904be86e3260ab8c43d4ee9fff861e91.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Parvovirus B 19 and HAV Screening of Whole Blood Donations SL Stramer, KL Kane, ML Beyers, RY Dodd, American Red Cross and RIF Smith, National Genetics Institute (NGI) AABB, 2001 Presented at FDA NAT Workshop, December 2001 and modified for Blood Products Advisory Committee, December 12, 2002 E 0202728 A 1

Background – 1 u Manufacturers of plasma derivatives have implemented NAT for nonenveloped viruses and such testing will likely be implemented for recovered plasma u Most parvovirus B 19 (B 19 V) NAT programs target the elimination of units ³ 1 x 106 copies/m. L u Studies of HAV and B 19 V frequencies in recovered plasma are limited. Dodd et al. , 1997 (AABB) from screening pools of 512 (NGI) reported: – 0: 20, 000 for HAV RNA – 7: 10, 000 for B 19 V DNA E 0202728 A 2

Background – 2 u Three-year experience at Vitex for NAT screening final product (2, 500 donations, NGI) for HAV or minipools of 100 for B 19 V (in-house) report: – 1: 476, 000 for HAV RNA – » 1: 800 for B 19 V DNA u ARC has obtained units from positive subpools of 20 from positive minipools of 100 for identification/ characterization of B 19 V-positive units – Of >1000 units tested from 72 positive subpools, only 23 tested B 19 V positive at NGI (from 16 subpools) • 77% (56/72) were false positive minipool results E 0202728 A 3
