cd36df7c1be18853df547ead1176e3f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Patient Safety & Clinical Pharmacy Services Collaborative Rebecca Cheek Director of Pharmacy White House Clinics 606 -287 -7104

Questions to Run On • How can you implement Clinical Pharmacy Services at your site? • Do you have a method in place to track Adverse Drug Events (ADE’s) and potential Adverse Drug Events (p. ADE’s)?

PSPC w Similar to other HRSA sponsored collaboratives w All Teach, All Learn environment w Starting 3 rd year in October 2010 w White House Clinic has been involved since the beginning-August 2008

Our Collaborative Team Clinical Pharmacy Service Providers at the Primary Health Care Home Becky Cheek, Pharm. D Pharmacy Director Collaborative Lead Sharon Davidson, Pharm. D Other Providers at the Primary Health Care Home Melissa Zook, M. D. Family Physician Medical Director Steven Wagers, Pharm. D Sandra Dionisio, M. D. Internist

PSPC Collaborative AIM w To Save and Enhance thousands of lives each year by: – Achieving optimal health care outcomes and – Eliminating Adverse Drug Events through – Increased Clinical Pharmacy Services for the patients we serve w The Goal of Collaborative Services is to: – Improve patient safety – Improve patient health outcomes – Integration of cost-effective clinical pharmacy services

Our PSPC Aim Statement White House Clinics will strive to provide clinical pharmacy services to highrisk patients in an effort to decrease adverse events while encouraging those patients to become active partners in the management of their health condition.

What are Clinical Pharmacy Services? w CPS are patient-centered services that promote the appropriate selection and utilization of medications through: 1. Medication access* q 340 b formulary q Recommending generic alternatives q Patient Assistance Programs 2. Patient counseling * q Rx pick-up (required by OBRA-90) q Phone calls 3. Medication Therapy Management (MTM)* q Poly-pharmacy management q Recommendations given to patient or provider q Changes to therapy after DUR/ADE

CPS Services cont. 4. Preventive Care Programs q q q 5. BMI or blood pressure Immunizations Drug Information Services to Patients* q q Drug information leaflets Disease state pamphlets 6. Medication Reconciliation Services q Having 1 accurate medication list

CPS services cont. 7. Provider Education* q Pharmacist provides evidence based drug information to provider 8. Retrospective Drug Utilization Review* q Review patients on certain meds or with certain disease states to assess quality and safety 9. Disease State Management* q Medications managed to obtain health outcomes and improve safety q Labs ordered and evaluated

CPS services cont 10. Prospective chart review and provider consultation* q Review chart before visit and make recommendations to provider team *Clinical pharmacy services that we provide at WHC

Why Are We Doing This Work? w Increase in multiple chronic conditions w Institute of Medicine Report: ADEs are leading cause of death and injury w Every $ spent on a RX = a $ spent on an ADE w Aging population/chronic disease – leading to high prevalence of poly-pharmacy w Lack of integration of clinical pharmacy services w Alignment with HRSA Core Measures

Key Benefits w It’s the Right Thing to Do for the Patients We Serve – Safer – Increased and Better Pharmacy Services – Improved Health Outcomes w Reduces/Manages Risk – and Risk is Increasing w Builds on and Takes Prior Knowledge Base and Experience to a New Level w Takes HRSA Collaborative Experiences to the Next Power

Key Benefits w Integrates Services to Maximize Community Health w Reduces Inappropriate Use of Poly-pharmacy – Better Medication Management w Helps Create New Partnerships & Synergies Across Provider Organizations w Exposure to Cutting Edge People and Methods on Quality Improvement, Leadership & Change Management w Opportunity to be a Part of a Major National Movement in a Rewarding All Teach, All Learn Environment

