cd5232c828dc68283e8b21a86ae15ac3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 98

Pathway Bioinformatics Peter D. Karp, Ph. D Bioinformatics Research Group SRI International Menlo Park, CA pkarp@ai. sri. com Bio. Cyc. org

Overview l Definitions l Bio. Cyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases l Algorithms l Pathway for pathway bioinformatics Tools software l Navigation and analysis l Infer metabolic pathways from genomes l Pathway Tools ontology
Pathway Bioinformatics l The subfield of bioinformatics concerned with ontologies, algorithms, databases and visualizations of pathways l Examples: Inference of metabolic pathways from genomes l Schemas for pathway DBs l Exchange formats for pathway data l Classification systems for pathway data l Pathway diagram layout algorithms l
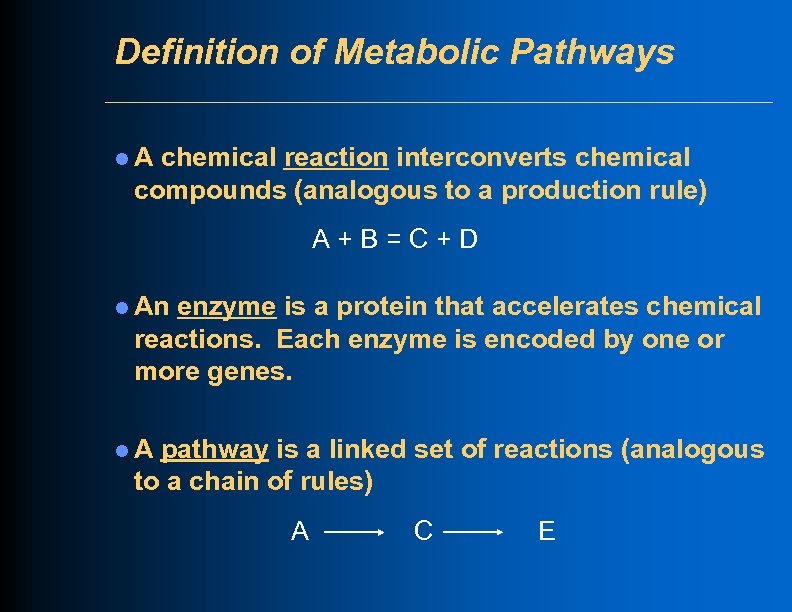
Definition of Metabolic Pathways l. A chemical reaction interconverts chemical compounds (analogous to a production rule) A+B=C+D l An enzyme is a protein that accelerates chemical reactions. Each enzyme is encoded by one or more genes. l. A pathway is a linked set of reactions (analogous to a chain of rules) A C E
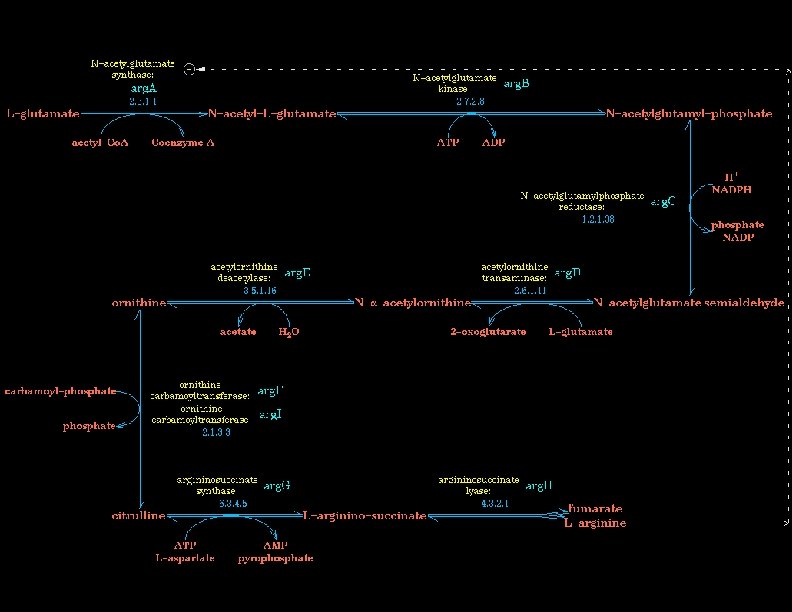
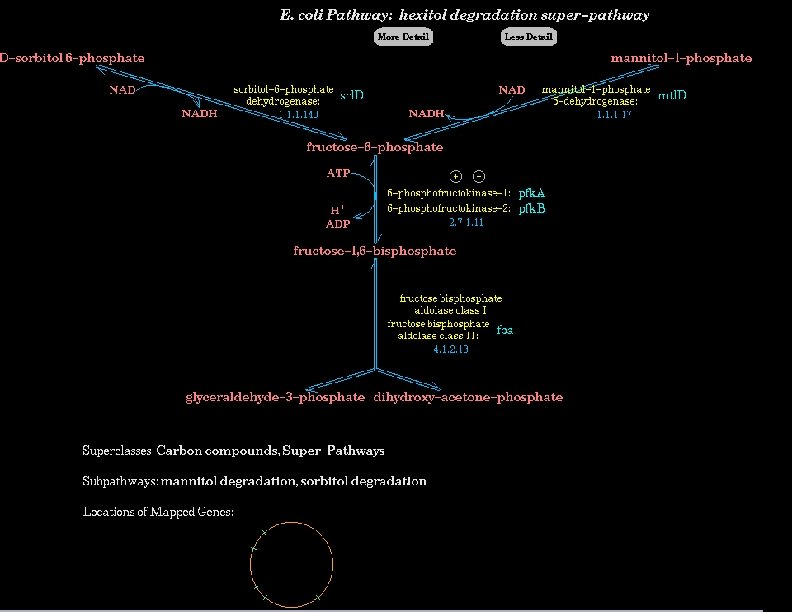
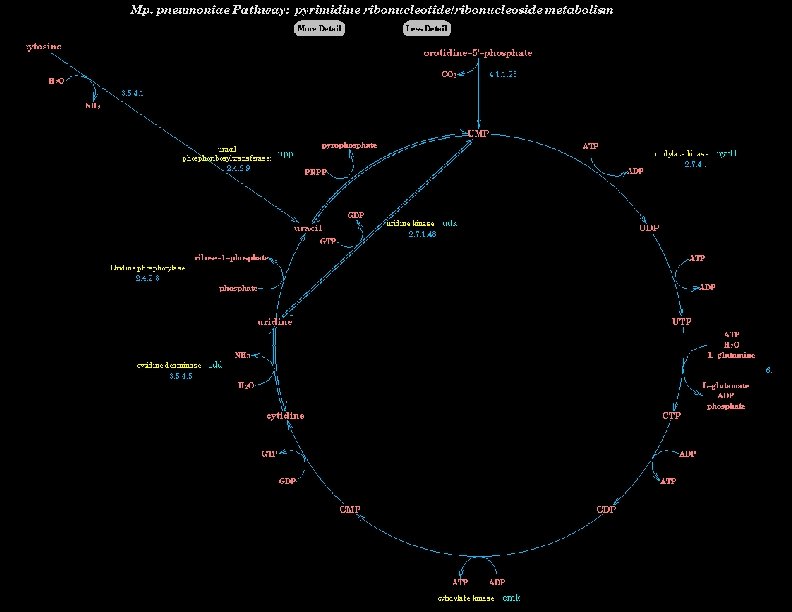

Definition of Small-Molecule Metabolism l Small-molecule metabolism l Biochemical factory within the cell l Hundreds of enzyme-catalyzed reactions operating principally on small-molecule substrates
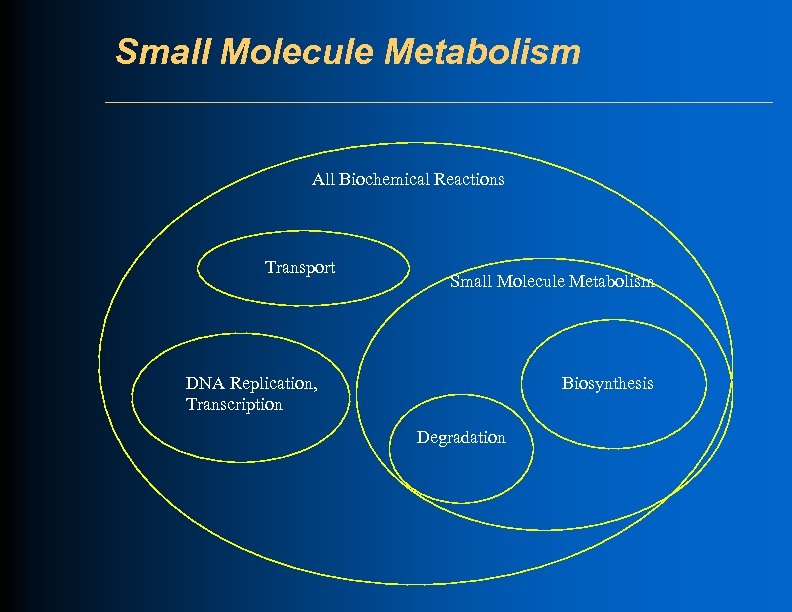
Small Molecule Metabolism All Biochemical Reactions Transport Small Molecule Metabolism DNA Replication, Transcription Biosynthesis Degradation

