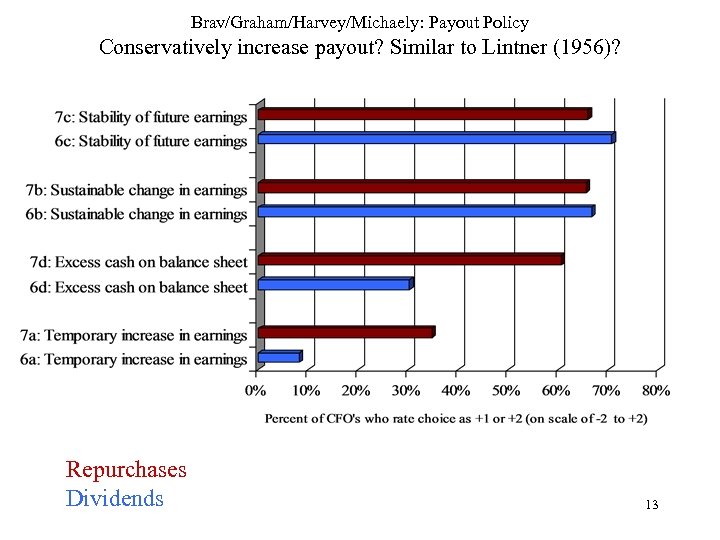 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conservatively increase payout? Similar to Lintner (1956)? Repurchases Dividends 13
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conservatively increase payout? Similar to Lintner (1956)? Repurchases Dividends 13
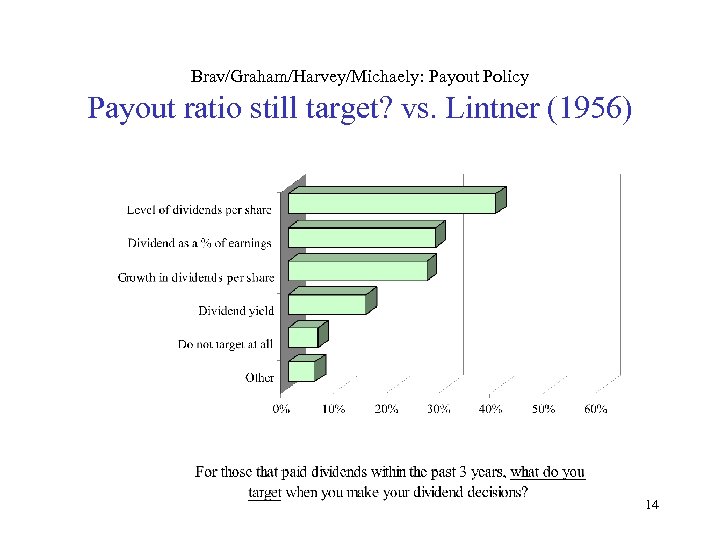 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout ratio still target? vs. Lintner (1956) 14
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout ratio still target? vs. Lintner (1956) 14
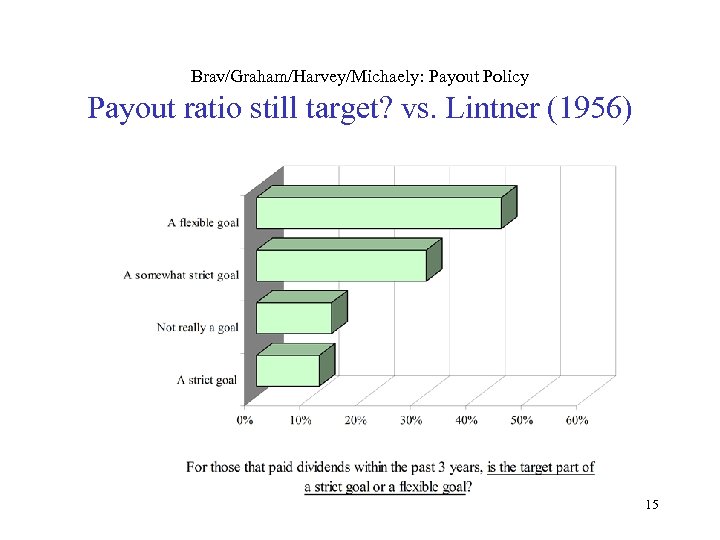 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout ratio still target? vs. Lintner (1956) 15
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout ratio still target? vs. Lintner (1956) 15
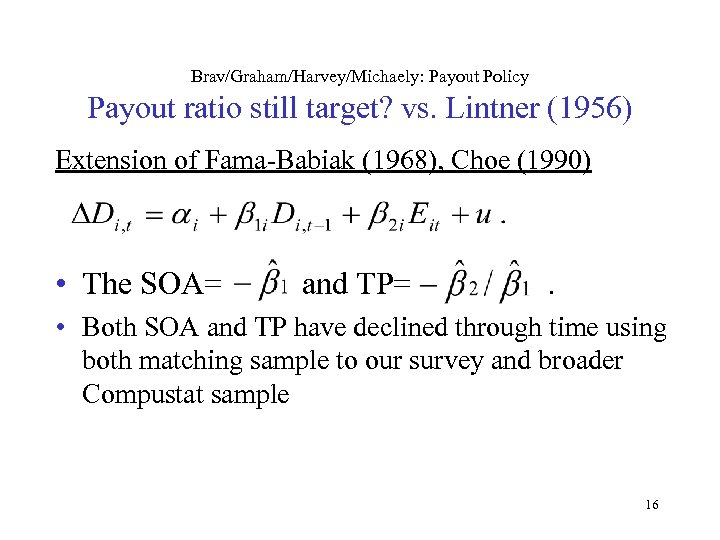 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout ratio still target? vs. Lintner (1956) Extension of Fama-Babiak (1968), Choe (1990) • The SOA= and TP= . • Both SOA and TP have declined through time using both matching sample to our survey and broader Compustat sample 16
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Payout ratio still target? vs. Lintner (1956) Extension of Fama-Babiak (1968), Choe (1990) • The SOA= and TP= . • Both SOA and TP have declined through time using both matching sample to our survey and broader Compustat sample 16
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Summary vs. Lintner (1956) • Dividend policy still very conservative • • • Payout ratio no longer target • • Modern cash cows live in (close to) Lintner world Repurchase policy is not (i. e. , it is more flexible) Targets very flexible Repurchases now very important 17
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Summary vs. Lintner (1956) • Dividend policy still very conservative • • • Payout ratio no longer target • • Modern cash cows live in (close to) Lintner world Repurchase policy is not (i. e. , it is more flexible) Targets very flexible Repurchases now very important 17
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Miller and Modigliani (1961) • Payout Policy irrelevant if capital markets perfect • Imperfections that could explain payout policy – – • Taxes Managerial agency conflict Information/signaling Other factors (EPS, float, credit ratings, etc) Clienteles could result from imperfections 18
