 Part VI – Contemporary Challenges in Entrepreneurship Chapter 18 – Acquisition and Valuation of Business Ventures Chapter 19 – Management Succession and Continuity: A Family Business Perspective Chapter 20 – Women and Minority Entrepreneurship Chapter 21 – Total Quality Management: The Continuous Improvement Challenge for Entrepreneurs Copyright (c) 2004 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved.
Part VI – Contemporary Challenges in Entrepreneurship Chapter 18 – Acquisition and Valuation of Business Ventures Chapter 19 – Management Succession and Continuity: A Family Business Perspective Chapter 20 – Women and Minority Entrepreneurship Chapter 21 – Total Quality Management: The Continuous Improvement Challenge for Entrepreneurs Copyright (c) 2004 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 – Acquisition and Valuation of Business Ventures
Chapter 18 – Acquisition and Valuation of Business Ventures
 The Importance of Business Valuation • Buying or selling a business • Establishing an employee stock option plan (ESOP) • Raising growth capital through stock warrants • Determining inheritance tax liability • Attempting to buy out a partner • Going public
The Importance of Business Valuation • Buying or selling a business • Establishing an employee stock option plan (ESOP) • Raising growth capital through stock warrants • Determining inheritance tax liability • Attempting to buy out a partner • Going public
 Acquisition of a Business Venture • • Personal Preferences Examination of Opportunities Evaluation of the Selected Venture Due Diligence
Acquisition of a Business Venture • • Personal Preferences Examination of Opportunities Evaluation of the Selected Venture Due Diligence
 Due Diligence A complete “due diligence, ” which means a thorough analysis of every facet of the existing business 1. Why is this business being sold? 2. What is the physical condition of the business? 3. How many key personnel will remain? 4. What is the degree of competition? 5. What are the conditions of the lease?
Due Diligence A complete “due diligence, ” which means a thorough analysis of every facet of the existing business 1. Why is this business being sold? 2. What is the physical condition of the business? 3. How many key personnel will remain? 4. What is the degree of competition? 5. What are the conditions of the lease?
 Due Diligence 6. Do any liens against the business exist? 7. Will the owner sign a covenant not to compete? 8. Are any special licenses required? 9. What are the future trends of the business? 10. How much capital is needed to buy?
Due Diligence 6. Do any liens against the business exist? 7. Will the owner sign a covenant not to compete? 8. Are any special licenses required? 9. What are the future trends of the business? 10. How much capital is needed to buy?
 Underlying Issues • Goals of the Buyer and Seller • Emotional Bias • Reasons for the Acquisition
Underlying Issues • Goals of the Buyer and Seller • Emotional Bias • Reasons for the Acquisition
 Analyzing the Business Many closely held ventures have the following shortcomings: • Lack of management depth • Undercapitalization • Insufficient controls • Divergent goals
Analyzing the Business Many closely held ventures have the following shortcomings: • Lack of management depth • Undercapitalization • Insufficient controls • Divergent goals
 Establishing A Firm’s Value • Valuation Methods – Adjusted Tangible Book Value – Price/Earnings Ratio (Multiple of Earnings) Method – Discounted Earnings Method
Establishing A Firm’s Value • Valuation Methods – Adjusted Tangible Book Value – Price/Earnings Ratio (Multiple of Earnings) Method – Discounted Earnings Method
 The Leveraged Buyout: An Alternative for Small Ventures This allows the entrepreneur to finance the transaction by borrowing on the target company’s assets. This method is the leveraged buyout (LBO).
The Leveraged Buyout: An Alternative for Small Ventures This allows the entrepreneur to finance the transaction by borrowing on the target company’s assets. This method is the leveraged buyout (LBO).
 Entrepreneurial Leveraged Buyout (E-LBO) Is characterized as having: 1. At least two-thirds of the purchase price generated from borrowed funds, 2. More than 50% of the stock after acquisition owned by single individuals or their family, and, 3. The majority investors devoting themselves to the active management of the company after acquisition.
Entrepreneurial Leveraged Buyout (E-LBO) Is characterized as having: 1. At least two-thirds of the purchase price generated from borrowed funds, 2. More than 50% of the stock after acquisition owned by single individuals or their family, and, 3. The majority investors devoting themselves to the active management of the company after acquisition.
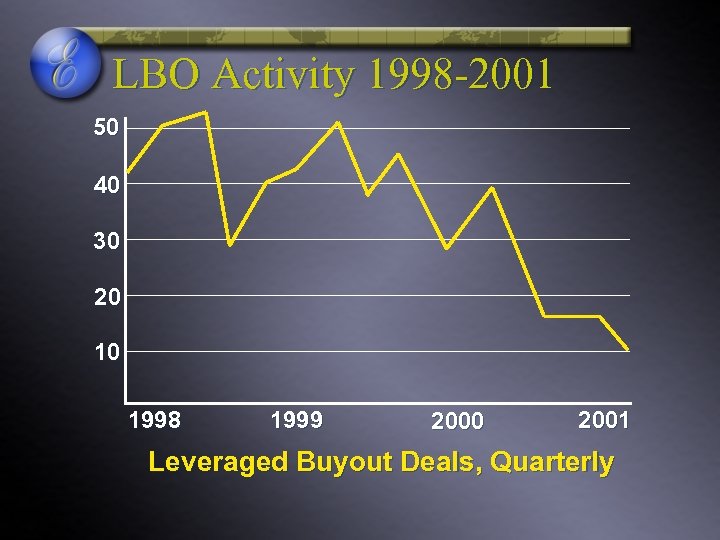 LBO Activity 1998 -2001 50 40 30 20 10 1998 1999 2000 2001 Leveraged Buyout Deals, Quarterly
LBO Activity 1998 -2001 50 40 30 20 10 1998 1999 2000 2001 Leveraged Buyout Deals, Quarterly
 Cash-Flow Leveraged Buyout (LBO) This type is different because a cashflow lender relies very heavily on the target company’s cash.
Cash-Flow Leveraged Buyout (LBO) This type is different because a cashflow lender relies very heavily on the target company’s cash.