555f8137f15dd73360d71f2265636246.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Part 1: An Introduction to Dictation Activities 1) 2) 3) Purposes of Doing Dictation Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling and Note-taking Skills
Part 1: An Introduction to Dictation Activities 1) 2) 3) Purposes of Doing Dictation Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling and Note-taking Skills
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Ø Ø Ø Development of phonics skills Development of listening and note-taking skills Development of writing skills Promoting autonomy in language learning Promoting assessment for learning
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Ø Ø Ø Development of phonics skills Development of listening and note-taking skills Development of writing skills Promoting autonomy in language learning Promoting assessment for learning
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Development of phonics skills • Dictation helps pupils develop phonics skills that facilitate pronunciation and spelling. Awareness of letter-sound relationships Phonics skills CG* p. 175 *CG stands for English Language Curriculum Guide (Primary 1 -6) (CDC, 2004) Spelling skills
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Development of phonics skills • Dictation helps pupils develop phonics skills that facilitate pronunciation and spelling. Awareness of letter-sound relationships Phonics skills CG* p. 175 *CG stands for English Language Curriculum Guide (Primary 1 -6) (CDC, 2004) Spelling skills
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Development of listening and note-taking skills Listening skills • Dictation helps pupils develop a range of listening skills. • Dictation is a useful tool to develop pupils’ note-taking skills. • discriminating sounds, stress and intonation • identifying key words • identifying the main ideas • understanding the connection between ideas CG pp. 51&52
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Development of listening and note-taking skills Listening skills • Dictation helps pupils develop a range of listening skills. • Dictation is a useful tool to develop pupils’ note-taking skills. • discriminating sounds, stress and intonation • identifying key words • identifying the main ideas • understanding the connection between ideas CG pp. 51&52
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Development of writing skills • By using dicto-comp / dictogloss, pupils can make use of the notes taken during listening to reconstruct texts and develop their writing skills. Note-taking of key words Applying language knowledge in writing Writing skills CG p. 177
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Development of writing skills • By using dicto-comp / dictogloss, pupils can make use of the notes taken during listening to reconstruct texts and develop their writing skills. Note-taking of key words Applying language knowledge in writing Writing skills CG p. 177
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Promoting autonomy in language learning • Dictation can be used to promote self-learning. • Pupils should be encouraged to collect more vocabulary related to theme / topic they are learning. CG pp. 176&177 Theme / Topic Vocabulary taught in class Vocabulary collected by pupils themselves Autonomy in learning
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Promoting autonomy in language learning • Dictation can be used to promote self-learning. • Pupils should be encouraged to collect more vocabulary related to theme / topic they are learning. CG pp. 176&177 Theme / Topic Vocabulary taught in class Vocabulary collected by pupils themselves Autonomy in learning
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Promoting assessment for learning • Dictation is a useful tool that helps teachers understand pupils’ learning progress. • Teachers should provide constructive feedback to pupils by analysing their problems and giving suggestions for improvement. Identifying and analysing pupils’ mistakes Giving suggestions for improvement Assessment for learning
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation Promoting assessment for learning • Dictation is a useful tool that helps teachers understand pupils’ learning progress. • Teachers should provide constructive feedback to pupils by analysing their problems and giving suggestions for improvement. Identifying and analysing pupils’ mistakes Giving suggestions for improvement Assessment for learning
 1) Purposes of Doing Dictation – Promoting assessment for learning Providing constructive feedback • Teachers should analyse pupils’ mistakes and give suggestions for improvement by guiding pupils to make use of - context, - grammar knowledge, and - phonics skills in writing the words with accurate spelling. • Teachers should design follow-up learning activities whenever appropriate to consolidate learning.
1) Purposes of Doing Dictation – Promoting assessment for learning Providing constructive feedback • Teachers should analyse pupils’ mistakes and give suggestions for improvement by guiding pupils to make use of - context, - grammar knowledge, and - phonics skills in writing the words with accurate spelling. • Teachers should design follow-up learning activities whenever appropriate to consolidate learning.