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Miller and Modigliani (1961) • Payout Policy irrelevant if capital markets perfect • Imperfections that could explain payout policy – – • Taxes Managerial agency conflict Information/signaling Other factors (EPS, float, credit ratings, etc) Clienteles could result from imperfections 18
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy A. Taxes • Theory: At least for individual investors, dividends are taxed move heavily than capital gains. • Therefore: – Firms should consider investors’ taxation when deciding about payout policy – Relative taxation should affect the amount of dividends they pay 19
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy A. Taxes • Theory: At least for individual investors, dividends are taxed move heavily than capital gains. • Therefore: – Firms should consider investors’ taxation when deciding about payout policy – Relative taxation should affect the amount of dividends they pay 19
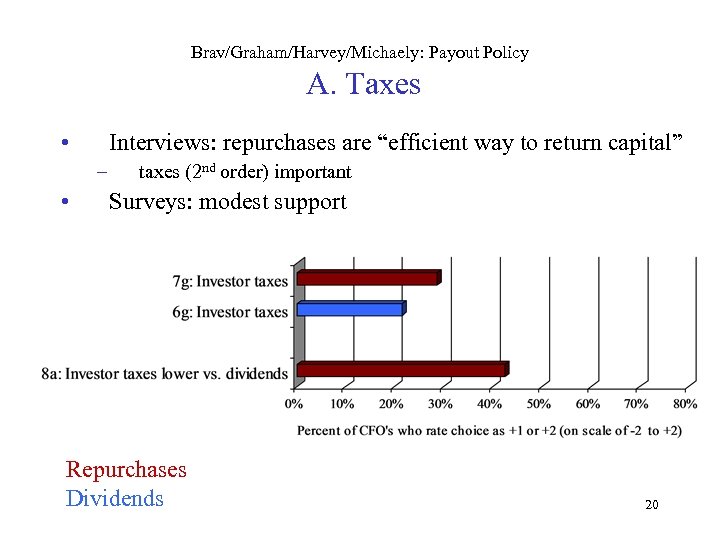 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy A. Taxes • Interviews: repurchases are “efficient way to return capital” – • taxes (2 nd order) important Surveys: modest support Repurchases Dividends 20
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy A. Taxes • Interviews: repurchases are “efficient way to return capital” – • taxes (2 nd order) important Surveys: modest support Repurchases Dividends 20
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy B. Clienteles • Investors that pay (relatively) more taxes on dividends should hold stocks that pay out through repurchases. – Translation: Individual investors should have an aversion to dividend paying stocks. By implications, institutions should be more attracted to such stocks. • Prudent man • Institutions as monitors 21
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy B. Clienteles • Investors that pay (relatively) more taxes on dividends should hold stocks that pay out through repurchases. – Translation: Individual investors should have an aversion to dividend paying stocks. By implications, institutions should be more attracted to such stocks. • Prudent man • Institutions as monitors 21