What is a Metabolic Pathway? l. A pathway is a conceptual unit of the metabolism l An ordered set of interconnected, directed biochemical reactions l A pathway forms a coherent unit: l Boundaries defined at high-connectivity substrates l Regulated as a single unit l Evolutionarily conserved across organisms as a single unit l Performs a single cellular function l Historically grouped together as a unit l All reactions in a single organism
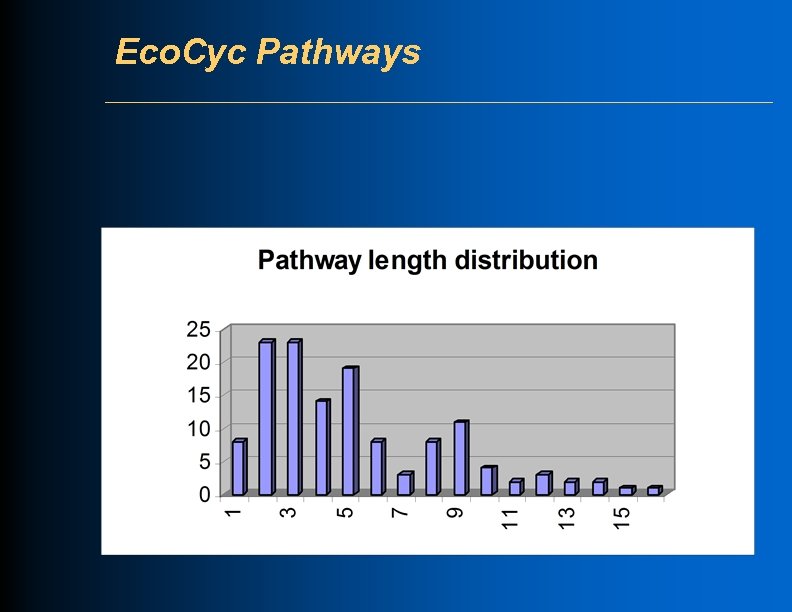
Eco. Cyc Pathways
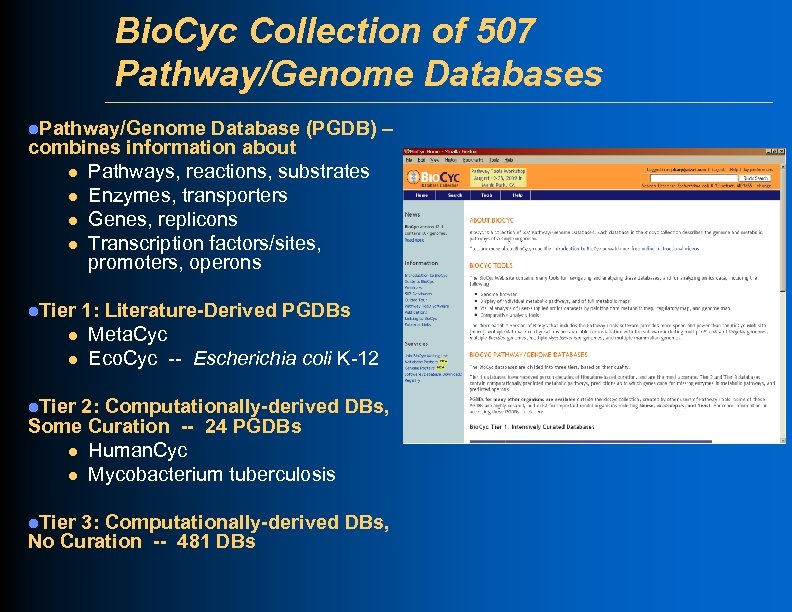
Bio. Cyc Collection of 507 Pathway/Genome Databases l. Pathway/Genome Database (PGDB) – combines information about l Pathways, reactions, substrates l Enzymes, transporters l Genes, replicons l Transcription factors/sites, promoters, operons l. Tier 1: Literature-Derived PGDBs l Meta. Cyc l Eco. Cyc -- Escherichia coli K-12 l. Tier 2: Computationally-derived DBs, Some Curation -- 24 PGDBs l Human. Cyc l Mycobacterium tuberculosis l. Tier 3: Computationally-derived DBs, No Curation -- 481 DBs
Family of Pathway/Genome Databases Meta. Cyc
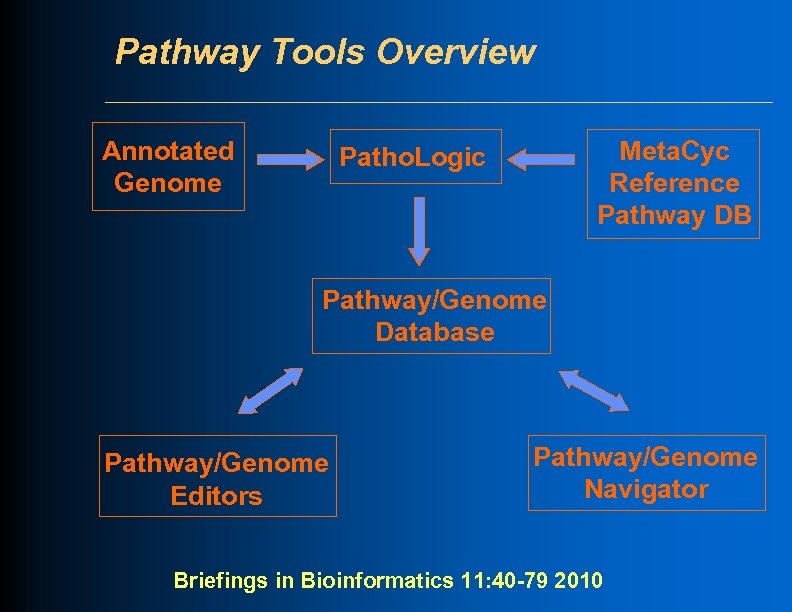
Pathway Tools Overview Annotated Genome Meta. Cyc Reference Pathway DB Patho. Logic Pathway/Genome Database Pathway/Genome Editors Pathway/Genome Navigator Briefings in Bioinformatics 11: 40 -79 2010

Pathway Tools Software: Patho. Logic l Computational creation of new Pathway/Genome Databases l Transforms genome into Pathway Tools schema and layers inferred information above the genome l Predicts operons l Predicts metabolic network l Predicts pathway hole fillers l Infers transport reactions

Pathway Tools Software: Pathway/Genome Editors l Interactively update PGDBs with graphical editors l Support geographically distributed teams of curators with object database system l Gene editor Protein editor Reaction editor Compound editor Pathway editor Operon editor Publication editor l l l

Pathway Tools Software: Pathway/Genome Navigator l Querying, visualization of pathways, chromosomes, operons l Analysis operations l Pathway visualization of gene-expression data l Global comparisons of metabolic networks l Comparative genomics l WWW publishing of PGDBs Desktop operation l
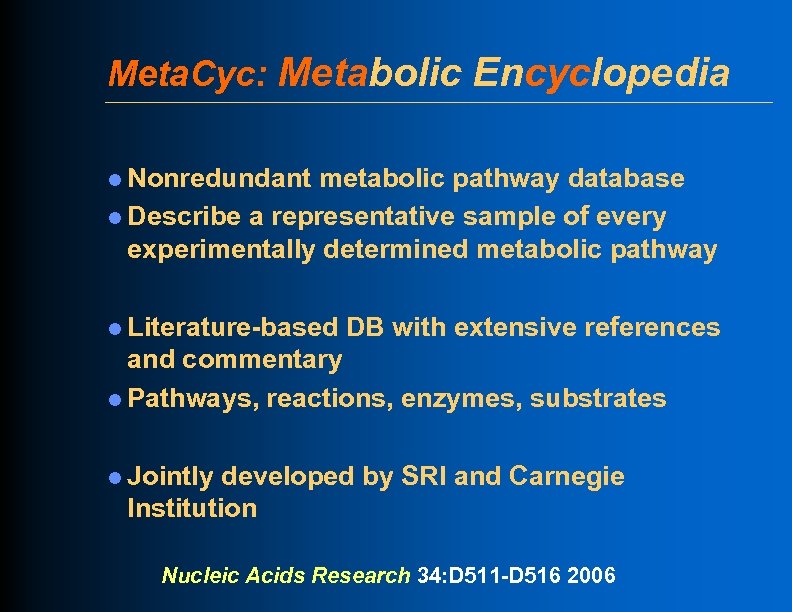
Meta. Cyc: Metabolic Encyclopedia l Nonredundant metabolic pathway database l Describe a representative sample of every experimentally determined metabolic pathway l Literature-based DB with extensive references and commentary l Pathways, reactions, enzymes, substrates l Jointly developed by SRI and Carnegie Institution Nucleic Acids Research 34: D 511 -D 516 2006

Meta. Cyc Data -- Version 13. 6 Pathways 1, 436 Reactions 8, 200 Enzymes 6, 060 Small Molecules 8, 400 Organisms 1, 800 Citations 21, 700
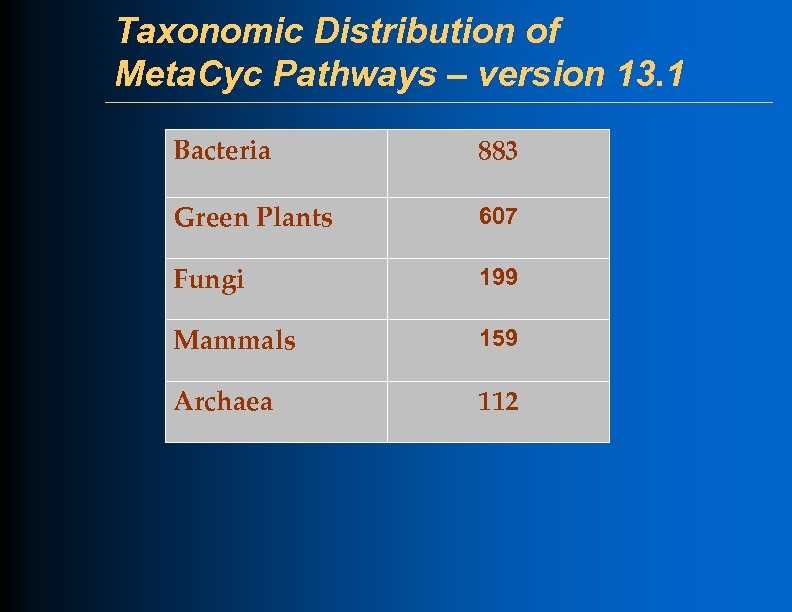
Taxonomic Distribution of Meta. Cyc Pathways – version 13. 1 Bacteria 883 Green Plants 607 Fungi 199 Mammals 159 Archaea 112

Meta. Cyc Enzyme Data l Reaction(s) catalyzed l Alternative substrates l Cofactors / prosthetic groups l Activators and inhibitors l Subunit structure l Molecular weight, p. I l Comment, literature citations l Species
Human. Cyc -- Human. Cyc. org l Derived from Ensembl and Locus. Link l Tier 2 PGDB l Curation has just resumed l 235 metabolic pathways l 1, 523 small-molecule reactions l 1, 188 substrates l Genome Biology 6: 1 -17 2004.