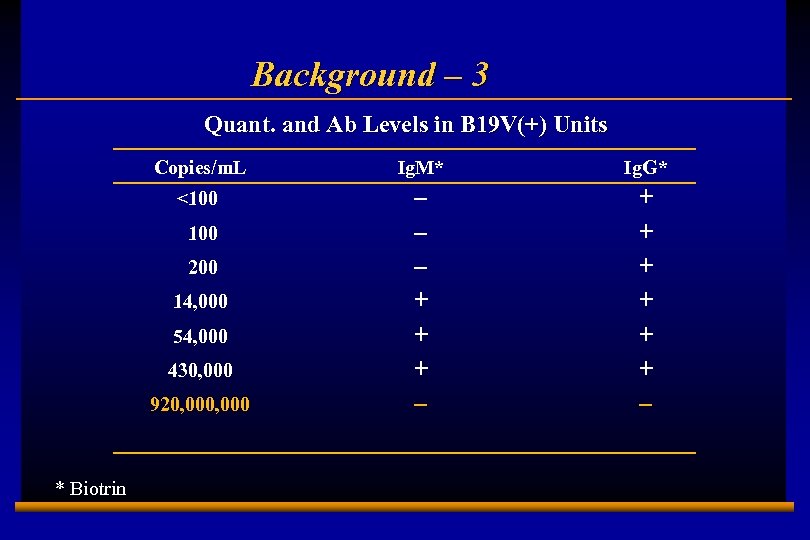
Background – 3 Quant. and Ab Levels in B 19 V(+) Units Copies/m. L Ig. M* Ig. G* <100 – – – + + + – 100 200 14, 000 54, 000 430, 000 920, 000 * Biotrin E 0202728 A 4
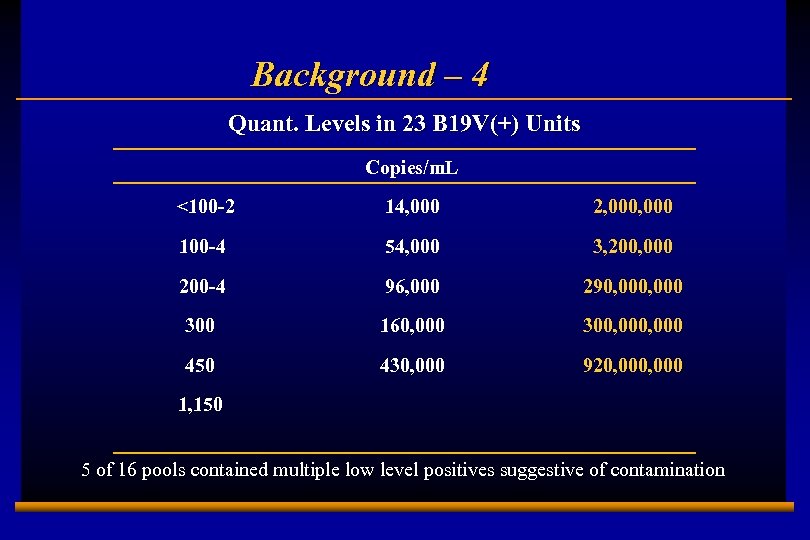
Background – 4 Quant. Levels in 23 B 19 V(+) Units Copies/m. L <100 -2 14, 000 2, 000 100 -4 54, 000 3, 200, 000 200 -4 96, 000 290, 000 300 160, 000 300, 000 450 430, 000 920, 000 1, 150 5 of 16 pools contained multiple low level positives suggestive of contamination E 0202728 A 5

Background – 5 Therefore, we know that: u HAV is infrequent u B 19 V NAT false positivity may be common u Low level B 19 V DNA positive, Ig. G positive samples occur u Individuals with early acute B 19 V infection have high viral titers E 0202728 A 6
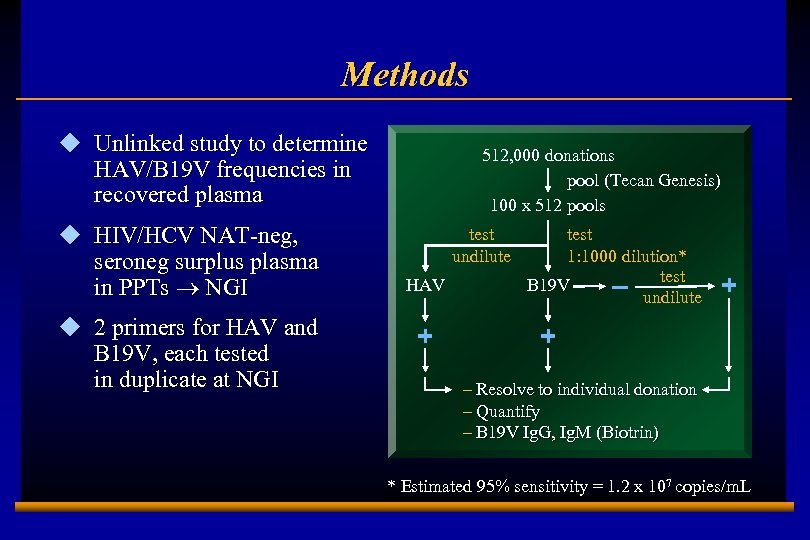
Methods u Unlinked study to determine HAV/B 19 V frequencies in recovered plasma u HIV/HCV NAT-neg, seroneg surplus plasma in PPTs ® NGI u 2 primers for HAV and B 19 V, each tested in duplicate at NGI 512, 000 donations pool (Tecan Genesis) 100 x 512 pools test undilute HAV + test 1: 1000 dilution* test B 19 V – undilute + + – Resolve to individual donation – Quantify – B 19 V Ig. G, Ig. M (Biotrin) * Estimated 95% sensitivity = 1. 2 x 107 copies/m. L E 0202728 A 7
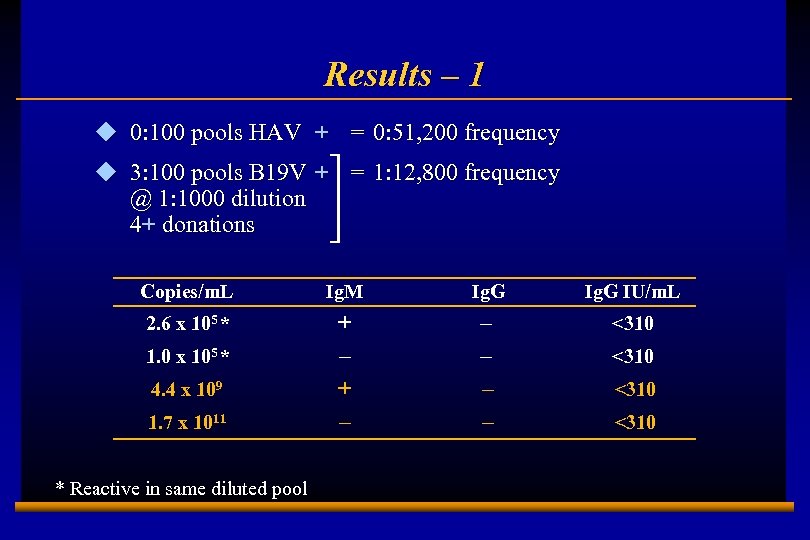
