cfdfac852632fc9ccf7ac0eede384f6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Part III: Vocabulary Background knowledge is the most important factor in reading comprehension. Vocabulary is the most important factor in background knowledge. Vocabulary provides access to concepts.

Best Practices in Vocabulary Instruction: Depth of processing: Multiple exposures Multiple meanings Multiple contexts Multiple forms of a word Opportunity to communicate Purposeful repetition Treating phrases as words Verbal and Nonverbal processing
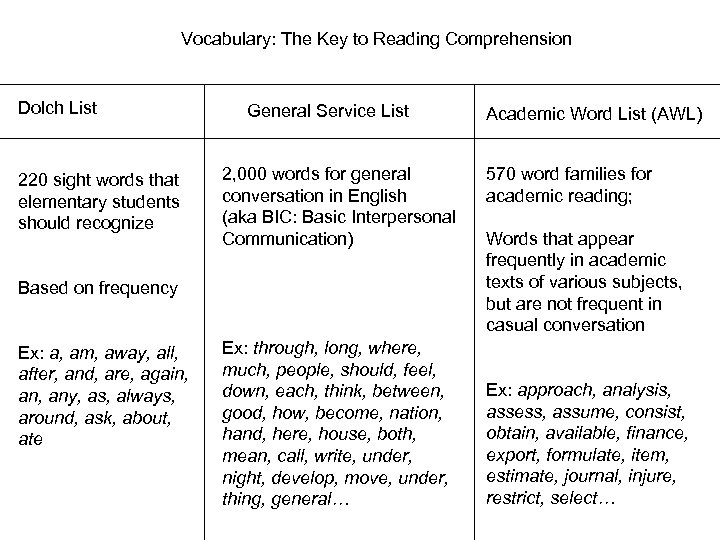
Vocabulary: The Key to Reading Comprehension Dolch List 220 sight words that elementary students should recognize General Service List 2, 000 words for general conversation in English (aka BIC: Basic Interpersonal Communication) Based on frequency Ex: a, am, away, all, after, and, are, again, any, as, always, around, ask, about, ate Ex: through, long, where, much, people, should, feel, down, each, think, between, good, how, become, nation, hand, here, house, both, mean, call, write, under, night, develop, move, under, thing, general… Academic Word List (AWL) 570 word families for academic reading; Words that appear frequently in academic texts of various subjects, but are not frequent in casual conversation Ex: approach, analysis, assess, assume, consist, obtain, available, finance, export, formulate, item, estimate, journal, injure, restrict, select…