Eco. Cyc Project – Eco. Cyc. org l E. coli Encyclopedia l Review-level Model-Organism Database for E. coli l Tracks evolving annotation of the E. coli genome and cellular networks l The two paradigms of Eco. Cyc l Collaborative development via Internet l Paulsen (TIGR) – Transport, flagella, DNA repair l Collado (UNAM) -- Regulation of gene expression l Keseler, Shearer (SRI) -- Metabolic pathways, Nuc. Acids. Res. 33: D 334 2005 ASM News 70: 25 2004 Science 293: 2040

Paradigm 1: Eco. Cyc as Textual Review Article l All gene products for which experimental literature exists are curated with a minireview summary l Found on protein and RNA pages, not gene pages! l 3257 gene products contain summaries l Summaries cover function, interactions, mutant phenotypes, crystal structures, regulation, and more l Additional summaries found in pages for operons, pathways l Eco. Cyc cites 14, 269 publications
Paradigm 2: Eco. Cyc as Computational Symbolic Theory l Highly structured, high-fidelity knowledge representation provides computable information l Each molecular species defined as a DB object l Genes, proteins, small molecules l Each molecular interaction defined as a DB object l Metabolic reactions l Transport reactions l Transcriptional regulation of gene expression l 220 database fields capture extensive properties and relationships

Demonstration

Pathway Tools Schema and Semantic Inference Layer
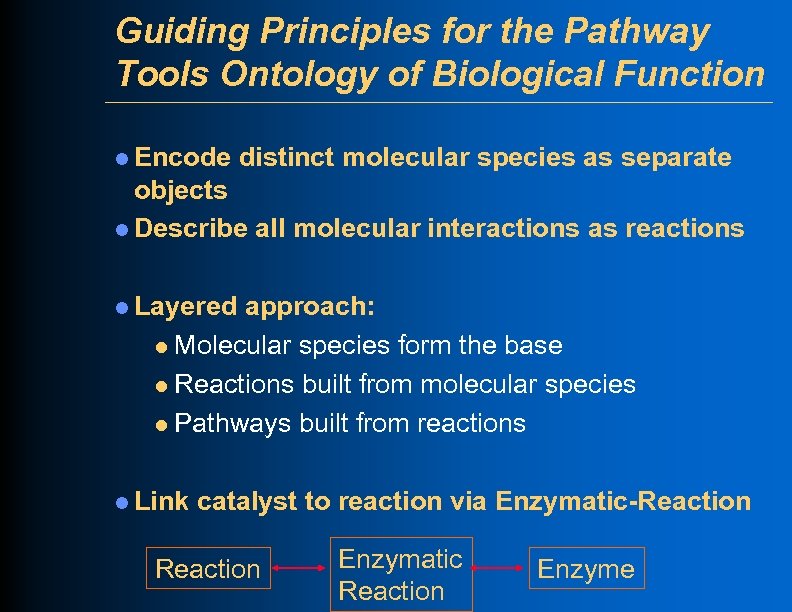
Guiding Principles for the Pathway Tools Ontology of Biological Function l Encode distinct molecular species as separate objects l Describe all molecular interactions as reactions l Layered approach: l Molecular species form the base l Reactions built from molecular species l Pathways built from reactions l Link catalyst to reaction via Enzymatic-Reaction Enzymatic Reaction Enzyme

Pathway Tools Ontology / Schema l Ontology classes: 1621 l Datatype classes: Define objects from genomes to pathways l Classification systems / controlled vocabularies u u Pathways, chemical compounds, enzymatic reactions (EC system) Protein Feature ontology Cell Component Ontology Evidence Ontology l Comprehensive relationships set of 279 attributes and

Overview of Schema Presentation l Survey l What l How of important classes slots are present within these classes objects are linked together to form a network

Use GKB Editor to Inspect the Pathway Tools Ontology l GKB Editor = Generic Knowledge Base Editor l Type in Navigator window: (GKB) or l [Right-Click] Edit->Ontology Editor l View->Browse Class Hierarchy l [Middle-Click] to expand hierarchy l To view classes or instances, select them and: l Frame -> List Frame Contents l Frame -> Edit Frame

Root Classes in the Pathway Tools Ontology l Chemicals Polymer-Segments Protein-Features Paralogous-Gene-Groups l Organisms l Generalized-Reactions Enzymatic-Reactions Regulation -- Reactions and pathways -- Link enzymes to reactions they catalyze -- Regulatory interactions CCO Evidence -- Cell Component Ontology -- Evidence ontology Notes Organizations People Publications -- Timestamped, person-stamped notes l l l -- All molecules -- Regions of polymers -- Features on proteins

Principal Classes l Class names are usually capitalized, plural, separated by dashes l Genetic-Elements, with subclasses: l Chromosomes l Plasmids Genes Transcription-Units RNAs l r. RNAs, sn. RNAs, t. RNAs, Charged-t. RNAs Proteins, with subclasses: l Polypeptides l Protein-Complexes l l

Principal Classes l Reactions l Enzymatic-Reactions l Pathways l Compounds-And-Elements l Regulation
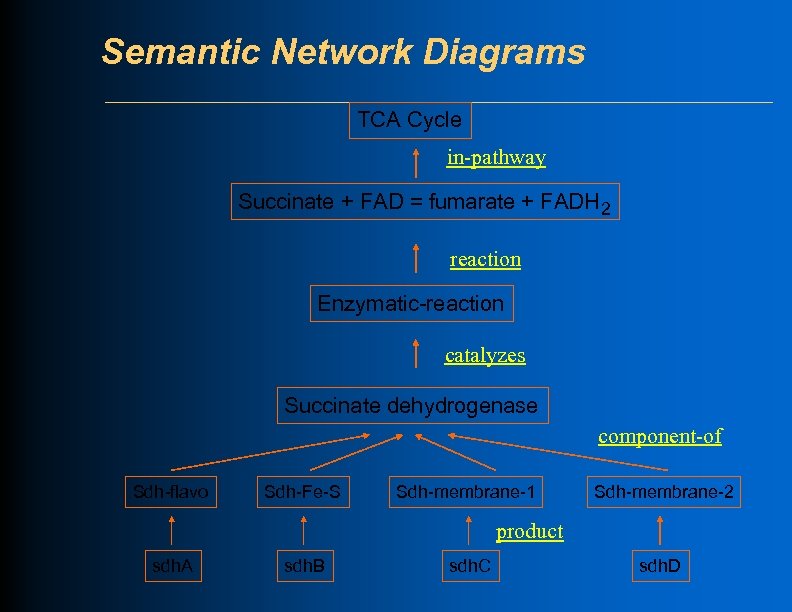
Semantic Network Diagrams TCA Cycle in-pathway Succinate + FAD = fumarate + FADH 2 reaction Enzymatic-reaction catalyzes Succinate dehydrogenase component-of Sdh-flavo Sdh-Fe-S Sdh-membrane-1 Sdh-membrane-2 product sdh. A sdh. B sdh. C sdh. D

Pathway Tools Schema and Semantic Inference Layer Genes, Operons, and Replicons
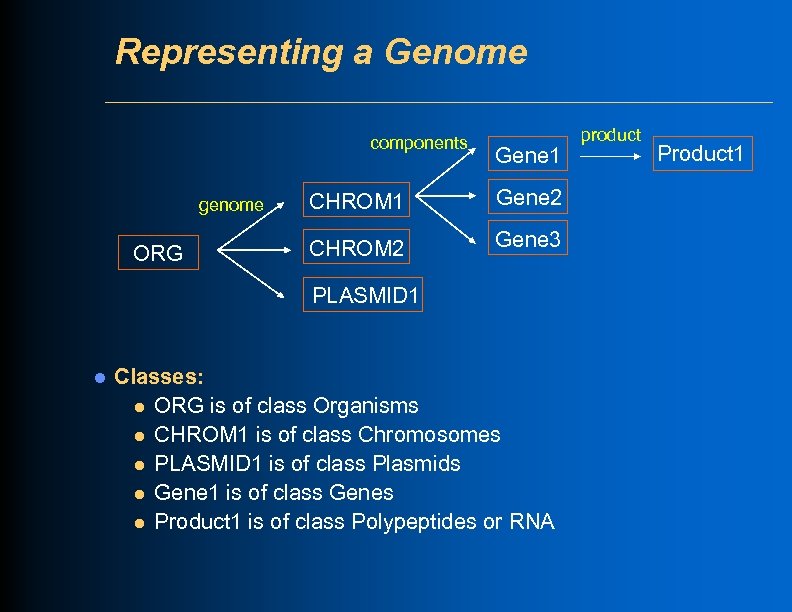
Representing a Genome components genome ORG Gene 1 CHROM 1 Gene 2 CHROM 2 Gene 3 PLASMID 1 l Classes: l ORG is of class Organisms l CHROM 1 is of class Chromosomes l PLASMID 1 is of class Plasmids l Gene 1 is of class Genes l Product 1 is of class Polypeptides or RNA product Product 1
Polynucleotides Review slots of COLI and of COLI-K 12
Polymer-Segments Review slots of Genes

