 Paths in One and Two Dimensions 1 -1 -1 Displacement and Distance
Paths in One and Two Dimensions 1 -1 -1 Displacement and Distance
 Scalar vs. Vector • SCALAR – A measured quantity that has NO DIRECTION – Examples • Distance, Time, Mass, Volume • VECTOR – A measured quantity that includes DIRECTION – SIGN SHOWS DIRECTION – Example • Displacement
Scalar vs. Vector • SCALAR – A measured quantity that has NO DIRECTION – Examples • Distance, Time, Mass, Volume • VECTOR – A measured quantity that includes DIRECTION – SIGN SHOWS DIRECTION – Example • Displacement
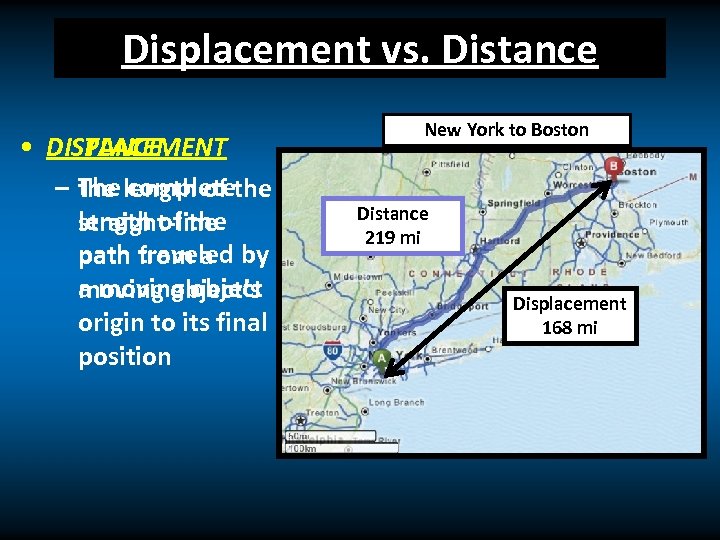 Displacement vs. Distance DISPLACEMENT • DISTANCE – The length of the complete length of the straight-line path traveled by from a a moving object’s origin to its final position New York to Boston Distance 219 mi Displacement 168 mi
Displacement vs. Distance DISPLACEMENT • DISTANCE – The length of the complete length of the straight-line path traveled by from a a moving object’s origin to its final position New York to Boston Distance 219 mi Displacement 168 mi
 Sign Conventions Positive Negative UP NORTH EAST RIGHT DOWN SOUTH WEST LEFT A bird flies. A ball rollsnorth, then 7 meters south A meters 5 meters north. 5 cat runs 8 west. Distance = 5 mm 12 8 m Displacement = +5 m -2 -8 m
Sign Conventions Positive Negative UP NORTH EAST RIGHT DOWN SOUTH WEST LEFT A bird flies. A ball rollsnorth, then 7 meters south A meters 5 meters north. 5 cat runs 8 west. Distance = 5 mm 12 8 m Displacement = +5 m -2 -8 m
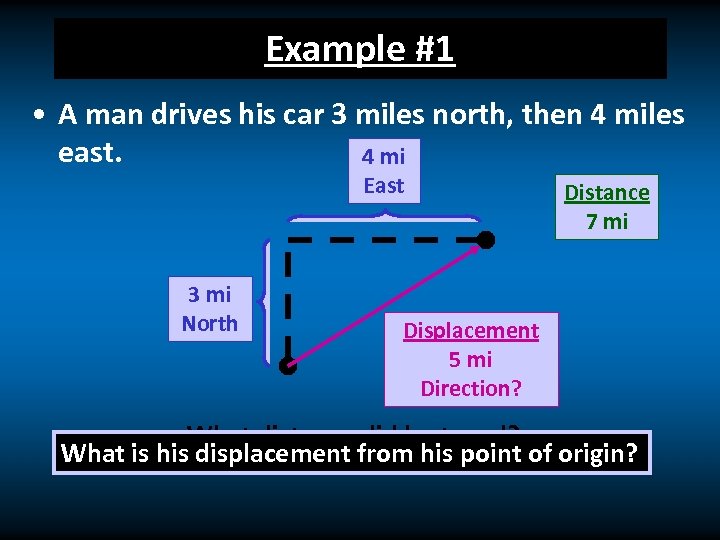 Example #1 • A man drives his car 3 miles north, then 4 miles east. 4 mi East 3 mi North Distance 7 mi Displacement 5 mi Direction? What distance did he travel? What is his displacement from his point of origin?
