c7a5a83b7689626d1af3e3091e3a0333.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 PARASITOLOGY IN THE CLINIC DEPARTMENT OF PARASITOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE PADJADJARAN UNIVERSITY
PARASITOLOGY IN THE CLINIC DEPARTMENT OF PARASITOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE PADJADJARAN UNIVERSITY
 INTRODUCTION PARASITIC DISEASE IN ASIA (A VERY COMMON DISEASE) w w Asia is in the tropic area Low grade of Social Economic Low grade of education The bad habit of the people
INTRODUCTION PARASITIC DISEASE IN ASIA (A VERY COMMON DISEASE) w w Asia is in the tropic area Low grade of Social Economic Low grade of education The bad habit of the people
 PARASITIC PROTOZOA w w w BALANTIDIASIS CRYPTOSPORIDIASIS GIARDIASIS PNEUMOCYSTOSIS SARCOSPORIDIOSIS TOXOPLASMOSIS
PARASITIC PROTOZOA w w w BALANTIDIASIS CRYPTOSPORIDIASIS GIARDIASIS PNEUMOCYSTOSIS SARCOSPORIDIOSIS TOXOPLASMOSIS
 PARASITIC HELMINTHES w ANGYOSTRONGYLIASIS w ASCARIASIS DIPYLIDIASIS w DIROFILARIASIS w FASCIOLIASIS w HYDATIDOSIS w HYMENOLEPIASIS w LARVA MIGRANS w w w w LINGUATULIASIS PHYSALOPTERIASIS SCHISTOSOMIASIS SPARGANOSIS STRONGYLOIDIASIS TAENIASIS SAGINATA TRICHINOSIS TRICHSTRONGYLIDIASIS
PARASITIC HELMINTHES w ANGYOSTRONGYLIASIS w ASCARIASIS DIPYLIDIASIS w DIROFILARIASIS w FASCIOLIASIS w HYDATIDOSIS w HYMENOLEPIASIS w LARVA MIGRANS w w w w LINGUATULIASIS PHYSALOPTERIASIS SCHISTOSOMIASIS SPARGANOSIS STRONGYLOIDIASIS TAENIASIS SAGINATA TRICHINOSIS TRICHSTRONGYLIDIASIS
 Cases found in Surgical clinic a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Ascariasis – as emergency cases : intestinal obstruction, intestinal perforation Severe Trichuriasis – prolapsus ani Trichinelliasis Filariasis – elephantiasis Cysticercosis cellulosae Hydatid cyst Coenuriasis Sparganosis Amoebic abscess, amoeboma Parasitic Pneumonia caused Pneumocystis carinii
Cases found in Surgical clinic a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Ascariasis – as emergency cases : intestinal obstruction, intestinal perforation Severe Trichuriasis – prolapsus ani Trichinelliasis Filariasis – elephantiasis Cysticercosis cellulosae Hydatid cyst Coenuriasis Sparganosis Amoebic abscess, amoeboma Parasitic Pneumonia caused Pneumocystis carinii

 Cases likely found in Neurosurgery examination a. Cysticercosis cellulosae in the brain b. Hydatidosis in the brain c. Coenuriasis in the brain d. Sparganosis in the brain e. Amoebic abces in the brain