Proteins
Proteins and Protein Complexes l Polypeptide: the monomer protein product of a gene (may have multiple isoforms, as indicated at gene level) l Protein complex: proteins consisting of multiple polypeptides or protein complexes l Example: DNA pol III l Dna. E is a polypeptide l pol III core enzyme contains Dna. E, Dna. Q, Hol. E l pol III holoenzyme contains pol III core enzyme plus three other complexes

Slots of Proteins (Dna. E) l comments, citations l p. I, molecular-weight l features l component-of l gene l catalyzes [link to Enzymatic-Reaction] l dblinks
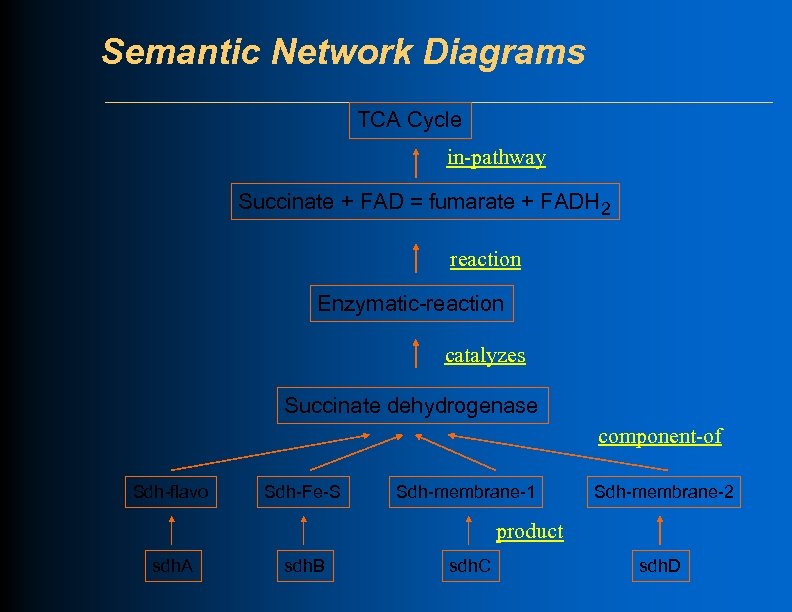
Semantic Network Diagrams TCA Cycle in-pathway Succinate + FAD = fumarate + FADH 2 reaction Enzymatic-reaction catalyzes Succinate dehydrogenase component-of Sdh-flavo Sdh-Fe-S Sdh-membrane-1 Sdh-membrane-2 product sdh. A sdh. B sdh. C sdh. D
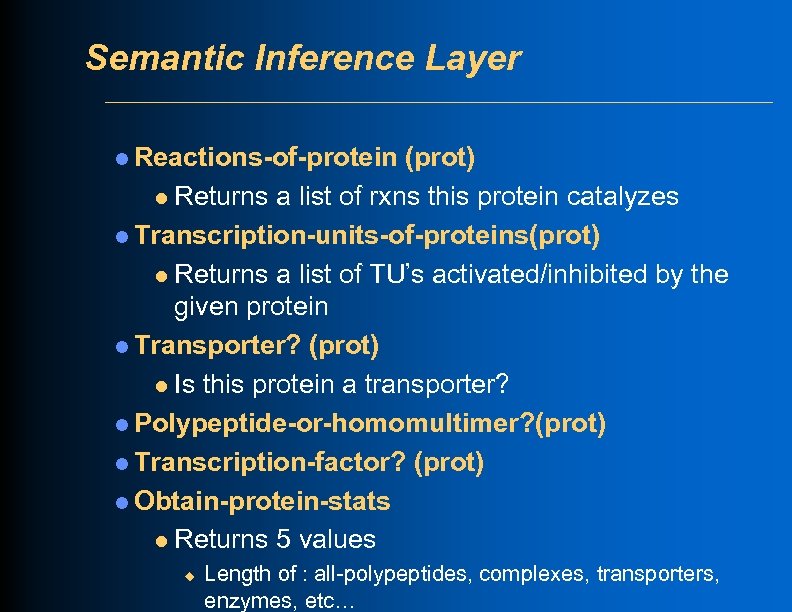
Semantic Inference Layer l Reactions-of-protein (prot) l Returns a list of rxns this protein catalyzes l Transcription-units-of-proteins(prot) l Returns a list of TU’s activated/inhibited by the given protein l Transporter? (prot) l Is this protein a transporter? l Polypeptide-or-homomultimer? (prot) l Transcription-factor? (prot) l Obtain-protein-stats l Returns 5 values u Length of : all-polypeptides, complexes, transporters, enzymes, etc…

Compounds / Reactions / Pathways
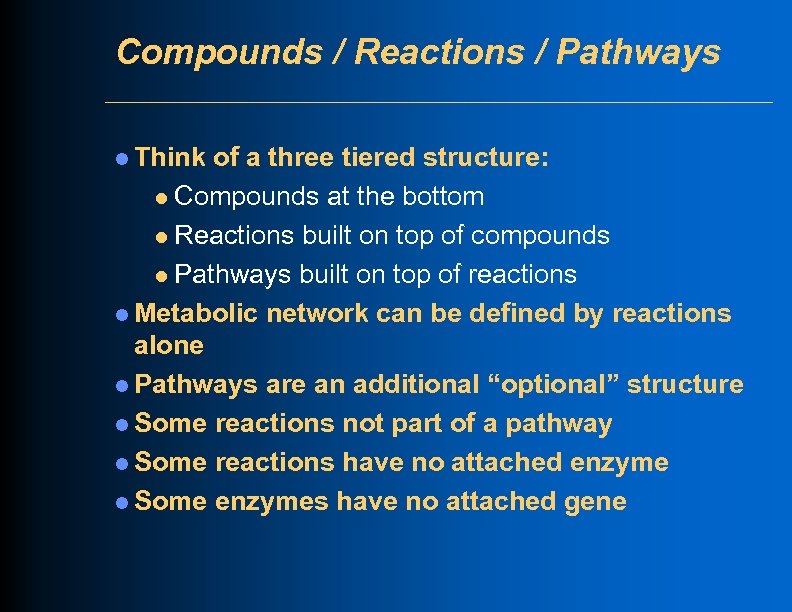
Compounds / Reactions / Pathways l Think of a three tiered structure: l Compounds at the bottom l Reactions built on top of compounds l Pathways built on top of reactions l Metabolic network can be defined by reactions alone l Pathways are an additional “optional” structure l Some reactions not part of a pathway l Some reactions have no attached enzyme l Some enzymes have no attached gene

Compounds

Slots of Compounds l common-name, abbrev-name, synonyms l comment, citations l charge, gibbs-0, molecular-weight l empirical-formula l structure-atoms, structure-bonds l appears-in-left-side-of, appears-in-right-side-of
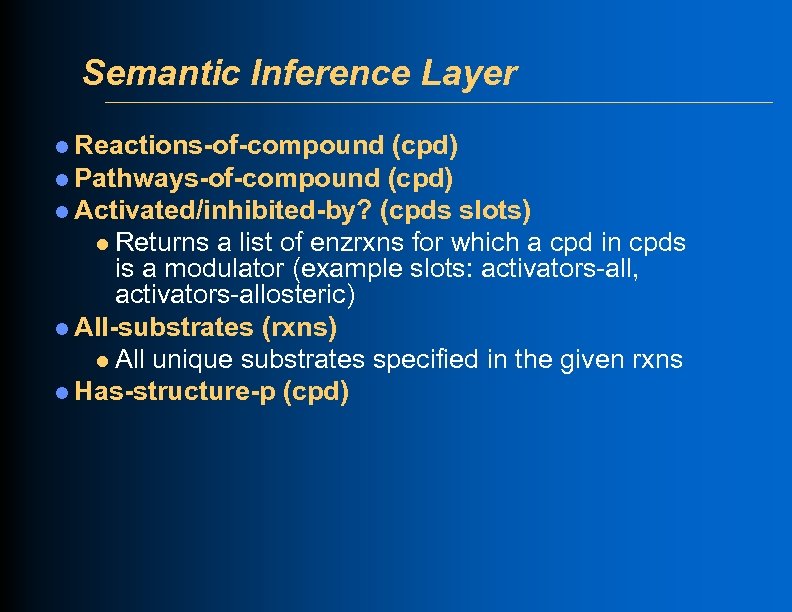
Semantic Inference Layer l Reactions-of-compound (cpd) l Pathways-of-compound (cpd) l Activated/inhibited-by? (cpds slots) l Returns a list of enzrxns for which a cpd in cpds is a modulator (example slots: activators-all, activators-allosteric) l All-substrates (rxns) l All unique substrates specified in the given rxns l Has-structure-p (cpd)

