MM1e Chapter 04 revised.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 part TWO INFORMATION DRIVES MARKETING DECISION MAKING chapter 04 PERSPECTIVES ON CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT chapter 05 MANAGING MARKETING INFORMATION chapter 06 UNDERSTANDING COMPETITORS: ANALYSIS TO ACTION chapter 07 UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMERS – BUSINESS TO CONSUMER MARKETS chapter 08 UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMERS – BUSINESS TO BUSINESS MARKETS Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
part TWO INFORMATION DRIVES MARKETING DECISION MAKING chapter 04 PERSPECTIVES ON CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT chapter 05 MANAGING MARKETING INFORMATION chapter 06 UNDERSTANDING COMPETITORS: ANALYSIS TO ACTION chapter 07 UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMERS – BUSINESS TO CONSUMER MARKETS chapter 08 UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMERS – BUSINESS TO BUSINESS MARKETS Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 CHAPTER 04 PERSPECTIVES ON CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
CHAPTER 04 PERSPECTIVES ON CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define CRM and articulate its objectives and capabilities Describe the CRM process cycle Understand the concept of customer touchpoints and why touchpoints are critical in CRM CHAPTER 04 Distinguish customer marketing from consumer marketing, and understand why the distinction is important Discuss what happens when CRM fails and how to avoid potential failure Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 3
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define CRM and articulate its objectives and capabilities Describe the CRM process cycle Understand the concept of customer touchpoints and why touchpoints are critical in CRM CHAPTER 04 Distinguish customer marketing from consumer marketing, and understand why the distinction is important Discuss what happens when CRM fails and how to avoid potential failure Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 3
 WHAT IS CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT? Cuts across the whole business enterprise Is a business strategy, set of operational processes, and analytic tools Is enabled by technology but is not just “the software” CHAPTER 04 Has the ultimate goal of maximizing performance of the customer side of the enterprise Requires a customer-centric philosophy and culture, as well as leadership and commitment to CRM from the top Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 4
WHAT IS CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT? Cuts across the whole business enterprise Is a business strategy, set of operational processes, and analytic tools Is enabled by technology but is not just “the software” CHAPTER 04 Has the ultimate goal of maximizing performance of the customer side of the enterprise Requires a customer-centric philosophy and culture, as well as leadership and commitment to CRM from the top Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 4
