8b38ebd732316ff55ac917c0261d882b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Parallel Connections Michael Fromwiller CS 147 Spring 08 Dr. Sin-Min Lee
Parallel Connections Michael Fromwiller CS 147 Spring 08 Dr. Sin-Min Lee
 Parallel Interfaces l Buses transfer data inside computers. l Monitors, printers, and other devices do not connect to the system bus. l External devices connect to interface circuits which are used to manage the connection. l Proper connections require the ability to send and receive data.
Parallel Interfaces l Buses transfer data inside computers. l Monitors, printers, and other devices do not connect to the system bus. l External devices connect to interface circuits which are used to manage the connection. l Proper connections require the ability to send and receive data.
 Centronics Printer Interface l Multi-wire parallel link. l Transfers 8 bits of ASCII code simultaneously. l Typical speed: 100 kbytes/sec over 10 meters. l Not considered a bus – Does not offer support for more than two devices.
Centronics Printer Interface l Multi-wire parallel link. l Transfers 8 bits of ASCII code simultaneously. l Typical speed: 100 kbytes/sec over 10 meters. l Not considered a bus – Does not offer support for more than two devices.
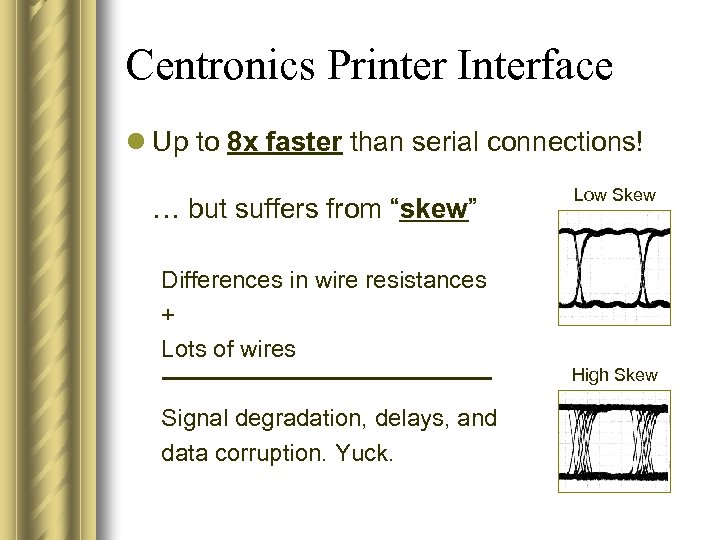 Centronics Printer Interface l Up to 8 x faster than serial connections! … but suffers from “skew” Low Skew Differences in wire resistances + Lots of wires High Skew Signal degradation, delays, and data corruption. Yuck.
Centronics Printer Interface l Up to 8 x faster than serial connections! … but suffers from “skew” Low Skew Differences in wire resistances + Lots of wires High Skew Signal degradation, delays, and data corruption. Yuck.
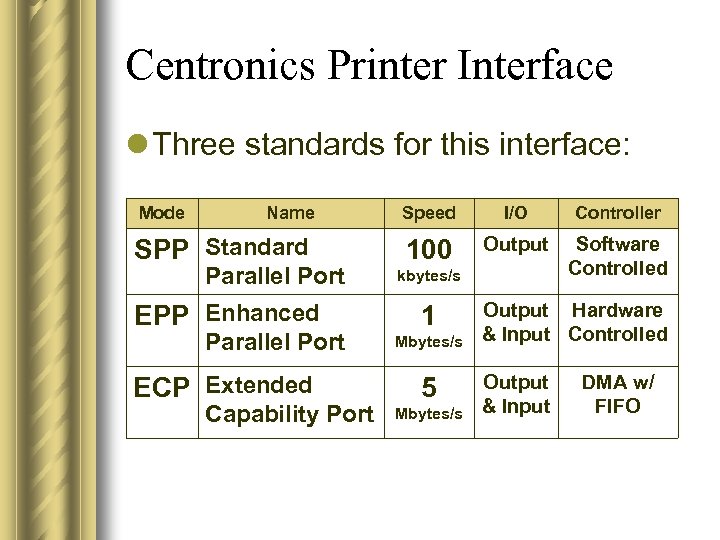 Centronics Printer Interface l Three standards for this interface: Mode Name SPP Standard Parallel Port EPP Enhanced Parallel Port ECP Extended Capability Port Speed I/O Controller 100 Output Software Controlled kbytes/s 1 Mbytes/s 5 Mbytes/s Output Hardware & Input Controlled Output & Input DMA w/ FIFO
Centronics Printer Interface l Three standards for this interface: Mode Name SPP Standard Parallel Port EPP Enhanced Parallel Port ECP Extended Capability Port Speed I/O Controller 100 Output Software Controlled kbytes/s 1 Mbytes/s 5 Mbytes/s Output Hardware & Input Controlled Output & Input DMA w/ FIFO
 Standard Parallel Port (SPP) l Software handles connection (slow) l Host sends important data (a print job, for example) to device. l Device sends status messages to the host: – – Accepting data Busy, try again later Out of paper Error found l Typical setup between devices for asynchronous handshaking.
