68e8360c2d3bbb90ca2cfce2b1fc2f9d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56

Part B vs. Part D Drug Coverage Issues Health Care Compliance Association 2 nd Medicare Conference Babette Edgar, Pharm. D. , MBA, Senior Vice President, Strategic Business Solutions Sept. 11, 2006

Agenda • Introduction and overview • Part B vs. Part D coverage issues • Considerations for Part B vs. Part D "crossover" drugs • Infusion drugs and injectables • Discussion

Foreseeing the Future of Medicare Part D and Part B

Part D vs. Part B • Legislative, legislative! • Will remain confusing until MMA opened up- not until after elections • Drugs covered under Part B before MMA remain Part B! • Plan need to do due diligence in order to be compliant with regulations and guidelines

What is a Part D Drug? (§ 423. 100) • A Part D drug includes any of the following if used for a medically accepted indication: • A drug dispensed only by prescription and approved by the FDA • A biological product dispensed only by a prescription, licensed under the Public Health Service Act (PHSA), and produced at establishment licensed under PHSA • Medical supplies associated with the injection of insulin (e. g. , syringes, needles, alcohol swabs, gauze) • A vaccine licensed under the PHSA

Where We Are Today

What is a Medically Accepted Indication? • Any use for a covered outpatient drug which is approved under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or supported in a citation included, or approved for inclusion, in any of the compendia below**: • American Hospital Formulary Service Drug Info. (AHFS-DI) • United States Pharmacopeia-Drug Information (USP-DI®) • DRUGDEX® Information System • Use of a drug for “off-label” indications not reflected in any of the 3 compendia would not meet the definition of a Part D drug • Plans should deny payment ** For oncology medications and Part B coverage, peer-reviewed literature can also be used if drug is not contraindicated in above compendia Reference: Social Security Act Section 1927(k)(6)

Part D Excluded Drugs • Part D excludes coverage for drugs, classes or uses of drugs that are already excluded or restricted under Medicaid 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Agents used for anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain Agents used to promote fertility Agents used for cosmetic purposes or hair growth Agents used for the symptomatic relief of cough and colds Prescription vitamins and mineral products (except prenatal vitamins and fluoride preparations) 6. Nonprescription drugs 7. Drugs for which the manufacturer requires that associated tests or monitoring services be purchased exclusively from the manufacturer or its designee 8. Barbiturates 9. Benzodiazepines 10. Agents used for sexual or erectile dysfunction (1/1/07) • Exception: Prescription smoking cessation agents Reference: Medicare Part B versus Part D Coverage Issues. CMS, July 27, 2005.

Part D Excluded Drugs – Non-Prescription Drugs • Not considered as Part D drugs • Cannot be included in supplemental benefits • Plans can provide them as part of plan utilization (step -therapy) programs at no cost to enrollees • E. g. , H 2 -blockers, proton pump inhibitors • As of 1/1/07, incorporation into step therapy not required for coverage • Cost of drugs included in plans’ admin costs • States: Possible coverage through Medicaid • 2006 state Medicaid coverage mostly mirrors the 2005 coverage • Long-term care facilities - floor stock consideration

Plan Due Diligence in PA of B vs. D Coverage Determination • CMS recommended that medical specialty group providers include additional information on prescriptions to help Part D plans and pharmacists differentiate between those drugs which may qualify as Part D drugs and those which may qualify as Part B drugs • To facilitate, but not replace, a Part D plan’s existing processes for determining Part D coverage Reference: Clarification of Plan Due Diligence in Prior Authorization of Part B vs. Part D Coverage Determinations. CMS, March 24, 2006.

Plan Due Diligence in PA of B vs. D Coverage Determination Question • If in accordance with CMS guidance a physician includes additional information on a prescription that is sufficient to determine whether the drug is covered, what further due diligence is required of the Part D plan for making a determination of Part D coverage? Reference: Clarification of Plan Due Diligence in Prior Authorization of Part B vs. Part D Coverage Determinations. CMS, March 24, 2006.

Plan Due Diligence in PA of B vs. D Coverage Determination Answer • Plans may rely on physician information included with script, such as: • Diagnosis information (e. g. , to determine if prescription is related to a Medicare covered transplant) • Location of administration (e. g. , to determine if prescription is being dispensed to beneficiary in a nursing home) • Same as when plans rely on physician information documented on prior authorization forms • If indication on prescription adequate to make coverage determination, no need for additional information from physician Reference: Clarification of Plan Due Diligence in Prior Authorization of Part B vs. Part D Coverage Determinations. CMS, March 24, 2006.

