Pathophysiology of gastro-intestinal tract Gastro-intestinal tract










pathophysiology_of_the_stomach.ppt
- Размер: 2.7 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 24
Описание презентации Pathophysiology of gastro-intestinal tract Gastro-intestinal tract по слайдам
 Pathophysiology of gastro-intestinal tract
Pathophysiology of gastro-intestinal tract
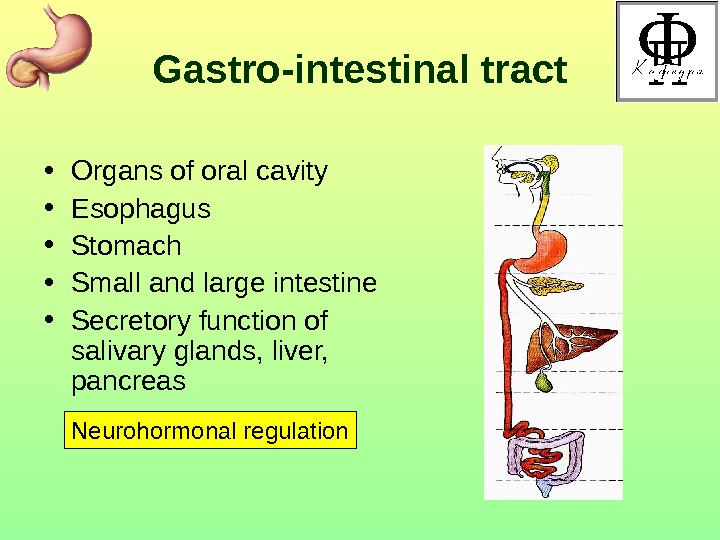
 Gastro-intestinal tract • Organs of oral cavity • Esophagus • Stomach • Small and large intestine • Secretory function of salivary glands, liver, pancreas Neurohormonal regulation
Gastro-intestinal tract • Organs of oral cavity • Esophagus • Stomach • Small and large intestine • Secretory function of salivary glands, liver, pancreas Neurohormonal regulation
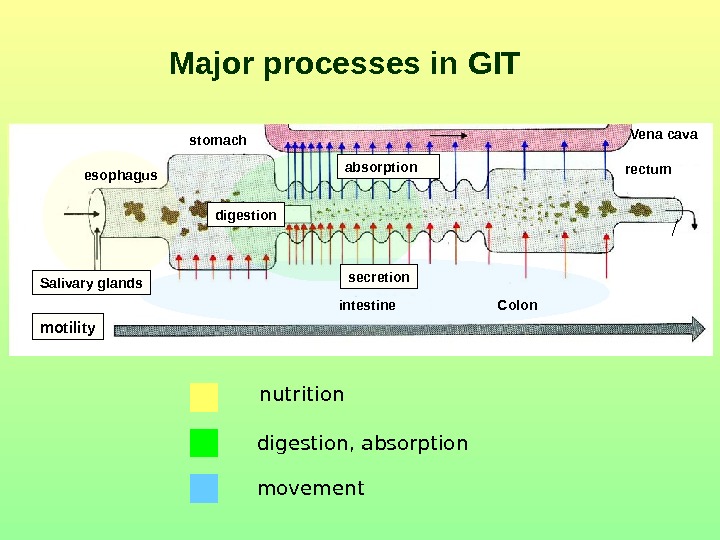
 Major processes in GIT nutrition digestion , absorption movement. Salivary glands absorption Vena cava rectumstomach esophagus Colonintestine secretiondigestion motility
Major processes in GIT nutrition digestion , absorption movement. Salivary glands absorption Vena cava rectumstomach esophagus Colonintestine secretiondigestion motility
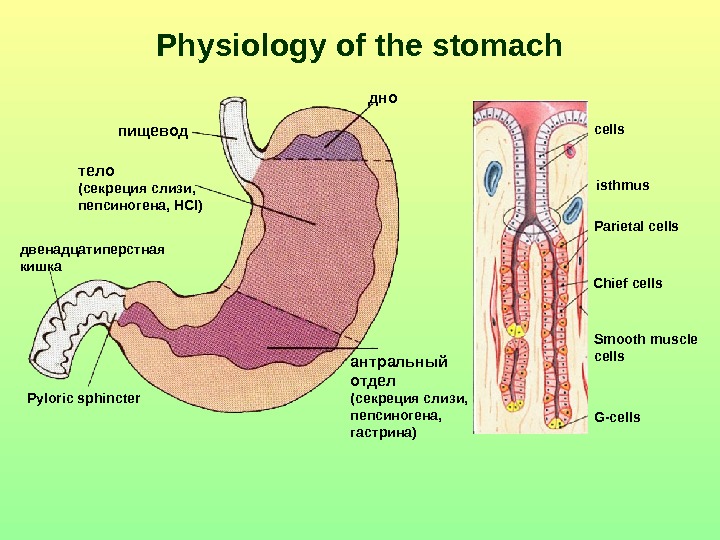
 Physiology of the stomach пищевод дно Pyloric sphincterдвенадцатиперстная кишка антральный отдел (секреция слизи, пепсиногена, гастрина) isthmus Parietal cells Smooth muscle cells G-cells. Chief cells тело (секреция слизи, пепсиногена, HCl)
