f54863c50f4a90106dd7a24ae7a34dc1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Partnership for a sustainable social enterprise in global health education in Bangladesh 1
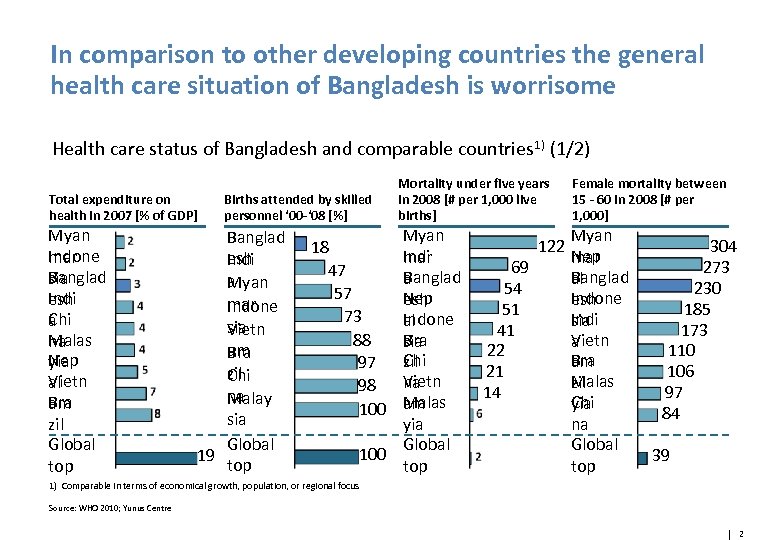
In comparison to other developing countries the general health care situation of Bangladesh is worrisome Health care status of Bangladesh and comparable countries 1) (1/2) Total expenditure on health in 2007 [% of GDP] Myan Indone mar Banglad sia Indi esh Chi a Malas na Nep yia Vietn al Bra am zil Global top Births attended by skilled personnel ‘ 00 -‘ 08 [%] Banglad esh Indi a Myan mar Indone sia Vietn am Bra zil Chi na Malay sia Global 19 top Mortality under five years in 2008 [# per 1, 000 live births] Myan Indi mar Banglad a Nep esh Indone al Bra sia Chi zil Vietn na Malas am yia Global 100 top 18 47 57 73 88 97 98 100 69 54 51 41 22 21 14 122 Female mortality between 15 - 60 in 2008 [# per 1, 000] Myan Nep mar Banglad al Indone esh Indi sia Vietn a Bra am Malas zil Chi yia na Global top 304 273 230 185 173 110 106 97 84 39 1) Comparable in terms of economical growth, population, or regional focus Source: WHO 2010; Yunus Centre 2 2

Bangladesh is ranked among countries with the lowest nurse density as well as a weak nurse vs. doctor ratio Health care status of Bangladesh and comparable countries (2/2) Density of nurses and midwives 1) [# per 10 k people] Brazil Malaysia India Myanmar China Indonesia Vietnam Nepal Bangladesh Ratio of nurses and midwives vs. doctors 1) 29 The regional average number of health care workers is 4 times higher than in Bangladesh according to the WHO Indonesia Malaysia Myanmar Nepal India Brazil Vietnam Bangladesh China 8. 0 2. 6 2. 5 2. 2 1. 7 1. 3 1. 0 0. 7 Only China has a worse ratio than Bangladesh – Neighboring countries show a much higher ratio 1) 2000 -2009 Source: WHO; Yunus Centre 3
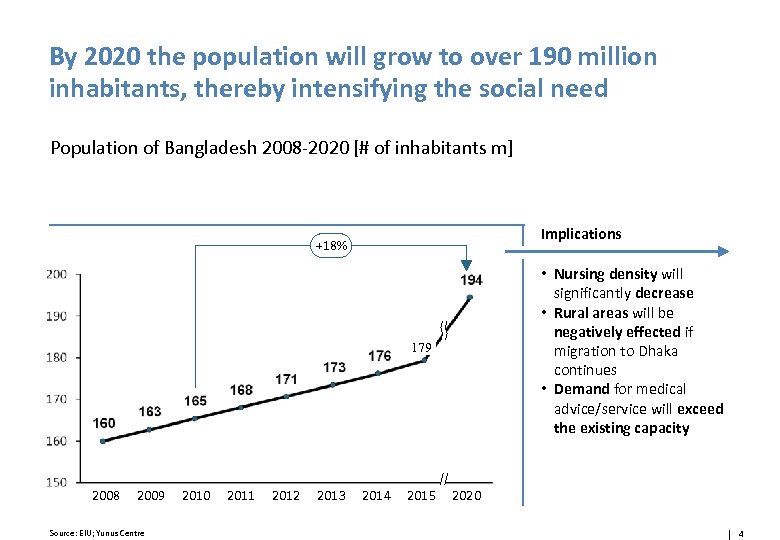
By 2020 the population will grow to over 190 million inhabitants, thereby intensifying the social need Population of Bangladesh 2008 -2020 [# of inhabitants m] Implications +18% • Nursing density will significantly decrease • Rural areas will be negatively effected if migration to Dhaka continues • Demand for medical advice/service will exceed the existing capacity 179 2008 2009 Source: EIU; Yunus Centre 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2020 4