Example #1 • A man drives his car 3 miles north, then 4 miles east. 4 mi East 3 mi North Distance 7 mi Displacement 5 mi Direction? What distance did he travel? What is his displacement from his point of origin?
 Example #2 • Three men leave the same house on foot. The first man walks 30 feet north, then 40 feet west. The second man walks 90 feet south, then 88 feet north. The third man walks 10 feet east, then 50 feet west. • Which man has traveled the greatest distance? The second man • Who is farthest from the house? The first man • Who is closest to the house? The second man
Example #2 • Three men leave the same house on foot. The first man walks 30 feet north, then 40 feet west. The second man walks 90 feet south, then 88 feet north. The third man walks 10 feet east, then 50 feet west. • Which man has traveled the greatest distance? The second man • Who is farthest from the house? The first man • Who is closest to the house? The second man
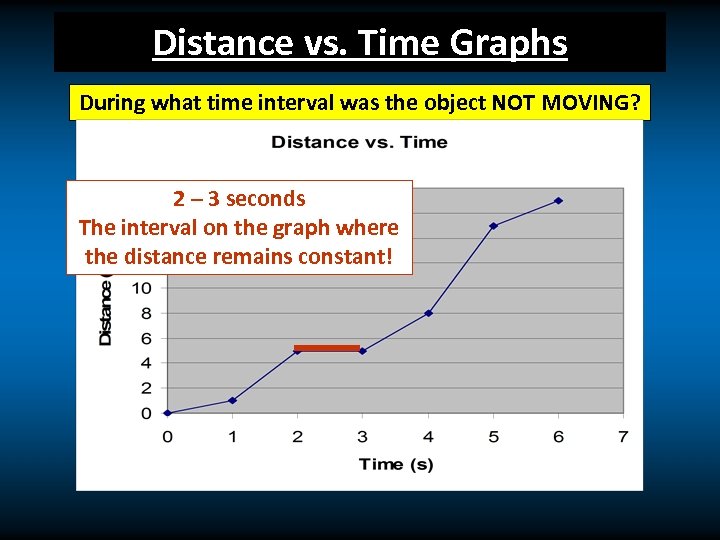 Distance vs. Time Graphs During what time interval was the object NOT MOVING? 2 – 3 seconds The interval on the graph where the distance remains constant!
Distance vs. Time Graphs During what time interval was the object NOT MOVING? 2 – 3 seconds The interval on the graph where the distance remains constant!
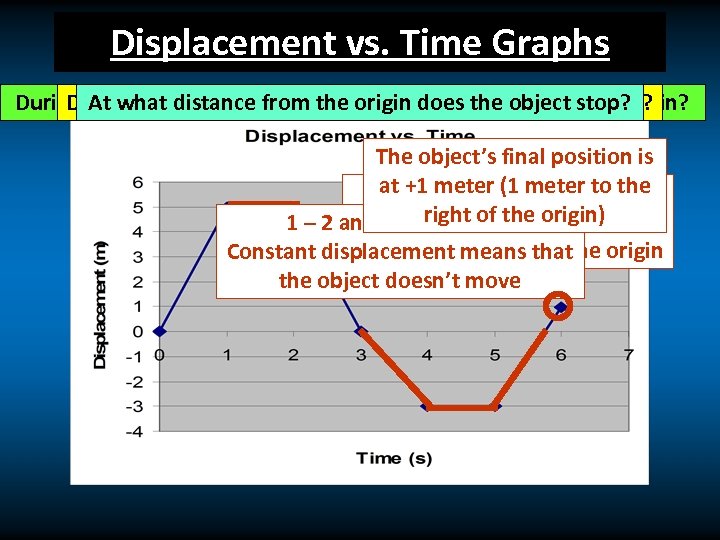 Displacement vs. Time Graphs During what interval(s) was the object tothe. NOT MOVING? During time interval(s) was the object stop? At what distance from the origin does the left of the origin? The object’s final position is at +1 the displacement is Whenmeter (1 meter to the 1 – 2 and negative, of the origin) a 4 – 5 right the object has seconds position to the left of the Constant displacement means that origin the object doesn’t move
Displacement vs. Time Graphs During what interval(s) was the object tothe. NOT MOVING? During time interval(s) was the object stop? At what distance from the origin does the left of the origin? The object’s final position is at +1 the displacement is Whenmeter (1 meter to the 1 – 2 and negative, of the origin) a 4 – 5 right the object has seconds position to the left of the Constant displacement means that origin the object doesn’t move