2d35205811893263f7c9436124ca4f3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

PASODOBLE Progress on the development of local and regional downstream services Martijn Schaap, Thilo Erbertseder & PASODOBLE consortium FAIRMODE 4 th plenary meeting SMHI, June 16, 2011, Norrköping, Sweden
PASODOBLE – Service Domains Focus on and cities, complementary to Focus on regions and complementary to MACC 35 downstream AQ services to support local actors

PASODOBLE - Goal Develop and demonstrate user-driven services for the regional and local air quality sector by combining space-based data, in-situ data and models in 4 service lines: • Health community support for people at risk, hospitals, pharmacies and doctors • Public forecasting and assessment support for agencies, tourist industries and sport event organizer • Compliance monitoring support on particulate matter for regional environmental agencies • Local forecast model evaluation support for local authorities and city bodies … embeded in a generic, harmonised technical infrastructure
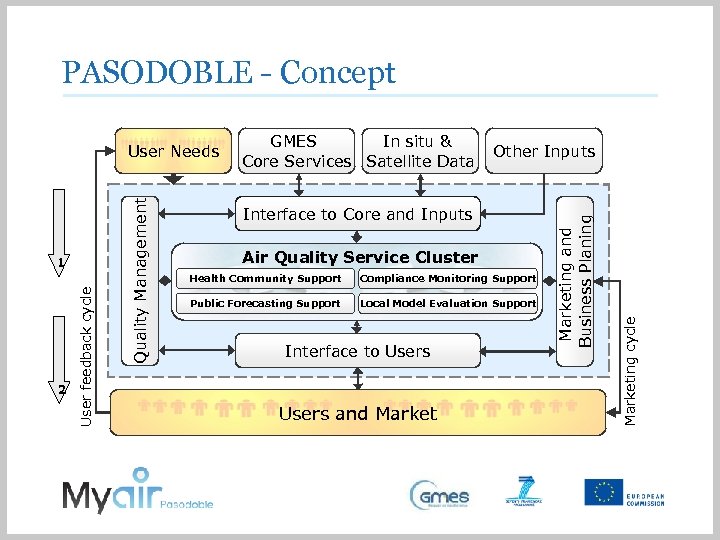
PASODOBLE - Concept Other Inputs Interface to Core and Inputs Air Quality Service Cluster Health Community Support Compliance Monitoring Support Public Forecasting Support Local Model Evaluation Support Interface to Users and Marketing and Business Planing GMES In situ & Core Services Satellite Data Marketing cycle 2 User feedback cycle 1 Quality Management User Needs