Results – 1 u 0: 100 pools HAV + = 0: 51, 200 frequency u 3: 100 pools B 19 V + = 1: 12, 800 frequency @ 1: 1000 dilution 4+ donations Copies/m. L Ig. M Ig. G IU/m. L 2. 6 x 105 * + – – – <310 1. 0 x 105 * 4. 4 x 109 1. 7 x 1011 * Reactive in same diluted pool E 0202728 A 8 <310
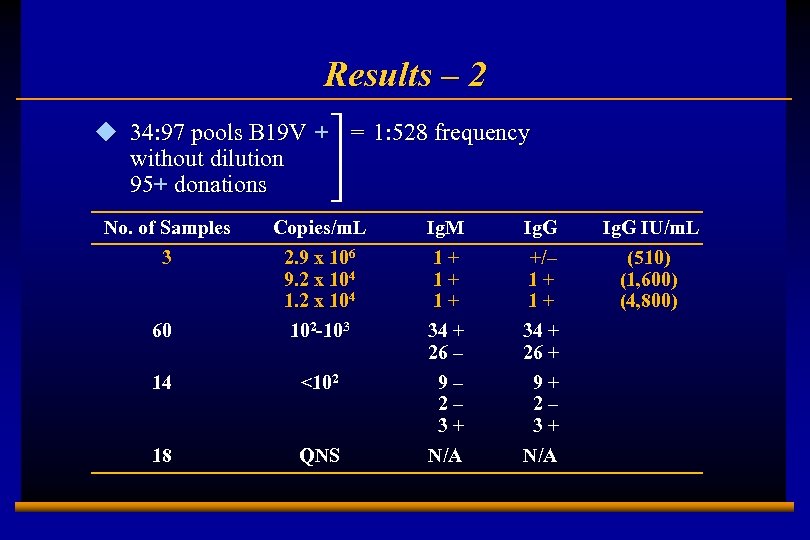
Results – 2 u 34: 97 pools B 19 V + = 1: 528 frequency without dilution 95+ donations No. of Samples 3 60 14 <102 18 E 0202728 A 9 Copies/m. L 2. 9 x 106 9. 2 x 104 102 -103 QNS Ig. M 1+ 1+ 1+ 34 + 26 – 9– 2– 3+ N/A Ig. G +/– 1+ 1+ 34 + 26 + 9+ 2– 3+ N/A Ig. G IU/m. L (510) (1, 600) (4, 800)

Parvovirus B 19 Prevalence Using Gen-Probe Assay u 2, 547 pools of 16 (April-May 2002 collections, N=40, 752) tested at Gen-Probe using a combination B 19 V/HAV NAT assay u 23 (0. 9%) pools of 16 repeat reactive and disc. B 19 V NAT reactive; no reactives for HAV u Assume one B 19 V-pos donation/reactive pool of 16 = 23/40, 752 = 1: 1, 772 versus 1: 12, 800 for NGI study (7 -fold higher) u Product loss, due to discard of all members of a reactive pool of 16 = 1: 111 (unacceptable) u Based on distribution of quant. results of 23 positive pools, the addition of a 1: 1, 000 predilution would result in a prevalence comparable to NGI (3/40, 752 = 1: 13, 584) E 0202728 A 10
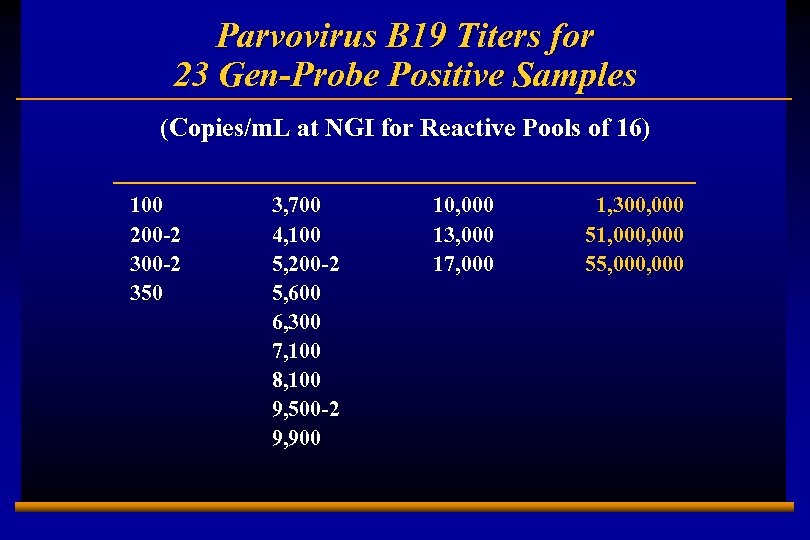
Parvovirus B 19 Titers for 23 Gen-Probe Positive Samples (Copies/m. L at NGI for Reactive Pools of 16) 100 200 -2 350 E 0202728 A 11 3, 700 4, 100 5, 200 -2 5, 600 6, 300 7, 100 8, 100 9, 500 -2 9, 900 10, 000 13, 000 17, 000 1, 300, 000 51, 000 55, 000