Physiology of the stomach пищевод дно Pyloric sphincterдвенадцатиперстная кишка антральный отдел (секреция слизи, пепсиногена, гастрина) isthmus Parietal cells Smooth muscle cells G-cells. Chief cells тело (секреция слизи, пепсиногена, HCl)
 Antral G-cell Parietal cell Gastrin Н + secretion К + , H + АТФ ase CNS Acetylcholine Antral receptor Local reflex Histamine Acetylcholine Stretch Parietal receptor Food (view, smell, test )Regulation of gastric secretion
Antral G-cell Parietal cell Gastrin Н + secretion К + , H + АТФ ase CNS Acetylcholine Antral receptor Local reflex Histamine Acetylcholine Stretch Parietal receptor Food (view, smell, test )Regulation of gastric secretion
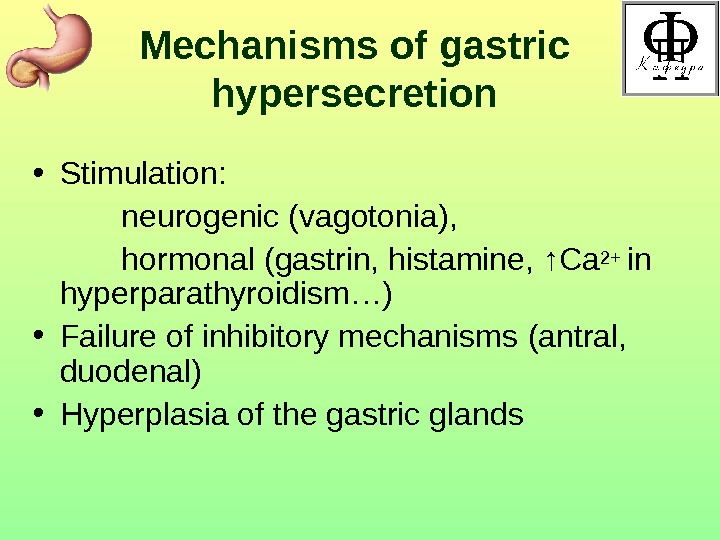
 Mechanisms of gastric hypersecretion • Stimulation : neurogenic (vagotonia) , hormonal ( gastrin, histamine, ↑Ca 2+ in hyperparathyroidism …) • Failure of inhibitory mechanisms ( antral , duodenal ) • Hyperplasia of the gastric glands
Mechanisms of gastric hypersecretion • Stimulation : neurogenic (vagotonia) , hormonal ( gastrin, histamine, ↑Ca 2+ in hyperparathyroidism …) • Failure of inhibitory mechanisms ( antral , duodenal ) • Hyperplasia of the gastric glands
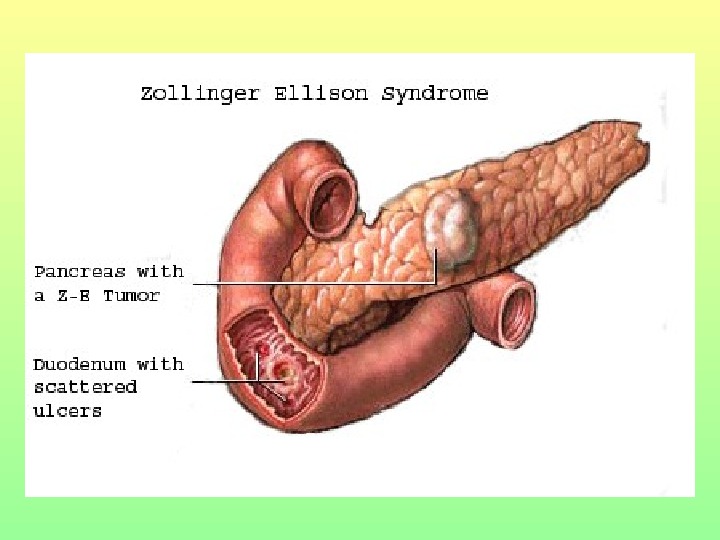
 Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) • Marked gastric hypersecretion • Diarrhea • Abdominal pain • Peptic ulcer(s) of upper GI tract • Gastro-esophageal reflux • Gastrin-secreting tumor of the duodenum (75%), pancreas (24%), stomach, liver, ovary (1%).
Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) • Marked gastric hypersecretion • Diarrhea • Abdominal pain • Peptic ulcer(s) of upper GI tract • Gastro-esophageal reflux • Gastrin-secreting tumor of the duodenum (75%), pancreas (24%), stomach, liver, ovary (1%).

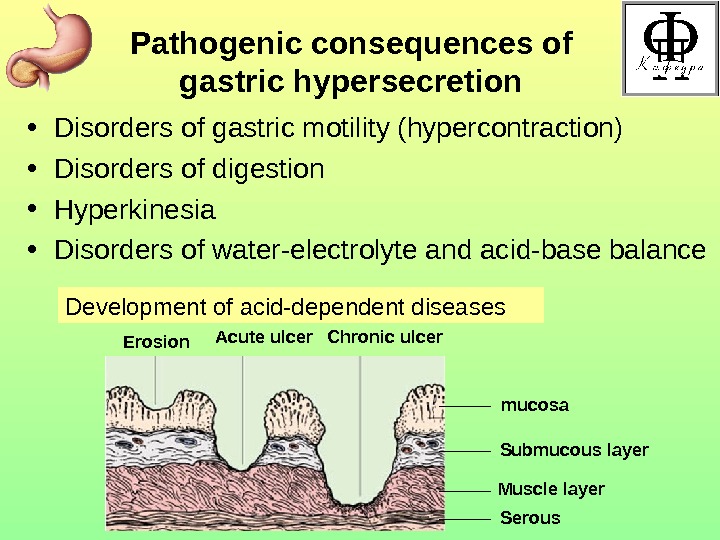
 Pathogenic consequences of gastric hypersecretion • Disorders of gastric motility (hypercontraction) • Disorders of digestion • Hyperkinesia • Disorders of water-electrolyte and acid-base balance Development of acid-dependent diseases Erosion Acute ulcer Chronic ulcer mucosa Submucous layer Muscle layer Serous
Pathogenic consequences of gastric hypersecretion • Disorders of gastric motility (hypercontraction) • Disorders of digestion • Hyperkinesia • Disorders of water-electrolyte and acid-base balance Development of acid-dependent diseases Erosion Acute ulcer Chronic ulcer mucosa Submucous layer Muscle layer Serous
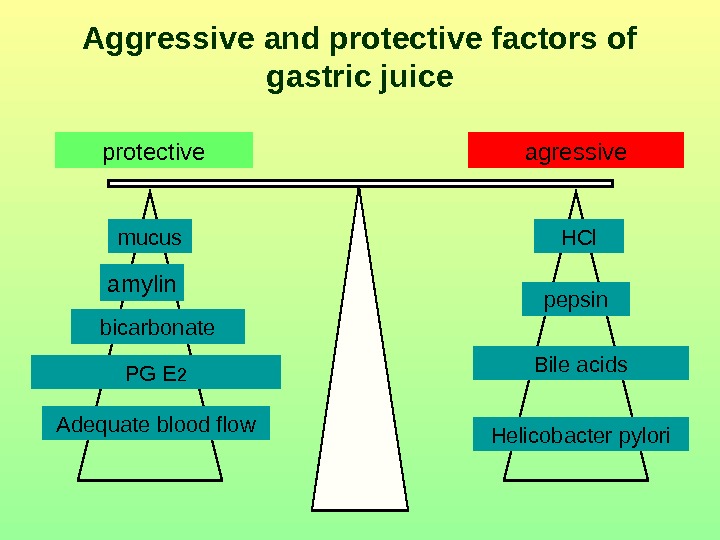
 mucus bicarbonate PG Е 2 Adequate blood flow HCl pepsin Bile acids Helicobacter р yloriagressive. Aggressive and protective factors of gastric juice amylinprotective
mucus bicarbonate PG Е 2 Adequate blood flow HCl pepsin Bile acids Helicobacter р yloriagressive. Aggressive and protective factors of gastric juice amylinprotective
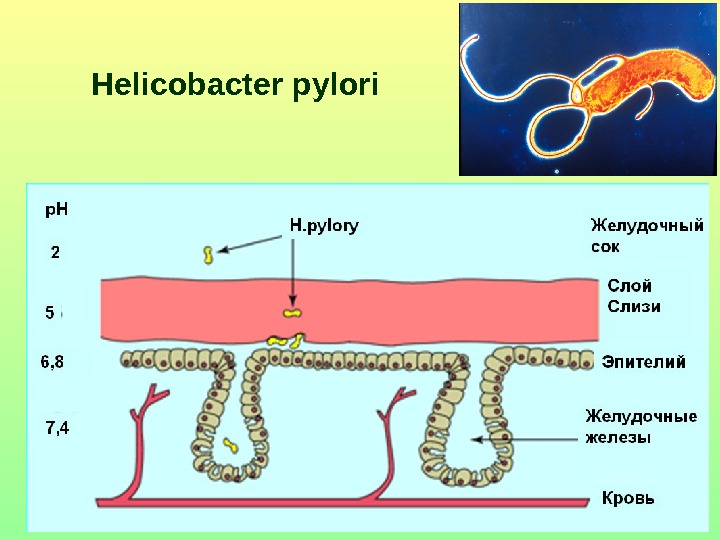
 Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
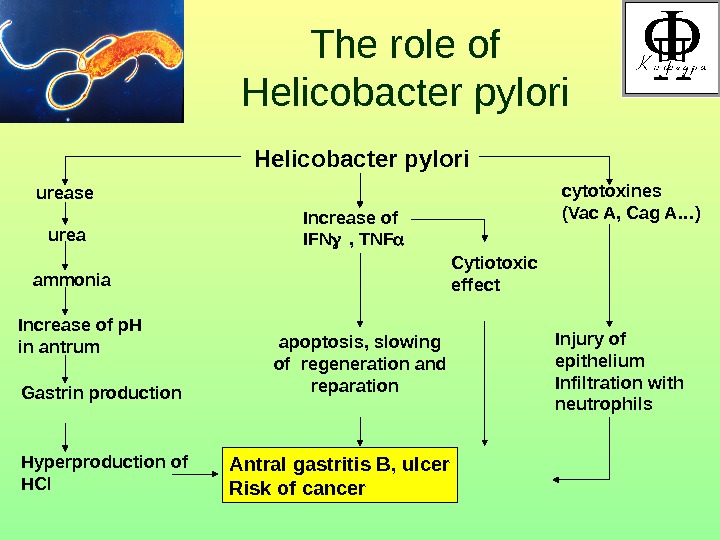
 The role of Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori urease urea ammonia Increase of p. H in antrum Gastrin production Hyperproduction of НС l Increase of IFN , TNF apoptosis , slowing of regeneration and reparation Antral gastritis B , ulcer Risk of cancer Cytiotoxic effect cytotoxines ( Vac A, Cag A…) Injury of epithelium Infiltration with neutrophils