Examples of Disease States in Collaborative w Diabetes-Hg. A 1 C w Hypertension-blood pressure w Hyperlipidemia-LDL, triglycerides w Asthma-peak flow, ACT test, controller meds w Anticoagulation-INR in range w HIV
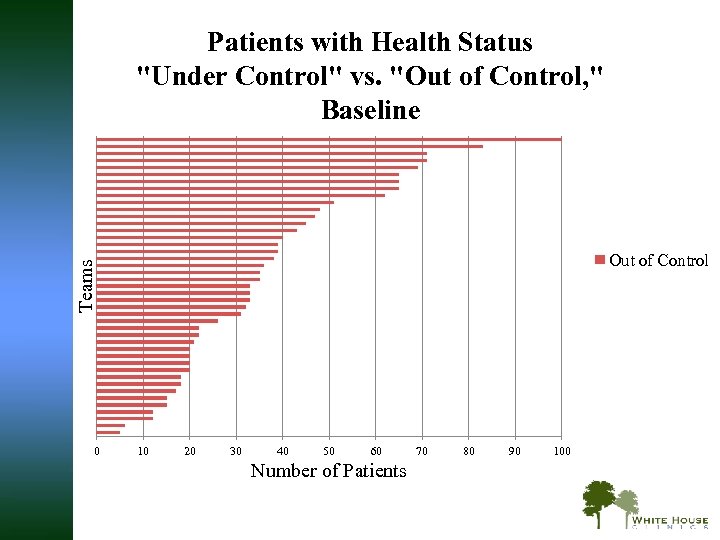
Patients with Health Status "Under Control" vs. "Out of Control, " Baseline Teams Out of Control 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Number of Patients 70 80 90 100
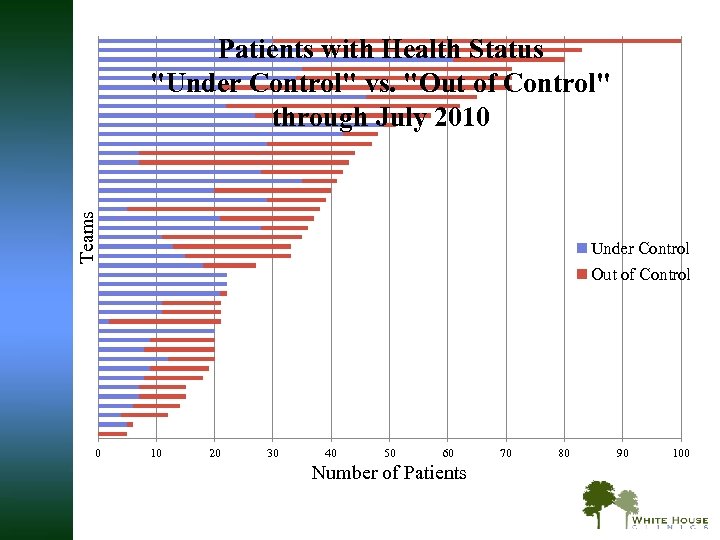
Teams Patients with Health Status "Under Control" vs. "Out of Control" through July 2010 Under Control Out of Control 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Number of Patients 70 80 90 100
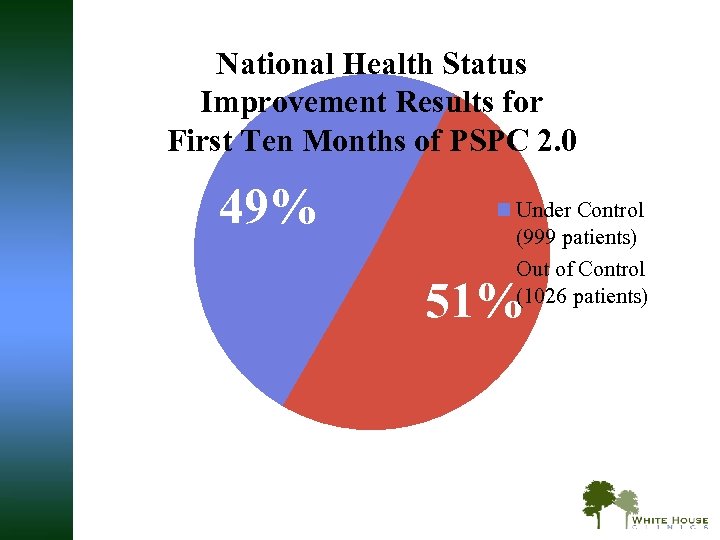
National Health Status Improvement Results for First Ten Months of PSPC 2. 0 49% Under Control (999 patients) Out of Control (1026 patients) 51%

PSPC Outcomes: Improvements in Health Status Average team improvement through July 2010 § 49% improved from health status “out of control” to “under control” § Across a range of chronic diseases, using standardized measures — such as A 1 C levels, blood pressure, LDL, INR ranges, depression scores, and viral load