PASODOBLE - Objectives • Development and demonstration of AQ services for European regions/cities, based on documented needs and demonstrated capabilities of the ESA GSE PROMOTE user federation and service providers • Development and testing of a sustainable generic service infrastructure for efficient and effective implementation of (future) services and user access. • Utilization of multiple cycles of delivery, use, assessment vs. requirements including market intelligence assessment wrt to self-supportiveness and sustainability • Promotion of use of best/good practise and harmonization
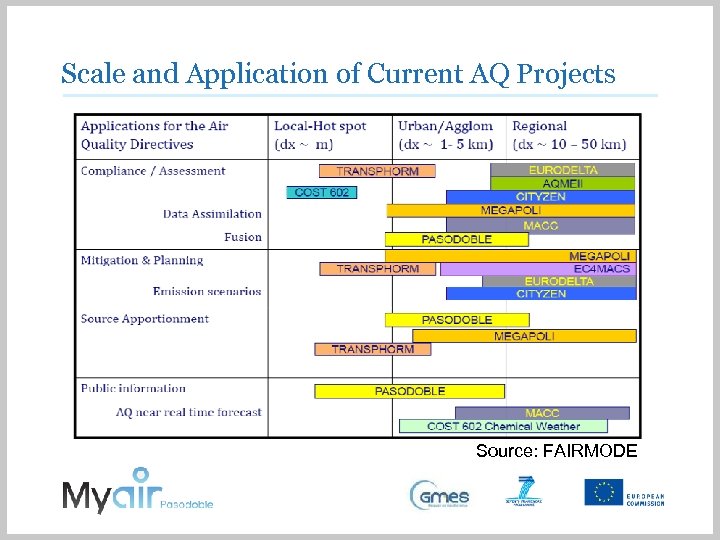
Scale and Application of Current AQ Projects Source: FAIRMODE
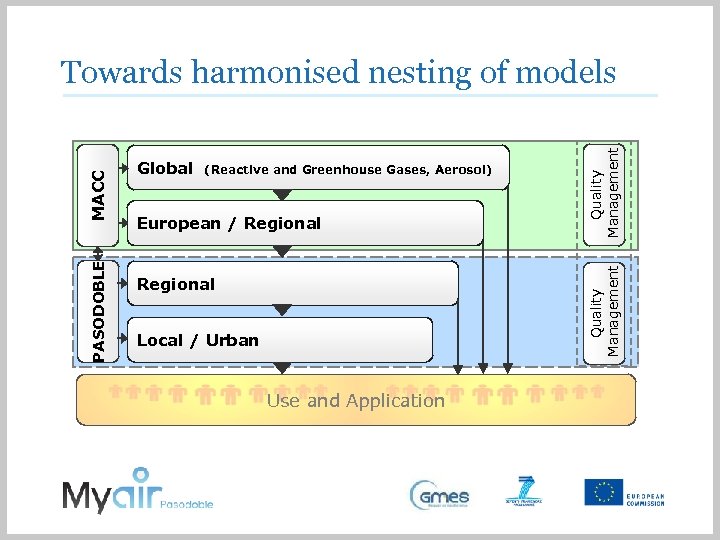
(Reactive and Greenhouse Gases, Aerosol) European / Regional Quality Management Global Quality Management PASODOBLE MACC Towards harmonised nesting of models Regional Local / Urban Use and Application
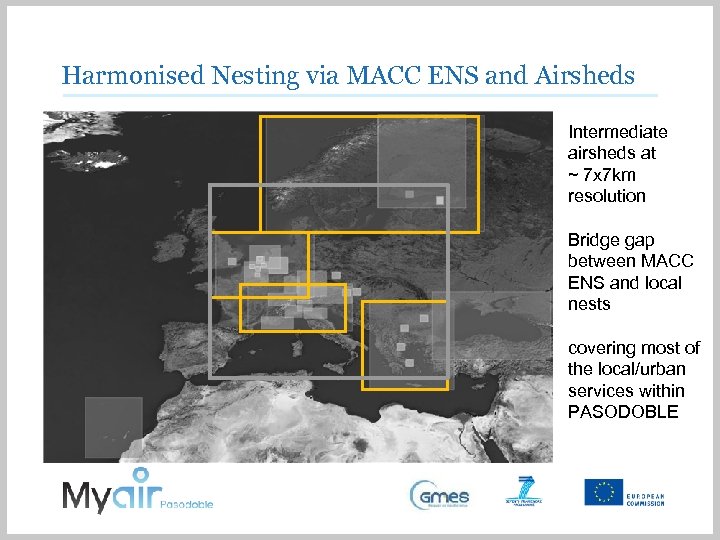
Harmonised Nesting via MACC ENS and Airsheds Intermediate airsheds at ~ 7 x 7 km resolution Bridge gap between MACC ENS and local nests covering most of the local/urban services within PASODOBLE

Nesting within MACC air quality ensemble • Currently airsheds nested into single MACC ensemble members • Currently tests are being performed using the MACC ensemble data as boundary conditions Issues: • • • Currently available O 3, NO 2, PM 10, SO 2 and CO. More species and vertical levels are required Timeliness: two nesting steps require availability of MACC data very early in morning NO 2 conc at 06: 00 for July 16, 2007 EURAD-IM IC-AIRSHED forecast system
