9525a638cbb0f6efbbff290763a476b8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Parkinson’s Disease Self-study Tutorial Created by: Holly A. Hepp, BSN, RN MSN Program Alverno College Milwaukee, WI May 2006 holly_hep@msn. com

Parkinson’s Disease - Objectives Introduction Objectives Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit http: //office. m icrosoft. com/e n-us/tou. aspx ♦ Identify Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) ♦ Understand possible causes of PD ♦ List treatment options for PD
Parkinson’s Disease - Introduction Parkinson's disease (PD): Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes ♦ Is a neurodegenerative disorder ♦ Develops around age 50 * incidence rises with age * affects 1 -2% of population > age 65 Quiz Treatments Quiz http: //office. m icrosoft. com/e n-us/tou. aspx ♦ Higher incidence in men (62%) compared to women (38%) Quit Porth, 2005 , Wooten, 2004

Parkinson’s Disease - Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit http: //office. microsoft. com /en-us/tou. aspx Increasing proportion of elderly individuals PLUS PD & related neurodegenerative disorders CREATES Growing burden on health care system
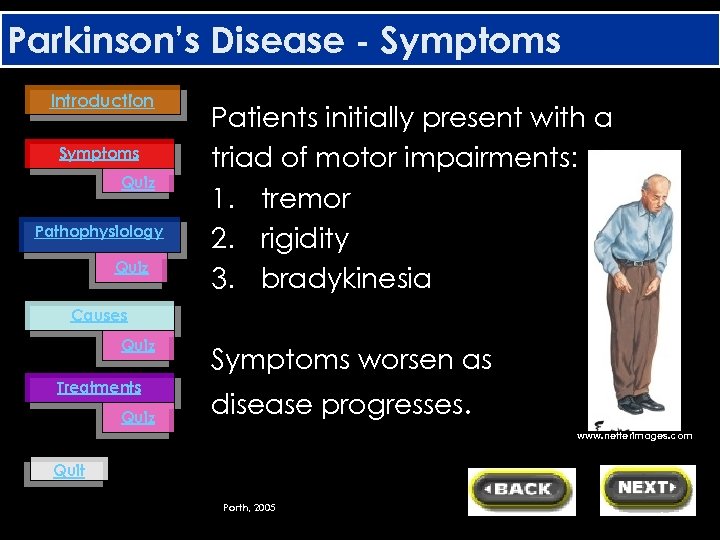
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Patients initially present with a triad of motor impairments: 1. tremor 2. rigidity 3. bradykinesia Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Symptoms worsen as disease progresses. www. netterimages. com Quit Porth, 2005
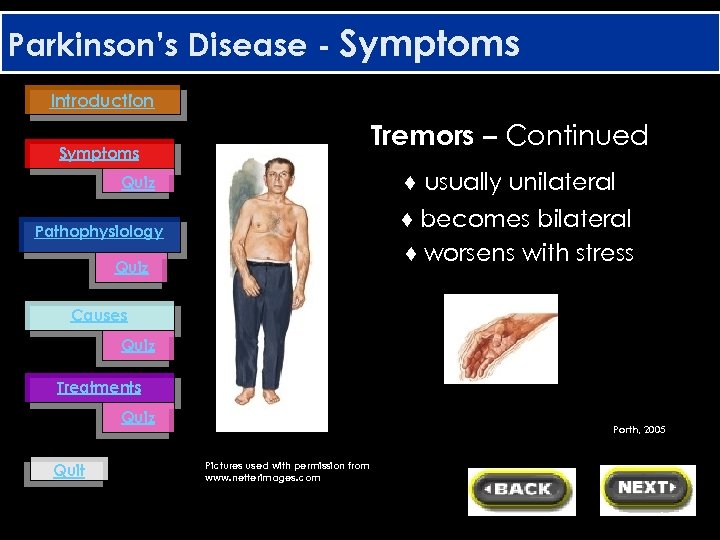