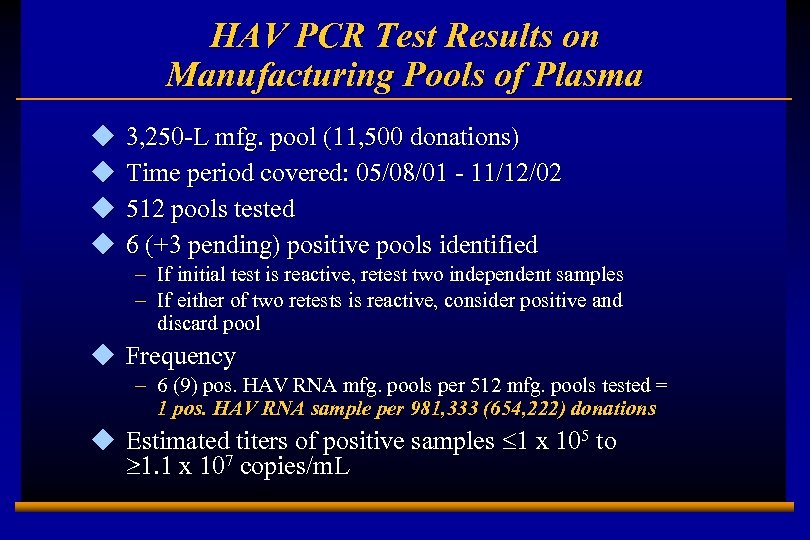
HAV PCR Test Results on Manufacturing Pools of Plasma u u 3, 250 -L mfg. pool (11, 500 donations) Time period covered: 05/08/01 - 11/12/02 512 pools tested 6 (+3 pending) positive pools identified – If initial test is reactive, retest two independent samples – If either of two retests is reactive, consider positive and discard pool u Frequency – 6 (9) pos. HAV RNA mfg. pools per 512 mfg. pools tested = 1 pos. HAV RNA sample per 981, 333 (654, 222) donations u Estimated titers of positive samples £ 1 x 105 to ³ 1. 1 x 107 copies/m. L E 0202728 A 12
E 0202728 A 13
Conclusions u Blood collectors considering implementation of B 19 V screening will have to evaluate NAT methods that are relatively insensitive to prevent issues from contamination and detection of low level NAT positives – 1: 12, 800 frequency using insensitive method • 1: 25, 600 high-titer, acute viremic donors, Ig. G-negative – 1: 528 frequency using sensitive method • 1: 17, 000 moderate-titer, Ig. G+/–, Ig. M+ • 1: 539 low-titer, Ig. G+, Ig. M+/– E 0202728 A 14

Conclusions u High-titer screening methods may not capture all infectious B 19 V-positive units; however, infectivity of Ab-reactive, low-titer positives is unknown u This study defines expected yields of B 19 V if sensitive and insensitive NAT methods are used u This study also demonstrates the infrequent occurrence of HAV in recovered plasma – 1: 476, 000 to 1: 981, 333 million donations E 0202728 A 15