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy B. Clienteles • Retail investors – – • Prefer dividends, in spite of tax disadvantage Firms like because loyal Institutions – – If anything, prefer repurchases Some can not invest in zero dividend stocks • 42% say pay dividends because of prudent man rules – Tax advantage not an issue to institutions – Firms like because they “have the money” 22
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy B. Clienteles • Retail investors – – • Prefer dividends, in spite of tax disadvantage Firms like because loyal Institutions – – If anything, prefer repurchases Some can not invest in zero dividend stocks • 42% say pay dividends because of prudent man rules – Tax advantage not an issue to institutions – Firms like because they “have the money” 22
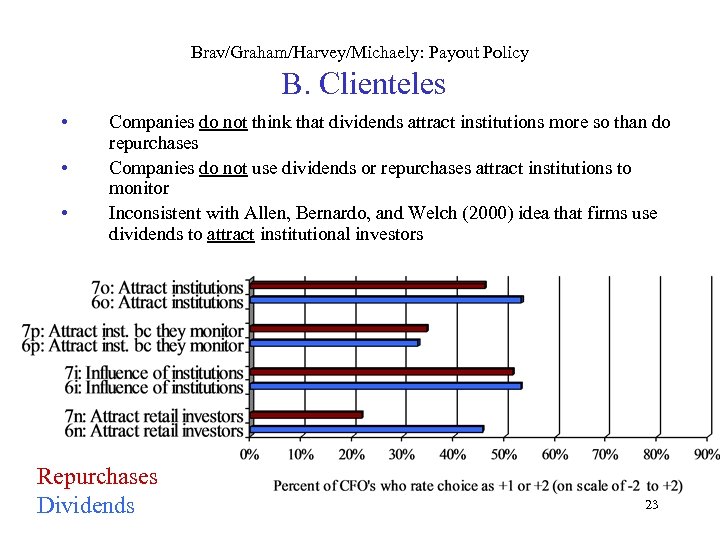 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy B. Clienteles • • • Companies do not think that dividends attract institutions more so than do repurchases Companies do not use dividends or repurchases attract institutions to monitor Inconsistent with Allen, Bernardo, and Welch (2000) idea that firms use dividends to attract institutional investors Repurchases Dividends 23
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy B. Clienteles • • • Companies do not think that dividends attract institutions more so than do repurchases Companies do not use dividends or repurchases attract institutions to monitor Inconsistent with Allen, Bernardo, and Welch (2000) idea that firms use dividends to attract institutional investors Repurchases Dividends 23
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy C. Agency Stories • Firms pay dividends to impose discipline on managers 24
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy C. Agency Stories • Firms pay dividends to impose discipline on managers 24
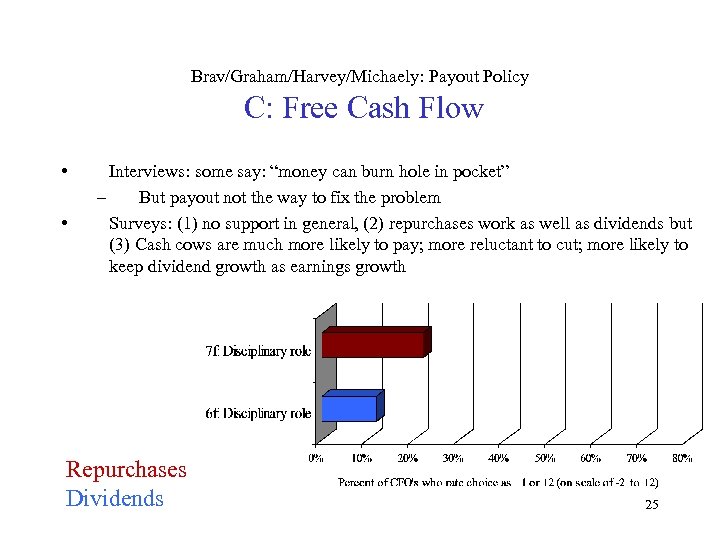 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy C: Free Cash Flow • • Interviews: some say: “money can burn hole in pocket” – But payout not the way to fix the problem Surveys: (1) no support in general, (2) repurchases work as well as dividends but (3) Cash cows are much more likely to pay; more reluctant to cut; more likely to keep dividend growth as earnings growth Repurchases Dividends 25