High-Incidence Academic Word List (AWL) 570 words Comprise 10% of the words in academic discourse Are outside of the 2, 000 -3, 000 words that are necessary for basic social communication in English CALP: Cognitive Academic Linguistic Proficiency 570 words on the AWL 2, 000 -3, 000 words for basic social communication BIC: Basic Interpersonal Communication

AWL is arranged in 10 sublists, in order of frequency 65% of the words on the AWL have Latin/Greek word components The words on the AWL can be used to form about 3, 000 words (by adding prefixes and suffixes)
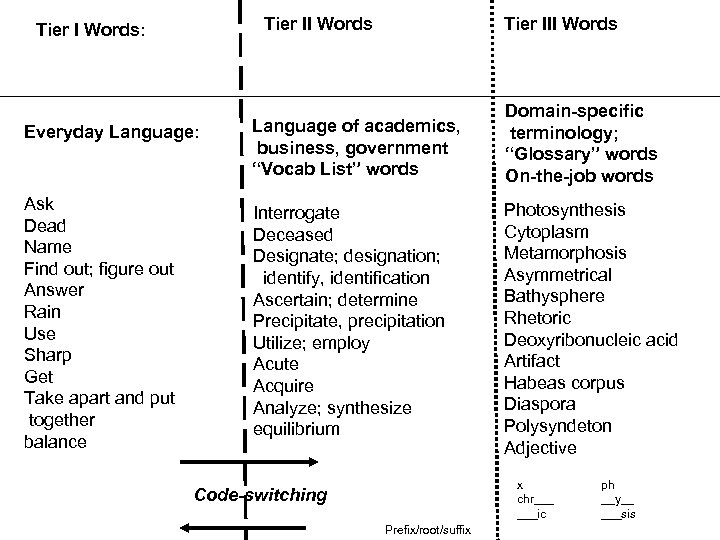
Tier II Words Tier I Words: Language of academics, business, government “Vocab List” words Domain-specific terminology; “Glossary” words On-the-job words Interrogate Deceased Designate; designation; identify, identification Ascertain; determine Precipitate, precipitation Utilize; employ Acute Acquire Analyze; synthesize equilibrium Everyday Language: Ask Dead Name Find out; figure out Answer Rain Use Sharp Get Take apart and put together balance Tier III Words Photosynthesis Cytoplasm Metamorphosis Asymmetrical Bathysphere Rhetoric Deoxyribonucleic acid Artifact Habeas corpus Diaspora Polysyndeton Adjective x chr___ ___ic Code-switching Prefix/root/suffix ph __y__ ___sis
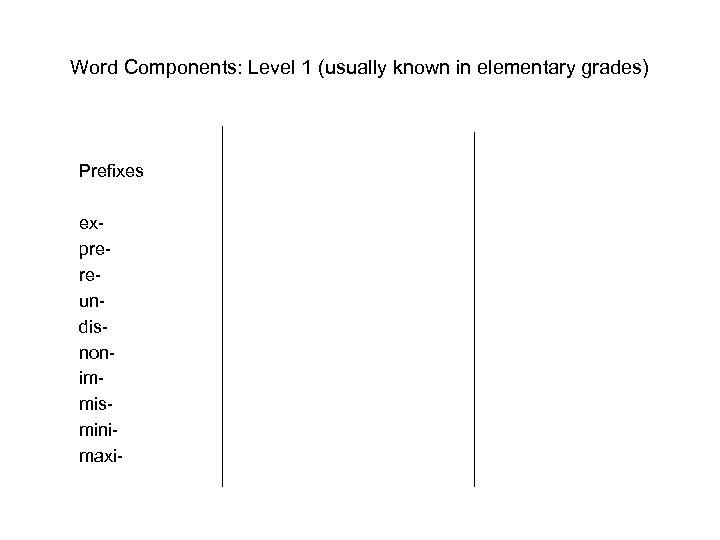
Word Components: Level 1 (usually known in elementary grades) Prefixes exprereundisnonimmisminimaxi-
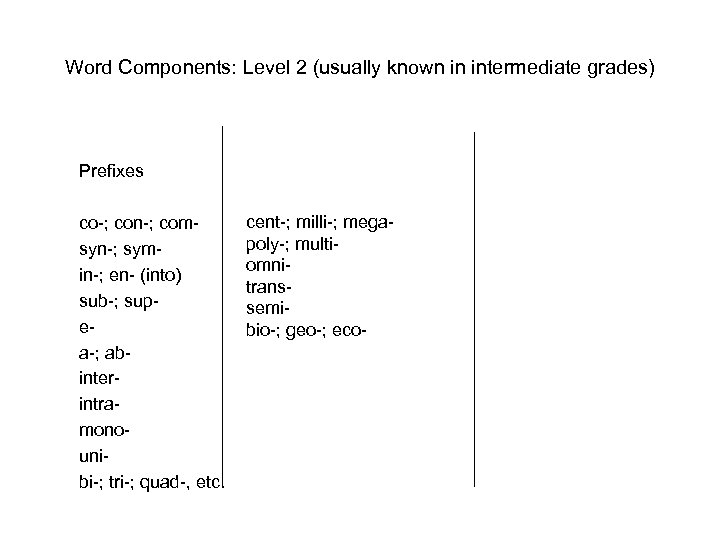
Word Components: Level 2 (usually known in intermediate grades) Prefixes co-; con-; comsyn-; symin-; en- (into) sub-; supea-; abinterintramonounibi-; tri-; quad-, etc. cent-; milli-; megapoly-; multiomnitranssemibio-; geo-; eco-