Plan Due Diligence in PA of B vs. D Coverage Determination • Plan may also rely on pharmacist’s report of appropriate information to determine Part D coverage • Same as how a plan requires contracted pharmacies to report the information provided on the prescription to determine Part B vs. Part D coverage • E. g. , if prednisone is prescribed for a condition other than immunosuppression secondary to a Medicare-covered transplant, and this is indicated on the prescription, a plan may authorize the pharmacy to dispense the drug under Part D without further contacting the prescribing physician Reference: Clarification of Plan Due Diligence in Prior Authorization of Part B vs. Part D Coverage Determinations. CMS, March 24, 2006.

Plan Due Diligence in PA of B vs. D Coverage Determination • Does not imply that plan may not impose PA or other steps to ensure appropriate coverage under Part D • Plan ultimately responsible for determining Part D coverage • CMS expects plan to have met appropriate due diligence standards without further contacting a physician if necessary and sufficient information is provided on the script and contracted pharmacy able to communicate this information to the plan to make the coverage determination Reference: Clarification of Plan Due Diligence in Prior Authorization of Part B vs. Part D Coverage Determinations. CMS, March 24, 2006.
PART B vs. PART D COVERAGE ISSUES

Parts A/B vs. Part D Drug Coverage • Part A and Part B of traditional Medicare do not cover most outpatient prescription drugs • Part A provides bundled payments to hospitals and skilled nursing facilities • Part B payments to physicians usually limited to drugs or biologicals that are usually not self-administered • Outpatient drugs covered under Parts A or B will not be paid for under Part D • Medicare Advantage (MA) plans must use coverage rules to determine whether to pay for a drug under Part A/B medical benefits or Part D prescription drug benefits Reference: Medicare Part B versus Part D Coverage Issues. CMS, July 27, 2005.

Part B vs. Part D “Crossover” Drugs • Certain drugs or uses of drugs may be covered either under Part B or Part D, also known as “crossover” drugs • Coverage determination factors include, but are not limited to: • Indication(s) of use • Who administers the drug • How the drug is administered

Part B vs. Part D “Crossover” Drugs • MA-PDs can only bill Part B or Part D each time a “crossover” drug is dispensed: • Part B billing: J code-based • Part D billing: National Drug Code (NDC)-based • PDPs and MA-PDs cannot routinely • Deny coverage under Part D for crossover medications • Require a Part B claim rejection before processing a Part D claim

Additional Coverage Considerations • To bill under the Part B benefit, a retail pharmacy must be an accredited Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics, and Supplies (DMEPOS) supplier

CONSIDERATIONS FOR “CROSSOVER” DRUGS
Part B Coverage: Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Supply Drugs • Part B covers certain drugs that are required for a Part Bcovered DME to perform its function at home • Major categories include: • Inhalation drugs administered using a nebulizer • Drugs for which administration with an infusion pump is medically necessary and covered by Medicare • For inhalation drugs, other forms of inhalation are not covered under Part B

Part B Coverage: Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Supply Drugs • The following facilities are not considered a home under the Medicare DME benefit and will not meet Part B coverage requirements: • A hospital • A skilled nursing facility (SNF) or a distinct part SNF • A nursing home dually-certified as both a Medicare SNF and a Medicaid nursing facility (NF) • A Medicaid-only NF that primarily furnishes skilled care • A non-participating nursing home (i. e. , neither Medicare or Medicaid) that provides primarily skilled care • An institution with a distinct part SNF and which also primarily furnishes skilled care
Part B Coverage: Immunosuppressive Drugs • Part B covers immunosuppressive therapy if beneficiary has: • A Medicare-covered transplant or • Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) coverage for the transplant • Transplant must be performed at a Medicare-approved facility • Plan determination of Medicare transplant coverage • No “one” database to determine this

Part B Coverage: Hemophilia Clotting Factors • Part B covers clotting factors for hemophiliacs who fulfill specific criteria • Part B coverage includes items associated with the administration of clotting factors

Part B Coverage: Oral Anti-Cancer Drugs • Part B covers oral anti-cancer drugs if they contain the same active ingredients and are used for the same indications as Part B-covered chemotherapy drugs furnished incident to a physician’s service • These drugs include: • Busulfan • Capecitabine • Cyclophosphamide • Etoposide • Melphalan • Methotrexate • Temozolamide

