84c4cd48c4fb7dd47142c47dec087edc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Paul R Schapper May 2009
Paul R Schapper May 2009
 INTRODUCTION E-GP as a key component of Procurement Reform
INTRODUCTION E-GP as a key component of Procurement Reform
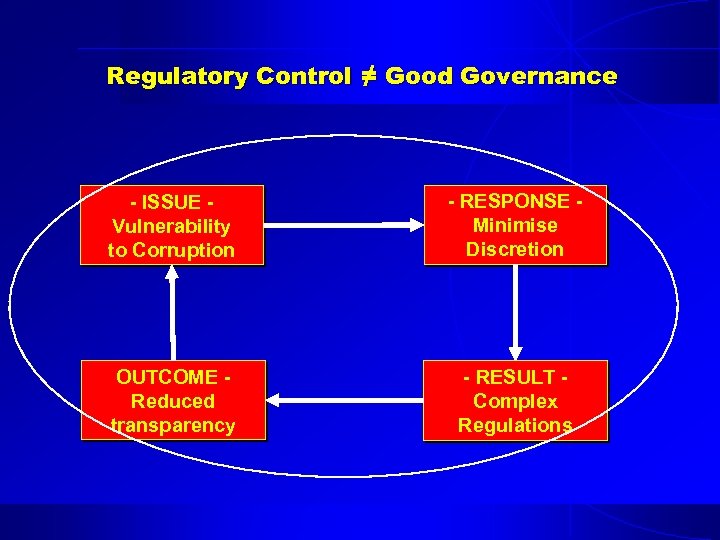 Regulatory Control ≠ Good Governance - ISSUE Vulnerability to Corruption - RESPONSE Minimise Discretion OUTCOME Reduced transparency - RESULT Complex Regulations
Regulatory Control ≠ Good Governance - ISSUE Vulnerability to Corruption - RESPONSE Minimise Discretion OUTCOME Reduced transparency - RESULT Complex Regulations
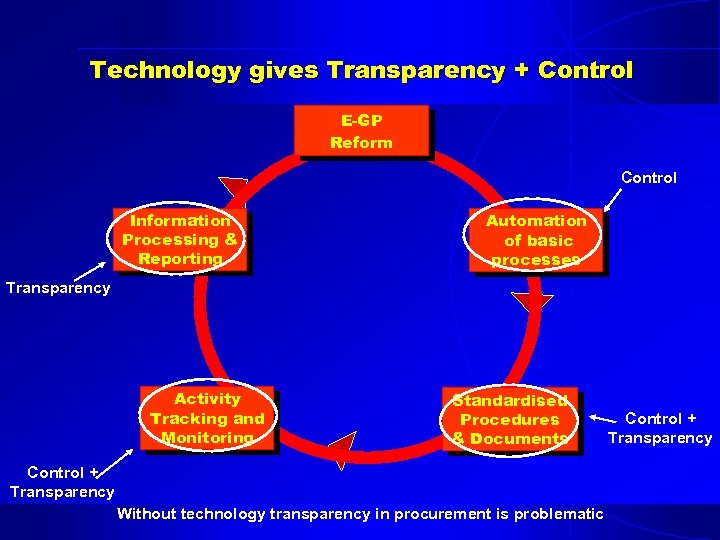 Technology gives Transparency + Control E-GP Reform Control Information Processing & Reporting Automation of basic processes Transparency Activity Tracking and Monitoring Standardised Procedures & Documents Control + Transparency Without technology transparency in procurement is problematic Control + Transparency
Technology gives Transparency + Control E-GP Reform Control Information Processing & Reporting Automation of basic processes Transparency Activity Tracking and Monitoring Standardised Procedures & Documents Control + Transparency Without technology transparency in procurement is problematic Control + Transparency
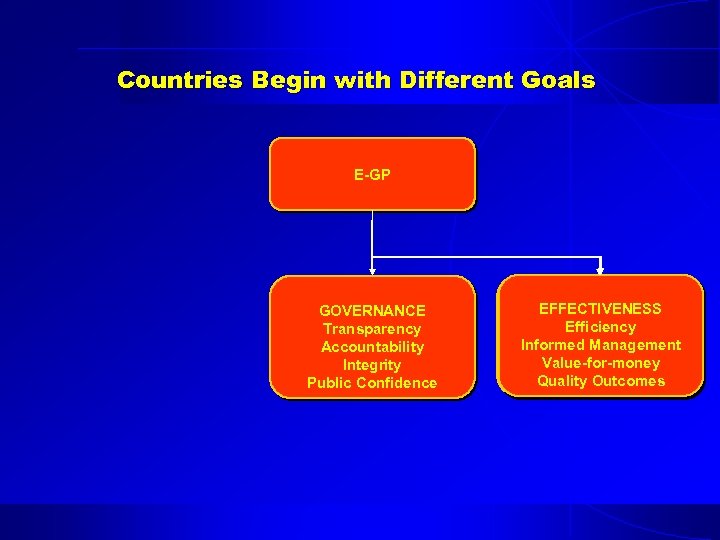 Countries Begin with Different Goals E-GP GOVERNANCE Transparency Accountability Integrity Public Confidence EFFECTIVENESS ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Efficiency Business development Informed Management Competitiveness Value-for-money Technological Enablement Quality Outcomes Market Access
Countries Begin with Different Goals E-GP GOVERNANCE Transparency Accountability Integrity Public Confidence EFFECTIVENESS ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Efficiency Business development Informed Management Competitiveness Value-for-money Technological Enablement Quality Outcomes Market Access
 DEFINITION Common understanding of e-GP in general and in particular e-GP: just another IT system? How can electronic means be used to support public procurement systems including principles, objectives, legislation, and procedures? What are the basic differences between e-Tendering and e. Purchasing?