The standard of nursing education is inadequate and a career in nursing is seen as an unattractive profession Major reasons of the nursing shortage in Bangladesh (1/3) 1| Education standard • Lack of qualified teachers and schools • Existing schools have very poor conditions and facilities 2| Unattractiveness • Young people have little motivation to enter the profession as self-esteem is low • Nursing is regarded as a very low level occupation in Bangladesh Source: Yunus Centre 5
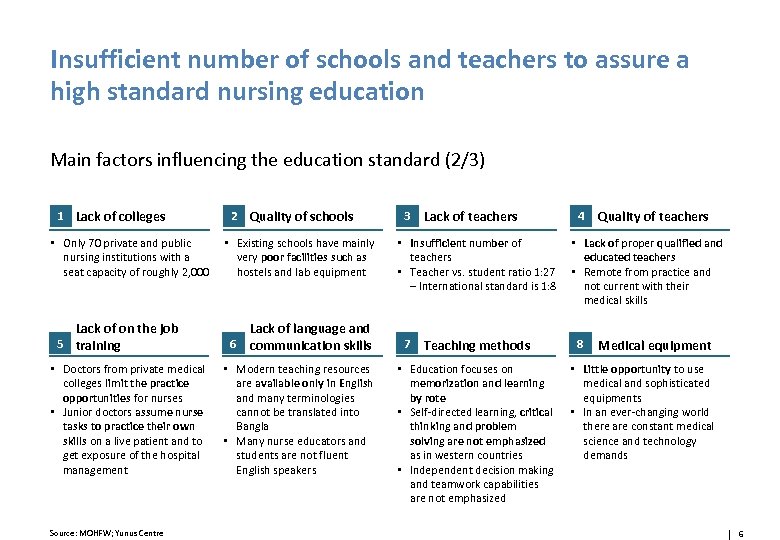
Insufficient number of schools and teachers to assure a high standard nursing education Main factors influencing the education standard (2/3) 1 Lack of colleges • Only 70 private and public nursing institutions with a seat capacity of roughly 2, 000 Lack of on the job 5 training • Doctors from private medical colleges limit the practice opportunities for nurses • Junior doctors assume nurse tasks to practice their own skills on a live patient and to get exposure of the hospital management Source: MOHFW; Yunus Centre 2 Quality of schools • Existing schools have mainly very poor facilities such as hostels and lab equipment Lack of language and 6 communication skills • Modern teaching resources are available only in English and many terminologies cannot be translated into Bangla • Many nurse educators and students are not fluent English speakers 3 Lack of teachers • Insufficient number of teachers • Teacher vs. student ratio 1: 27 – International standard is 1: 8 7 Teaching methods • Education focuses on memorization and learning by rote • Self-directed learning, critical thinking and problem solving are not emphasized as in western countries • Independent decision making and teamwork capabilities are not emphasized 4 Quality of teachers • Lack of proper qualified and educated teachers • Remote from practice and not current with their medical skills 8 Medical equipment • Little opportunity to use medical and sophisticated equipments • In an ever-changing world there are constant medical science and technology demands 6