Part B Coverage: Oral Anti-Emetic Drugs Used With IV Chemotherapy • Covered under Part B if used as a “full therapeutic replacement” for an intravenous (IV) anti-emetic drug within 48 hours of IV chemotherapy administration • For granisetron and dolasetron, coverage is limited to the loading dose plus 24 hours of therapy • CMS requires physicians to indicate on prescription that oral anti-emetic is being used as a “full therapeutic replacement for an IV anti-emetic drug as part of a cancer chemotherapeutic regimen” • Part D coverage considerations-split prescriptions

Part B Coverage: Emend® (Aprepitant) • CMS: Aprepitant cannot function alone as a full replacement for IV anti-emetic agents • Aprepitant has Part B coverage if given as part of a 3 -drug regimen • Part B coverage for the oral anti-emetic 3 -drug regimen applies only to patients receiving one or more of the following anti-cancer drugs: • Carmustine, cisplatin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazine, doxorubicin, epirubicin, lomustine, mechlorethamine, streptozocin

Part B Coverage: Pneumococcal Vaccine • Pneumococcal vaccine – always Part B • Physician order is not required per Medicare Benefit Policy Manual* * In CMS’ 7/27/05 guidance on “Medicare Part B vs. Part D Drug Coverage Issues”, it was stated that a physician order is required for pneumococcal vaccine.
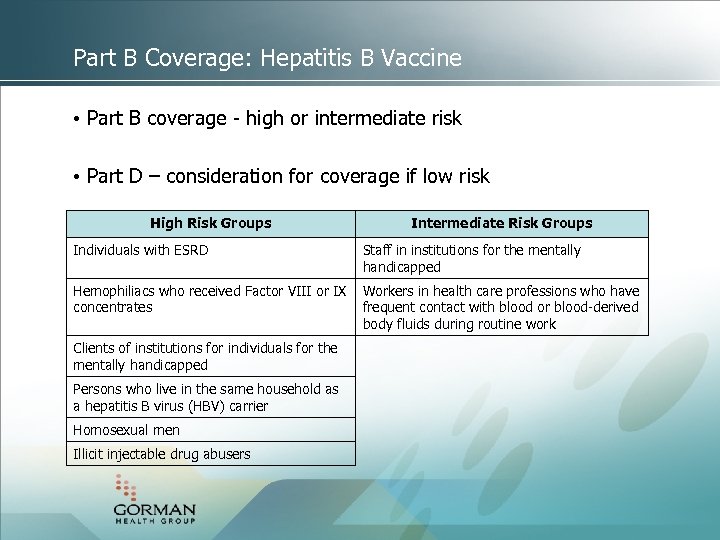
Part B Coverage: Hepatitis B Vaccine • Part B coverage - high or intermediate risk • Part D – consideration for coverage if low risk High Risk Groups Individuals with ESRD Intermediate Risk Groups Staff in institutions for the mentally handicapped Hemophiliacs who received Factor VIII or IX Workers in health care professions who have concentrates frequent contact with blood or blood-derived body fluids during routine work Clients of institutions for individuals for the mentally handicapped Persons who live in the same household as a hepatitis B virus (HBV) carrier Homosexual men Illicit injectable drug abusers

Part B Coverage: Influenza Vaccine • Part B coverage - applicable state law • Beneficiary may receive the vaccine upon request • Influenza vaccine – no Part D coverage

Part B Coverage: Miscellaneous Vaccines • Vaccines given directly related to the treatment of an injury or direct exposure to a disease or condition: Part B coverage • Other miscellaneous vaccines: excluded under Part B
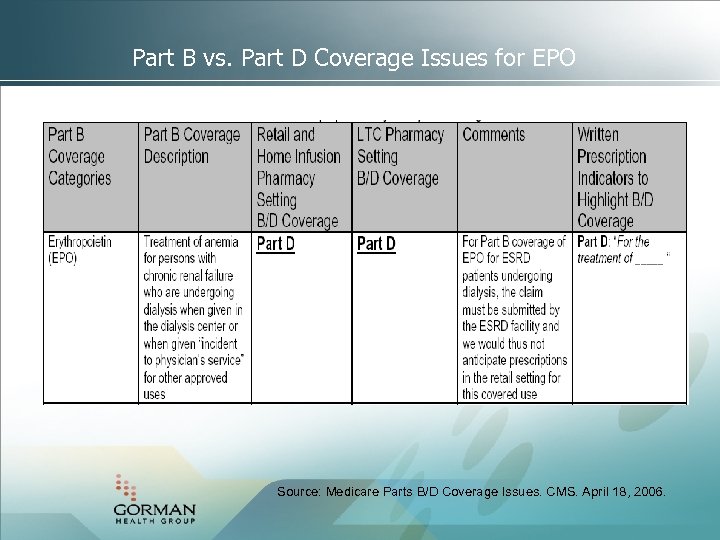
Part B vs. Part D Coverage Issues for EPO Source: Medicare Parts B/D Coverage Issues. CMS. April 18, 2006.
INFUSION DRUGS