 WHY CRM? CRM is a timely and relevant topic that ties together a number of important concepts of modern marketing management. CRM is an important enabler of great marketing. CHAPTER 04 Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 5
WHY CRM? CRM is a timely and relevant topic that ties together a number of important concepts of modern marketing management. CRM is an important enabler of great marketing. CHAPTER 04 Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 5
 OBJECTIVES AND CAPABILITIES OF CRM Customer Relationship Management (CRM): a comprehensive business model for increasing revenues and profits by focusing on customers. CHAPTER 04 Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 6
OBJECTIVES AND CAPABILITIES OF CRM Customer Relationship Management (CRM): a comprehensive business model for increasing revenues and profits by focusing on customers. CHAPTER 04 Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 6
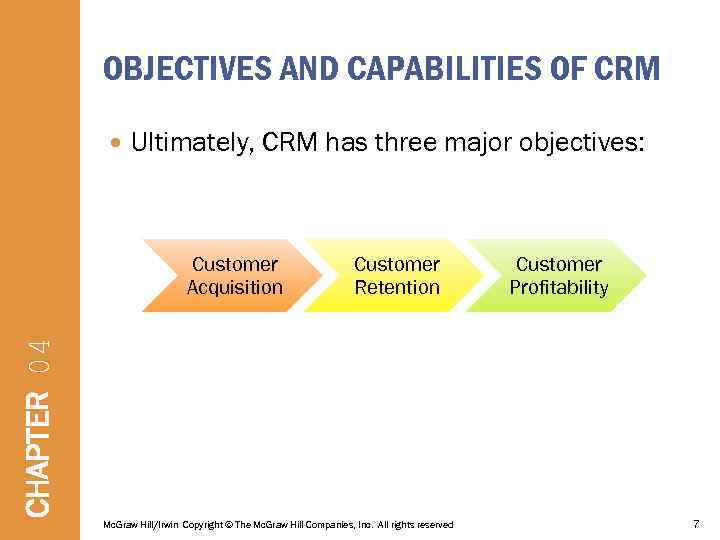 OBJECTIVES AND CAPABILITIES OF CRM Ultimately, CRM has three major objectives: Customer Retention CHAPTER 04 Customer Acquisition Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved Customer Profitability 7
OBJECTIVES AND CAPABILITIES OF CRM Ultimately, CRM has three major objectives: Customer Retention CHAPTER 04 Customer Acquisition Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved Customer Profitability 7
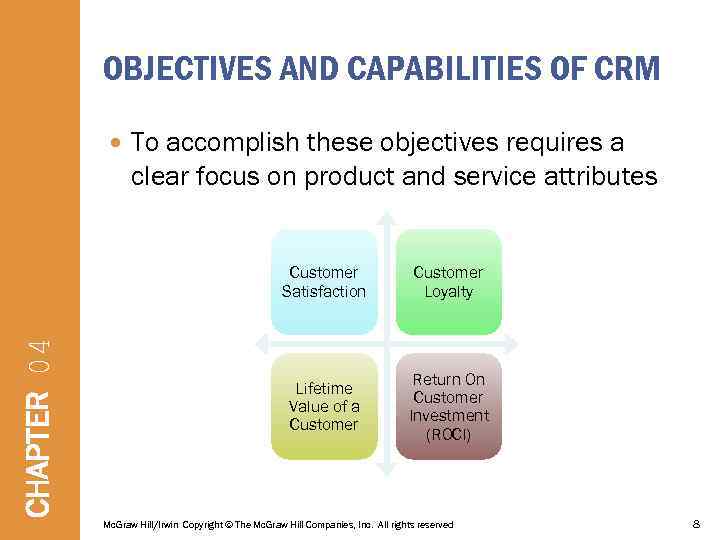 OBJECTIVES AND CAPABILITIES OF CRM To accomplish these objectives requires a clear focus on product and service attributes CHAPTER 04 Customer Satisfaction Customer Loyalty Lifetime Value of a Customer Return On Customer Investment (ROCI) Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 8
OBJECTIVES AND CAPABILITIES OF CRM To accomplish these objectives requires a clear focus on product and service attributes CHAPTER 04 Customer Satisfaction Customer Loyalty Lifetime Value of a Customer Return On Customer Investment (ROCI) Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 8
 THE CRM PROCESS CYCLE Knowledge Discovery 2. Market Planning 3. Customer Interaction 4. Analysis and Refinement CHAPTER 04 1. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 9
THE CRM PROCESS CYCLE Knowledge Discovery 2. Market Planning 3. Customer Interaction 4. Analysis and Refinement CHAPTER 04 1. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 9
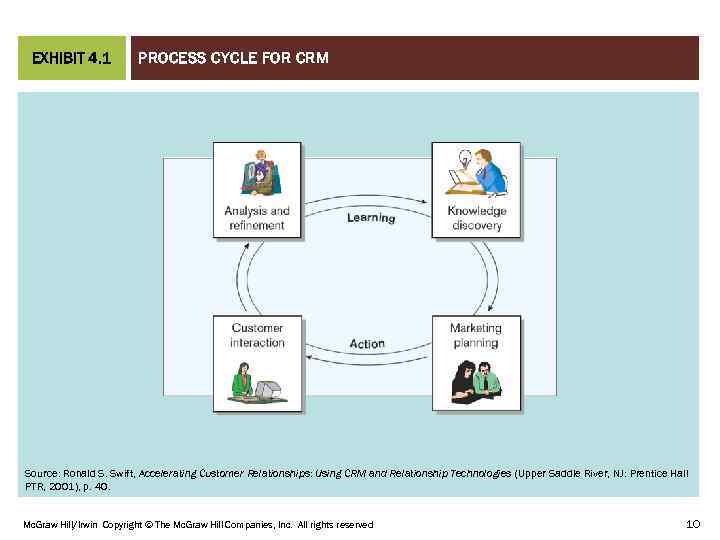 PROCESS CYCLE FOR CRM CHAPTER 01 EXHIBIT 4. 1 Source: Ronald S. Swift, Accelerating Customer Relationships: Using CRM and Relationship Technologies (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR, 2001), p. 40. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 10
PROCESS CYCLE FOR CRM CHAPTER 01 EXHIBIT 4. 1 Source: Ronald S. Swift, Accelerating Customer Relationships: Using CRM and Relationship Technologies (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR, 2001), p. 40. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 10
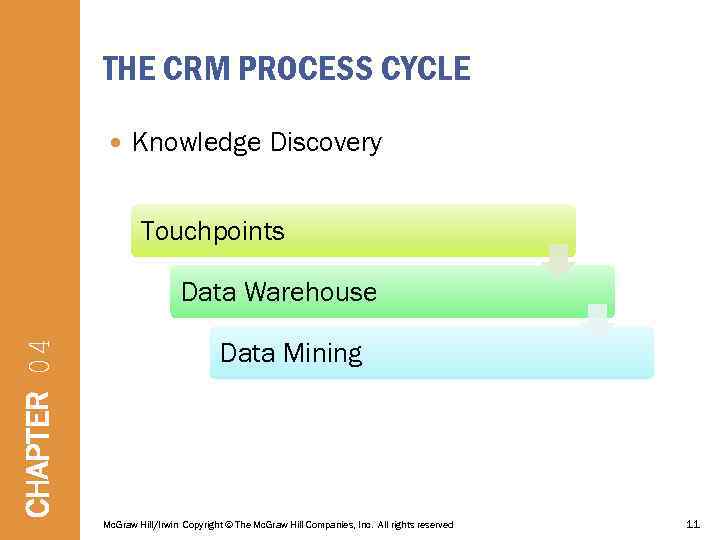 THE CRM PROCESS CYCLE Knowledge Discovery Touchpoints CHAPTER 04 Data Warehouse Data Mining Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 11