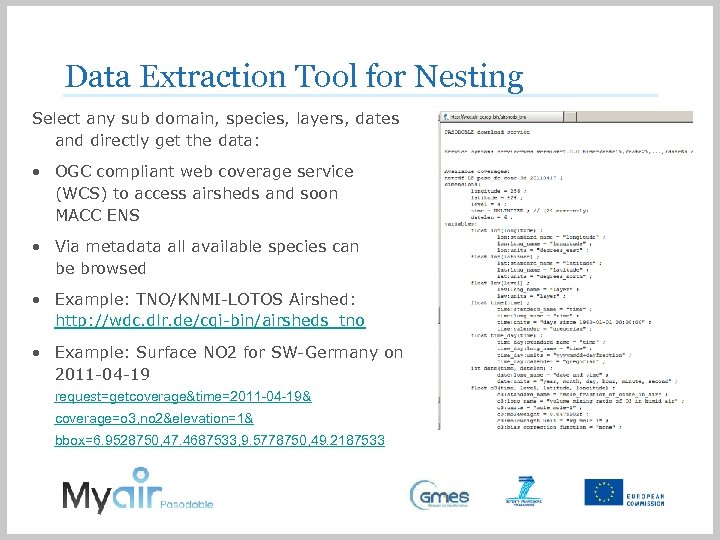
Data Extraction Tool for Nesting Select any sub domain, species, layers, dates and directly get the data: • OGC compliant web coverage service (WCS) to access airsheds and soon MACC ENS • Via metadata all available species can be browsed • Example: TNO/KNMI-LOTOS Airshed: http: //wdc. dlr. de/cgi-bin/airsheds_tno • Example: Surface NO 2 for SW-Germany on 2011 -04 -19 request=getcoverage&time=2011 -04 -19& coverage=o 3, no 2&elevation=1& bbox=6. 9528750, 47. 4687533, 9. 5778750, 49. 2187533
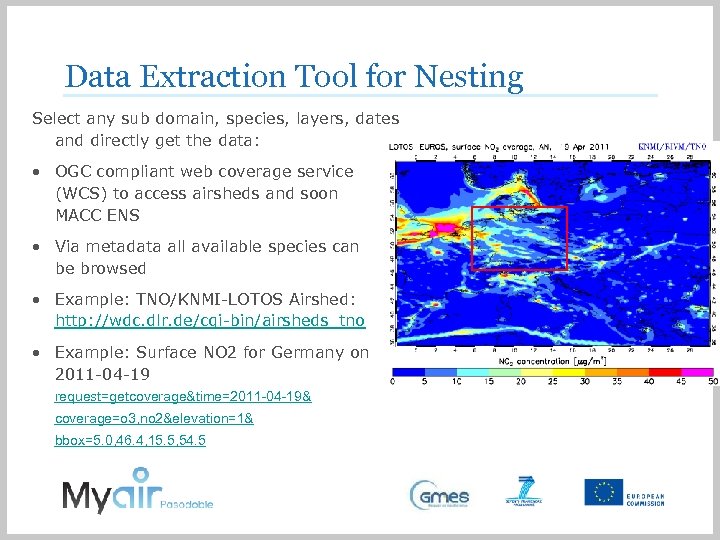
Data Extraction Tool for Nesting Select any sub domain, species, layers, dates and directly get the data: • OGC compliant web coverage service (WCS) to access airsheds and soon MACC ENS • Via metadata all available species can be browsed • Example: TNO/KNMI-LOTOS Airshed: http: //wdc. dlr. de/cgi-bin/airsheds_tno • Example: Surface NO 2 for Germany on 2011 -04 -19 request=getcoverage&time=2011 -04 -19& coverage=o 3, no 2&elevation=1& bbox=5. 0, 46. 4, 15. 5, 54. 5
Public Information and Assessment Support Services • Improvement of existing AQ services in 25 regions and cities • Regional harmonisation w. r. t INSPIRE and FAIRMODE guidance • Thematic integration (physical, chemical and biological weather forecasting) • Examples: – Harbour Management Support Antwerp – Road traffic management (NL) – Olympic Games London 2012 – Tourism Information Systems