What did we need to do for the collaborative? w We needed to choose a Population of Focus (POF) w We needed to track ADE’s and p. ADE’s to improve safety
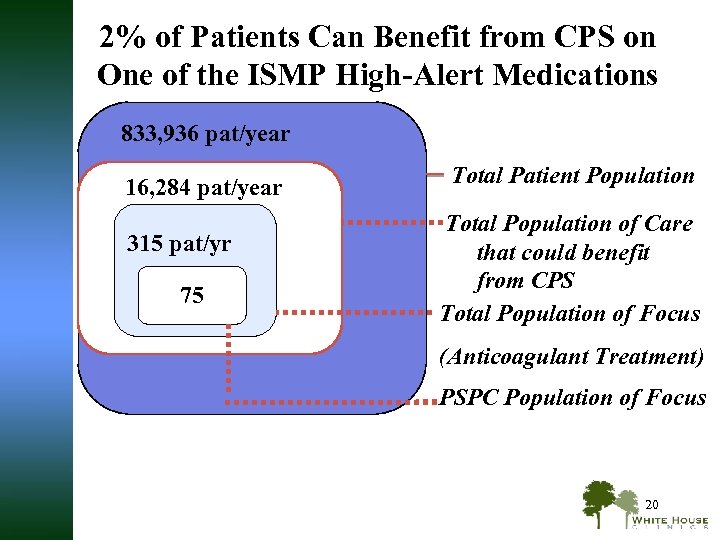
2% of Patients Can Benefit from CPS on One of the ISMP High-Alert Medications 833, 936 pat/year 16, 284 pat/year 315 pat/yr 75 Total Patient Population Total Population of Care that could benefit from CPS Total Population of Focus (Anticoagulant Treatment) PSPC Population of Focus 20

White House Clinics Improvement Story w Population of Focus – Patients receiving Coumadin® (Warfarin) therapy referred to the Coumadin Clinic for anticoagulation management w Baseline data unavailable as no data tracking methods in place w After enrolling, developed plan to collect data-manual, EMR template, EMR reports

Population of Focus § Indications • • • CVA – 6% Atrial Fibrillation – 61. 4% Mitral Valve Replacement – 10. 8% Deep Vein Thrombosis – 13. 3% Pulmonary Embolism – 8. 4% § Patient Age § § § <50 = 11 50 – 65 = 24 65 – 74 = 22 75 – 84 = 20 85 – 94 = 3 § Setting • Ambulatory – 75 • Home Health - 5

High Risk Qualities in POF Panel • Medications per Patient – 7 to 8 • Providers per Patient – 3 • Largest Safety Issues – Bleeding, Thrombotic Event • Largest Health Status Problems – Hypertension, Atrial Fibrillation, Diabetes

Anticoagulation Management Data w %INR values within range (goal 2. 0 -3. 0) – Usual medical care with physician: 29. 6% – Pharmacist-run Anticoagulation Clinic: 64% Chiquette E, Amato MG, and Bussey HI. Comparison of an Anticoagulation Clinic with Usual Medical Care. Arch Itern Med. 1998; 158: 1641 -1647.
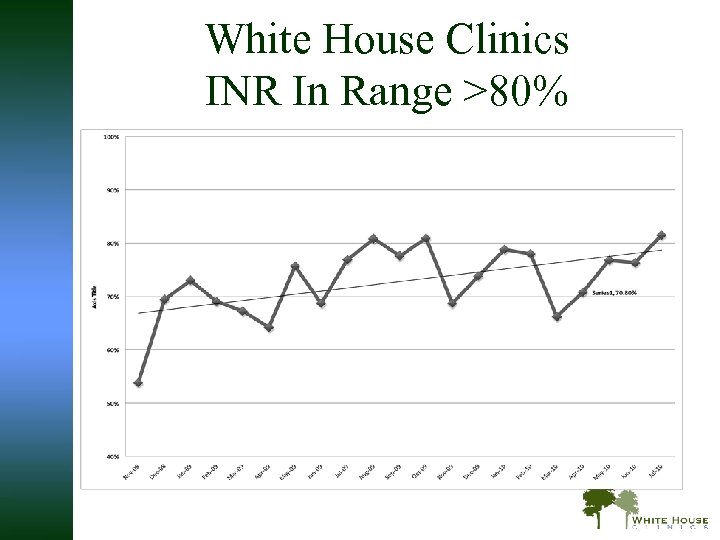
White House Clinics INR In Range >80%

Improving Safety and Eliminating Adverse Events Tracking ADEs & p. ADE w ADE – Adverse Drug Event – Events that result in harm or injury to the patient due to medication use • Example – Bleeding as a result of Coumadin® (Warfarin) administration w p. ADE – Potential Adverse Drug Event – Potential harm that was identified and avoided with appropriate interventions before reaching the patient • Example – Pharmacist catches an allergy to Penicillin and calls the physician to change Amoxicillin to Azithromycin prior to dispensing • Example – A Pharmacist notices a duplication of drug therapy (Lisinopril & Ramipril) and intervenes to have one of the medications discontinued before the patient receives the medication