Standard Parallel Port (SPP) l Software handles connection (slow) l Host sends important data (a print job, for example) to device. l Device sends status messages to the host: – – Accepting data Busy, try again later Out of paper Error found l Typical setup between devices for asynchronous handshaking.
 EPP and ECP Modes l Both offer bi-directional lines for data communication between device and host. l Important for Plug-and-Play process. l Hardware handles data transmission – Software writes data to port buffer – Hardware handles the rest (fast!)
EPP and ECP Modes l Both offer bi-directional lines for data communication between device and host. l Important for Plug-and-Play process. l Hardware handles data transmission – Software writes data to port buffer – Hardware handles the rest (fast!)
 SCSI - Small Computer Systems Interface l Fast asynchronous byte-wide bus (5 Mbytes/sec) connecting up to 8 devices l A secondary bus which relieves the traffic from the main bus. l Intended for: – Hard disk drives – CD-ROM drives – Tape units
SCSI - Small Computer Systems Interface l Fast asynchronous byte-wide bus (5 Mbytes/sec) connecting up to 8 devices l A secondary bus which relieves the traffic from the main bus. l Intended for: – Hard disk drives – CD-ROM drives – Tape units
 SCSI - Small Computer Systems Interface l Variations of SCSI standards: – Fast SCSI • (10 Mbytes/sec synchronous transfer mode) – Wide SCSI • (40 Mbytes/sec with 32 bit data bus) l Useful for: – Multiple computers with shared drives – Multiple CD-ROM burners for mass production – Tape drives
SCSI - Small Computer Systems Interface l Variations of SCSI standards: – Fast SCSI • (10 Mbytes/sec synchronous transfer mode) – Wide SCSI • (40 Mbytes/sec with 32 bit data bus) l Useful for: – Multiple computers with shared drives – Multiple CD-ROM burners for mass production – Tape drives
 IDE – Intelligent Drive Electronics l Simplified version of the ISA bus. l Standard was quickly accepted. – Used by cheapest hard disk drives – Used by most common hard disk drives l Ribbon connections support two devices: – Master – Slave. l Plugs directly into the AT bus.
IDE – Intelligent Drive Electronics l Simplified version of the ISA bus. l Standard was quickly accepted. – Used by cheapest hard disk drives – Used by most common hard disk drives l Ribbon connections support two devices: – Master – Slave. l Plugs directly into the AT bus.
 AT / ISA bus l Appeared around the time the Intel 8088 processor came out. – Ran at 4. 77 Mhz – Later topped off at 8. 33 Mhz l Faster processors would wait till the ISA bus was finished, affecting speed. l Pentium CPUs made the speed difference clear. l Extended ISA (EISA) clocked at 33 Mhz, but was overshadowed by the new PCI bus.
AT / ISA bus l Appeared around the time the Intel 8088 processor came out. – Ran at 4. 77 Mhz – Later topped off at 8. 33 Mhz l Faster processors would wait till the ISA bus was finished, affecting speed. l Pentium CPUs made the speed difference clear. l Extended ISA (EISA) clocked at 33 Mhz, but was overshadowed by the new PCI bus.
 PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnection l PCI bus isolated from main bus by a “bridge” device, such as the i 82443. l “North Bridge” – Handles PCI components l “South Bridge” – PCI to ISA bridging device, such as the i 82371 l Development of the mini-PCI was brought about by laptop computers, for PC add-ons.
PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnection l PCI bus isolated from main bus by a “bridge” device, such as the i 82443. l “North Bridge” – Handles PCI components l “South Bridge” – PCI to ISA bridging device, such as the i 82371 l Development of the mini-PCI was brought about by laptop computers, for PC add-ons.
 PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnection l PCI bus operates in two modes: – Multiplexed Mode • A single 32 bit bus that is shared by address and data information. • Increased bus width, but reduced data rate. – Burst Mode • Same idea as EDO DRAM. After one address has been sent, several data items follow in quick succession. • Bridge is capable of assembling these “packets” of data and bursting it to the PCI bus when ready.
PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnection l PCI bus operates in two modes: – Multiplexed Mode • A single 32 bit bus that is shared by address and data information. • Increased bus width, but reduced data rate. – Burst Mode • Same idea as EDO DRAM. After one address has been sent, several data items follow in quick succession. • Bridge is capable of assembling these “packets” of data and bursting it to the PCI bus when ready.
 Plug-and-Play l Introduced by Microsoft. l Main purposes: – Allow computer to auto-configure hardware. – Simplify hardware installation. – Make the PC more user friendly … l “Released” with Windows 95. l Fully supported by Windows 2000/XP.
Plug-and-Play l Introduced by Microsoft. l Main purposes: – Allow computer to auto-configure hardware. – Simplify hardware installation. – Make the PC more user friendly … l “Released” with Windows 95. l Fully supported by Windows 2000/XP.
 PCMCIA – Personal Computer Memory Card International Association l Credit card sized l Originally intended for memory expansion for laptops. l Designed for “hot swapping. ” No need to turn off or reboot laptops. Just pop and go! l Manufacturers took it a lot further: – – – Modems and Ethernet interfaces Video cards Parallel ports Disk drives Pretty much anything!
PCMCIA – Personal Computer Memory Card International Association l Credit card sized l Originally intended for memory expansion for laptops. l Designed for “hot swapping. ” No need to turn off or reboot laptops. Just pop and go! l Manufacturers took it a lot further: – – – Modems and Ethernet interfaces Video cards Parallel ports Disk drives Pretty much anything!
 Sources l All information from this presentation can be found in: Computer Systems Architecture – A Networking Approach Rob Williams. Chapter 11 l “Low and high skew” images: – http: //www. spectra-strip. amphenol. com l “Parallel printer cable” image: – http: //www. nuggetlab. com/comptia_files/equipment/ cable_Parallel%20 Cable%20 showing%2025 -pin%20 end. jpg l “SCSI ribbon cable” image: – http: //www. qvs. com/prodimages/SCU 160 -4 T_LR. jpg l “IDE ribbon cable” image: – http: //www. cable-house. com/images/cables/internal%20 cables/ ide_ata 133_ribbon_cable. jpg l “Granny with computer” image: – http: //www. boston. com/business/blog/filter/momtechsupport. jpg l “PCMCIA card” image: – http: //upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/b/b 1/ Pcmcia-type-ii-and-iii. jpg
Sources l All information from this presentation can be found in: Computer Systems Architecture – A Networking Approach Rob Williams. Chapter 11 l “Low and high skew” images: – http: //www. spectra-strip. amphenol. com l “Parallel printer cable” image: – http: //www. nuggetlab. com/comptia_files/equipment/ cable_Parallel%20 Cable%20 showing%2025 -pin%20 end. jpg l “SCSI ribbon cable” image: – http: //www. qvs. com/prodimages/SCU 160 -4 T_LR. jpg l “IDE ribbon cable” image: – http: //www. cable-house. com/images/cables/internal%20 cables/ ide_ata 133_ribbon_cable. jpg l “Granny with computer” image: – http: //www. boston. com/business/blog/filter/momtechsupport. jpg l “PCMCIA card” image: – http: //upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/b/b 1/ Pcmcia-type-ii-and-iii. jpg