Word Components: Level 3 (usually known in high school) Prefixes pseudodemiendo-; ectoproperperihemiobbenemal- photonomigmunicontraphilo-


Indigenous people
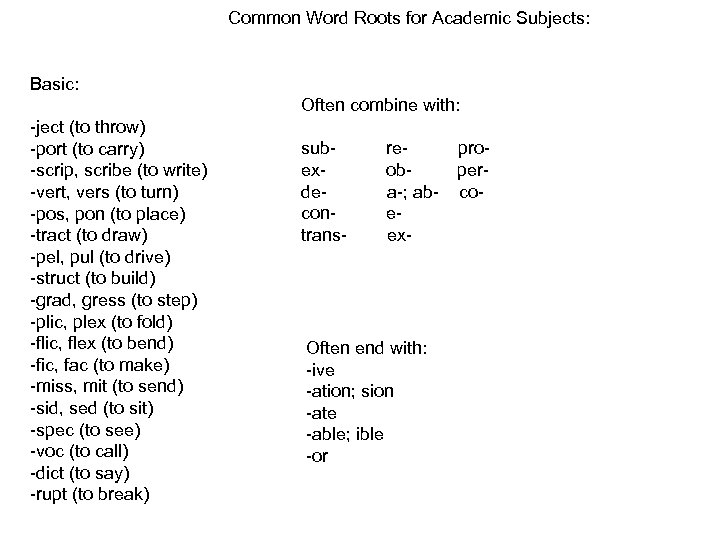
Common Word Roots for Academic Subjects: Basic: Often combine with: -ject (to throw) -port (to carry) -scrip, scribe (to write) -vert, vers (to turn) -pos, pon (to place) -tract (to draw) -pel, pul (to drive) -struct (to build) -grad, gress (to step) -plic, plex (to fold) -flic, flex (to bend) -fic, fac (to make) -miss, mit (to send) -sid, sed (to sit) -spec (to see) -voc (to call) -dict (to say) -rupt (to break) subexdecontrans- reproobpera-; ab- coeex- Often end with: -ive -ation; sion -ate -able; ible -or
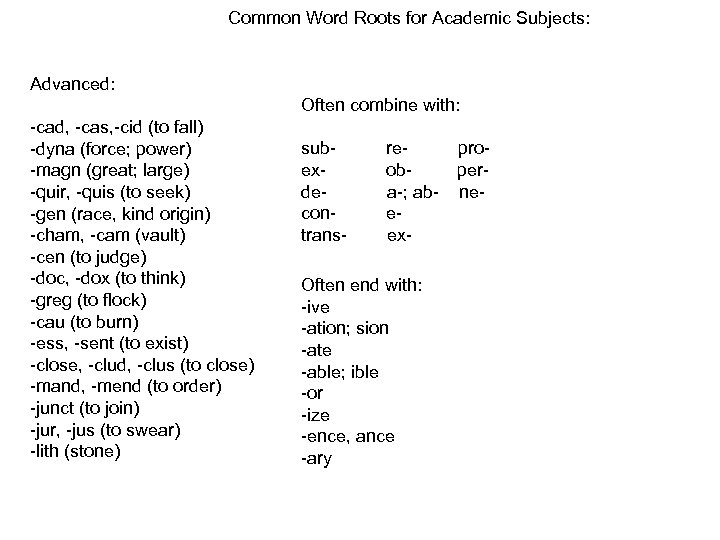
Common Word Roots for Academic Subjects: Advanced: Often combine with: -cad, -cas, -cid (to fall) -dyna (force; power) -magn (great; large) -quir, -quis (to seek) -gen (race, kind origin) -cham, -cam (vault) -cen (to judge) -doc, -dox (to think) -greg (to flock) -cau (to burn) -ess, -sent (to exist) -close, -clud, -clus (to close) -mand, -mend (to order) -junct (to join) -jur, -jus (to swear) -lith (stone) subexdecontrans- reproobpera-; ab- neeex- Often end with: -ive -ation; sion -ate -able; ible -or -ize -ence, ance -ary

Brainstorming Multiple Meanings Volume: volume of music, volume of a cube, trade volume, volumes in the library, volume control on the remote Degree: college degree; degrees of heat; degrees of an angle; degree of pain

Rule of Thumb New learners need SIX (meaningful) exposures to a new word during the initial lesson and at least THIRTY additional exposures during the ensuing month.