ADE’s & p. ADE’s w No tracking prior to starting collaborative w Through the collaborative many organizations have observed a significant amount of ADE’s and p. ADE’s due to a lack in tracking data w Clinical Pharmacy Services have allowed these same organizations to see a decline in them over time
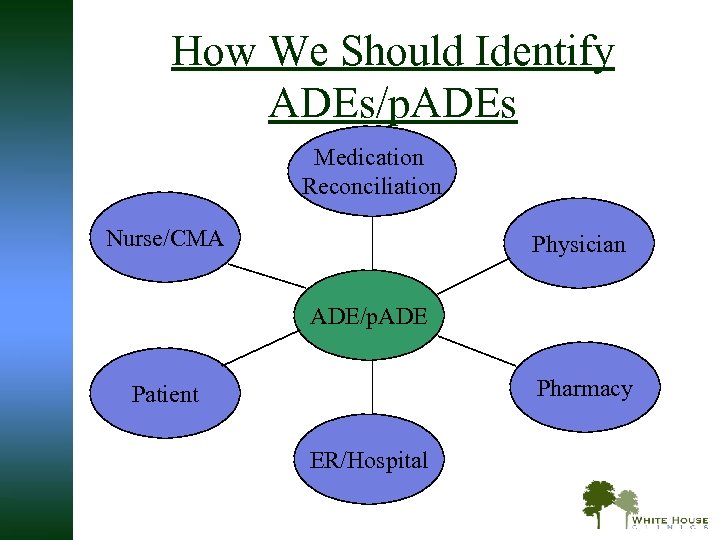
How We Should Identify ADEs/p. ADEs Medication Reconciliation Nurse/CMA Physician ADE/p. ADE Pharmacy Patient ER/Hospital
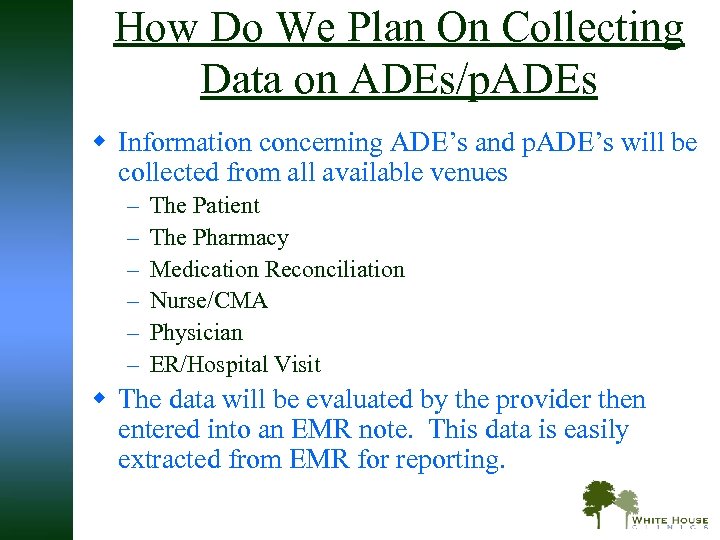
How Do We Plan On Collecting Data on ADEs/p. ADEs w Information concerning ADE’s and p. ADE’s will be collected from all available venues – – – The Patient The Pharmacy Medication Reconciliation Nurse/CMA Physician ER/Hospital Visit w The data will be evaluated by the provider then entered into an EMR note. This data is easily extracted from EMR for reporting.

p. ADE’s and ADE’s for White House Clinic POF w p. ADE’s-low or high INR ranges, drug interactions, interruptions in therapy w ADE’s-bleeding, thrombosis