The role of Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori urease urea ammonia Increase of p. H in antrum Gastrin production Hyperproduction of НС l Increase of IFN , TNF apoptosis , slowing of regeneration and reparation Antral gastritis B , ulcer Risk of cancer Cytiotoxic effect cytotoxines ( Vac A, Cag A…) Injury of epithelium Infiltration with neutrophils

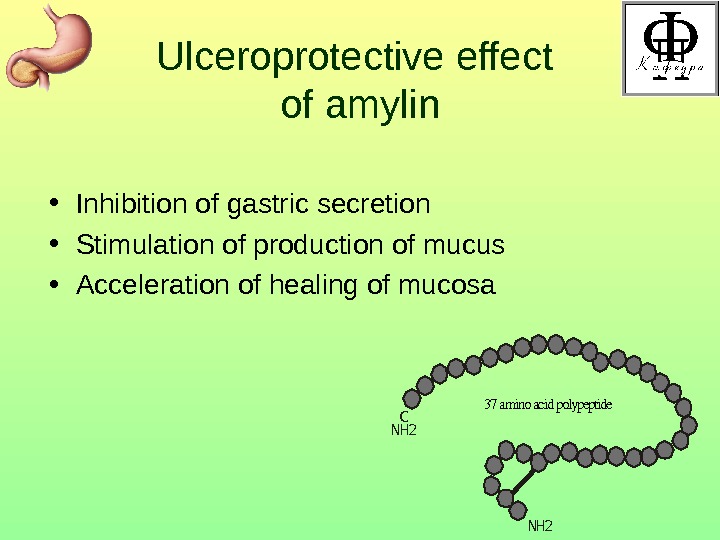
 Ulceroprotective effect of amylin • Inhibition of gastric secretion • Stimulation of production of mucus • Acceleration of healing of mucosa C N H 23 7 a m i n o a c i d p o l y p e p t i d e
Ulceroprotective effect of amylin • Inhibition of gastric secretion • Stimulation of production of mucus • Acceleration of healing of mucosa C N H 23 7 a m i n o a c i d p o l y p e p t i d e
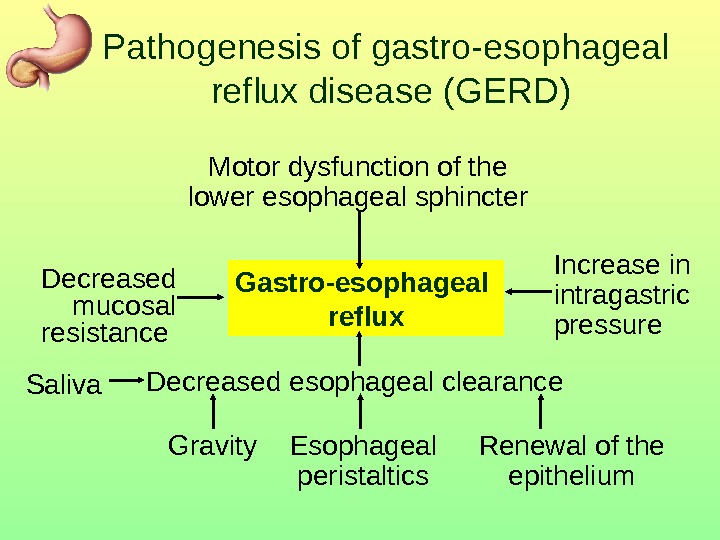
 Pathogenesis of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) Motor dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter Gastro-esophageal reflux. Decreased mucosal resistance Increase in intragastric pressure Decreased esophageal clearance Gravity Esophageal peristaltics. Saliva Renewal of the epithelium
Pathogenesis of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) Motor dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter Gastro-esophageal reflux. Decreased mucosal resistance Increase in intragastric pressure Decreased esophageal clearance Gravity Esophageal peristaltics. Saliva Renewal of the epithelium
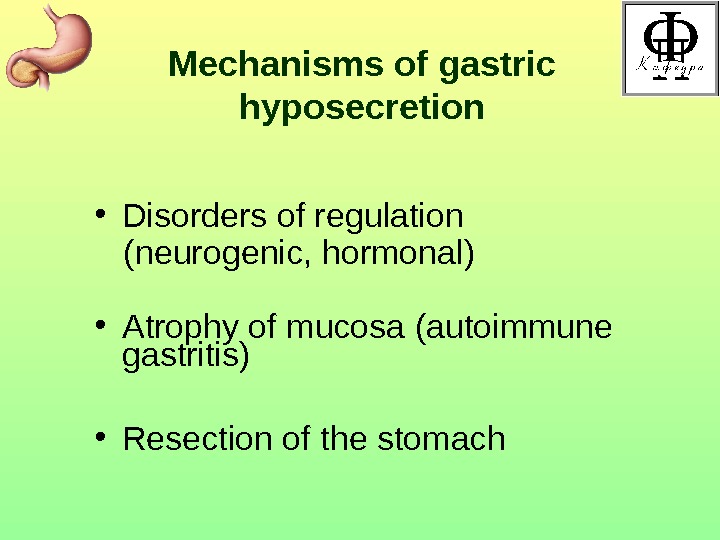
 Mechanisms of gastric hyposecretion • Disorders of regulation ( neurogenic , hormonal ) • Atrophy of mucosa (autoimmune gastritis) • Resection of the stomach
Mechanisms of gastric hyposecretion • Disorders of regulation ( neurogenic , hormonal ) • Atrophy of mucosa (autoimmune gastritis) • Resection of the stomach
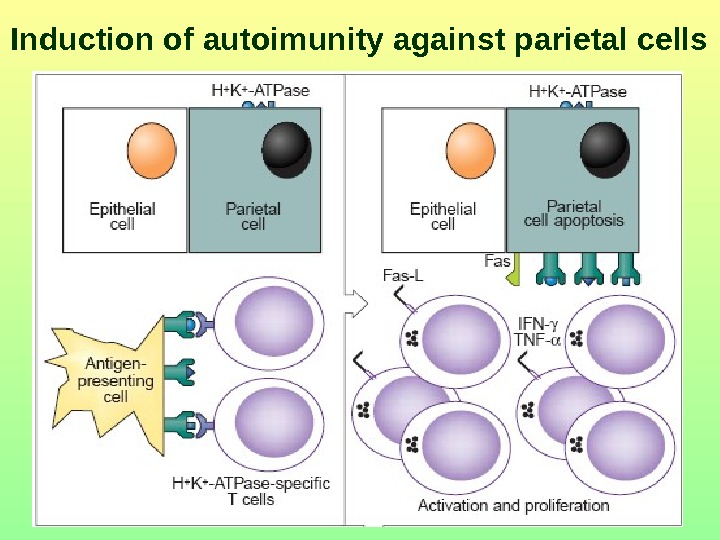