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Tremors – Continued Symptoms ♦ usually unilateral Quiz ♦ becomes bilateral ♦ worsens with stress Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Porth, 2005 Pictures used with permission from www. netterimages. com
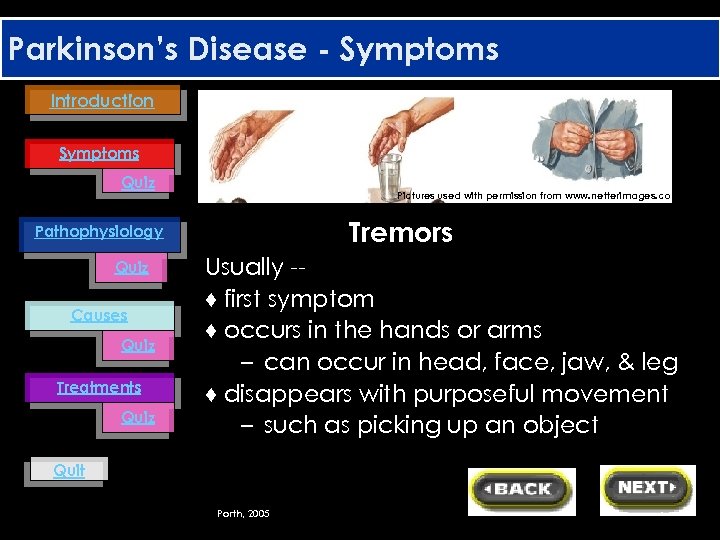
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pictures used with permission from www. netterimages. com Tremors Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Usually -♦ first symptom ♦ occurs in the hands or arms – can occur in head, face, jaw, & leg ♦ disappears with purposeful movement – such as picking up an object Quit Porth, 2005
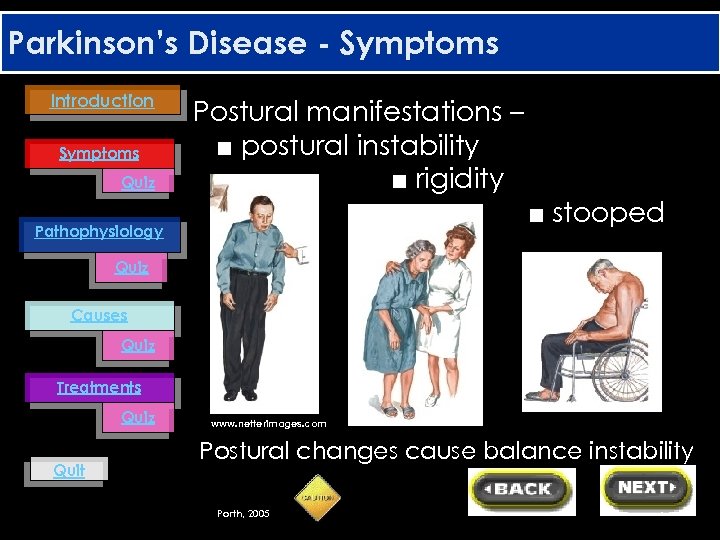
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Postural manifestations – ■ postural instability ■ rigidity ■ stooped Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit www. netterimages. com Postural changes cause balance instability Porth, 2005
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Patients also suffer from nonmotor symptoms such as: ♦ cognitive impairments ♦ olfactory impairments ♦ dysphagia ♦ GI dysfunction ♦ sleep disturbances ♦ depression http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx Fleming, Fernaut, & Chesselet, 2005 Quit Microsoft©
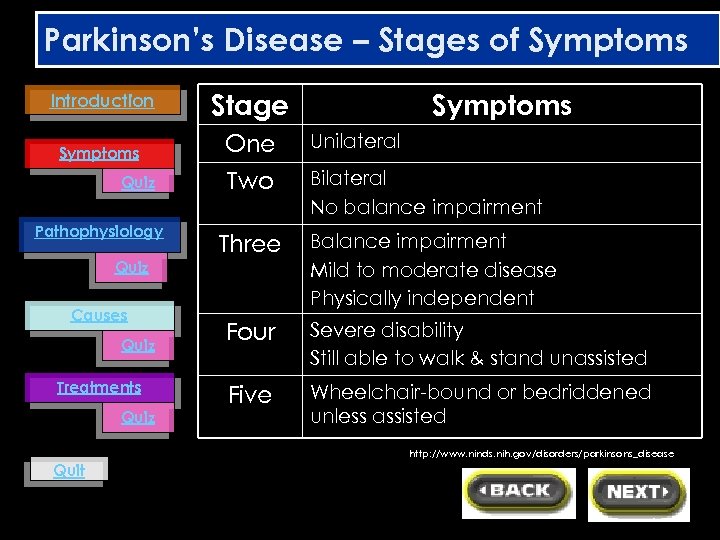
Parkinson’s Disease – Stages of Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Stage Symptoms One Unilateral Two Bilateral No balance impairment Three Balance impairment Mild to moderate disease Physically independent Four Severe disability Still able to walk & stand unassisted Five Wheelchair-bound or bedriddened unless assisted http: //www. ninds. nih. gov/disorders/parkinsons_disease Quit