DEFINITION Common understanding of e-GP in general and in particular e-GP: just another IT system? How can electronic means be used to support public procurement systems including principles, objectives, legislation, and procedures? What are the basic differences between e-Tendering and e. Purchasing?
 What is e-GP? Ø E-GP is the application of technology to public procurement Ø An e-GP implementation strategy is a management and reform programme Ø E-GP is not a software programme but includes software Ø E-GP is not centralisation of procurement but requires centrally determined standards and procedures Ø It applies to the acquisition of works, goods and services. Ø Objectives include to improve governance and efficiency E-GP reduces the need for detailed and complex regulation to prescribe all the procurement processes and allows greater focus on objectives and outcomes. Ir is the capacity to change the quality of governance that makes e-GP so significant and changes the regulatory needs
What is e-GP? Ø E-GP is the application of technology to public procurement Ø An e-GP implementation strategy is a management and reform programme Ø E-GP is not a software programme but includes software Ø E-GP is not centralisation of procurement but requires centrally determined standards and procedures Ø It applies to the acquisition of works, goods and services. Ø Objectives include to improve governance and efficiency E-GP reduces the need for detailed and complex regulation to prescribe all the procurement processes and allows greater focus on objectives and outcomes. Ir is the capacity to change the quality of governance that makes e-GP so significant and changes the regulatory needs
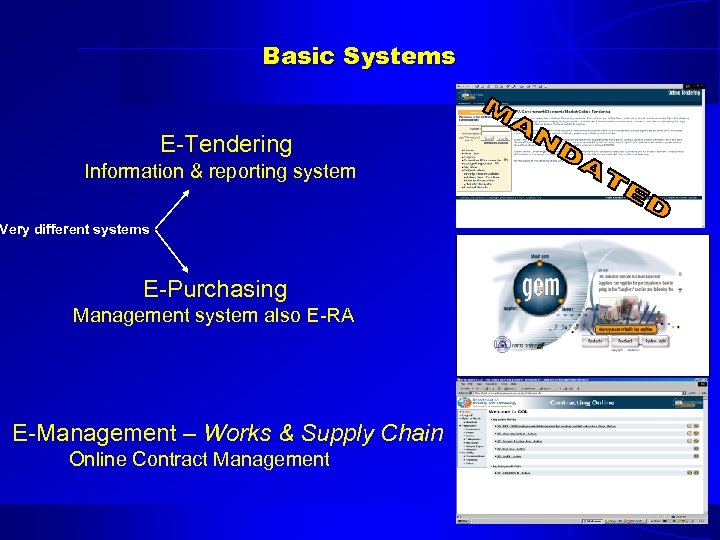 Basic Systems E-Tendering Information & reporting system Very different systems E-Purchasing Management system also E-RA E-Management – Works & Supply Chain Online Contract Management
Basic Systems E-Tendering Information & reporting system Very different systems E-Purchasing Management system also E-RA E-Management – Works & Supply Chain Online Contract Management