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy C: Free Cash Flow • • Interviews: some say: “money can burn hole in pocket” – But payout not the way to fix the problem Surveys: (1) no support in general, (2) repurchases work as well as dividends but (3) Cash cows are much more likely to pay; more reluctant to cut; more likely to keep dividend growth as earnings growth Repurchases Dividends 25
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy D. Asymmetric Information • Conveying information • Costly self-imposed action—Signaling • Adverse selection – • Do informed investors benefit from repurchase programs, at expense of uninformed? Stock undervaluation 26
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy D. Asymmetric Information • Conveying information • Costly self-imposed action—Signaling • Adverse selection – • Do informed investors benefit from repurchase programs, at expense of uninformed? Stock undervaluation 26
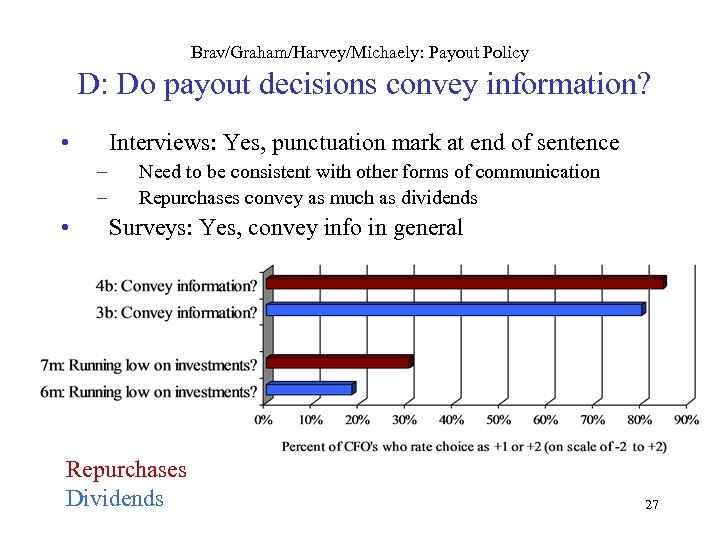 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy D: Do payout decisions convey information? • Interviews: Yes, punctuation mark at end of sentence – – • Need to be consistent with other forms of communication Repurchases convey as much as dividends Surveys: Yes, convey info in general Repurchases Dividends 27
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy D: Do payout decisions convey information? • Interviews: Yes, punctuation mark at end of sentence – – • Need to be consistent with other forms of communication Repurchases convey as much as dividends Surveys: Yes, convey info in general Repurchases Dividends 27
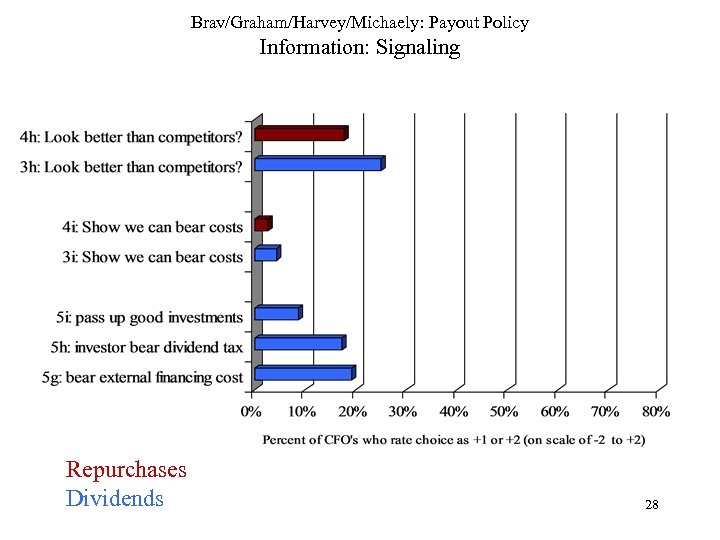 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Information: Signaling Repurchases Dividends 28
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Information: Signaling Repurchases Dividends 28
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy • Surveys – – – • D. Information: Signaling No supporting evidence Scores are even lower for growth/risky firms 39% (16%) say keep div (repurchase) policy of peers Interviews – – – Spent hours on this issue Generally try to group selves with peers (not separate) No evidence of • • – increasing dividend to show market that firm is strong viewing dividend as self-imposed cost Avoiding dividend cut • • • Possibly a signal (costly for bad firms, separate from bad) Cuts are rare – can’t explain dividend policy for most firms Does not explain why firms pay dividends in the first place 29