Reactions

Reactions l Represent information about a reaction that is independent of enzymes that catalyze the reaction l Connected to enzyme(s) via enzymatic reaction frames l Classified l Example: with EC system when possible 2. 7. 7. 7 – DNA-directed DNA polymerization l Carried out by five enzymes in E. coli
Slots of Reaction Frames l Keq l Left and Right (reactants / products) l Can include modified forms of proteins, RNAs, etc here l Enzymatic-reaction l In-pathway
Semantic Inference Layer l. Genes-of-reaction (rxn) l. Substrates-of-reaction (rxn) l. Enzymes-of-reaction (rxn) l. Lacking-ec-number (organism) l Returns list of rxns with no ec numbers in that database l. Get-reaction-direction-in-pathway (pwy rxn) l. Reaction-type(rxn) u Indicates types of Rxn as: Small molecule rxn, transport rxn, proteinsmall-molecule rxn (one substrate is protein and one is a small molecule), protein rxn (all substrates are proteins), etc. All-rxns(type) l Specify the type of reaction (see above for type) l. Obtain-rxn-stats l Returns six values l u Length of : all-rxns, transport, non-transport, etc…
Enzymatic Reactions (Dna. E and 2. 7. 7. 7) l. A necessary bridge between enzymes and “generic” versions of reactions l Carry information specific to an enzyme/reaction combination: l Cofactors and prosthetic groups l Alternative substrates l Links to regulatory interactions l Frame is generated when protein is associated with reaction (via protein or reaction editor)
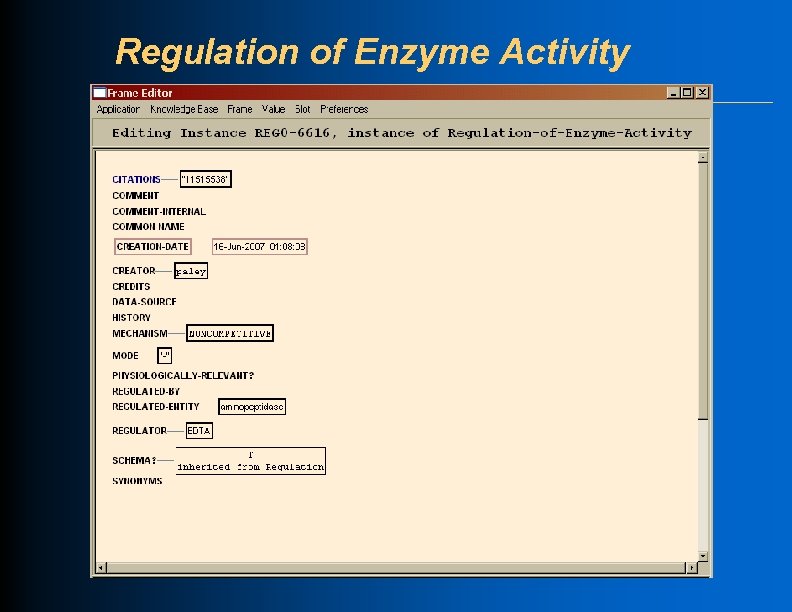
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
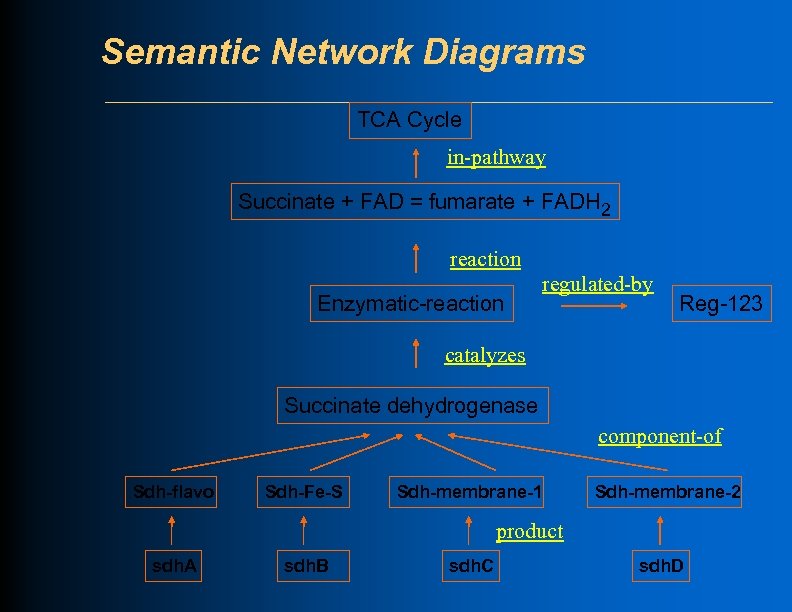
Semantic Network Diagrams TCA Cycle in-pathway Succinate + FAD = fumarate + FADH 2 reaction Enzymatic-reaction regulated-by Reg-123 catalyzes Succinate dehydrogenase component-of Sdh-flavo Sdh-Fe-S Sdh-membrane-1 Sdh-membrane-2 product sdh. A sdh. B sdh. C sdh. D

Pathway Tools Schema and Semantic Inference Layer: Pathways
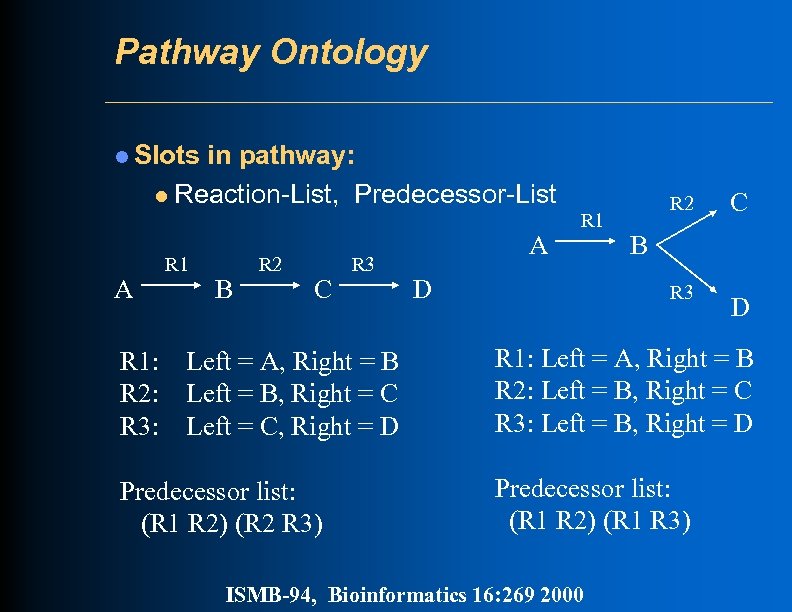
Pathway Ontology l Slots in pathway: l Reaction-List, Predecessor-List A R 1 B R 2 C R 3 A R 1 D R 2 C B R 3 D R 1: Left = A, Right = B R 2: Left = B, Right = C R 3: Left = C, Right = D R 1: Left = A, Right = B R 2: Left = B, Right = C R 3: Left = B, Right = D Predecessor list: (R 1 R 2) (R 2 R 3) Predecessor list: (R 1 R 2) (R 1 R 3) ISMB-94, Bioinformatics 16: 269 2000

Super-Pathways l Collection of pathways that connect to each other via common substrates or reactions, or as part of some larger logical unit l Can contain both sub-pathways and additional connecting reactions l Can be nested arbitrarily l REACTION-LIST: a pathway ID instead of a reaction ID in this slot means include all reactions from the specified pathway l PREDECESSORS: a pathway ID instead of a tuple in this slot means include all predecessor tuples from the specified pathway

Querying Pathways Programmatically l l l See http: //bioinformatics. ai. sri. com/ptools-resources. html (all-pathways) (base-pathways) l Returns list of all pathways that are not super-pathways (genes-of-pathway pwy) (unique-genes-of-pathway pwy) l Returns list of all genes of a pathway that are not also part of other pathways (enzymes-of-pathway pwy) (substrates-of-pathway pwy) (variants-of-pathway pwy) l Returns all pathways in the same variant class as a pathway (get-predecessors rxn pwy), (get-successors rxn pwy) (get-rxn-direction-in-pathway pwy rxn) (pathway-inputs pwy), (pathway-outputs pwy) l Returns all compounds consumed (produced) but not produced (consumed) by pathway (ignores stoichiometry)

Regulation
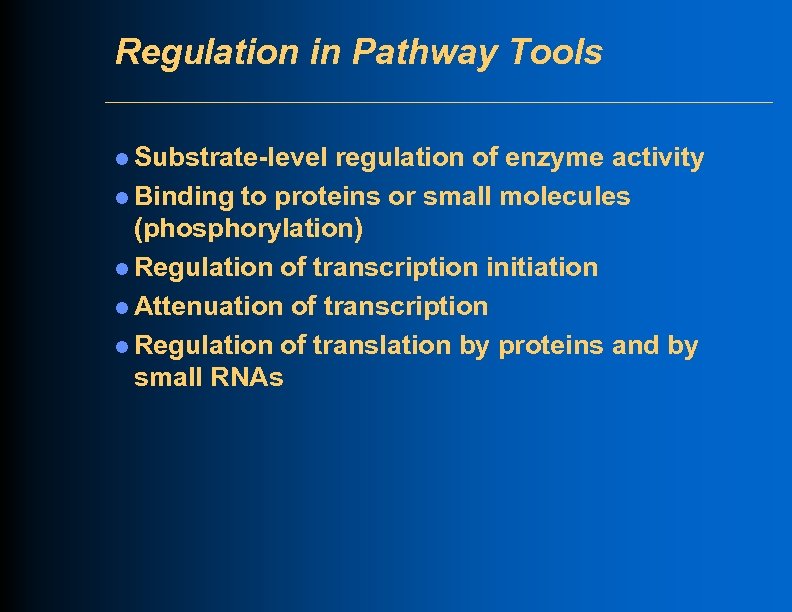
Regulation in Pathway Tools l Substrate-level regulation of enzyme activity l Binding to proteins or small molecules (phosphorylation) l Regulation of transcription initiation l Attenuation of transcription l Regulation of translation by proteins and by small RNAs