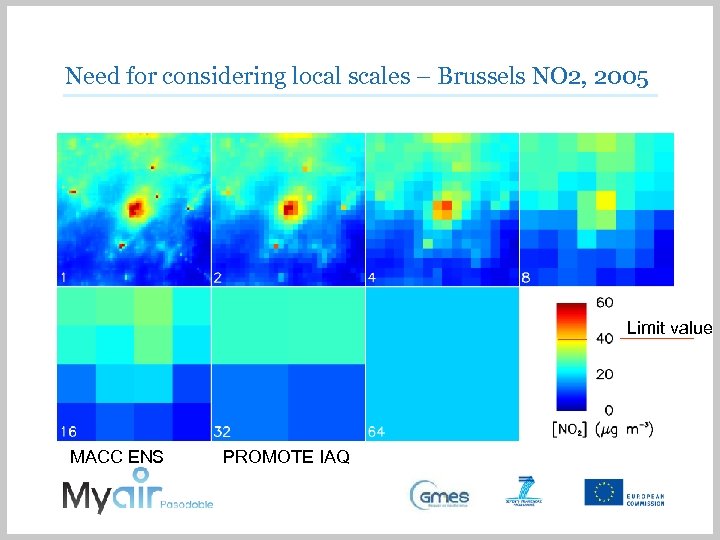
Need for considering local scales – Brussels NO 2, 2005 Limit value MACC ENS PROMOTE IAQ
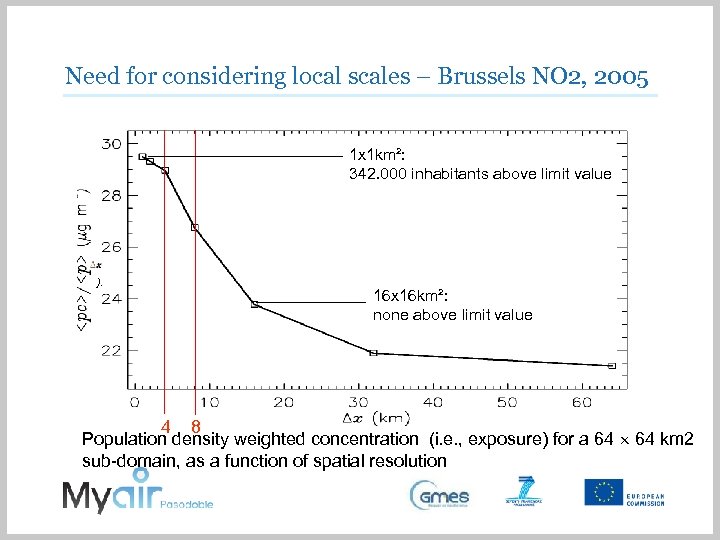
Need for considering local scales – Brussels NO 2, 2005 1 x 1 km²: 342. 000 inhabitants above limit value ). 16 x 16 km²: none above limit value 4 8 Population density weighted concentration (i. e. , exposure) for a 64 km 2 sub-domain, as a function of spatial resolution

Compliance Monitoring Support Services • Collaboration with agencies with AQ Directive compliance duties to facilitate their reporting • Provide explanation of exceedance of local emissions or advected dust • Use satellite data complementary to ground-based data • Improve upon existing desert dust services to provide daily quantitative analysis of dust (not forecasting) • Develop a satellite-based mapping tool for PM threshold exceedances
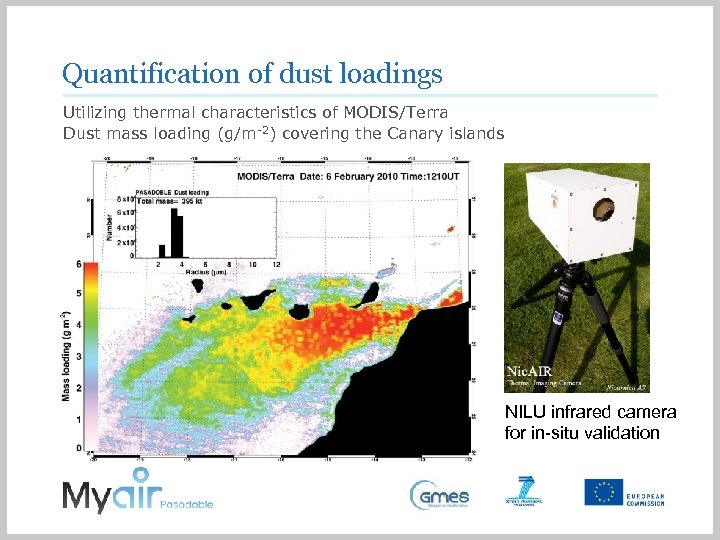
Quantification of dust loadings Utilizing thermal characteristics of MODIS/Terra Dust mass loading (g/m-2) covering the Canary islands NILU infrared camera for in-situ validation
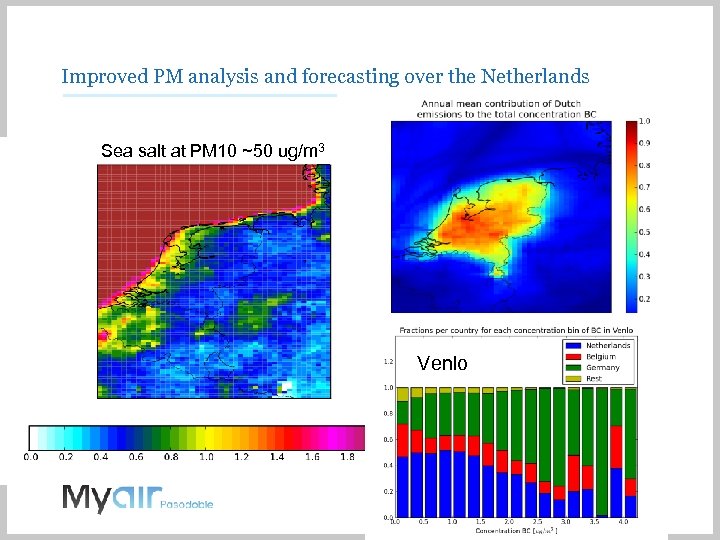
Improved PM analysis and forecasting over the Netherlands Sea salt at PM 10 ~50 ug/m 3 Venlo