 2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Ø Ø Design Coverage Frequency Weighting and Marking
2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Ø Ø Design Coverage Frequency Weighting and Marking
 2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Design • Dictation should be contextualised to illustrate the communicative use of language and help pupils progress towards the Learning Targets. • Dictation could be conducted in combination with a range of activities to develop pupils’ language skills. CG pp. 176&177
2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Design • Dictation should be contextualised to illustrate the communicative use of language and help pupils progress towards the Learning Targets. • Dictation could be conducted in combination with a range of activities to develop pupils’ language skills. CG pp. 176&177
 2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Coverage • Not every word in the learning materials must be learnt by heart. • Pupils should not be asked to study formulaic expressions or classroom instructions for dictation. • Pupils should not be asked to spell the spoken form of the date in full words. CG p. 175
2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Coverage • Not every word in the learning materials must be learnt by heart. • Pupils should not be asked to study formulaic expressions or classroom instructions for dictation. • Pupils should not be asked to spell the spoken form of the date in full words. CG p. 175
 2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Frequency • Teachers should not overburden pupils with excessive dictation as it may kill their interest in learning English and deprive them of the opportunities to engage in other meaningful English learning activities. CG p. 174
2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Frequency • Teachers should not overburden pupils with excessive dictation as it may kill their interest in learning English and deprive them of the opportunities to engage in other meaningful English learning activities. CG p. 174
 2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Weighting and Marking • Dictation should not take up more than 10% of the subject marks. • Marks should not be deducted for repeated mistakes. • Bonus marks can be given to promote autonomy in language learning. CG pp. 175&177
2) Guiding Principles for Conducting Dictation Weighting and Marking • Dictation should not take up more than 10% of the subject marks. • Marks should not be deducted for repeated mistakes. • Bonus marks can be given to promote autonomy in language learning. CG pp. 175&177
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling and Note-taking Skills Spelling Skills Ø Developing pupils’ awareness of letter-sound relationships Ø Dividing words into small parts Ø Identifying affixes to root words Ø Looking for letter patterns Ø Highlighting problem parts Ø Understanding the meanings of words Note-taking Skills Ø Helping pupils understand the meanings of key words through demonstration Ø Listening for key words Ø Identifying main ideas and supporting details Ø Using headings to organise ideas Ø Using tables and other graphic organisers to organise ideas Ø Using short forms, abbreviations, numbers and symbols to take notes