Cases likely found in Neurosurgery examination a. Cysticercosis cellulosae in the brain b. Hydatidosis in the brain c. Coenuriasis in the brain d. Sparganosis in the brain e. Amoebic abces in the brain
 INTERNAL MEDICINE MAY BE FOUND a. b. c. Ascariasis Trichuriasis d. Strongyloidiasis e. Enterobiasis (rare in adult age) f. Trichostrongyliasis g. Capillariasis (find in Philippines and Thailand, never yet find in Indonesia) Hookworm infektion
INTERNAL MEDICINE MAY BE FOUND a. b. c. Ascariasis Trichuriasis d. Strongyloidiasis e. Enterobiasis (rare in adult age) f. Trichostrongyliasis g. Capillariasis (find in Philippines and Thailand, never yet find in Indonesia) Hookworm infektion
 INTERNAL MEDICINE MAY BE FOUND h. Visceral Larva Migrans (VLM) i. Diphyllobothriasis j. Taeniasis saginata k. Taeniasis solium l. Hymenolepsiasis Nana m. Diphylidiasis caninum n. Echinococcosis
INTERNAL MEDICINE MAY BE FOUND h. Visceral Larva Migrans (VLM) i. Diphyllobothriasis j. Taeniasis saginata k. Taeniasis solium l. Hymenolepsiasis Nana m. Diphylidiasis caninum n. Echinococcosis
 CASES COMMONLY FOUND IN PEDIATRIC WARD a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Ascariasis Trichuriasis Hookworm infection (rare ini the children) Strongyloidiasis Enterobiasis Trichostrongyliasis Capillariasis (find in Philippines and Thailand, never yet find in Indonesia)
CASES COMMONLY FOUND IN PEDIATRIC WARD a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Ascariasis Trichuriasis Hookworm infection (rare ini the children) Strongyloidiasis Enterobiasis Trichostrongyliasis Capillariasis (find in Philippines and Thailand, never yet find in Indonesia)
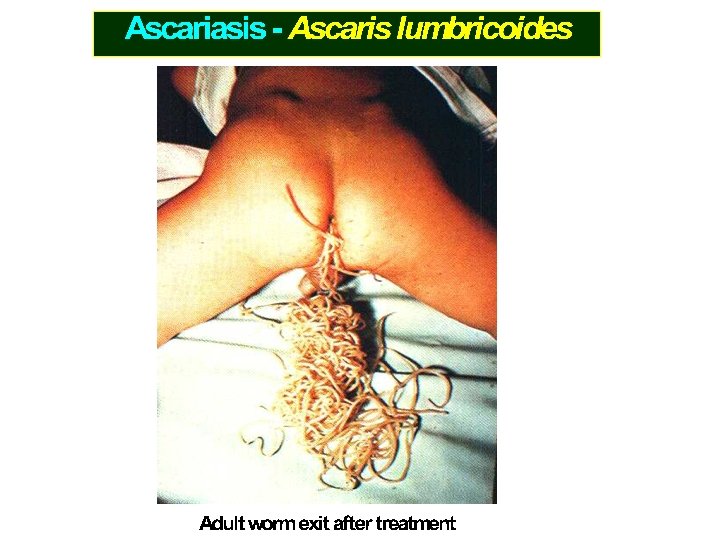
 CASES COMMONLY FOUND IN PEDIATRIC WARD h. Visceral Larva Migrans (VLM) i. Diphyllobothriasis j. Taeniasis saginata k. Taeniasis solium l. Hymenolepsiasis nana m. Hymenolepsiasis diminuta n. Diphylidiasis caninum o. Echinococcosis
CASES COMMONLY FOUND IN PEDIATRIC WARD h. Visceral Larva Migrans (VLM) i. Diphyllobothriasis j. Taeniasis saginata k. Taeniasis solium l. Hymenolepsiasis nana m. Hymenolepsiasis diminuta n. Diphylidiasis caninum o. Echinococcosis
 CASES LIKELY FOUND DURING SKIN EXAMINATION a. Cutaneous Larva Migrans (Creeping Eruption) b. Trichinelliasis c. Ground Itch d. Swimmer's Itch e. Cutaneous Amoebiasis f. Sarcosporidiosis caused by Sarcocystis sp. g. Arthropod infection : Cutaneous Myiasis; Scabies; Pediculosis