Part B Infusion Drugs • Limited to drugs that require a pump for administration in the home • Limited to specific indications • Requires a Certificate of Medical Necessity (CMN) submitted by the DMERC Supplier • Covers medication, supplies, equipment and patient monitoring • Drugs administered by a prolonged infusion of at least 8 hours due to proven clinical efficacy

Part B Infusion Drugs • Deferoxamine for chronic iron overload • Chemotherapy for primary hepatocellular or colorectal carcinoma • Morphine for cancer-related pain • Continuous subcutaneous insulin for diabetes mellitus
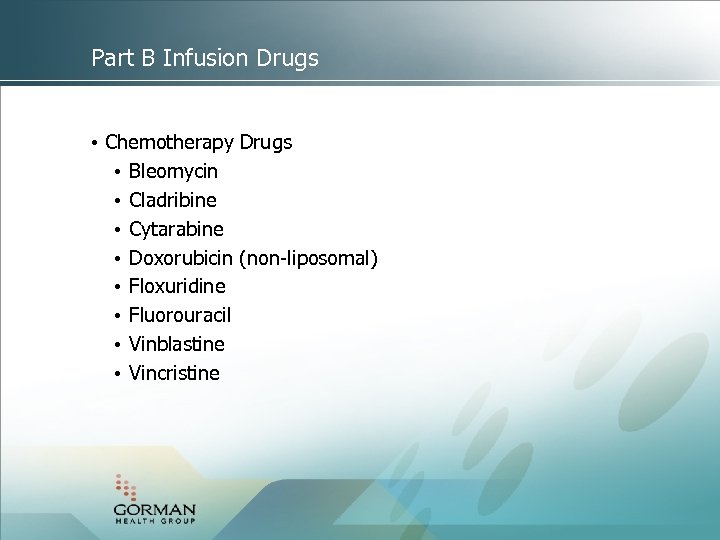
Part B Infusion Drugs • Chemotherapy Drugs • Bleomycin • Cladribine • Cytarabine • Doxorubicin (non-liposomal) • Floxuridine • Fluorouracil • Vinblastine • Vincristine

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of narcotic analgesics, except meperidine, in place of morphine for intractable cancer pain

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of antifungal or antiviral drugs • Acyclovir • Amphotericin B • Foscarnet • Ganciclovir • Liposomal amphotericin B preparations are only covered for patients who: • Have suffered significant toxicity with standard amphotericin B • Have significantly impaired renal function

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of parenteral inotropic therapy • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Milrinone • For patients with CHF who meet specific criteria

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) • Diagnosis of Primary Immune Deficiency disease only • Part B coverage is limited to the IVIG only - Does not include pumps, supplies, and equipment for administration • Administration of Subcutaneous Immune Globulin • Diagnosis of Primary Immune Deficiency disease only • Pump, supplies and equipment are covered

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of epoprostenol and treprostinil for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension • Patient must meet specific criteria

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of gallium nitrate • For the treatment of symptomatic cancer-related hypercalcemia

Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of ziconotide (Prialt®) • For the management of severe chronic pain in patients who meet specific criteria
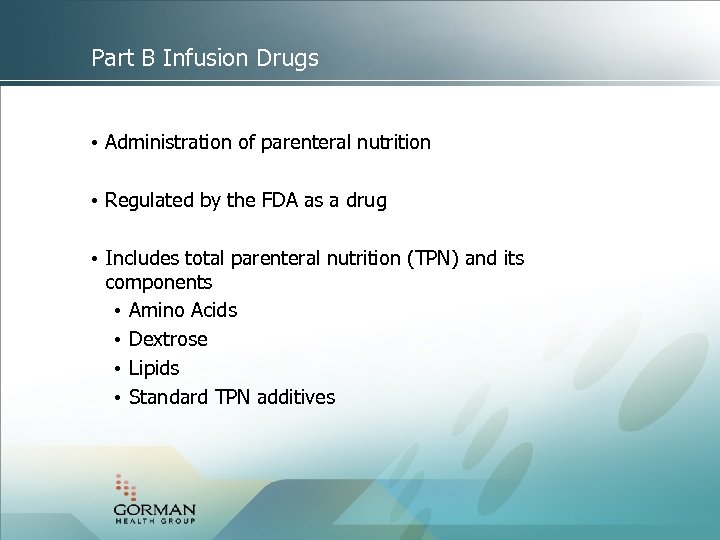
Part B Infusion Drugs • Administration of parenteral nutrition • Regulated by the FDA as a drug • Includes total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and its components • Amino Acids • Dextrose • Lipids • Standard TPN additives