Local Model Evaluation Support Service • Target: city bodies and authorities • Develop and demonstrate a toolbox • Set standard criteria and protocols for performance evaluation • Promote good practice wrt FAIRMODE and AQME II • Standardize interfaces • Support accountability/apportionment studies • Test cases with city authorities Sofia, Bratislava, Prague, Athens, Thessaloniki, London, Rotterdam • Demonstration during the next months

What will it be like? Methodology • Web based, structured advice and a toolbox • Evaluation of model output with respect to satellite and in situ measurements Aspects • basic criteria/fitness for purpose check list e. g. is model resolution consistent with application? • scientific assessment • model evaluation methodologies (concentrations) based on FAIRMODE guidance and AQME II • forecast accuracy criteria (metrics) e. g. AQ index, number of episodes correctly forecast, systematic/unsystematic etc

Difference to existing approaches • Focus on the local and urban scale • Focus on air quality forecasting • Focus on evaluation of operational models (probabilistic and operational) • Online Evaluation Support Service
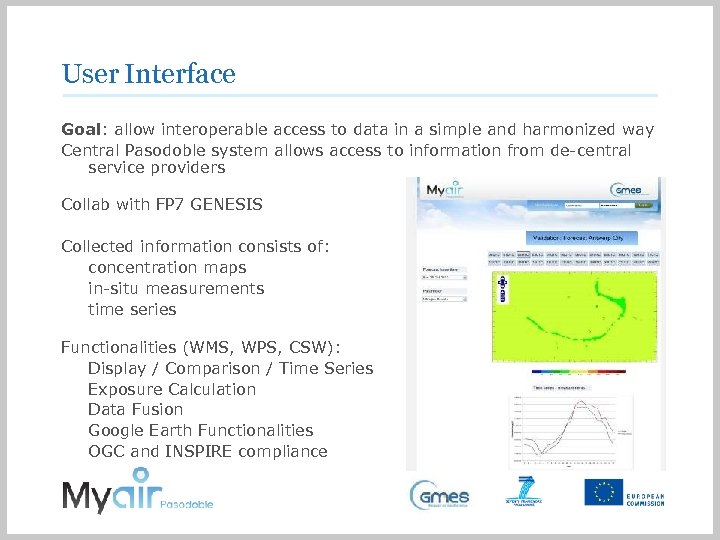
User Interface Goal: allow interoperable access to data in a simple and harmonized way Central Pasodoble system allows access to information from de-central service providers Collab with FP 7 GENESIS Collected information consists of: concentration maps in-situ measurements time series Functionalities (WMS, WPS, CSW): Display / Comparison / Time Series Exposure Calculation Data Fusion Google Earth Functionalities OGC and INSPIRE compliance