Regulation l Class Regulation with subclasses that describe different biochemical mechanisms of regulation l Slots: l Regulator l Regulated-Entity l Mode l Mechanism
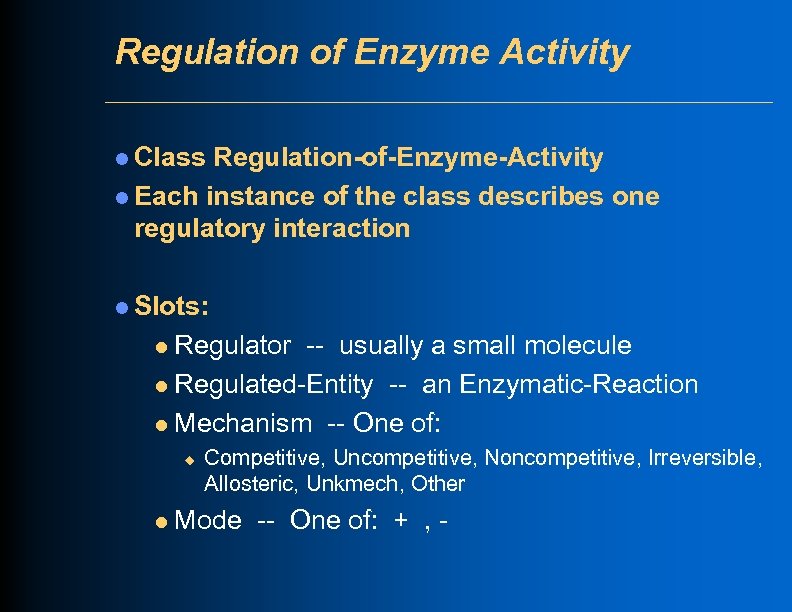
Regulation of Enzyme Activity l Class Regulation-of-Enzyme-Activity l Each instance of the class describes one regulatory interaction l Slots: Regulator -- usually a small molecule l Regulated-Entity -- an Enzymatic-Reaction l Mechanism -- One of: l u l Competitive, Uncompetitive, Noncompetitive, Irreversible, Allosteric, Unkmech, Other Mode -- One of: + , -
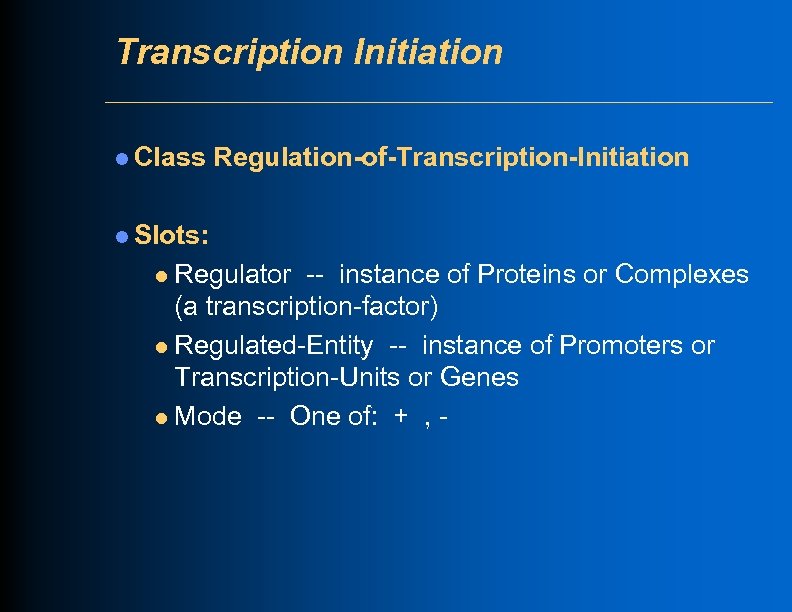
Transcription Initiation l Class Regulation-of-Transcription-Initiation l Slots: Regulator -- instance of Proteins or Complexes (a transcription-factor) l Regulated-Entity -- instance of Promoters or Transcription-Units or Genes l Mode -- One of: + , l

Other Features of Ontology l Evidence l Curator codes crediting system

Inference Algorithms
Patho. Logic: Inference of Pathway Complement l An additional level of inference after genome annotation l Place predicted genes in their biochemical context l Information reduction device l Assess coherence of the set of genes in a genome l Identify pathway holes and singleton enzymes l Provides a framework for analysis of functionalgenomics data
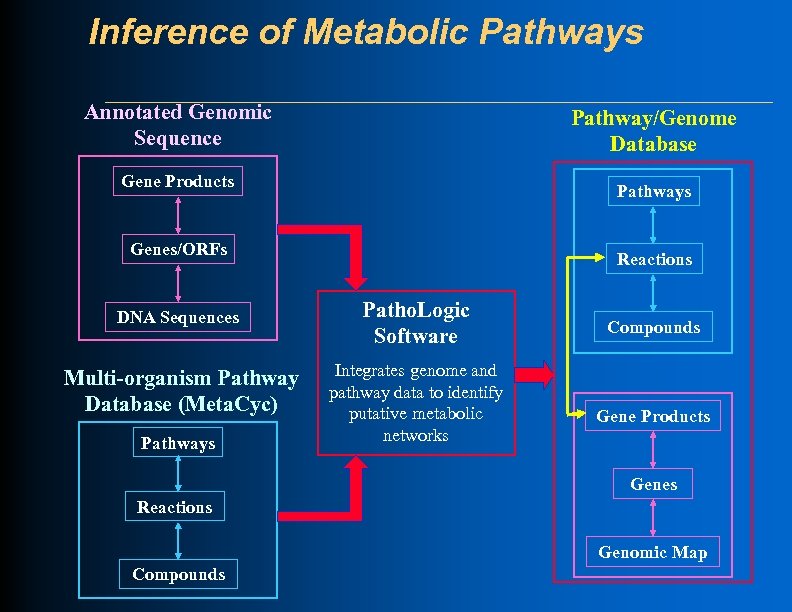
Inference of Metabolic Pathways Annotated Genomic Sequence Pathway/Genome Database Gene Products Pathways Genes/ORFs DNA Sequences Multi-organism Pathway Database (Meta. Cyc) Pathways Reactions Patho. Logic Software Integrates genome and pathway data to identify putative metabolic networks Compounds Gene Products Genes Reactions Genomic Map Compounds


Pathway Prediction l Step 1: Infer reactome l Step 2: Infer metabolic pathways from reactome

Inference of Reactome l Given genome annotation, infer metabolic reactions that can be catalyzed by the genome l EC numbers l Enzyme names l Gene Ontology annotations l Complications: Most genomes contain a subset of above annotations l Enzyme names sometimes ambiguous l Some reactions occur in multiple pathways l u l 99 of 744 reactions in E. coli Pathway variants
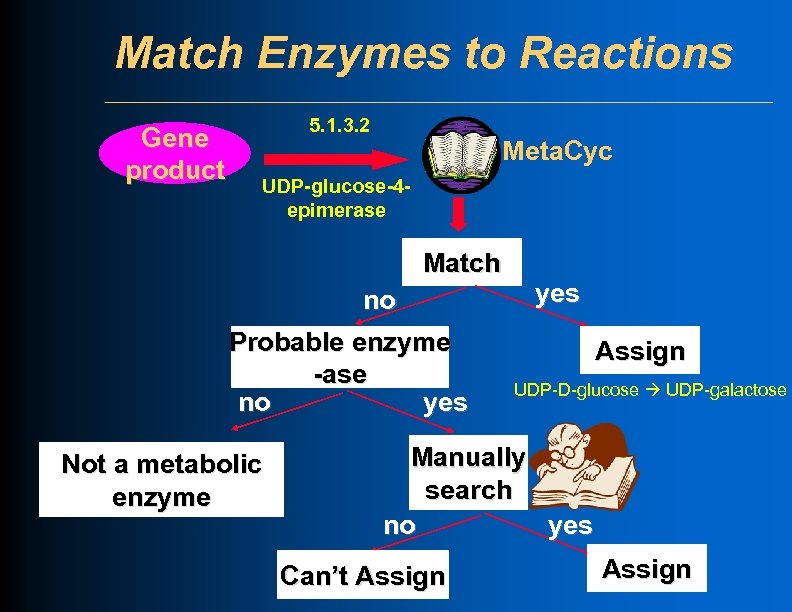
Match Enzymes to Reactions Gene product 5. 1. 3. 2 Meta. Cyc UDP-glucose-4 epimerase Match no Probable enzyme -ase no yes Not a metabolic enzyme yes Assign UDP-D-glucose UDP-galactose Manually search no yes Can’t Assign
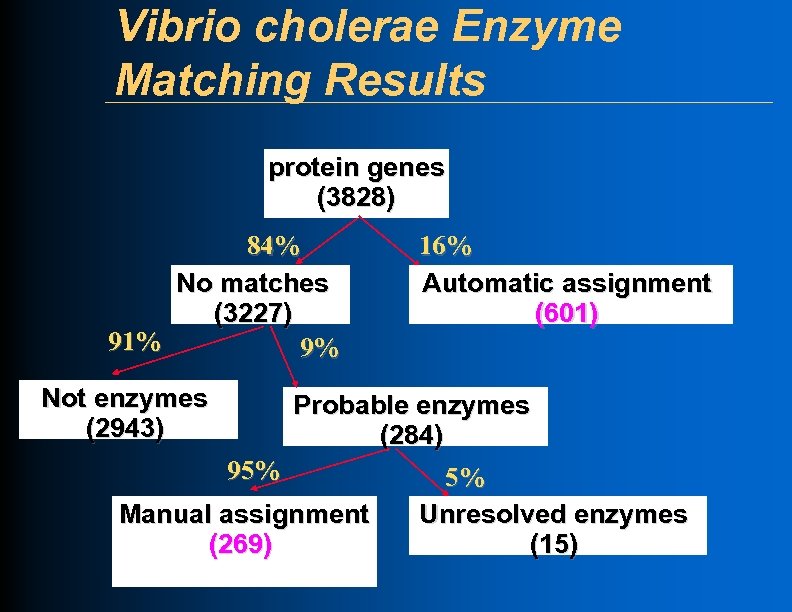
Vibrio cholerae Enzyme Matching Results protein genes (3828) 84% No matches (3227) 91% 9% Not enzymes (2943) 16% Automatic assignment (601) Probable enzymes (284) 95% Manual assignment (269) 5% Unresolved enzymes (15)

Pathway Prediction Algorithm l Two pathway lists: l U: Undecided status l K: Keep l Initialize U to contain all Meta. Cyc pathways for which at least one reaction has an enzyme