Part B Infusion Drugs • Parenteral Nutrition is covered under the Part B prosthetic benefit • Beneficiaries must meet specific criteria for permanent alimentary tract dysfunction

Part B Coverage: Parenteral Nutrition • Specific criteria include: • Sole source of nutrition • Specific diagnosis to include a non-functioning GI tract • Use of TPN for a minimum of 90 days • Included in coverage: • IV vitamins • Trace elements/minerals • Heparin and saline flush • Supplies and equipment for administration

Part D Coverage: Parenteral Nutrition • Parenteral nutrition is covered under Part D (not Part B) if patient has a functioning GI tract whose need for parenteral nutrition is due to: • A swallowing disorder • A temporary defect in gastric emptying such as a metabolic or electrolyte disorder • A psychological disorder impairing food intake such as depression • A metabolic disorder inducing anorexia such as cancer • A physical disorder impairing food intake such as the dyspnea of severe pulmonary or cardiac disease • A side effect of a medication • Renal failure and/or dialysis

Part D Coverage: Parenteral Nutrition • For all Part D plans, CMS will reimburse the Part D drug components in a parenteral nutrition solution • Multivitamin and trace mineral/elements additives: • May be added to the solution per standard of practice • These components do NOT meet the definition of a Part D drug and may NOT be billed under Part D • Supplies and equipment for TPN administration are NOT covered under Part D

Overview of Medicare Part D Infusion Drugs • Medicare Part D covers infusion therapies that do not fulfill Part B criteria • Covers the medication only • Patient financially responsible for supplies and equipment • No coverage for monitoring or education of therapy • No coverage of heparin and saline for IV line maintenance

Part B Infusion Drugs • Place of service helps determine Part B versus Part D coverage • Infusion by pump, IV push, IV drip or injectable medications administered in a physician’s office are considered for coverage under Part B

Part B vs. Part D Infusion Drugs • Method of administration in the home determines B vs. D coverage • IV pump – covered under Part B for specific drugs and if certain criteria are met • If criteria not fulfilled, coverage considered under Part D • IV push – Part D • IV drip – Part D • Subcutaneous – Part D • Self-administered – Part D
Reimbursement for Part B vs. Part D • Part B • Patient must meet very specific criteria • Reimbursement includes the medication, supplies, equipment, and professional services • Part D • Reimbursement for the medication only • No provision for supplies, equipment, or professional services

Additional Considerations • Intravenous Medications/TPN – Additional Considerations • A number of professional organizations are working to address gaps in care for this issue - American Society of Consultant Pharmacists (ASCP) - Hospice Association of America (HAA) - National Home Infusion Association (NHIA) • Discussion regarding covering infusion therapy under Medicare Part B vs. Part D • Variations in coverage from each PDP in 2006

CMS Issues • Minimal changes for 2007 • Audit • Due diligence • Operational policies and procedures in place • Plans responsible for subcontractors

Conclusion • Plans must exercise due diligence in determining appropriate Part B vs. Part D drug coverage • Plans must have appropriate operational policies and procedures in place • Plans must have reliable information source that is updated frequently relating to Part B vs. Part D drugs and coverage determinations • Accurate and expedient Part B vs. Part D coverage delineation is important to ensure beneficiaries have timely access to medications they need while paying the appropriate cost share

How to Contact Us Gorman Health Group, LLC www. gormanhealthgroup. com 2176 Wisconsin Avenue, N. W. , Washington, D. C. 20007 Phone: 202. 364. 8283 Fax: 202. 244. 8324 Bedgar@gormanhealthgroup. com
68e8360c2d3bbb90ca2cfce2b1fc2f9d.ppt