CASES LIKELY FOUND DURING SKIN EXAMINATION a. Cutaneous Larva Migrans (Creeping Eruption) b. Trichinelliasis c. Ground Itch d. Swimmer's Itch e. Cutaneous Amoebiasis f. Sarcosporidiosis caused by Sarcocystis sp. g. Arthropod infection : Cutaneous Myiasis; Scabies; Pediculosis
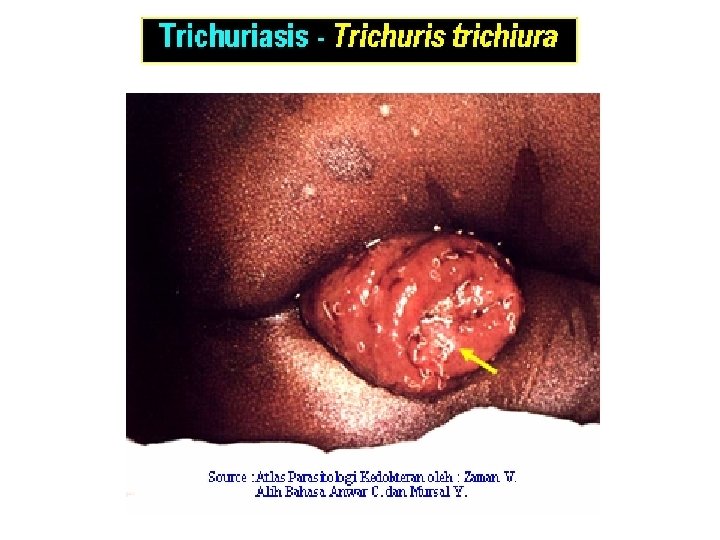
 OPHTHALMOLOGIST MAY FIND a. Toxoplasmosis b. Disturbance of the eye by Acanthamoeba sp. c. Case never reported in Indonesia : loaiasis (worm in subconjunctiva); blinding filariasis or river blindness by Onchocerca volvulus
OPHTHALMOLOGIST MAY FIND a. Toxoplasmosis b. Disturbance of the eye by Acanthamoeba sp. c. Case never reported in Indonesia : loaiasis (worm in subconjunctiva); blinding filariasis or river blindness by Onchocerca volvulus
 PARASITES MAY BE FOUND IN OBSTETRIC WARD a. Toxoplasmosis b. Trichomoniasis vaginalis
PARASITES MAY BE FOUND IN OBSTETRIC WARD a. Toxoplasmosis b. Trichomoniasis vaginalis
 PARASITES MAY BE FOUND IN NEUROLOGICAL CLINIC a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Trichinosis Angiostrongyliasis Gnathostomiasis Schistosomiasis Paragonimiasis Cysticercosis Hydatidosis Draconcoliasis
PARASITES MAY BE FOUND IN NEUROLOGICAL CLINIC a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Trichinosis Angiostrongyliasis Gnathostomiasis Schistosomiasis Paragonimiasis Cysticercosis Hydatidosis Draconcoliasis
 PARASITES WHICH MAY BE FOUND IN NEUROLOGICAL CLINIC w w w Coenuriasis Amebic Brain Abscess Toxoplasmosis Cerebral Malaria Trypanosomiasis Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) w Tick paralysis
PARASITES WHICH MAY BE FOUND IN NEUROLOGICAL CLINIC w w w Coenuriasis Amebic Brain Abscess Toxoplasmosis Cerebral Malaria Trypanosomiasis Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) w Tick paralysis
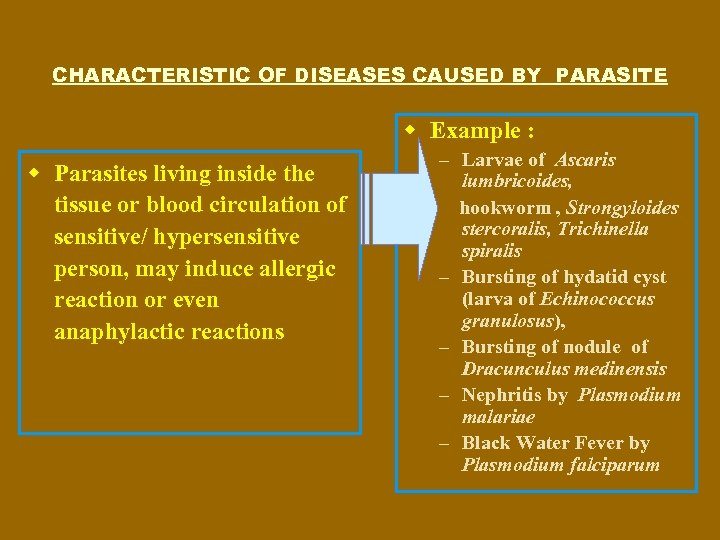 CHARACTERISTIC OF DISEASES CAUSED BY PARASITE w Example : w Parasites living inside the tissue or blood circulation of sensitive/ hypersensitive person, may induce allergic reaction or even anaphylactic reactions – Larvae of Ascaris lumbricoides, hookworm , Strongyloides stercoralis, Trichinella spiralis – Bursting of hydatid cyst (larva of Echinococcus granulosus), – Bursting of nodule of Dracunculus medinensis – Nephritis by Plasmodium malariae – Black Water Fever by Plasmodium falciparum