Parkinson’s Disease – Symptoms & Stress Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Question: Does daily stress worsen PD symptoms? Answer: Yes, but only temporarily ♦ Stress is not the cause of PD ♦ Any stress can briefly worsen PD symptoms ♦ Stress-related symptoms resolve after stress is relieved. Quit Hakansson, et al. , 2005
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Quiz --PD Symptoms Question #1 Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Are all the following symptoms of PD? • bradykinesia • tremor • rigidity • gastrointestinal dysfunction • postural instability • sleep disturbances • cognitive impairments. True False microsoft©
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms You are correct! Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx Quit

Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Wrong! The correct answer is true. All the following are symptoms of PD bradykinesia tremor rigidity gastrointestinal dysfunction postural instability sleep disturbances cognitive impairments.
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Quiz --PD Symptoms Question #2 Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Postural instability, rigidity, and stooped posture places the PD patient at greatest risk for: Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz a. b. c. d. Sleeping Sneezing Falling Dying microsoft© Quit
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms You are correct! Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx Quit

Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Wrong! Postural instability, rigidity, and stooped posture places the PD patient at greatest risk for falling.
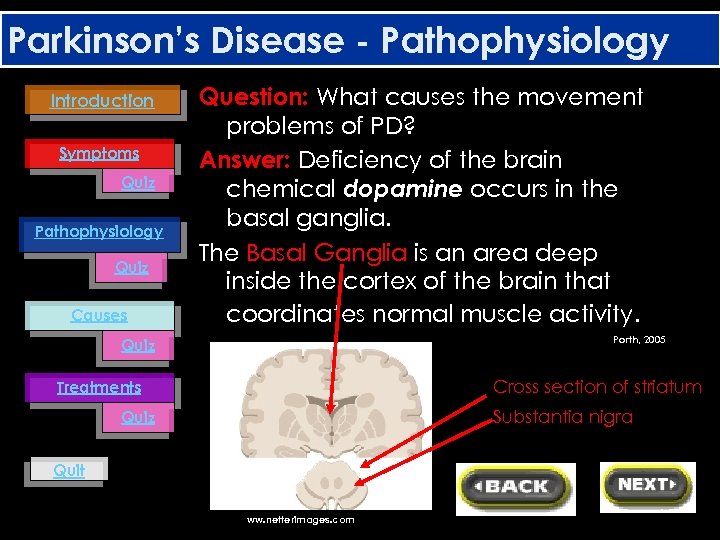
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Question: What causes the movement problems of PD? Answer: Deficiency of the brain chemical dopamine occurs in the basal ganglia. The Basal Ganglia is an area deep inside the cortex of the brain that coordinates normal muscle activity. Porth, 2005 Quiz Cross section of striatum Treatments Substantia nigra Quiz Quit ww. netterimages. com
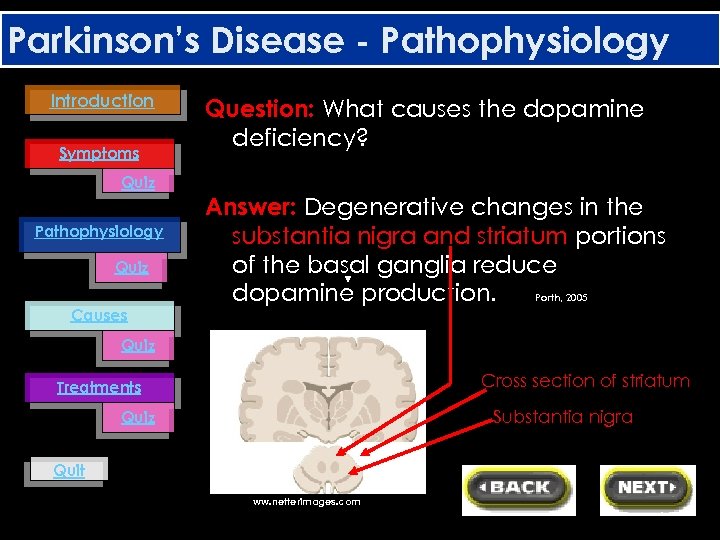
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Question: What causes the dopamine deficiency? Answer: Degenerative changes in the substantia nigra and striatum portions of the basal ganglia reduce Porth, 2005 dopamine production. Quiz Cross section of striatum Treatments Substantia nigra Quiz Quit ww. netterimages. com