 Online Tender Service - LHF Ø Ø Ø STATISTICS Cost to develop $US 500, 000 Time to develop v 2 3 -9 months Firms registered 25, 000 Tenders 100 / day Staff required 4 Electronic downloads 70% ETL 50% Access rate 2000 / day User charges $0. 0 Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Transparent and open Audit trails, access logs Promotes competition Downloads tender documents and drawings Uploads documents and drawings Request a hardcopy Search facilities Early tender advice Electronic lodgment Tenders Seek facility Pending Award, tracking Awarded contract information Archived contracts Industry e-activation
Online Tender Service - LHF Ø Ø Ø STATISTICS Cost to develop $US 500, 000 Time to develop v 2 3 -9 months Firms registered 25, 000 Tenders 100 / day Staff required 4 Electronic downloads 70% ETL 50% Access rate 2000 / day User charges $0. 0 Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Transparent and open Audit trails, access logs Promotes competition Downloads tender documents and drawings Uploads documents and drawings Request a hardcopy Search facilities Early tender advice Electronic lodgment Tenders Seek facility Pending Award, tracking Awarded contract information Archived contracts Industry e-activation
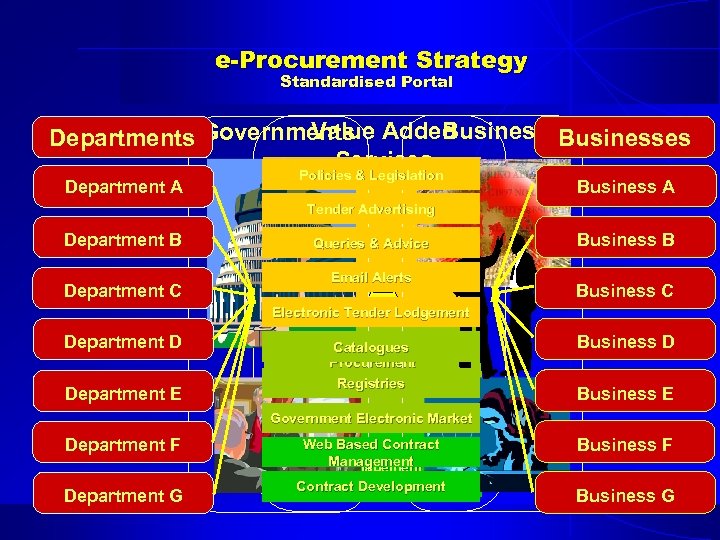 e-Procurement Strategy Standardised Portal Businesses Value Departments Governments Added Services Department A Department B Department C Policies & Legislation Tender Advertising High Value, Low Volume Procurement Queries & Advice (E-TENDERS) Email Alerts Business A Business B Business C Electronic Tender Lodgement Department D Department E Low Value, High Volume Catalogues Procurement (E-PURCHASING) Registries Business D Business E Government Electronic Market Department F Web Based Contract Management E-Management Business F Department G Contract Development Business G
e-Procurement Strategy Standardised Portal Businesses Value Departments Governments Added Services Department A Department B Department C Policies & Legislation Tender Advertising High Value, Low Volume Procurement Queries & Advice (E-TENDERS) Email Alerts Business A Business B Business C Electronic Tender Lodgement Department D Department E Low Value, High Volume Catalogues Procurement (E-PURCHASING) Registries Business D Business E Government Electronic Market Department F Web Based Contract Management E-Management Business F Department G Contract Development Business G
 CHALLENGES Key success factors of e. GP implementation Risks of e-GP Suggested roadmap