 Induction of autoimunity against parietal cells
Induction of autoimunity against parietal cells
 Mechanisms of immune-mediated parietal cell death leading to gastric atrophy
Mechanisms of immune-mediated parietal cell death leading to gastric atrophy
 Complications of gastric hyposecretion • Disorders of protein digestion • Hypokinesia • Disorders in barrier function • Disorders of iron and vitamin В 12 absorption • Disorders of intestinal secretion and digestion
Complications of gastric hyposecretion • Disorders of protein digestion • Hypokinesia • Disorders in barrier function • Disorders of iron and vitamin В 12 absorption • Disorders of intestinal secretion and digestion
 Increased gastric motility (gastric hyperkinesia) • Neurogenic • Increased production of НС l , gastrin , motilin … • Hypercalcemia • Pylorostenosis Complications : • Decrease volume adaptation • Increase in intragastric pressure • Increased tone of the stomach • Dyspepsia
Increased gastric motility (gastric hyperkinesia) • Neurogenic • Increased production of НС l , gastrin , motilin … • Hypercalcemia • Pylorostenosis Complications : • Decrease volume adaptation • Increase in intragastric pressure • Increased tone of the stomach • Dyspepsia
 Decrease of gastric motility • Neurogenic — reflex gastroparesis — authonomic neuropathy (diabetes, alcoholism) — vagotomia • Humoral — hyposecretion of Н CL — increased production of HCl , GIP , amylin … • Disorders of smooth muscle cell metabolism — anorexia — chronic intoxication — hypokalemia — ischemia
Decrease of gastric motility • Neurogenic — reflex gastroparesis — authonomic neuropathy (diabetes, alcoholism) — vagotomia • Humoral — hyposecretion of Н CL — increased production of HCl , GIP , amylin … • Disorders of smooth muscle cell metabolism — anorexia — chronic intoxication — hypokalemia — ischemia