THE CRM PROCESS CYCLE Knowledge Discovery Touchpoints CHAPTER 04 Data Warehouse Data Mining Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 11
 CUSTOMER MARKETING VERSUS CONSUMER MARKETING Mass Marketing Consumer Marketing Customer Marketing CHAPTER 04 Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 12
CUSTOMER MARKETING VERSUS CONSUMER MARKETING Mass Marketing Consumer Marketing Customer Marketing CHAPTER 04 Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 12
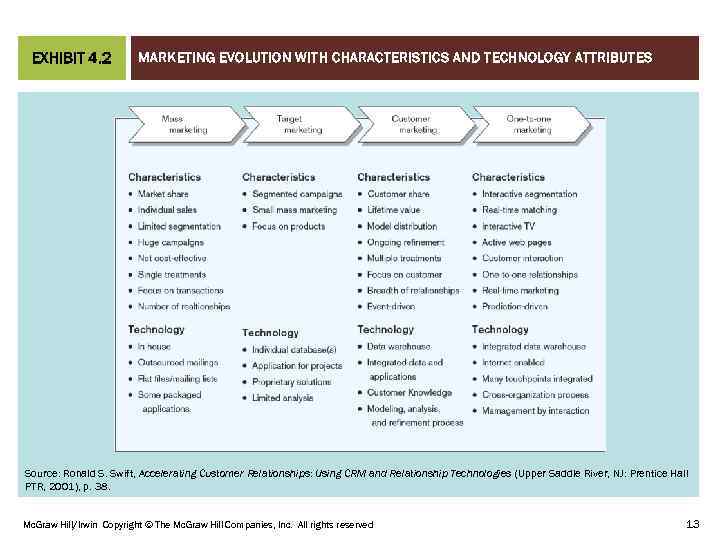 MARKETING EVOLUTION WITH CHARACTERISTICS AND TECHNOLOGY ATTRIBUTES CHAPTER 01 EXHIBIT 4. 2 Source: Ronald S. Swift, Accelerating Customer Relationships: Using CRM and Relationship Technologies (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR, 2001), p. 38. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 13
MARKETING EVOLUTION WITH CHARACTERISTICS AND TECHNOLOGY ATTRIBUTES CHAPTER 01 EXHIBIT 4. 2 Source: Ronald S. Swift, Accelerating Customer Relationships: Using CRM and Relationship Technologies (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR, 2001), p. 38. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 13
 ADVANTAGES OF CUSTOMER MARKETING Reduced Promotional Costs Improved Targeting Improved Capability CHAPTER 04 Increased Effectiveness Increased Sensitivity Increased Speed Improved Use of the Customer Channel Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 14
ADVANTAGES OF CUSTOMER MARKETING Reduced Promotional Costs Improved Targeting Improved Capability CHAPTER 04 Increased Effectiveness Increased Sensitivity Increased Speed Improved Use of the Customer Channel Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 14
 CRM FACILITATES A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC CULTURE Adopting a relationship or partnership business model overall, with mutually shared rewards and risk management. 2. Redefining the selling role within the firm to focus on customer business consultation and solutions. 3. Increasing formalization of customer analysis processes. 4. CHAPTER 04 1. Taking a proactive leadership role in educating customers about value chain opportunities available by developing a business relationship. 5. Focusing on continuous improvement principles stressing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 15
CRM FACILITATES A CUSTOMER-CENTRIC CULTURE Adopting a relationship or partnership business model overall, with mutually shared rewards and risk management. 2. Redefining the selling role within the firm to focus on customer business consultation and solutions. 3. Increasing formalization of customer analysis processes. 4. CHAPTER 04 1. Taking a proactive leadership role in educating customers about value chain opportunities available by developing a business relationship. 5. Focusing on continuous improvement principles stressing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 15
 CRM ENABLES TRANSFORMATION INTO A RELATIONSHIP-BASED ENTERPRISE Customers 1. Who are our customers? 2. What do our customers want and expect? CHAPTER 04 3. What is the value proposition of our customers? Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 16