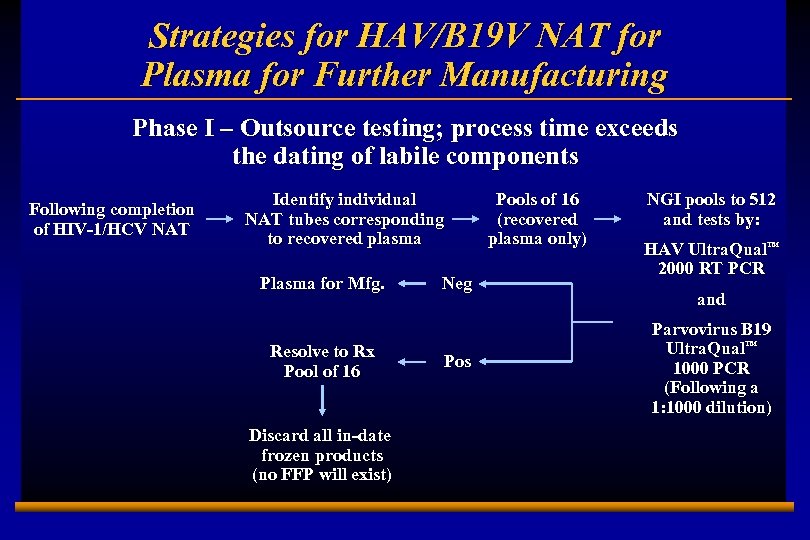
Strategies for HAV/B 19 V NAT for Plasma for Further Manufacturing Phase I – Outsource testing; process time exceeds the dating of labile components Following completion of HIV-1/HCV NAT Identify individual NAT tubes corresponding to recovered plasma Plasma for Mfg. Resolve to Rx Pool of 16 Discard all in-date frozen products (no FFP will exist) E 0202728 A 16 Neg Pos Pools of 16 (recovered plasma only) NGI pools to 512 and tests by: HAV Ultra. Qual™ 2000 RT PCR and Parvovirus B 19 Ultra. Qual™ 1000 PCR (Following a 1: 1000 dilution)

Strategies for HAV/B 19 V NAT for Plasma for Further Manufacturing Phase II –HAV/B 19 V Testing In-House (commercial kit) u “Real-time” pool testing (pool size TBD) u Reactives resolved to individual donation u No product release unless HAV/B 19 V NAT neg u B 19 V sensitivity level initially set for the removal of high-titer units (³ 106 copies/m. L) for plasma only – No “claims” for labile products – Determine needs for recipients of labile products u Donor notification, management of products from NAT-Rx donors’ previous donations and recipient tracing TBD u Timeline dependent on regulatory policy/availability of test kit E 0202728 A 17
904be86e3260ab8c43d4ee9fff861e91.ppt