Example of p. ADE/ADE w 22 y. o female dx: hypercoagulable state, s/p DVT/PE x 5 Patient referred by primary care physician after INR had been followed by cardiologist. She could no longer afford to have INR monitored at cardio office. INR at initial visit =1. 2. After CPS, we were able to bring her INR in range in a month. She was also determine to conceive. We assisted her with a Patient Assistance Program to get Lovenox and educated her on its use during pregnancy. We also provided counseling and an option to receive Chantix to stop smoking. She has been able to achieve appropriate anticoagulation levels and is now 3 months pregnant. Hopefully, our service avoided potential adverse drug events and actual adverse drug events for the patient and her unborn child.
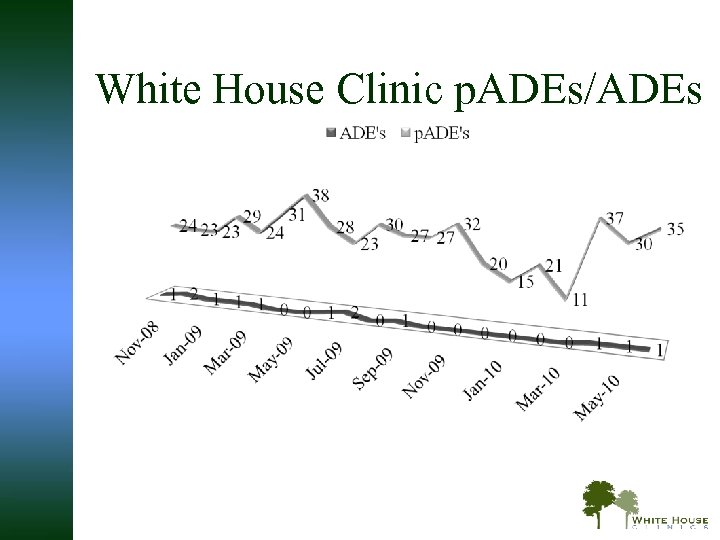
White House Clinic p. ADEs/ADEs

Institute for Healthcare Improvement Assessment Scale The Assessment Scale is divided into the following categories: § § § § § 1. 0 — Forming team 1. 5 — Planning for the project has begun 2. 0 — Activity, but no changes 2. 5 — Changes tested, but no improvement 3. 0 — Modest improvement 3. 5 — Improvement 4. 0 — Significant Improvement-White House Clinic 4. 5 — Sustainable Improvement 5. 0 — Outstanding sustainable results
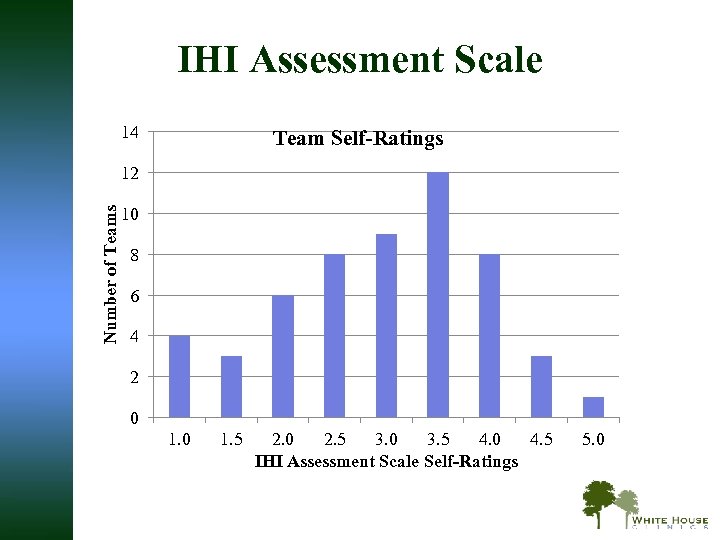
IHI Assessment Scale 14 Team Self-Ratings Number of Teams 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1. 5 2. 0 2. 5 3. 0 3. 5 4. 0 4. 5 IHI Assessment Scale Self-Ratings 5. 0

PSPC 1 Awards w Health Outcomes Management Award – Successfully gathered data and reported it w Life Saving Patient Safety Award – Established systems to identify and prevent ADE’s and have an example of a life threatening ADE that was resolved w PSPC Performance Award – Showed overall excellence during the collaborative

PSPC 2. 0 Awards w Health Outcomes Management Award

How did we do it? w w Better, more focused education for patients Closer patient follow-up Better data tracking methods Quality improvement efforts such as Byeth and CHADS 2 scores w Collaborative competition w Communicated data to our providers w Required continuing education in disease state

The Next Step…PSPC 3 w Spread of anticoagulation management to other sites w Asthma-working with pediatrician w Diabetes-working with Physician Assistant

What do we need? w Time – Hard to balance with other duties of a pharmacist w Staff – Hiring a new pharmacist w Resources – Pharmacy Expansion Grant, provider status for billing services, other funding w Support of our providers

Contact Information w Rebecca Cheek, Pharm. D becky. cheek@whitehouseclinics. com w Office of Pharmacy Affairs www. hrsa. gov/opa w Healthcare Communities www. healthcarecommunities. org
cd36df7c1be18853df547ead1176e3f8.ppt