CHARACTERISTIC OF DISEASES CAUSED BY PARASITE w Example : w Parasites living inside the tissue or blood circulation of sensitive/ hypersensitive person, may induce allergic reaction or even anaphylactic reactions – Larvae of Ascaris lumbricoides, hookworm , Strongyloides stercoralis, Trichinella spiralis – Bursting of hydatid cyst (larva of Echinococcus granulosus), – Bursting of nodule of Dracunculus medinensis – Nephritis by Plasmodium malariae – Black Water Fever by Plasmodium falciparum
 CHARACTERISTIC OF DISEASES CAUSED BY PARASITE w The course of disease caused by parasite is usually chronic mixed with periods of latency without symptoms and sometimes with acute exacerbation – Example : quartan malaria by Plasmodium malariae
CHARACTERISTIC OF DISEASES CAUSED BY PARASITE w The course of disease caused by parasite is usually chronic mixed with periods of latency without symptoms and sometimes with acute exacerbation – Example : quartan malaria by Plasmodium malariae
 SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE GASTRO INTESTINAL SYMPTOMS w ABDOMINAL PAIN w – CRAMPY ABDOMINAL PAIN : AMEBIC COLITIS – INTESTINAL OR BILLIARY OBSTRUCTION : A. lumbricoides – DUODENAL ULCERS : Strongyloides stercoralis DIARRHEA: INTESTINAL PROTOZOA – BULKY AND HAS AN OFFENSIVE ODOR : AMEBIASIS – BULKY AND FATTY : GIARDIASIS – WATERY DIARRHEA : CRYPTOSPORIDIASIS – MINIMAL GASTRO INTESTINAL SYMPTOMS : INTESTINAL HELMINTH INFECTION – BLOODY DIARRHEA : AMEBIASIS, TRICHURIASIS, SCHISTOSOMIASIS
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE GASTRO INTESTINAL SYMPTOMS w ABDOMINAL PAIN w – CRAMPY ABDOMINAL PAIN : AMEBIC COLITIS – INTESTINAL OR BILLIARY OBSTRUCTION : A. lumbricoides – DUODENAL ULCERS : Strongyloides stercoralis DIARRHEA: INTESTINAL PROTOZOA – BULKY AND HAS AN OFFENSIVE ODOR : AMEBIASIS – BULKY AND FATTY : GIARDIASIS – WATERY DIARRHEA : CRYPTOSPORIDIASIS – MINIMAL GASTRO INTESTINAL SYMPTOMS : INTESTINAL HELMINTH INFECTION – BLOODY DIARRHEA : AMEBIASIS, TRICHURIASIS, SCHISTOSOMIASIS
 SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE RESPIRATORY SYMPTOMS w COUGH AND WHEEZE – – MIGRATION OF Ascaris lumbricoides THROUGH THE LUNGS PNEUMOCYSTIS INFECTION PARAGONIMIASIS WESTERMANI HOUSE DUST MITES NEUROLOGICAL SYMPTOMS w w w CYSTICERCOSIS CELLULOSAE TOXOPLASMOSIS MALARIA TROPICA EOSINOPHILIC MENINGITIS P. A. M. (Naegleria fowleri)
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE RESPIRATORY SYMPTOMS w COUGH AND WHEEZE – – MIGRATION OF Ascaris lumbricoides THROUGH THE LUNGS PNEUMOCYSTIS INFECTION PARAGONIMIASIS WESTERMANI HOUSE DUST MITES NEUROLOGICAL SYMPTOMS w w w CYSTICERCOSIS CELLULOSAE TOXOPLASMOSIS MALARIA TROPICA EOSINOPHILIC MENINGITIS P. A. M. (Naegleria fowleri)
 SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE CUTANEUS SYMPTOMS w w PRURITUS ANI GROUND ITCH SWIMMER’S ITCH CREEPING ERUPTION HEPATOSPLENOMEGALI w MALARIA w VISCERAL LARVA MIGRAN w TOXOPLASMOSIS
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE CUTANEUS SYMPTOMS w w PRURITUS ANI GROUND ITCH SWIMMER’S ITCH CREEPING ERUPTION HEPATOSPLENOMEGALI w MALARIA w VISCERAL LARVA MIGRAN w TOXOPLASMOSIS
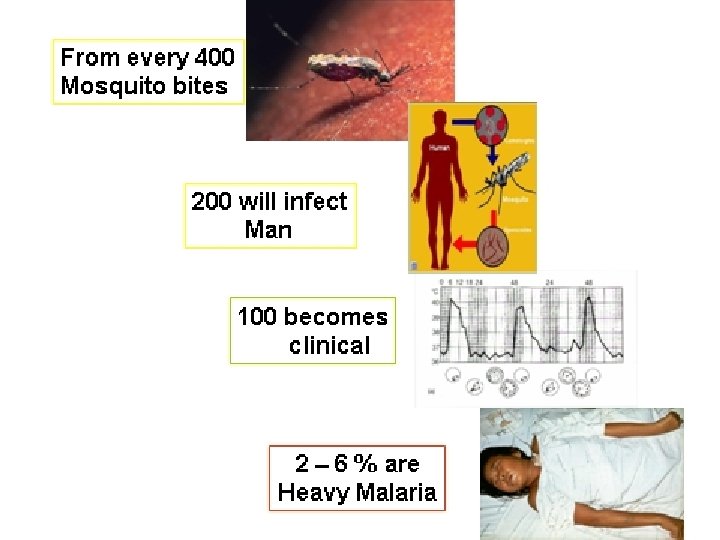
 SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE ANEMIA w w MALARIA ANCYLOSTOMIASIS ASCARIASIS DIPHYLLOBOTHRIASIS STEATORRHEA w GIARDIASIS
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE ANEMIA w w MALARIA ANCYLOSTOMIASIS ASCARIASIS DIPHYLLOBOTHRIASIS STEATORRHEA w GIARDIASIS
 SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE w KERANDEL’S SIGN – AFRICAN SLEEPING SICKNESS w ROMANA’S SIGN – INFECTION WITH Trypanosoma cruzi w WINTER BOTTOM’S SIGN – AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS w KERATITIS – Acanthamoeba sp. – Onchocerca volvulus w RETINOCHOROIDITIS – Toxoplasma gondii
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF PARASITIC DISEASE w KERANDEL’S SIGN – AFRICAN SLEEPING SICKNESS w ROMANA’S SIGN – INFECTION WITH Trypanosoma cruzi w WINTER BOTTOM’S SIGN – AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS w KERATITIS – Acanthamoeba sp. – Onchocerca volvulus w RETINOCHOROIDITIS – Toxoplasma gondii
 DIAGNOSIS w Clinical manifestations caused by parasitic infection are commonly very unspecific, therefore laboratory examination is necessary for definite diagnosis w The aim of laboratory examination is to look for any stages of parasite life cycle in the examination materials w To do accurate laboratory examination, requires decision on: – Correct selection of type of sample material (according to parasite life cycle) – Accurate laboratory technique
DIAGNOSIS w Clinical manifestations caused by parasitic infection are commonly very unspecific, therefore laboratory examination is necessary for definite diagnosis w The aim of laboratory examination is to look for any stages of parasite life cycle in the examination materials w To do accurate laboratory examination, requires decision on: – Correct selection of type of sample material (according to parasite life cycle) – Accurate laboratory technique
 TREATMENT w Individual w Type of treatment w Mass treatment
TREATMENT w Individual w Type of treatment w Mass treatment