CHALLENGES Key success factors of e. GP implementation Risks of e-GP Suggested roadmap
 Why are Standards Important? Mars Polar Lander Example: Five clients – five systems
Why are Standards Important? Mars Polar Lander Example: Five clients – five systems
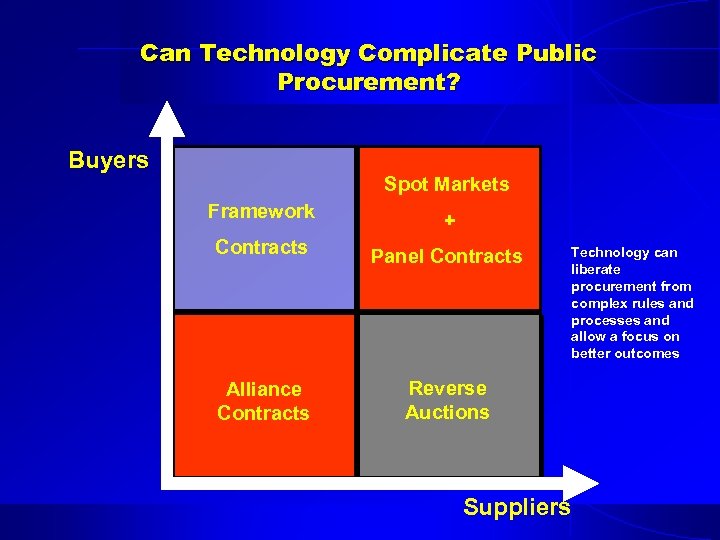 Can Technology Complicate Public Procurement? Buyers Spot Markets Framework + Contracts Panel Contracts Alliance Contracts Reverse Auctions Technology can liberate procurement from complex rules and processes and allow a focus on better outcomes Suppliers
Can Technology Complicate Public Procurement? Buyers Spot Markets Framework + Contracts Panel Contracts Alliance Contracts Reverse Auctions Technology can liberate procurement from complex rules and processes and allow a focus on better outcomes Suppliers
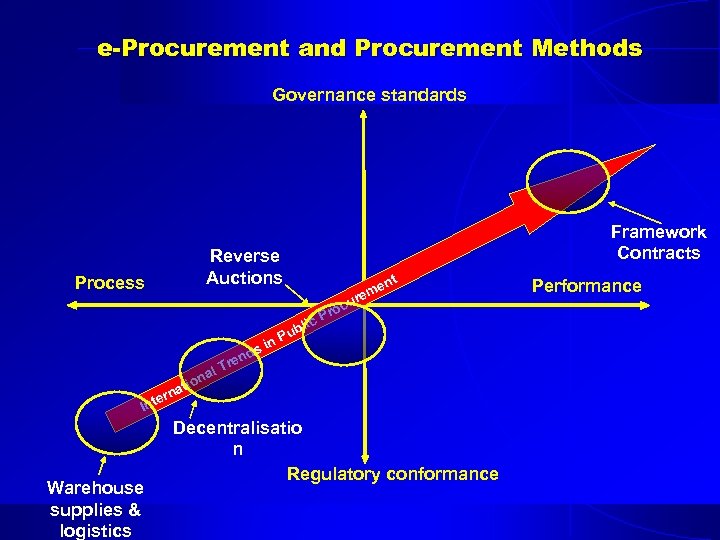 e-Procurement and Procurement Methods Governance standards Framework Contracts Reverse Auctions Process nt lic ub ti rna P n. P si d ren T al on e rem u roc e Int Warehouse supplies & logistics Decentralisatio n Regulatory conformance Performance
e-Procurement and Procurement Methods Governance standards Framework Contracts Reverse Auctions Process nt lic ub ti rna P n. P si d ren T al on e rem u roc e Int Warehouse supplies & logistics Decentralisatio n Regulatory conformance Performance
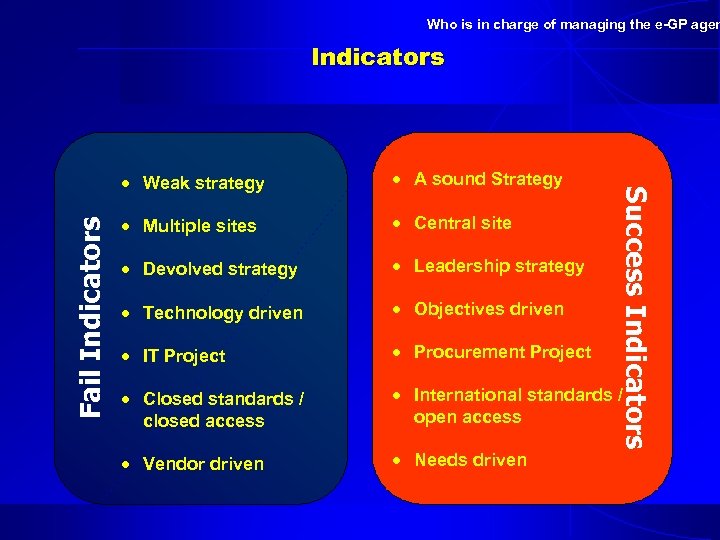 Who is in charge of managing the e-GP agen Indicators Fail Indicators A sound Strategy Multiple sites Central site Devolved strategy Leadership strategy Technology driven Objectives driven IT Project Procurement Project Closed standards / closed access International standards / open access Vendor driven Needs driven Success Indicators Weak strategy
Who is in charge of managing the e-GP agen Indicators Fail Indicators A sound Strategy Multiple sites Central site Devolved strategy Leadership strategy Technology driven Objectives driven IT Project Procurement Project Closed standards / closed access International standards / open access Vendor driven Needs driven Success Indicators Weak strategy