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling and Note-taking Skills Spelling Skills Ø Developing pupils’ awareness of letter-sound relationships Ø Dividing words into small parts Ø Identifying affixes to root words Ø Looking for letter patterns Ø Highlighting problem parts Ø Understanding the meanings of words Note-taking Skills Ø Helping pupils understand the meanings of key words through demonstration Ø Listening for key words Ø Identifying main ideas and supporting details Ø Using headings to organise ideas Ø Using tables and other graphic organisers to organise ideas Ø Using short forms, abbreviations, numbers and symbols to take notes
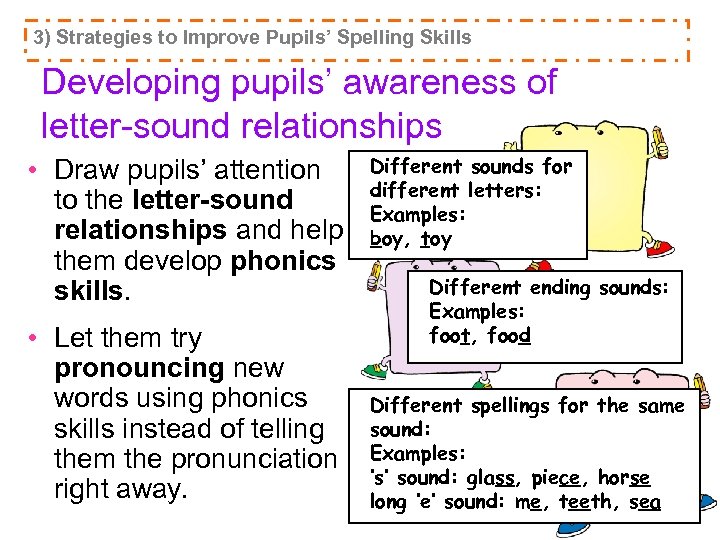 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Developing pupils’ awareness of letter-sound relationships • Draw pupils’ attention to the letter-sound relationships and help them develop phonics skills. • Let them try pronouncing new words using phonics skills instead of telling them the pronunciation right away. Different sounds for different letters: Examples: boy, toy Different ending sounds: Examples: foot, food Different spellings for the same sound: Examples: ‘s’ sound: glass, piece, horse long ‘e’ sound: me, teeth, sea
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Developing pupils’ awareness of letter-sound relationships • Draw pupils’ attention to the letter-sound relationships and help them develop phonics skills. • Let them try pronouncing new words using phonics skills instead of telling them the pronunciation right away. Different sounds for different letters: Examples: boy, toy Different ending sounds: Examples: foot, food Different spellings for the same sound: Examples: ‘s’ sound: glass, piece, horse long ‘e’ sound: me, teeth, sea
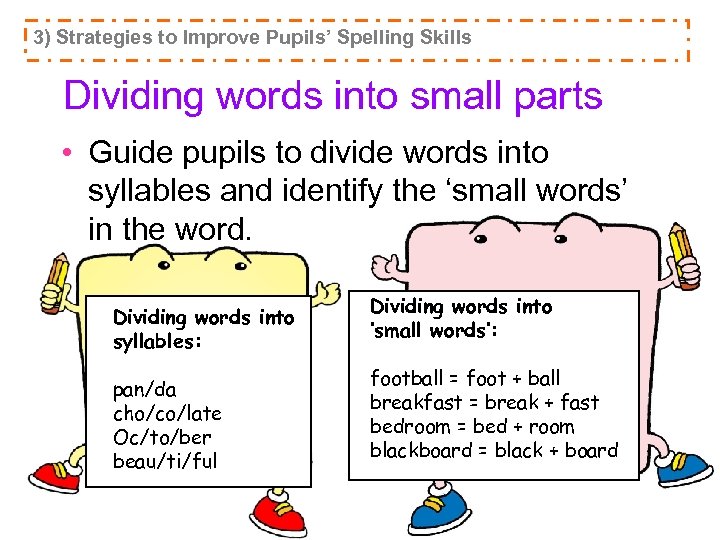 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Dividing words into small parts • Guide pupils to divide words into syllables and identify the ‘small words’ in the word. Dividing words into syllables: pan/da cho/co/late Oc/to/ber beau/ti/ful Dividing words into ‘small words’: football = foot + ball breakfast = break + fast bedroom = bed + room blackboard = black + board
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Dividing words into small parts • Guide pupils to divide words into syllables and identify the ‘small words’ in the word. Dividing words into syllables: pan/da cho/co/late Oc/to/ber beau/ti/ful Dividing words into ‘small words’: football = foot + ball breakfast = break + fast bedroom = bed + room blackboard = black + board
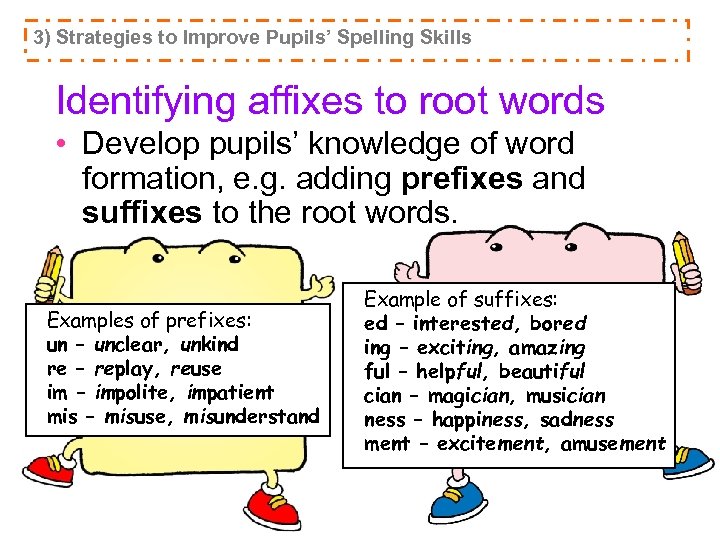 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Identifying affixes to root words • Develop pupils’ knowledge of word formation, e. g. adding prefixes and suffixes to the root words. Examples of prefixes: un – unclear, unkind re – replay, reuse im – impolite, impatient mis – misuse, misunderstand Example of suffixes: ed – interested, bored ing – exciting, amazing ful – helpful, beautiful cian – magician, musician ness – happiness, sadness ment – excitement, amusement