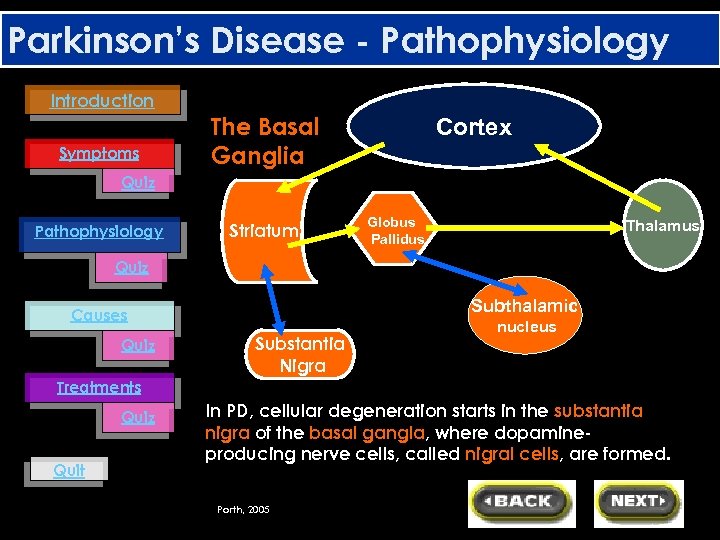
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Symptoms The Basal Ganglia Cortex Quiz Pathophysiology Striatum Globus Pallidus Thalamus Quiz Subthalamic Causes Quiz Substantia Nigra nucleus Treatments Quiz Quit In PD, cellular degeneration starts in the substantia nigra of the basal gangla, where dopamineproducing nerve cells, called nigral cells, are formed. Porth, 2005
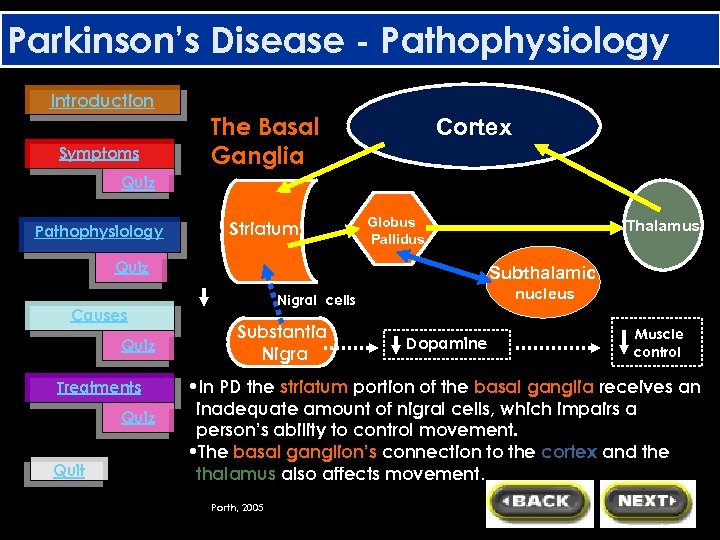
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Symptoms The Basal Ganglia Cortex Quiz Pathophysiology Striatum Globus Pallidus Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Thalamus Subthalamic nucleus Nigral cells Substantia Nigra Dopamine Muscle control • In PD the striatum portion of the basal ganglia receives an inadequate amount of nigral cells, which impairs a person’s ability to control movement. • The basal ganglion’s connection to the cortex and the thalamus also affects movement. Porth, 2005
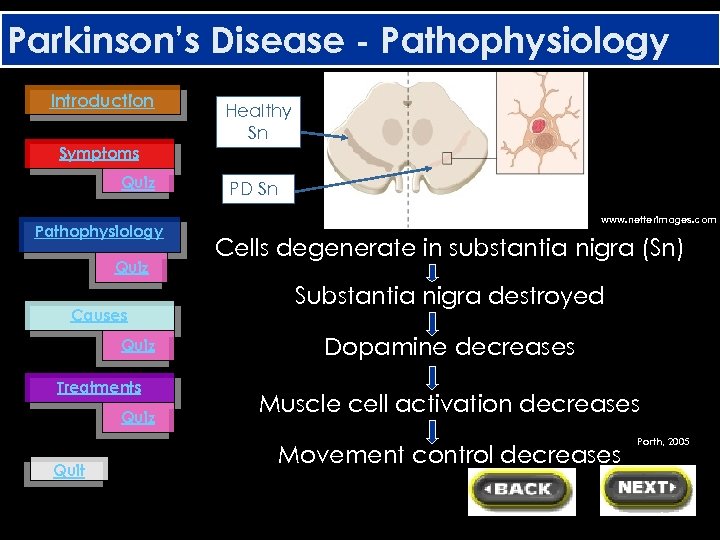
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Healthy Sn Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit PD Sn www. netterimages. com Cells degenerate in substantia nigra (Sn) Substantia nigra destroyed Dopamine decreases Muscle cell activation decreases Movement control decreases Porth, 2005
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Question: What causes PD? Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Answer: Process not understood completely Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Microsoft© - May be combination of factors involving genetics, environmental agents, & abnormalities in cellular process. Quit Microsoft©
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Symptoms Quiz --PD Pathophysiology What causes the movement problems of PD? Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit A. B. C. D. Excess amount of epinephrine Inadequate amount of epinephrine Excess amount of dopamine Inadequate amount of dopamine
Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction You are correct! Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx Treatments Quiz Quit Deficiency of the brain chemical dopamine cause movement disorders.