Summary • PASODOBLE builds on the achievements of PROMOTE and MACC and utilizes guidance from FAIRMODE • Develops a number of targeted and sustainable air quality services throughout Europe to support local actors • Develops a modular, generic and harmonized service infrastructure for efficient implementation of (future) services and user access • Follows a combined approach (modelling, in-situ, remote sensing) • Contributions to FAIRMODE on harmonised nesting, local model evaluation support, source attribution • Service prototypes have been developed, next step validation
www. myair-eu. org Contact: thilo. erbertseder@dlr. de pasodoble@dlr. de

PASODOBLE - Consortium DLR Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (coordinator), DE ACRI – ST, FR AEA Technology, UK AUTH Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, EL BMT ARGOSS, NL IASB Institut d’Aeronomie Spatiale de Belgique, BE BAS Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, GPh. I, BG CERC Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants, UK CGS Carlo Gavazzi Space, IT CHU Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nice, FR MUW Medical Uni Vienna / European Aeroallergen Network, AT EMA European Medical Association, INT FMI Finish Meteorological Institut, FI KNMI Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut, NL NILU Norsk Institutt for Luftforskning, NO RIU Rheinisches Institut für Umweltforschung, DE TAS-F Thales Alenia Space France, FR TNO Ned. Org. v. Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek, NL VITO Vlaamse instelling voor technologisch onderzoek, BE Nowcasting International, IE Outdoor Concepts, DE RIVM National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, NL