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Identifying affixes to root words • Develop pupils’ knowledge of word formation, e. g. adding prefixes and suffixes to the root words. Examples of prefixes: un – unclear, unkind re – replay, reuse im – impolite, impatient mis – misuse, misunderstand Example of suffixes: ed – interested, bored ing – exciting, amazing ful – helpful, beautiful cian – magician, musician ness – happiness, sadness ment – excitement, amusement
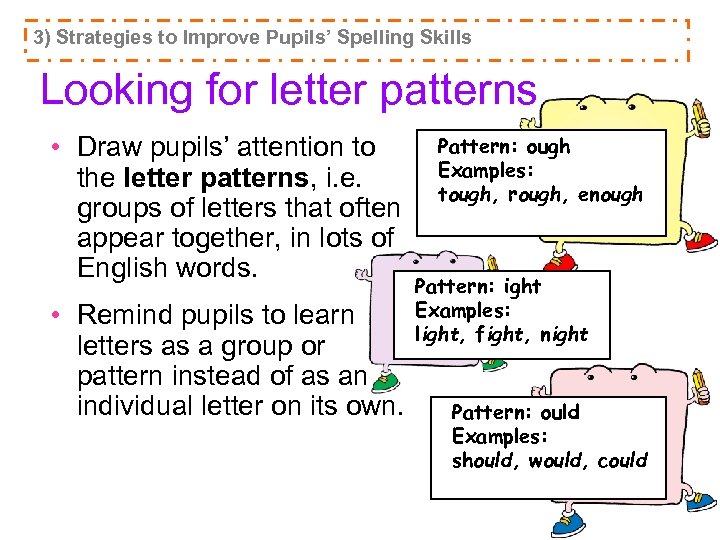 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Looking for letter patterns • Draw pupils’ attention to the letter patterns, i. e. groups of letters that often appear together, in lots of English words. • Remind pupils to learn letters as a group or pattern instead of as an individual letter on its own. Pattern: ough Examples: tough, rough, enough Pattern: ight Examples: light, fight, night Pattern: ould Examples: should, would, could
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Looking for letter patterns • Draw pupils’ attention to the letter patterns, i. e. groups of letters that often appear together, in lots of English words. • Remind pupils to learn letters as a group or pattern instead of as an individual letter on its own. Pattern: ough Examples: tough, rough, enough Pattern: ight Examples: light, fight, night Pattern: ould Examples: should, would, could
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Highlighting problem parts • Draw pupils’ attention to the silent letters in some words. • Highlight that some contractions and words sound the same / similar. Examples of silent letters: Silent d – sandwich, badge Silent k – knife, know Silent h – honest, hour Silent w – whole, wrong Examples of contractions and words with the same / similar sounds: it’s vs. its you’re vs. your we’re vs. were who’s vs. whose they’re vs. their / there
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Highlighting problem parts • Draw pupils’ attention to the silent letters in some words. • Highlight that some contractions and words sound the same / similar. Examples of silent letters: Silent d – sandwich, badge Silent k – knife, know Silent h – honest, hour Silent w – whole, wrong Examples of contractions and words with the same / similar sounds: it’s vs. its you’re vs. your we’re vs. were who’s vs. whose they’re vs. their / there
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Understanding the meanings of words • Guide pupils to understand the meanings of the words learnt. • Draw pupils’ attention to the confusing words, i. e. words with the same / similar pronunciation but different meanings. sun? son? It is very hot. The son / sun is shining. pan? pen? I use a pen / pan to fry an egg. Pronunciation vs. Meaning
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Spelling Skills Understanding the meanings of words • Guide pupils to understand the meanings of the words learnt. • Draw pupils’ attention to the confusing words, i. e. words with the same / similar pronunciation but different meanings. sun? son? It is very hot. The son / sun is shining. pan? pen? I use a pen / pan to fry an egg. Pronunciation vs. Meaning
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Ø Helping pupils understand the meanings of key words through demonstration Ø Listening for key words Ø Identifying main ideas and supporting details Ø Using headings to organise ideas Ø Using tables and other graphic organisers to organise ideas Ø Using short forms, abbreviations, numbers and symbols to take notes