Pathway Prediction Algorithm l For each P in U: l If current organism is outside taxonomic range of P AND at least one reaction in P lacks an enzyme, delete P from U l If all reactions of P designated as key reactions have no enzyme, delete P from U
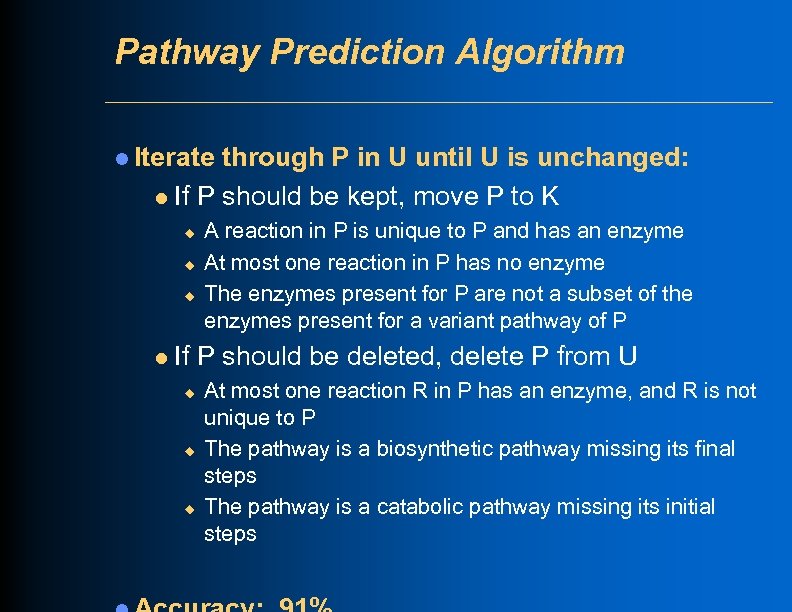
Pathway Prediction Algorithm l Iterate through P in U until U is unchanged: l If P should be kept, move P to K u u u l A reaction in P is unique to P and has an enzyme At most one reaction in P has no enzyme The enzymes present for P are not a subset of the enzymes present for a variant pathway of P If P should be deleted, delete P from U u u u At most one reaction R in P has an enzyme, and R is not unique to P The pathway is a biosynthetic pathway missing its final steps The pathway is a catabolic pathway missing its initial steps
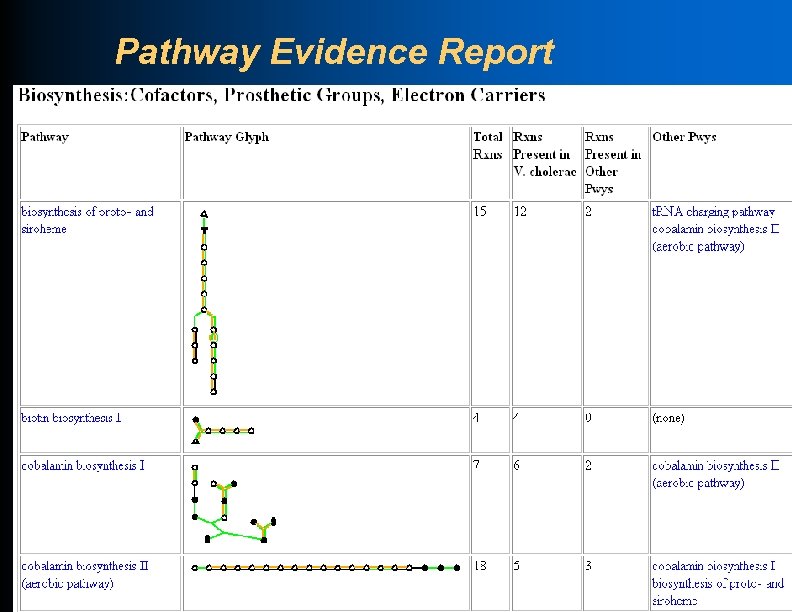
Pathway Evidence Report

Limitations of Pathway Inference l Can be misled by missing or incorrect functional assignments l No sequences known for many enzymes l Uncertainty for short pathways
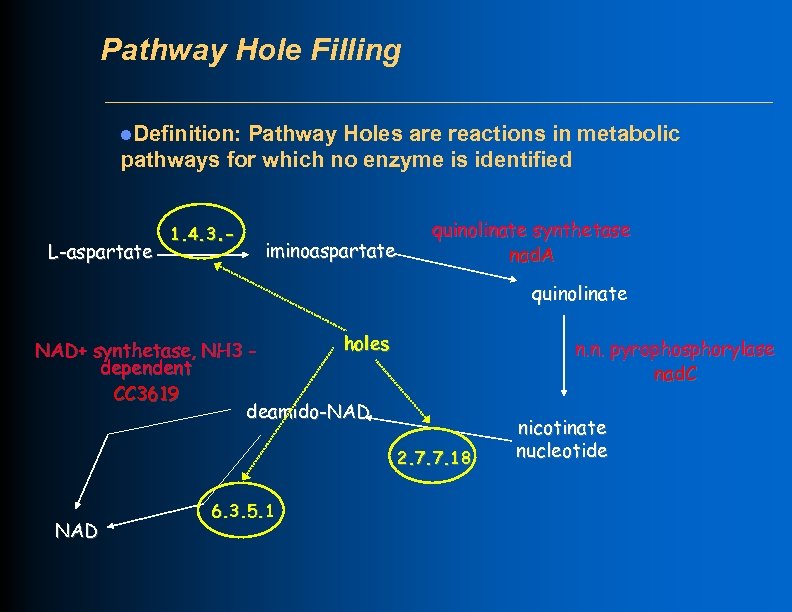
Pathway Hole Filling l. Definition: Pathway Holes are reactions in metabolic pathways for which no enzyme is identified L-aspartate 1. 4. 3. - iminoaspartate quinolinate synthetase nad. A quinolinate holes NAD+ synthetase, NH 3 dependent CC 3619 deamido-NAD n. n. pyrophosphorylase nad. C 2. 7. 7. 18 NAD 6. 3. 5. 1 nicotinate nucleotide
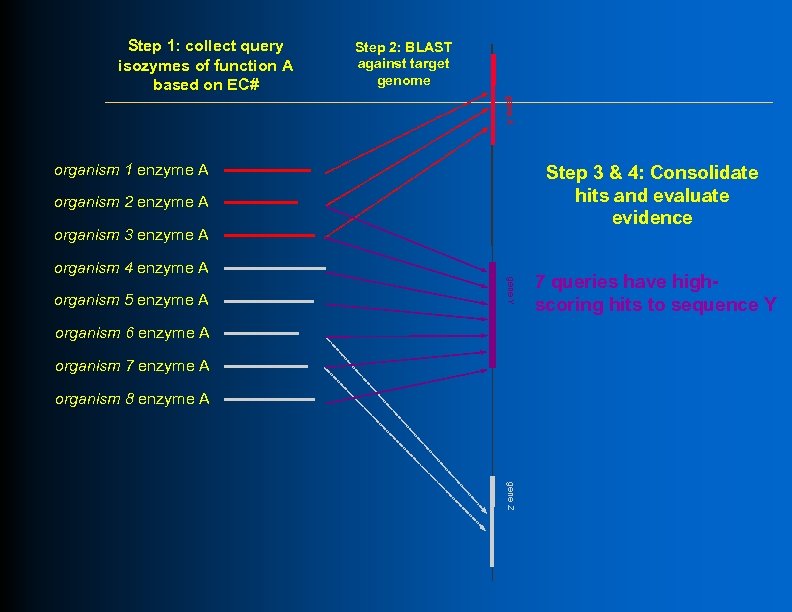
Step 1: collect query isozymes of function A based on EC# Step 2: BLAST against target genome gene X organism 1 enzyme A Step 3 & 4: Consolidate hits and evaluate evidence organism 2 enzyme A organism 3 enzyme A organism 4 enzyme A gene Y organism 5 enzyme A organism 6 enzyme A organism 7 enzyme A organism 8 enzyme A 7 queries have highscoring hits to sequence Y gene Z
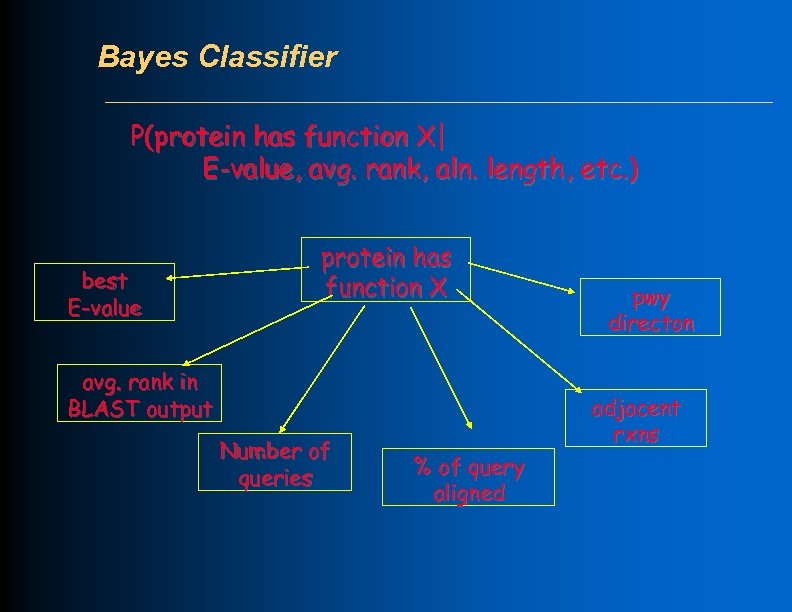
Bayes Classifier P(protein has function X| E-value, avg. rank, aln. length, etc. ) best E-value protein has function X avg. rank in BLAST output Number of queries pwy directon adjacent rxns % of query aligned

Pathway Hole Filler l Why should hole filler find things beyond the original genome annotation? l Reverse BLAST searches more sensitive l Reverse BLAST searches find second domains l Integration of multiple evidence types