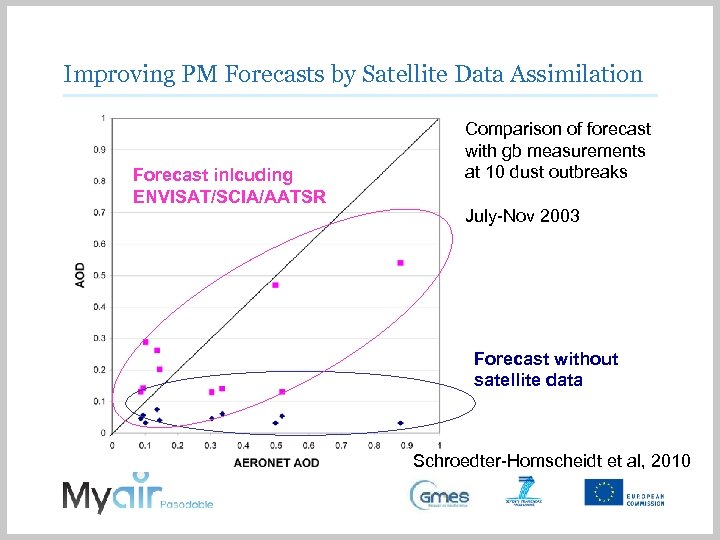
Improving PM Forecasts by Satellite Data Assimilation Forecast inlcuding ENVISAT/SCIA/AATSR Comparison of forecast with gb measurements at 10 dust outbreaks July-Nov 2003 Forecast without satellite data Schroedter-Homscheidt et al, 2010
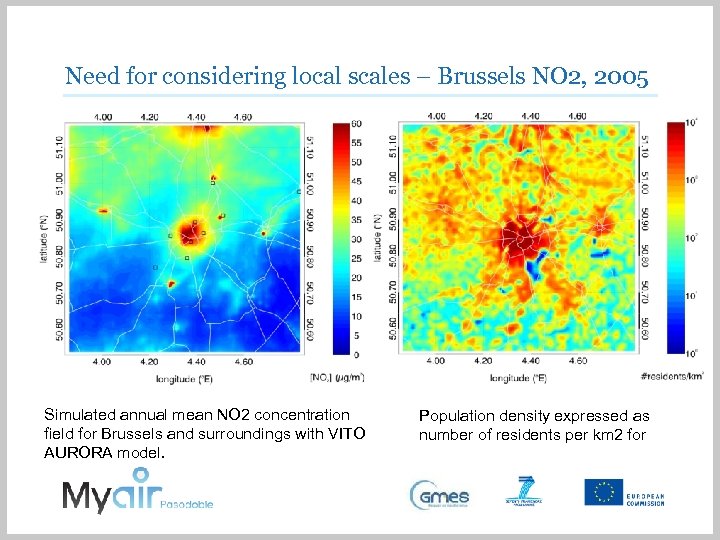
Need for considering local scales – Brussels NO 2, 2005 Simulated annual mean NO 2 concentration field for Brussels and surroundings with VITO AURORA model. Population density expressed as number of residents per km 2 for
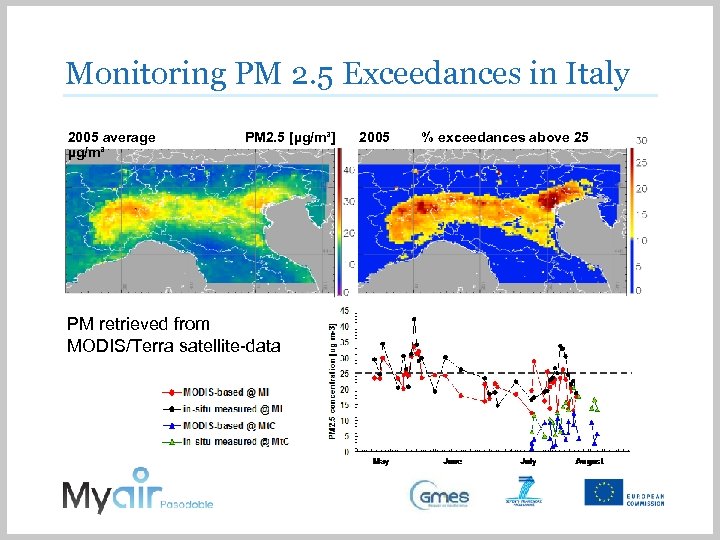
PASDOBLE: Compliance Monitoring DS COMP 3. 3 Monitoring PM 2. 5 Exceedances in Italy 2005 average µg/m³ PM 2. 5 [µg/m³] PM retrieved from MODIS/Terra satellite-data 2005 % exceedances above 25
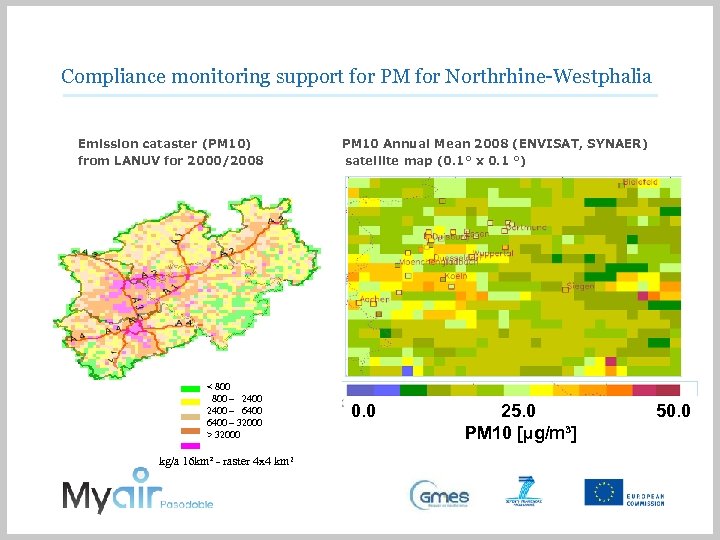
Compliance monitoring support for PM for Northrhine-Westphalia Emission cataster (PM 10) from LANUV for 2000/2008 < 800 – 2400 – 6400 – 32000 > 32000 kg/a 16 km² - raster 4 x 4 km 2 PM 10 Annual Mean 2008 (ENVISAT, SYNAER) satellite map (0. 1° x 0. 1 °) 0. 0 25. 0 PM 10 [µg/m³] 50. 0
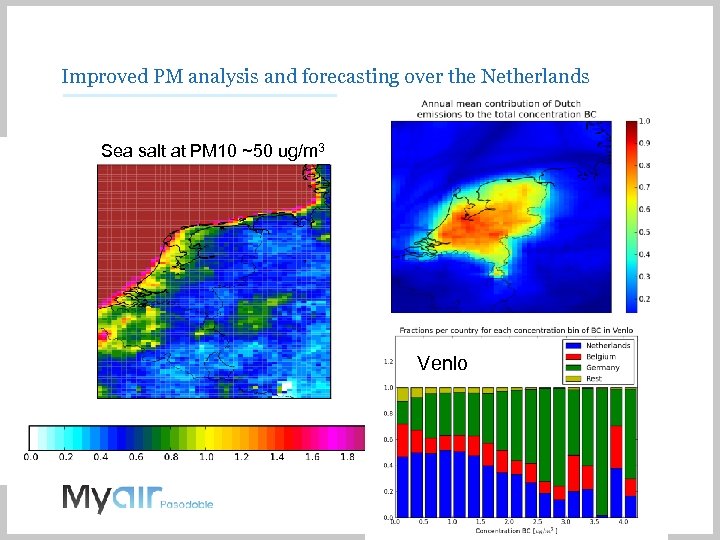
Improved PM analysis and forecasting over the Netherlands Sea salt at PM 10 ~50 ug/m 3 Venlo
2d35205811893263f7c9436124ca4f3a.ppt