Parkinson’s Disease - Pathophysiology Introduction Symptoms Wrong! Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Please try again!

Parkinson’s Disease – Causes Introduction Question: Is Genetics a Factor in PD? Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Answer: ♦ Recent discoveries support a genetic component to some familial forms of PD in both early-age and late-age onset ♦ 15 -25% of PD patients have relative with PD ♦ Majority of PD cases occur without apparent genetic factor Berg, 2005, Duovisin, 2004, Foroud, 2005, Gasser, 2005, Paisàn-Ruiz, 2005.
Parkinson’s Disease - Causes Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Recent studies discovered several genes that can cause PD ♦ Some genes effect dopamine cell functions ♦ Some genes affects are unknown ♦ PD genetics research is on-going Treatments Quiz Foroud, 2005 Quit http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx

Parkinson’s Disease - Causes Introduction Question: How will Identification of genetic mutation affect PD? Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Answer: 1. might help scientists better understand how PD damages the brain & causes symptoms of the disease. 2. might lead to better therapies for Parkinson's disease and, hopefully, a cure! Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Foroud, 2005

Parkinson’s Disease – Causes Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Question: Is PD an immune/inflammatory response? Answer: Not certain. ♦ Pathogenesis of PD as an immune response being studied ♦ Link between PD and a proinflammatory cytokine shown in three recent studies Treatments Quiz ♦ Indications are present but inconclusive Quit Hakansson, et al. , 2005

Parkinson’s Disease – Causes Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Question: Do environmental agents cause PD? Answer: Not certain. Microsoft© ♦ Environmental link may be present ♦ - genetic factor may place person at increase risk when exposed to pesticides ♦ Indications present but inconclusive Jiang, , Ellis, & Greenlee, 2004 Quit

Parkinson’s Disease – Causes Introduction Quiz-- PD Causes Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz All of the following are true except: A. Majority of PD cases are due to an inherited gene. B. PD is contagious C. A link between PD and a proinflammatory cytokine shown in three recent studies D. Pesticide exposure may be linked to PD. Quit Berg, 2005, Duovisin, 2004, Foroud, 2005, Gasser, 2005, Paisàn-Ruiz, 2005.

Parkinson’s Disease - Causes Introduction Symptoms Correct! Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit While the majority of PD cases do not have a known cause, it is not contagious.

Parkinson’s Disease - Genes & Things Introduction Symptoms Wrong! Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Please try again!

Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Question: What are some treatment approaches for PD? Answer: a. Medical therapy b. Surgical therapy. c. General lifestyle modifications * rest and exercise * physical therapy * speech therapy

Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Question: Do the treatments cure Parkinson's Disease or stop it from progressing? Answer: No. • Treatments do not cure the disease • Goal is to alleviate symptoms and maintain independent function

Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Question: Is there a “best” treatment for PD? Answer: No standard exists Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Surgical treatment for PD is considered for patients who respond to medications but have intolerable side effects.
Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Medical Approaches Question: Are PD patients given dopamine? Answer: No. • Dopamine, itself, does not pass the blood-brain barrier • Levodopa (L-dopa) is given to pass into the brain and the nerve cells then use it to make dopamine Treatments Quiz Quit http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx

Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Other Medical Approaches Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Dopamine-agonists: acts on dopamine receptors, mimics natural dopamine, not as effective as L-dopa Meds: Bromocriptine, Pergolide, Pramipexole, Ropinirole Anticholenergic: helps relieves tremor in mild to moderate disease Meds: Benztropine, Biperidan, Orphenadrine, Trihexyphenidyl Hickey, 2000 Quiz Quit http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx
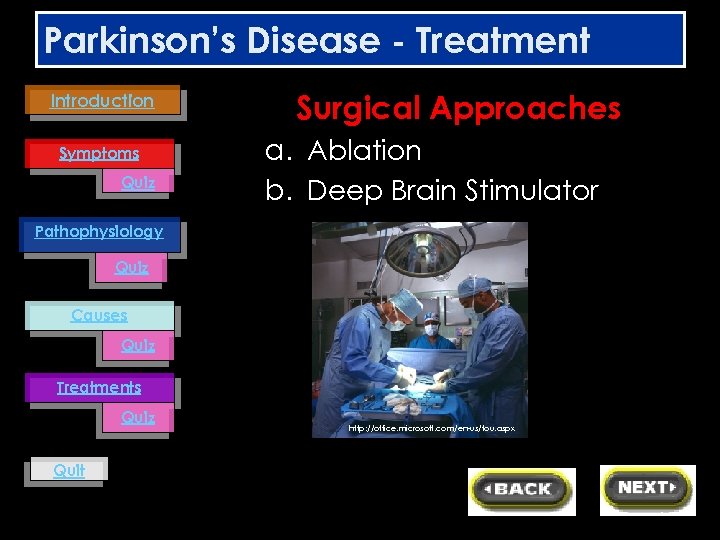
Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Surgical Approaches a. Ablation b. Deep Brain Stimulator Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx
Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Surgical Approach--Ablation An area of the brain affected by PD is ablated (destroyed) Purpose: destroy tissue that produces abnormal chemical or electrical impulses that produce abnormal movements
Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Surgical Approach – Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Surgically implanted, batteryoperated device delivers electrical stimulation to targeted areas in the brain Purpose: block abnormal nerve signals that cause tremor and PD symptoms
Parkinson’s Disease - Treatment Introduction Quiz-- PD Treatment Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit All of the following approaches are used to treat PD? a. L-dopa pills b. Dopamine pills c. Deep Brain Stimulation surgery True False

Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz YES! You are correct! Dopamine does not cross the bloodbrain barrier when delivered in pill form. • Levodopa (L-dopa) is given to pass into the brain and the nerve cells then use it to make dopamine http: //office. microsoft. com/en-us/tou. aspx Quit
Parkinson’s Disease - Symptoms Introduction Symptoms Wrong! Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Dopamine pills would not cross the blood brain barrier. Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit • Levodopa (L-dopa) is given to pass into the brain and the nerve cells then use it to make dopamine

Parkinson’s Disease – Nursing Implications Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology 1) PD has many different symptoms ask patients about intensity, frequency, & duration of symptoms. Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit 2) PD is chronic, with no known cure Psychosocial & other nursing interventions could decrease stress & symptoms.