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy • Surveys – – – • D. Information: Signaling No supporting evidence Scores are even lower for growth/risky firms 39% (16%) say keep div (repurchase) policy of peers Interviews – – – Spent hours on this issue Generally try to group selves with peers (not separate) No evidence of • • – increasing dividend to show market that firm is strong viewing dividend as self-imposed cost Avoiding dividend cut • • • Possibly a signal (costly for bad firms, separate from bad) Cuts are rare – can’t explain dividend policy for most firms Does not explain why firms pay dividends in the first place 29
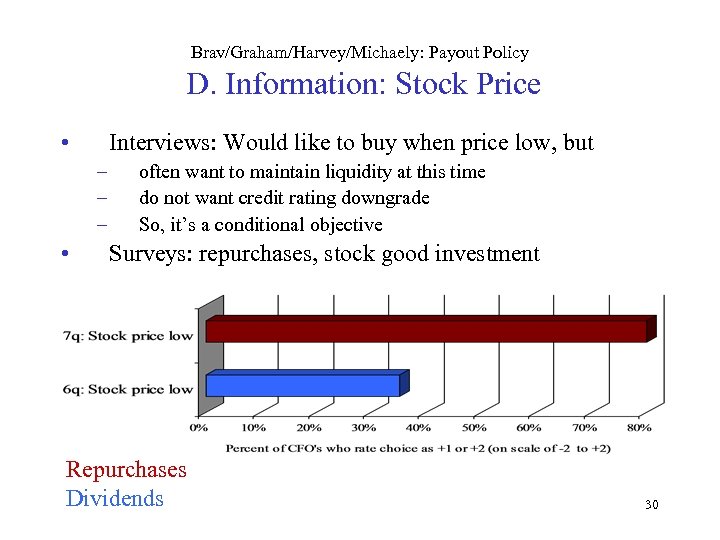 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy D. Information: Stock Price • Interviews: Would like to buy when price low, but – – – • often want to maintain liquidity at this time do not want credit rating downgrade So, it’s a conditional objective Surveys: repurchases, stock good investment Repurchases Dividends 30
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy D. Information: Stock Price • Interviews: Would like to buy when price low, but – – – • often want to maintain liquidity at this time do not want credit rating downgrade So, it’s a conditional objective Surveys: repurchases, stock good investment Repurchases Dividends 30
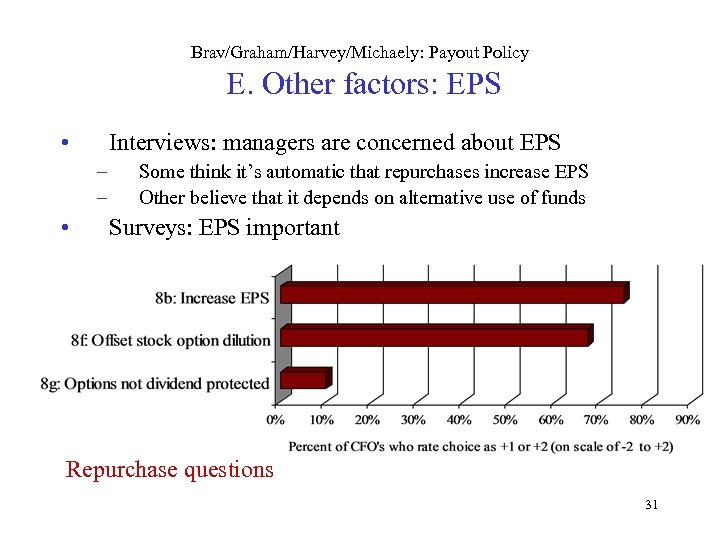 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy E. Other factors: EPS • Interviews: managers are concerned about EPS – – • Some think it’s automatic that repurchases increase EPS Other believe that it depends on alternative use of funds Surveys: EPS important Repurchase questions 31
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy E. Other factors: EPS • Interviews: managers are concerned about EPS – – • Some think it’s automatic that repurchases increase EPS Other believe that it depends on alternative use of funds Surveys: EPS important Repurchase questions 31
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy E. Other factors: Float and credit ratings • Interviews: Float very important – • Execs think they need to have a large number of shareholders Interviews: credit rating important – – Hoard cash to improve rating Especially for financial firms or firms with financial divisions Repurchases Dividends 32