CRM ENABLES TRANSFORMATION INTO A RELATIONSHIP-BASED ENTERPRISE Customers 1. Who are our customers? 2. What do our customers want and expect? CHAPTER 04 3. What is the value proposition of our customers? Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 16
 CRM ENABLES TRANSFORMATION INTO A RELATIONSHIP-BASED ENTERPRISE The Relationship 4. What kind of relationship do we want to build with our customers? CHAPTER 04 5. How do we foster exchange of value between us and our customers? 6. How do we work together and share control? Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 17
CRM ENABLES TRANSFORMATION INTO A RELATIONSHIP-BASED ENTERPRISE The Relationship 4. What kind of relationship do we want to build with our customers? CHAPTER 04 5. How do we foster exchange of value between us and our customers? 6. How do we work together and share control? Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 17
 CRM ENABLES TRANSFORMATION INTO A RELATIONSHIP-BASED ENTERPRISE Managerial Decision Making 7. Who are we and what is our value proposition? CHAPTER 04 8. What do our products and brands represent to customers? 9. How do we organize to move value closer to our customers? 10. How do we measure and manage our performance? 11. How do we increase our capacity for change? Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 18
CRM ENABLES TRANSFORMATION INTO A RELATIONSHIP-BASED ENTERPRISE Managerial Decision Making 7. Who are we and what is our value proposition? CHAPTER 04 8. What do our products and brands represent to customers? 9. How do we organize to move value closer to our customers? 10. How do we measure and manage our performance? 11. How do we increase our capacity for change? Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 18
 WHAT HAPPENS WHEN CRM FAILS? Flavor of the Month Club No Allowances for Organization al Change Poor Training CHAPTER 04 Why? Business Units Silos Low Level of Employee Buy-in Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 19
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN CRM FAILS? Flavor of the Month Club No Allowances for Organization al Change Poor Training CHAPTER 04 Why? Business Units Silos Low Level of Employee Buy-in Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 19
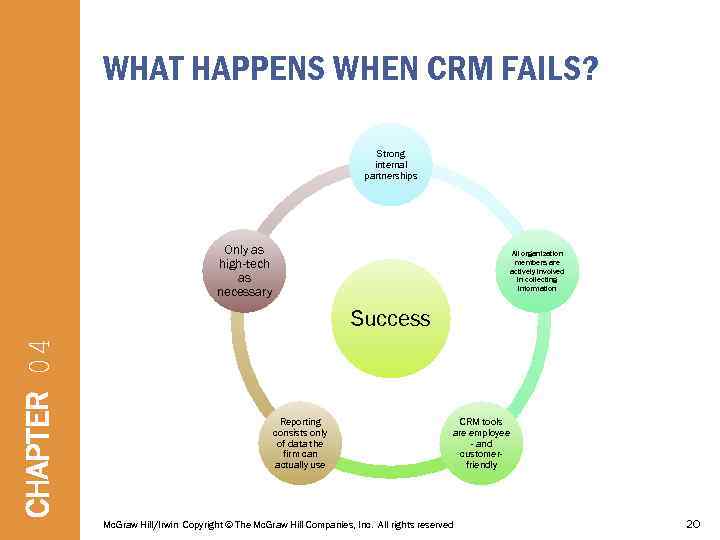 WHAT HAPPENS WHEN CRM FAILS? Strong internal partnerships Only as high-tech as necessary All organization members are actively involved in collecting information CHAPTER 04 Success Reporting consists only of data the firm can actually use CRM tools are employee - and customerfriendly Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 20
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN CRM FAILS? Strong internal partnerships Only as high-tech as necessary All organization members are actively involved in collecting information CHAPTER 04 Success Reporting consists only of data the firm can actually use CRM tools are employee - and customerfriendly Mc. Graw Hill/Irwin Copyright © The Mc. Graw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 20