 TREATMENT Things to observe during therapy : - Efficacy of drugs against parasite vs. side effect against the host - Sometimes surgery is needed to maximize result of treatment - Consider also the patient’s general condition and immunity status - Also important with treatment of parasite is the improvement of environmental sanitation
TREATMENT Things to observe during therapy : - Efficacy of drugs against parasite vs. side effect against the host - Sometimes surgery is needed to maximize result of treatment - Consider also the patient’s general condition and immunity status - Also important with treatment of parasite is the improvement of environmental sanitation
 PREVENTION The prevention against parasitic disease may be done by the following steps - Source reduction: to reduce the source of infection by treating all infected patients - Health education: to prevent the distribution of parasite - Eradication of host reservoir and vector control - Increase of biological immunity against infection - Control of hygiene and sanitation
PREVENTION The prevention against parasitic disease may be done by the following steps - Source reduction: to reduce the source of infection by treating all infected patients - Health education: to prevent the distribution of parasite - Eradication of host reservoir and vector control - Increase of biological immunity against infection - Control of hygiene and sanitation
 IMMUNITY TWO MECHANISM OF IMMUNITY w Humoral immunity produces antibodies w Cellular immunity (Cell Mediated Immunity/CMI) is the response produced by specific immune cells (T cells)
IMMUNITY TWO MECHANISM OF IMMUNITY w Humoral immunity produces antibodies w Cellular immunity (Cell Mediated Immunity/CMI) is the response produced by specific immune cells (T cells)
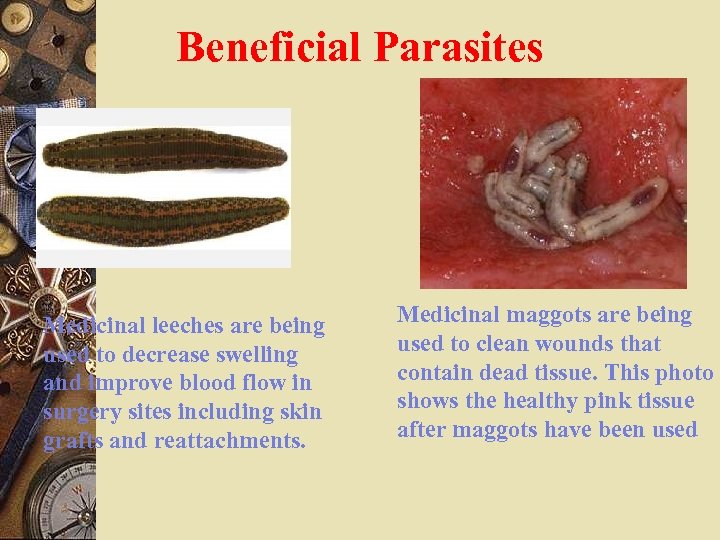 Beneficial Parasites Medicinal leeches are being used to decrease swelling and improve blood flow in surgery sites including skin grafts and reattachments. Medicinal maggots are being used to clean wounds that contain dead tissue. This photo shows the healthy pink tissue after maggots have been used
Beneficial Parasites Medicinal leeches are being used to decrease swelling and improve blood flow in surgery sites including skin grafts and reattachments. Medicinal maggots are being used to clean wounds that contain dead tissue. This photo shows the healthy pink tissue after maggots have been used
 Thank you …………………. April 2005
Thank you …………………. April 2005