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy E. Other factors: Float and credit ratings • Interviews: Float very important – • Execs think they need to have a large number of shareholders Interviews: credit rating important – – Hoard cash to improve rating Especially for financial firms or firms with financial divisions Repurchases Dividends 32
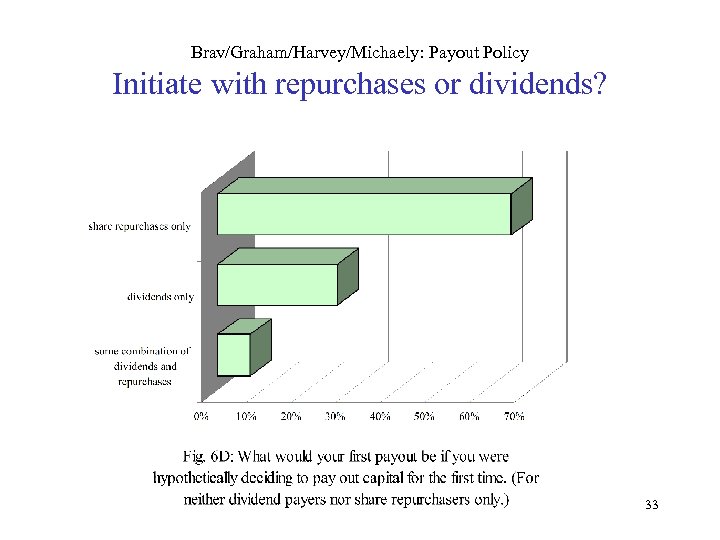 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Initiate with repurchases or dividends? 33
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Initiate with repurchases or dividends? 33
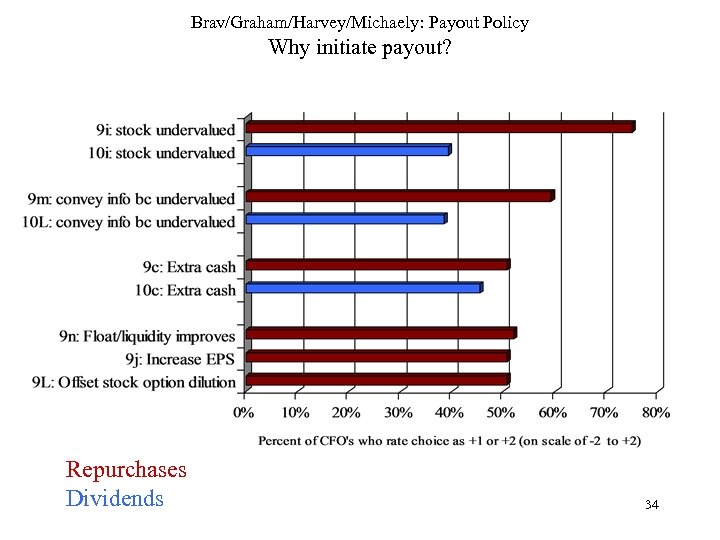 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Why initiate payout? Repurchases Dividends 34
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Why initiate payout? Repurchases Dividends 34
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conclusions • Payout policy is not first-order important* (M&M) • Repurchases: decided de novo • Dividends: level very important • Managers prefer repurchases over dividends because they are more flexible. – Not because of taxes. 35
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conclusions • Payout policy is not first-order important* (M&M) • Repurchases: decided de novo • Dividends: level very important • Managers prefer repurchases over dividends because they are more flexible. – Not because of taxes. 35
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conclusions • According to managers, payout – convey information – NOT being used as a costly signal – NOT being used to attract institutions • Managers do not use dividends over repurchases to attract institutions • Institutions do not push for more dividends 36
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conclusions • According to managers, payout – convey information – NOT being used as a costly signal – NOT being used to attract institutions • Managers do not use dividends over repurchases to attract institutions • Institutions do not push for more dividends 36
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conclusions • Managers of cash cows believe more strongly that – Dividends should be stable – Keeping dividend growth rate with earnings growth • But all managers reject the notion that they need dividends so that they will not spend cash unwisely. 37