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Ø Helping pupils understand the meanings of key words through demonstration Ø Listening for key words Ø Identifying main ideas and supporting details Ø Using headings to organise ideas Ø Using tables and other graphic organisers to organise ideas Ø Using short forms, abbreviations, numbers and symbols to take notes
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Helping pupils understand the meanings of key words through demonstration • • • Read a short text with the whole class. Underline the key words, which carry the important messages in the text Explain to pupils that function words are less important. Dear Mark, How are you? I am going to visit Hong Kong with my parents at Christmas! We will stay for four days. On the first day, we are going to do some shopping. At night, we are going to watch the beautiful lights in Tsim Sha Tsui. Over the next few days, we can visit theme parks and the Peak together. We will be in Hong Kong on 23 December. The plane leaves Beijing at a quarter past eight in the morning and arrives at around eleven o’clock. See you soon. Leo
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Helping pupils understand the meanings of key words through demonstration • • • Read a short text with the whole class. Underline the key words, which carry the important messages in the text Explain to pupils that function words are less important. Dear Mark, How are you? I am going to visit Hong Kong with my parents at Christmas! We will stay for four days. On the first day, we are going to do some shopping. At night, we are going to watch the beautiful lights in Tsim Sha Tsui. Over the next few days, we can visit theme parks and the Peak together. We will be in Hong Kong on 23 December. The plane leaves Beijing at a quarter past eight in the morning and arrives at around eleven o’clock. See you soon. Leo
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Listening for key words • Divide the text into smaller parts and read aloud the text bit by bit. • Use guiding questions to help pupils jot down the relevant information. • Read aloud the text several times if necessary. • Allow time for pupils to tidy up their work. Guiding questions Part 1 1. When will Leo visit Hong Kong? 2. How many days will he stay in Hong Kong? Part 2 1. What will he do on the first day? 2. What will he do over the next few days? Part 3 1. When will he be in Hong Kong? 2. What time will the plane arrive?
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Listening for key words • Divide the text into smaller parts and read aloud the text bit by bit. • Use guiding questions to help pupils jot down the relevant information. • Read aloud the text several times if necessary. • Allow time for pupils to tidy up their work. Guiding questions Part 1 1. When will Leo visit Hong Kong? 2. How many days will he stay in Hong Kong? Part 2 1. What will he do on the first day? 2. What will he do over the next few days? Part 3 1. When will he be in Hong Kong? 2. What time will the plane arrive?