The nursing profession is seen as a limited and low paid career opportunity Main factors influencing the unattractiveness (3/3) 1 Low salary • Low compensation (e. g. clinics: Tk 5 k ~7 k per month for a Diploma nurse) • Emigration – Better career opportunities in neighboring countries 6 Public opinion • Media does not play a positive role to improve the image • Cultural sensitivities • Public negative perception decreases the bride value Source: Yunus Centre 2 Bad reputation 3 Career chances 4 No motivation • Regarded as a very low level occupation • Only considered by girls from less affluent society and with relatively weaker educational qualification • Frustration due to the lack of career development and job enrichment • Young generation is keen to study new courses like MBA, etc. • Low standards of education and selfesteem 7 Aid nurses • Aid nurses are doing many of the jobs which are meant for real nurses • Their lack of competence is giving a bad name to the whole nursing profession 8 Lack of respect • Doctors and patients do not show proper respect towards the nursing profession 9 Patient care • Nurses are often unprofessional with patients, scolding or ignoring them, and often leaving actual patient care to untrained assistants 5 Rural jobs • No interest to work in rural areas where vacancies are high • High tendency to stay in Dhaka or even migrate to Dhaka Lack of role 10 model • There are no existing education role models 7
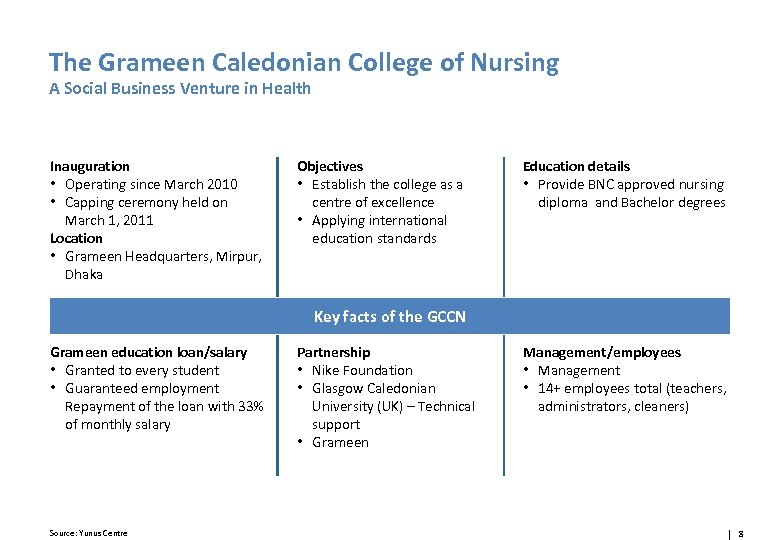
The Grameen Caledonian College of Nursing A Social Business Venture in Health Inauguration • Operating since March 2010 • Capping ceremony held on March 1, 2011 Location • Grameen Headquarters, Mirpur, Dhaka Objectives • Establish the college as a centre of excellence • Applying international education standards Education details • Provide BNC approved nursing diploma and Bachelor degrees Key facts of the GCCN Grameen education loan/salary • Granted to every student • Guaranteed employment Repayment of the loan with 33% of monthly salary Source: Yunus Centre Partnership • Nike Foundation • Glasgow Caledonian University (UK) – Technical support • Grameen Management/employees • Management • 14+ employees total (teachers, administrators, cleaners) 8

Grameen selection criteria are strict and more stringent than BNC criteria – Mother must be a Grameen borrower Overview of BNC and Grameen criteria – Student example Selection criteria 1. Wealth: Grameen – Mother of student must be a borrower of Grameen bank 2. Education: Grameen – HSC-GPA must be higher than 3 (BNC – GPA must be higher than 2, 5) 3. Subjects: Grameen – Science track mandatory (BNC – Science track preferable) 4. Age: Grameen – 3 years after graduation (BNC – 18 years and above) 5. Marital status: Grameen – Unmarried 6. Fitness: BNC – Medical certificate indicates good health and physical fitness Source: Yunus Centre 9

An education loan and job is granted to each student Sustainability approach for the college 1 Grameen education loan • Covers all tuition fees as well as accommodation and food • Every Grameen student is entitled for it 2 Guaranteed employment • Placement opportunity in one of the Grameen clinics 3 Payback terms • Approximately 33 % of monthly salary needs to be used for loan repayment Source: Yunus Centre 10

The Curriculum Education and fee details Diploma • Length: 3 years • Classes: – 2, 688 hours for clinical practice – 1, 440 hours for theoretical college classes • Subjects: 34 Source: Yunus Centre Diploma and Bachelor • Subjects: – English, chemistry, physics, biology, social science – Pharmacology, nursing, computer, leadership, management, midwifery, etc. • Timing: – 5 days a week – 8. 30 am till 4. 30 pm – One month summer holidays – One month winter holidays Bachelor • Length: – Option A: 3 years diploma + 2 years Bachelor – Option B: 4 years Bachelor • Classes: – Intensified lessons – According to affiliated university guidelines 11

We apply international standards for the nursing education to ensure quality New teaching approaches and methods • Use of international standard literature • Students taught to independently make decisions • Focus on teamwork Goals • Development of an educational role model Laboratory equipment • Equipped with the latest medical technology • Maintain high technology level • Educated nurses will be able to fulfill all relevant medical assignments Emphasis is on practical work • Strong guidance by experienced nurses and training with patients • Partnerships with well established hospitals • Nurse practitioners will be able to carry responsibility of independent primary healthcare providers Teacher and Professor qualification • Strict selection by the college management • International advisory by partner university Source: Yunus Centre 12

GCCN aims to improve the reputation of the nursing profession and doctor vs. nurse ratio and empower young women Objectives To contribute towards mitigating extreme shortage of nurses and to help to achieve the standard 1: 3 the doctor vs. nurse ratio in Bangladesh To strengthen the nursing components of the GK Health clinics and in other health service centers in Bangladesh with nurses of quality training To produce qualified nurses, leaders, with high level of professional standards To offer opportunities for higher income earning to the older adolescent girls and younger women through a career in nursing, thus empowering them To provide opportunities for potential Grameen Bank borrower’s children to be trained and employed To empower women from rural areas and enable them to generate income for their families To contribute towards improving the status of nursing in Bangladesh Source: Yunus Centre 13
f54863c50f4a90106dd7a24ae7a34dc1.ppt