Patho. Logic Step 6: Build Cellular Overview Diagram l Diagram encompassing metabolic, transport, and other cellular networks l Automatically generated for every Bio. Cyc DB using advanced graph layout algorithm l Harness the power of the human visual system to interpret patterns in a mechanistic context l Can be zoomed, interrogated, and painted with experimental or comparative data
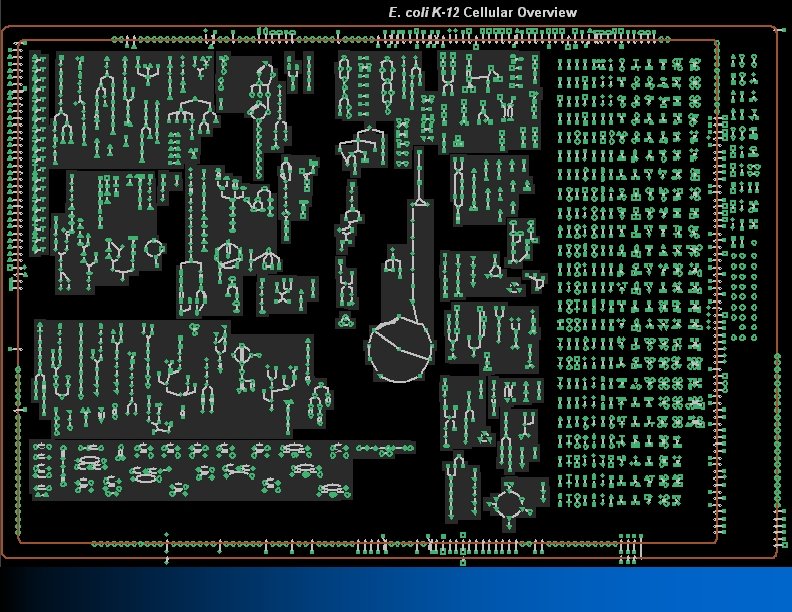
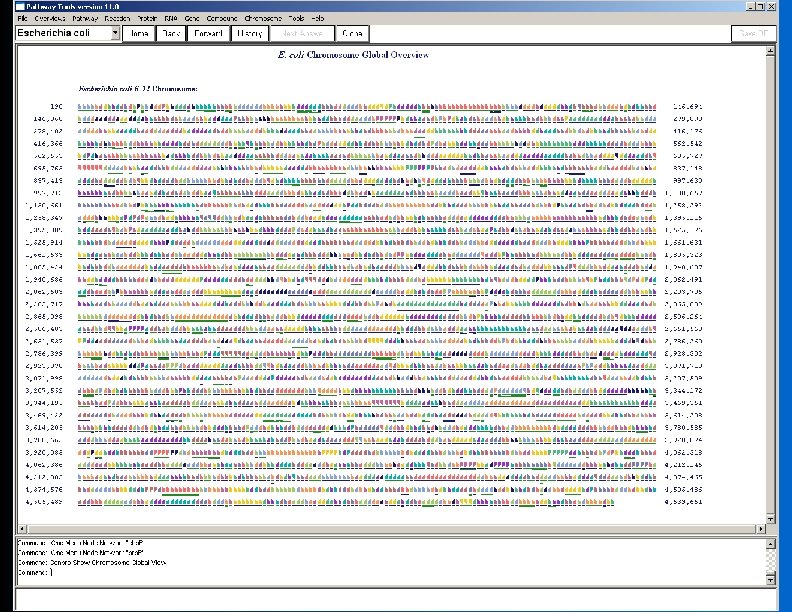
Pathway Algorithms l l l Automated layout of metabolic pathways l Bioinformatics and Genome Research Conference 1994 p 225 Automated layout of cellular overview diagram Automated generation of metabolic map poster Forward propagation of metabolites through the metabolic network l Consistency of a PGDB with respect to known growth-media requirements l Pacific Symp Biocomputing 2001: 471 Identify dead-end metabolites Infer drug targets as choke points in metabolic network l Genome Research 14: 917 2004

Dead End Metabolites l Clues to extra/missing reactions l A small molecule C is a dead-end if: l (Def 1 easier to compute; Def 2 more accurate) l Definition 1: l C is a substrate in only one reaction of the set of SMM reactions occurring in Compartment AND l No transporter acts on C in Compartment, nor on parent classes of C l Definition 2: l C is produced only by SMM reactions in Compartment, and no transporter acts on C in Compartment OR l C is consumed only by SMM reactions in Compartment, and no transporter acts on C in

Global Consistency Checking of Biochemical Network l Given: A PGDB for an organism l A set of initial metabolites l l Infer: l What set of products can be synthesized by the small-molecule metabolism of the organism l Can known growth medium yield known essential compounds? Romero and Karp, Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, 2001
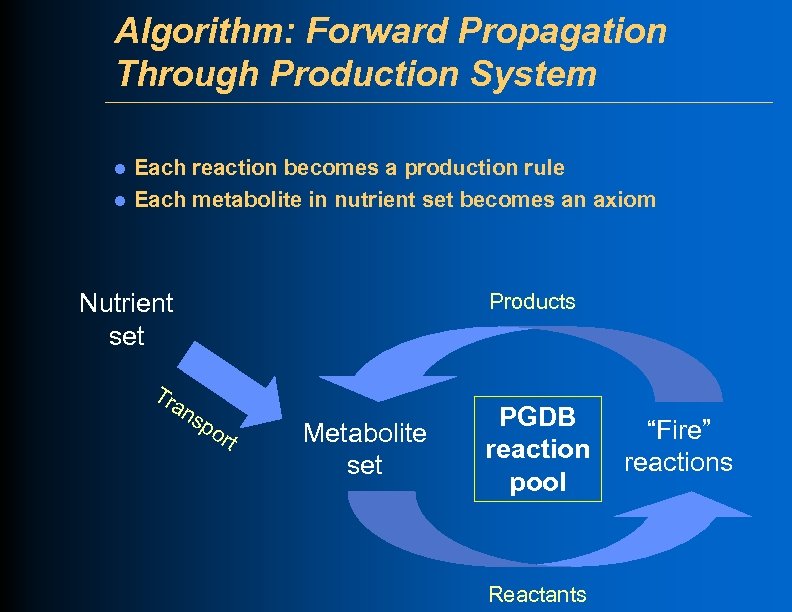
Algorithm: Forward Propagation Through Production System l l Each reaction becomes a production rule Each metabolite in nutrient set becomes an axiom Nutrient set Tr an Products sp ort Metabolite set PGDB reaction pool Reactants “Fire” reactions

Initial Metabolite Nutrient Set (Total: 21 compounds)
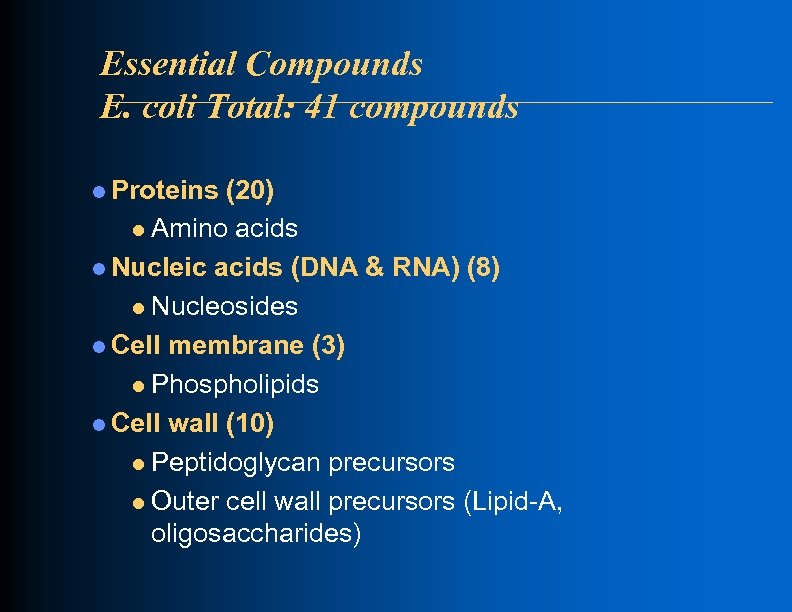
Essential Compounds E. coli Total: 41 compounds l Proteins (20) l Amino acids l Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) (8) l Nucleosides l Cell membrane (3) l Phospholipids l Cell wall (10) l Peptidoglycan precursors l Outer cell wall precursors (Lipid-A, oligosaccharides)

Nutrients: A, B, C, E, F A+B W C+D X E+F Y W+Y Z Produced Compounds: W, Y, Z

Results l Phase I: Forward propagation l 21 initial compounds yielded only half of the 41 essential compounds for E. coli l Phase II: Manually identify l Bugs in Eco. Cyc (e. g. , two objects for tryptophan) u l l A+B C+D “Bootstrap compounds” Missing initial protein substrates (e. g. , ACP) u l B’ C Incomplete knowledge of E. coli metabolic network u l A B Protein synthesis not represented Phase III: Forward propagation with 11 more initial metabolites l Yielded all 41 essential compounds
Summary l Pathway/Genome Databases l Meta. Cyc non-redundant DB of literature-derived pathways l Additional organism-specific PGDBs available through SRI at Bio. Cyc. org l Computational theories of biochemical machinery l Pathway Tools software l Extract pathways from genomes l Morph annotated genome into structured ontology l Distributed curation tools for MODs

How to Learn More l Bio. Cyc Webinars l See Bio. Cyc. org l Bio. Cyc publications page l Bio. Cyc. org l Pathway Tools training course l Pathway Tools feedback sessions l ptools-support@ai. sri. com l Try out Pathway Tools

Additional Pathway Tools Algorithms l Predict metabolic pathway complement l Automatic layout of Cellular Overview diagram l Paint Omics datasets onto Cellular Overview l Compare metabolic networks l Reaction balance checker l Chemical substructure search l Predict operons l Predict pathway hole fillers l Qualitative path tracing from network inputs to network outputs
cd5232c828dc68283e8b21a86ae15ac3.ppt