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Identifying main ideas and supporting details Mr Chan is my favourite teacher. He’s a great teacher in many ways. First, he’s humorous. He looks funny and has many interesting topics to talk about, so we like him very much. Mr Chan is also helpful. When we tell him our troubles, he gives us useful advice. We’re lucky to have such a good teacher. Lastly, Mr Chan is a healthy person. He doesn’t get sick easily. He’s good at water sports. He’s been my PE teacher for many years. What makes Mr Chan a good teacher? 1. Humorous - looks funny - has many interesting topics 2. Helpful - tell him our troubles - gives us useful advice 3. Healthy - does not get sick easily - good at water sports
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Identifying main ideas and supporting details Mr Chan is my favourite teacher. He’s a great teacher in many ways. First, he’s humorous. He looks funny and has many interesting topics to talk about, so we like him very much. Mr Chan is also helpful. When we tell him our troubles, he gives us useful advice. We’re lucky to have such a good teacher. Lastly, Mr Chan is a healthy person. He doesn’t get sick easily. He’s good at water sports. He’s been my PE teacher for many years. What makes Mr Chan a good teacher? 1. Humorous - looks funny - has many interesting topics 2. Helpful - tell him our troubles - gives us useful advice 3. Healthy - does not get sick easily - good at water sports
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Using headings to organise ideas Hi! My name is Judy. I’m a primary two pupil and I’m studying at Green Tree School. Let me tell you more about myself. I was born on 20 February 2004. I love swimming and playing badminton. My favourite subject is English. My telephone number is 7345 1237. My address is Room A, eleventh floor, Lucky Street, North Point, Hong Kong.
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Using headings to organise ideas Hi! My name is Judy. I’m a primary two pupil and I’m studying at Green Tree School. Let me tell you more about myself. I was born on 20 February 2004. I love swimming and playing badminton. My favourite subject is English. My telephone number is 7345 1237. My address is Room A, eleventh floor, Lucky Street, North Point, Hong Kong.
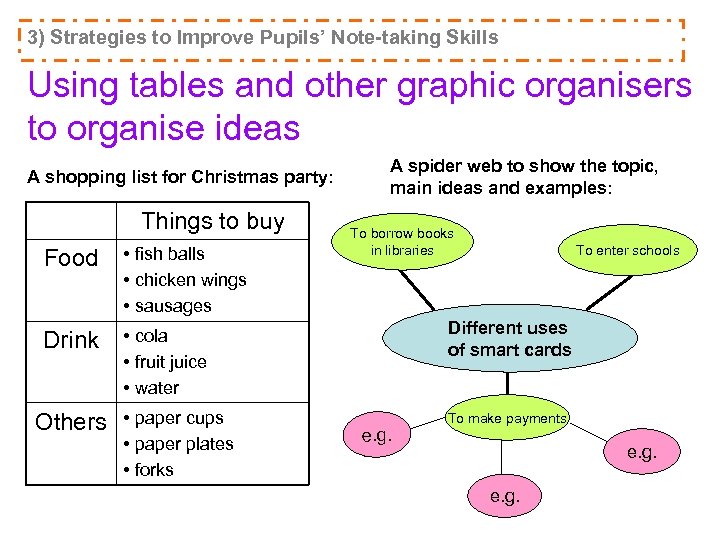 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Using tables and other graphic organisers to organise ideas A shopping list for Christmas party: Things to buy Food • fish balls • chicken wings • sausages Drink A spider web to show the topic, main ideas and examples: To borrow books in libraries • cola • fruit juice • water Others • paper cups • paper plates • forks To enter schools Different uses of smart cards e. g. To make payments e. g.
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Using tables and other graphic organisers to organise ideas A shopping list for Christmas party: Things to buy Food • fish balls • chicken wings • sausages Drink A spider web to show the topic, main ideas and examples: To borrow books in libraries • cola • fruit juice • water Others • paper cups • paper plates • forks To enter schools Different uses of smart cards e. g. To make payments e. g.
 3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Using short forms, abbreviations, numbers and symbols to take notes • Using short forms / abbreviations for units of measurements, places and subjects • Writing numbers (e. g. telephone number, date, time) • Using symbols (e. g. for increase, for decrease) • Creating own abbreviations and symbols (e. g. 6 sandwiches 6 )
3) Strategies to Improve Pupils’ Note-taking Skills Using short forms, abbreviations, numbers and symbols to take notes • Using short forms / abbreviations for units of measurements, places and subjects • Writing numbers (e. g. telephone number, date, time) • Using symbols (e. g. for increase, for decrease) • Creating own abbreviations and symbols (e. g. 6 sandwiches 6 )