Polysemes: Words whose meanings change from one domain to another Examples: function, property, reaction, origin, tangent, variable, solve, mean, graphic, base, extreme, factor, fact, imaginary, rational, Irrational, determine power, prime, product, multiple, operation, radical, remainder, range, regular, proof, difference, cell, value, area, cube, root, plot, complementary, common, depression, digit, operation, frequency…
Math English Social Studies Science
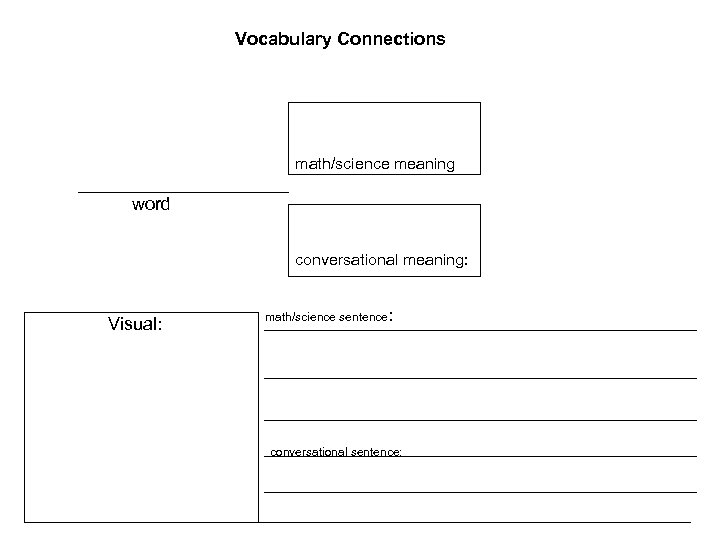
Vocabulary Connections math/science meaning word conversational meaning: Visual: math/science sentence: conversational sentence:
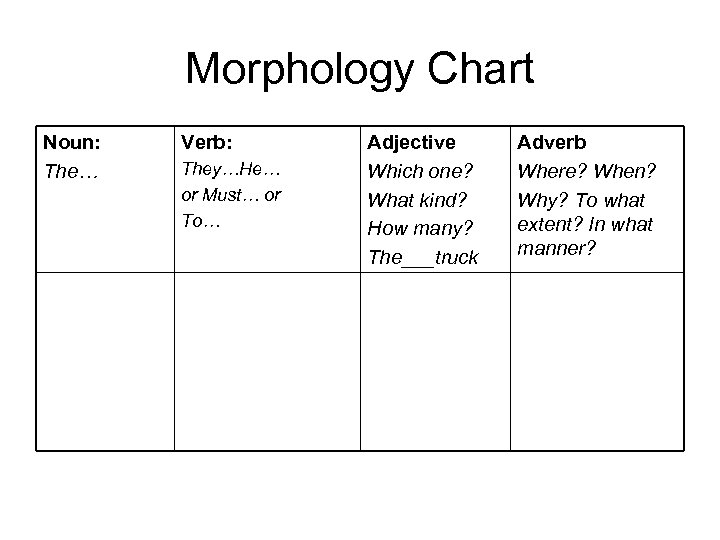
Morphology Chart Noun: The… Verb: They…He… or Must… or To… Adjective Which one? What kind? How many? The___truck Adverb Where? When? Why? To what extent? In what manner?
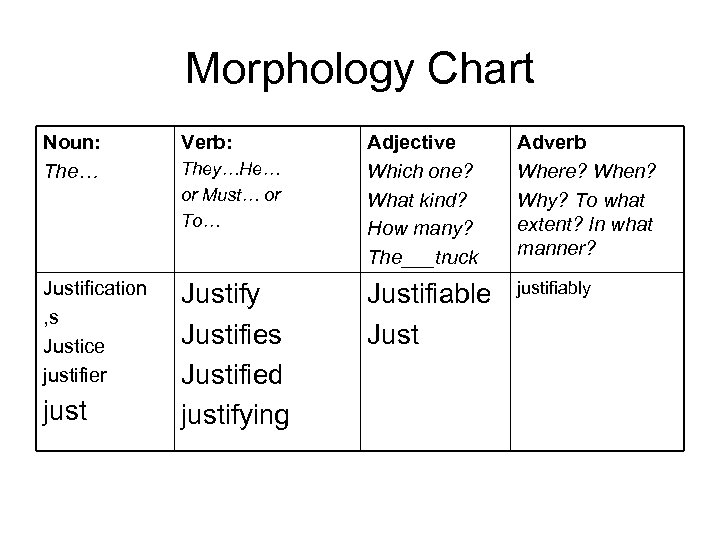
Morphology Chart Noun: The… Verb: Justification , s Justice justifier Justify Justifies Justified justifying just They…He… or Must… or To… Adjective Which one? What kind? How many? The___truck Adverb Where? When? Why? To what extent? In what manner? Justifiable Just justifiably