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Conclusions • Managers of cash cows believe more strongly that – Dividends should be stable – Keeping dividend growth rate with earnings growth • But all managers reject the notion that they need dividends so that they will not spend cash unwisely. 37
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Rules of the Game: How payout policies are determined • Make investment plans first* • Take care of cash/liquidity needs • *BUT, remember, level of dividends fixed • Only reduce dividends in extraordinary circumstances • • • Severe penalty for cutting dividend because the market believes that “cuts precede bad news” So, don’t ever cut dividends • unless you have an amazing investment opportunity • smaller penalty if competitors cut Think very carefully before initiating dividends 38
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Rules of the Game: How payout policies are determined • Make investment plans first* • Take care of cash/liquidity needs • *BUT, remember, level of dividends fixed • Only reduce dividends in extraordinary circumstances • • • Severe penalty for cutting dividend because the market believes that “cuts precede bad news” So, don’t ever cut dividends • unless you have an amazing investment opportunity • smaller penalty if competitors cut Think very carefully before initiating dividends 38
 Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Rules of the Game • Desire to maintain the level of dividend “at any cost” consistent with findings in Graham, Harvey and Rajgopal, 2004, “The Economic Implications of Corporate Financial Reporting” • • • Here managers desire to hit consensus EPS “at any cost” 55% would knowingly sacrifice value (not pursue a very positive NPV project) if it would cause the firm to miss next quarter’s target! 78% would knowingly sacrifice value to smooth earnings 39
Brav/Graham/Harvey/Michaely: Payout Policy Rules of the Game • Desire to maintain the level of dividend “at any cost” consistent with findings in Graham, Harvey and Rajgopal, 2004, “The Economic Implications of Corporate Financial Reporting” • • • Here managers desire to hit consensus EPS “at any cost” 55% would knowingly sacrifice value (not pursue a very positive NPV project) if it would cause the firm to miss next quarter’s target! 78% would knowingly sacrifice value to smooth earnings 39