 The Lessons Learnt Ø Ø Small Business friendly Ø Management not technology Ø Get right expertise Ø Needs vs vendor driven Ø International standards based Ø Architecture Ø Small steps not big bang Ø . Vision and leadership - national Education and training are essential How should the use of electronic means be addressed in the procurement policy and legislation? How to activate buyers and suppliers and ensure connectivity? Applying technology to automate some existing processes is a waste of time and money
The Lessons Learnt Ø Ø Small Business friendly Ø Management not technology Ø Get right expertise Ø Needs vs vendor driven Ø International standards based Ø Architecture Ø Small steps not big bang Ø . Vision and leadership - national Education and training are essential How should the use of electronic means be addressed in the procurement policy and legislation? How to activate buyers and suppliers and ensure connectivity? Applying technology to automate some existing processes is a waste of time and money
 Which Path? Where, when, and what to start with? Ø Ø Ø Ø How to start? Where to start? Lead Agency? E-Tendering? E-Reverse Auctions? E-Contract Management? E-Purchasing? Phased or Big Bang? Timeframes? Costs? Security? Policy Sovereignty? FMIS? Evaluation? Pre-qualification? BOOT? SLA? Legislation
Which Path? Where, when, and what to start with? Ø Ø Ø Ø How to start? Where to start? Lead Agency? E-Tendering? E-Reverse Auctions? E-Contract Management? E-Purchasing? Phased or Big Bang? Timeframes? Costs? Security? Policy Sovereignty? FMIS? Evaluation? Pre-qualification? BOOT? SLA? Legislation
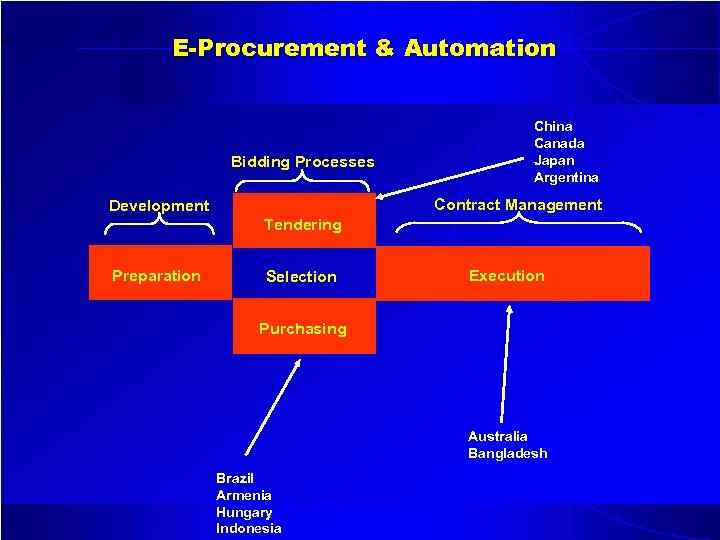 . E-Procurement & Automation Bidding Processes China Canada Japan Argentina Contract Management Development Tendering Preparation Selection Execution Purchasing Australia Bangladesh Brazil Armenia Hungary Indonesia
. E-Procurement & Automation Bidding Processes China Canada Japan Argentina Contract Management Development Tendering Preparation Selection Execution Purchasing Australia Bangladesh Brazil Armenia Hungary Indonesia
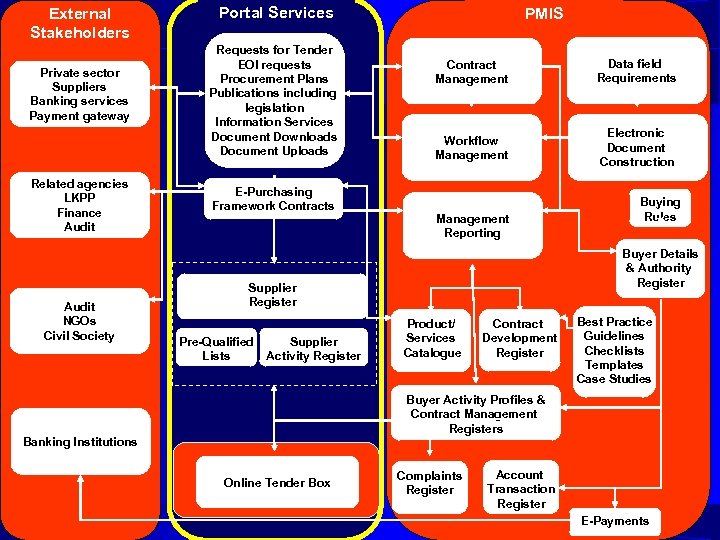 External Stakeholders Private sector Suppliers Banking services Payment gateway Related agencies LKPP Finance Audit NGOs Civil Society Portal Services Requests for Tender EOI requests Procurement Plans Publications including legislation Information Services Document Downloads Document Uploads E-Purchasing Framework Contracts PMIS Contract Management Data field