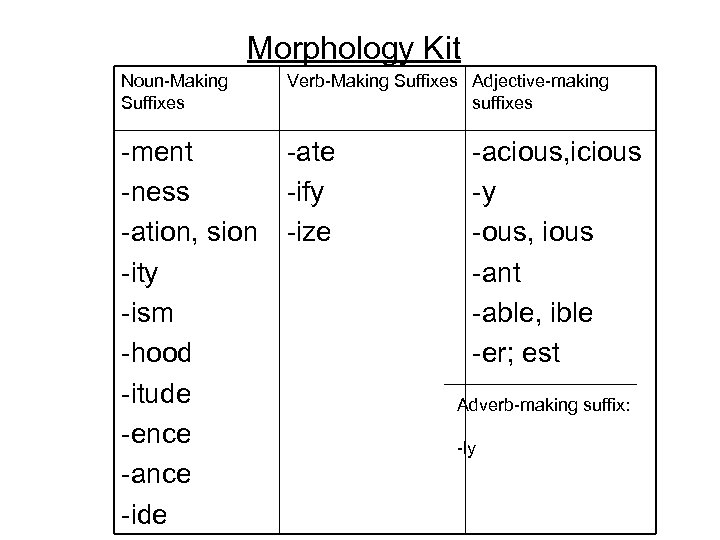
Morphology Kit Noun-Making Suffixes Verb-Making Suffixes Adjective-making suffixes -ment -ness -ation, sion -ity -ism -hood -itude -ence -ance -ide -ate -ify -ize -acious, icious -y -ous, ious -ant -able, ible -er; est Adverb-making suffix: -ly
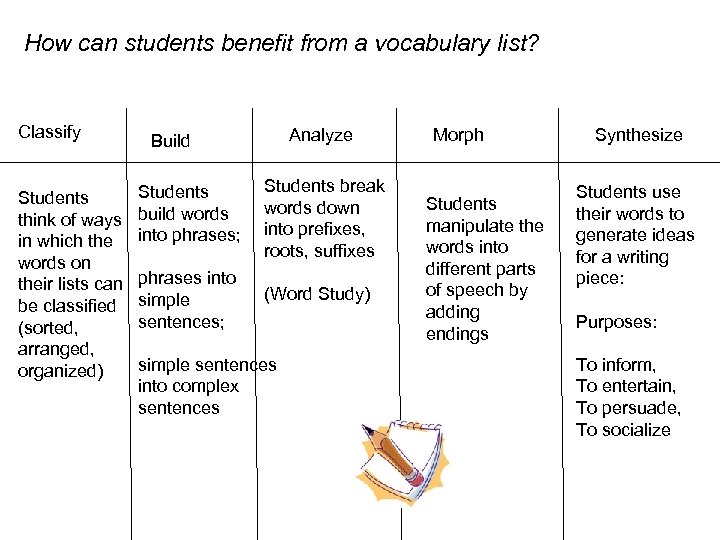
How can students benefit from a vocabulary list? Classify Students think of ways in which the words on their lists can be classified (sorted, arranged, organized) Analyze Build Students build words into phrases; Students break words down into prefixes, roots, suffixes phrases into simple sentences; (Word Study) simple sentences into complex sentences Morph Students manipulate the words into different parts of speech by adding endings Synthesize Students use their words to generate ideas for a writing piece: Purposes: To inform, To entertain, To persuade, To socialize
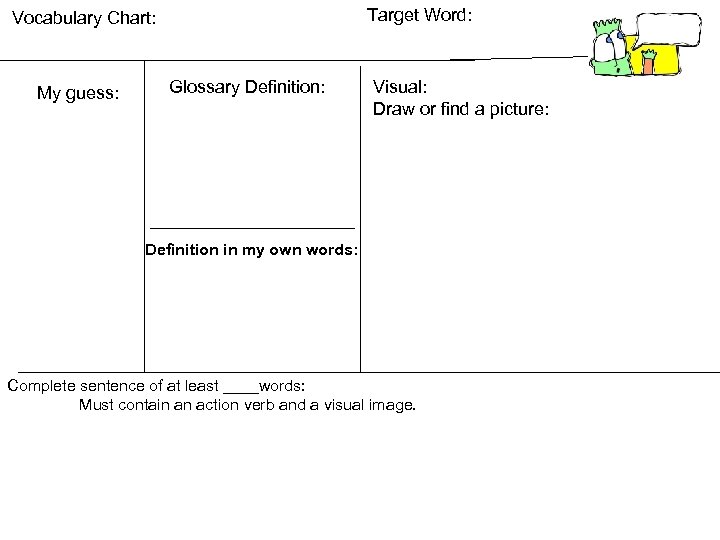
Target Word: Vocabulary Chart: My guess: Glossary Definition: Visual: Draw or find a picture: Definition in my own words: Complete sentence of at least ____words: Must contain an action verb and a visual image.
cfdfac852632fc9ccf7ac0eede384f6a.ppt