Parkinson’s Disease – References (page 1 of 2) Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Duvoisin, R. C. , Golbe, L. I. , Mark, M. H. , Sage, J. , Walters, AS. (2004). Parkinson’s disease handbook: A guide for patients and their families [Electronic version]. The Parkinson Disease Association, Inc. Retrieved February 9, 2006 http: //www. apdaparkinson. org/data/Booklets/Parkinson%20 Handbook. pdf. American Fleming, S. M. , Fernagut, O. , Chesselet, M. (2005). Genetic Mouse Models of Parkinsonism: Strengths and Limitations [Electronic version]. Neuro. Rx, 2(3), 495– 503. Retrieved February 22, 2006 from http: //www. pubmedcentral. gov/articlerender. fcgi? tool=pubmed&pubmedid=16389313 Foroud, , Y. (2005). LRRK 2 -Both a cause and a risk factor for parkinson’s disease [Electronic version]. Neurolog, 65(5), 664 -665. Retrieved February 9, 2006 from http: //gateway. ut. ovid. com/gw 1/ovidweb. cgi Accession Number: 00006114 -200509130 -00004. Gasser, T. (2005). Genetics of Parkinson’s disease [Electronic version]. Current opinon in neurology, 18: 363 -369. Retrieved February 9, 2006 from http: //gateway. ovid. com/ovidweb. cgi? T=JS& NEWS=N&PAGE=fulltext&AN=00019052 -200508000 -00003&LSLINK=80&D=ovft Hakansson, A. , Westberg, L. , Nilsson, S. , Buervenich, S. , Carmine, A. , Holmberg, B. , Sydow, O. , Olson, L. , Johnels, B. , Eriksson, E. , Nissbrandt, H. (2005). Investigation of genes coding for inflammatory components in parkinson’ s disease [Electronic version]. Movement disorders, 20(5), 569 -573. Retrieved March 3, 2006 from Movement Disorders http: //www 3. interscience. wiley. com/cgi-bin/fulltext/109865259 Hickey, J. V. (2000). The Clinical Practice of Neurological and Neurosurgoical Nursing (5 th ed. ). Philidelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Jiang, Y. , Ellis, T. , Greenlee, A. R. (2004). Genotyping parkinson’s disease-associated mitochondrial polymorphisms [Electronic version]. Clinical Medicine & Research, 2(2), 99 -106. Retrieved February 22, 2006 from http: //www. pubmedcentralgov/articlerender. fcgi? tool=pubmed&pubmedid=15931342

Parkinson’s Disease – References (page 2 of 2) Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit O’Brien, J. T. , Colloby, S. , Fenwick, J. , Williams, E. D. , Firbasnk, M. , Burn, D. , Aarsland, D. , Mc. Keith, I. G. (2004). Dopamine tramnsporter loss visualized with FP-CIT SPECT in the differential diagnosis of dementia with lewey bodies [Electronic version]. Archives of Neurology, 61(6), 619 -625. Retrieved March 29, 2006 from http: //archneur. ama-assn. org/icons/home/title. gif Paisàn-Ruiz, C. , Sàenz, A. , Lopez de Munain, A. , Marti, I. , Gil, A. M. , Marti-Massp, J. , Perez-Tur, J. (2005). Familial Parkinson; s disease: Clinical and genetic analysis of four basque families [Electronic version]. Annuals of Neurology, 57, 365 -372. Retrieved February 9, 2006 from http: //www 3. interscience. wiley. com/cgi-bin/fulltext/109931600 Pankratz, N. , Foroud, T. (2004). Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease [Electronic version]. Neuro. Rx, 1(2), 235 - 242. Retrieved February 22, 2006 from http: //www. pubmedcentral. gov/articlerender. fcgi? tool=pubmed&pubmedid=157 1702 Porth, C (2005) Pathophysiology: Concepts of Altered Health States (7 th ed. ). Philidelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. Wooten, G. F. , L J Currie, L. J. , V E Bovbjerg, V. E. , Lee, J. K. , J Patrie, J. (2004). Are men at greater risk for parkinson’s disease than women? [Electronic version]. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 75, 637 -639. Retrieved February 9, 2006 http: //jnnp. bmjjournals. com/cgi/content/full/75/4/637 Youdim, M. B. H. , Reider, P. (1997) Understanding Parkinson's disease. [Electronic version] Scientific American, 276(1), 52 -59. Retrieved February 10, 2006 from http: //search. epnet. com/login. aspx? direct=true&db=afh&an=9704275992

Parkinson’s Disease Introduction Symptoms Quiz Pathophysiology Quiz Causes Quiz Treatments Quiz Quit Thank You for viewing this tutorial on Parkinson’s Disease holly_hep@msn. com
9525a638cbb0f6efbbff290763a476b8.ppt