Requirements Workflow Management Electronic Document Construction Management Reporting Buyer Details & Authority Register Supplier Register Pre-Qualified Lists Supplier Activity Register Buying Rules Product/ Services Catalogue Contract Development Register Best Practice Guidelines Checklists Templates Case Studies Buyer Activity Profiles & Contract Management Registers Banking Institutions Online Tender Box Complaints Register Account Transaction Register E-Payments
External Stakeholders Private sector Suppliers Banking services Payment gateway Related agencies LKPP Finance Audit NGOs Civil Society Portal Services Requests for Tender EOI requests Procurement Plans Publications including legislation Information Services Document Downloads Document Uploads E-Purchasing Framework Contracts PMIS Contract Management Data field Requirements Workflow Management Electronic Document Construction Management Reporting Buyer Details & Authority Register Supplier Register Pre-Qualified Lists Supplier Activity Register Buying Rules Product/ Services Catalogue Contract Development Register Best Practice Guidelines Checklists Templates Case Studies Buyer Activity Profiles & Contract Management Registers Banking Institutions Online Tender Box Complaints Register Account Transaction Register E-Payments
 IMPACT EVALUATION Performance indicators
IMPACT EVALUATION Performance indicators
 Performance Qualitative and Quantitative Ø Integrated with BP Ø User friendly Ø Cost recovery Ø Transparent Ø Take-up Ø Satisfaction – buyers Ø Satisfaction – suppliers Ø KPIs……
Performance Qualitative and Quantitative Ø Integrated with BP Ø User friendly Ø Cost recovery Ø Transparent Ø Take-up Ø Satisfaction – buyers Ø Satisfaction – suppliers Ø KPIs……
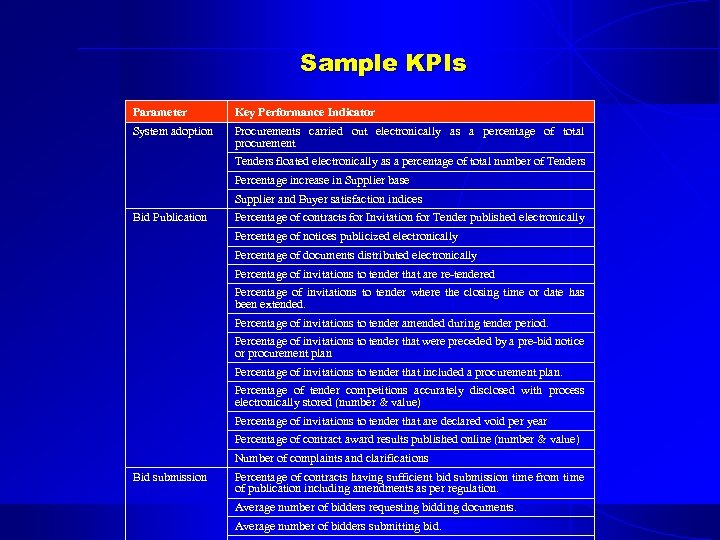 Sample KPIs Parameter Key Performance Indicator System adoption Procurements carried out electronically as a percentage of total procurement Tenders floated electronically as a percentage of total number of Tenders Percentage increase in Supplier base Supplier and Buyer satisfaction indices Bid Publication Percentage of contracts for Invitation for Tender published electronically Percentage of notices publicized electronically Percentage of documents distributed electronically Percentage of invitations to tender