 The passage of chyme through GI tract in normal conditions (A) and after resection of stomach (B)
The passage of chyme through GI tract in normal conditions (A) and after resection of stomach (B)
 The consequences of stomach resection • Disorders in reservoir function of the stomach • Decreased number of secretory cells ( achlorhydria) • Vitamin B 12 deficiency → anemia • Disturbance of fractional influx of chyme into the duodenum • Disturbances in the regulation of secretory function of pancreas and liver • Accelerated passage of chyme through the small intestine
The consequences of stomach resection • Disorders in reservoir function of the stomach • Decreased number of secretory cells ( achlorhydria) • Vitamin B 12 deficiency → anemia • Disturbance of fractional influx of chyme into the duodenum • Disturbances in the regulation of secretory function of pancreas and liver • Accelerated passage of chyme through the small intestine
 Mechanisms of jejunal (postgastrectomy, dumping) syndrome Early ( ~75% ) Dumping of the hyperosmolar chyme into the intestine • Influx of water into the lumen • Stimulation of intestinal peristaltics • Stimulation of BAS formation ( 5 -HT, VIP, kinins etc. ) Late ( ~25% ) Absorption of high amount of carbohydrates into the blood • Hyperglycemia insulin release hypoglycemia activation of sympathetic nervous system tachycardia, perspiration
Mechanisms of jejunal (postgastrectomy, dumping) syndrome Early ( ~75% ) Dumping of the hyperosmolar chyme into the intestine • Influx of water into the lumen • Stimulation of intestinal peristaltics • Stimulation of BAS formation ( 5 -HT, VIP, kinins etc. ) Late ( ~25% ) Absorption of high amount of carbohydrates into the blood • Hyperglycemia insulin release hypoglycemia activation of sympathetic nervous system tachycardia, perspiration