that are re-tendered Percentage of invitations to tender where the closing time or date has been extended. Percentage of invitations to tender amended during tender period. Percentage of invitations to tender that were preceded by a pre-bid notice or procurement plan Percentage of invitations to tender that included a procurement plan. Percentage of tender competitions accurately disclosed with process electronically stored (number & value) Percentage of invitations to tender that are declared void per year Percentage of contract award results published online (number & value) Number of complaints and clarifications Bid submission Percentage of contracts having sufficient bid submission time from time of publication including amendments as per regulation. Average number of bidders requesting bidding documents. Average number of bidders submitting bid.
Sample KPIs Parameter Key Performance Indicator System adoption Procurements carried out electronically as a percentage of total procurement Tenders floated electronically as a percentage of total number of Tenders Percentage increase in Supplier base Supplier and Buyer satisfaction indices Bid Publication Percentage of contracts for Invitation for Tender published electronically Percentage of notices publicized electronically Percentage of documents distributed electronically Percentage of invitations to tender that are re-tendered Percentage of invitations to tender where the closing time or date has been extended. Percentage of invitations to tender amended during tender period. Percentage of invitations to tender that were preceded by a pre-bid notice or procurement plan Percentage of invitations to tender that included a procurement plan. Percentage of tender competitions accurately disclosed with process electronically stored (number & value) Percentage of invitations to tender that are declared void per year Percentage of contract award results published online (number & value) Number of complaints and clarifications Bid submission Percentage of contracts having sufficient bid submission time from time of publication including amendments as per regulation. Average number of bidders requesting bidding documents. Average number of bidders submitting bid.
 Paul R Schapper May 2009
Paul R Schapper May 2009


