de35097c5509067d9b6138709d312501.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Parallel and Distributed Intelligent Systems: Multi-Agent Systems and e. Commerce Virendrakumar C. Bhavsar Professor and Director, Advanced Computational Research Laboratory Faculty of Computer Science, University of New Brunswick Fredericton, NB, Canada bhavsar@unb. ca

Outline l l l l Past Research Work Current Research Work Multi-Agent Systems ACORN and Extensions Multi-Agent Systems and E-Commerce Applications Areas for Collaboration Conclusion

Past Research Work n. B. Eng. (Electronics and Telecommunications) University of Poona, India Project: 4 -Bit Calculator n. M. Tech. (Electrical Eng. - specialization: Instrumentation, Control, and Computers) Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India Thesis: Special Purpose Computers for Military Applications with Emphasis on Digital Differential Analysers (DDAs) Ph. D. (Electrical Eng. ) Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India Parallel Algorithms for Monte Carlo Solutions of Linear Operator Problems
Past Research Work Parallel/Distributed Processing - Parallel Computer Architecture -Design and Analysis of Parallel Algorithms for Monte Carlo Methods, Pattern Recognition, Computer Graphics, Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Physics, and other applications -Real-time and Fault-Tolerant Systems for Process Control and On-Board Applications Artificial Neural Networks - with Dr. Ghorbani Learning Machines and Evolutionary Computation - with Dr. Ghorbani and Dr. Goldfarb

Past Research Work n Computer Graphics (with Prof. Gujar) - Modeling of 3 -D Solids Generation and Rendering of Interpolated Objects Algebraic and Geometric Fractals Parallelization of Computer Graphics Algorithms n Visualization (with Dr. Ware) PVMtrace: Visualization of Parallel and Distributed Programs


Past Research Work Multimedia for Education -Intelligent Tutoring Systems for Discrete Mathematics ( a NCE Tele. Learning Project) with Dr. Jane Fritz and Prof. Uday Gujar - Animated Computer Organization n. Multi-Lingual Systems and Transliteration n Web Portal for an NB company -Clustifier and Extractor -Intelligent User Profile Generator Supervision/co-supervision - 50 master's theses; - 4 doctoral theses - 5 post-doctoral fellows/research associates
Current Research Work Bioinformatics -Canadian Potato Genomics Project - databases, multi-agent systems, pattern recognition Parallel/Distributed Processing - C 3 -Grid development Design and analysis of parallel/distributed applications Dr. Aubanel (Research Associate)

Current Research Work Multi-Agent Systems - with Dr. Ghorbani and Dr. Marsh (NRC, Ottawa) - Intelligent agents - Keyphrase-based Information sharing between agents - Scalability and Performance Evaluation - Applications to e-commerce and bioinformatics - with Dr. Mironov Specification and verification of multi-agent systems

Advanced Computational Research Laboratory (ACRL) Dr. Virendra Bhavsar (Director) Dr. Eric Aubanel (Research Associate) Mr. Sean Seeley (Technical Support) ACRL Management Committee • AC 3 – Atlantic Canada High Performance Computing Consortium • C 3. ca Association Inc.

ARCL Advanced Computational Research Laboratory High Performance Computational Problem-Solving Environment and Visualization Environment Computational Experiments in multiple disciplines: Computer Science, Science and Engineering Located in the Information Technology Center (ITC)
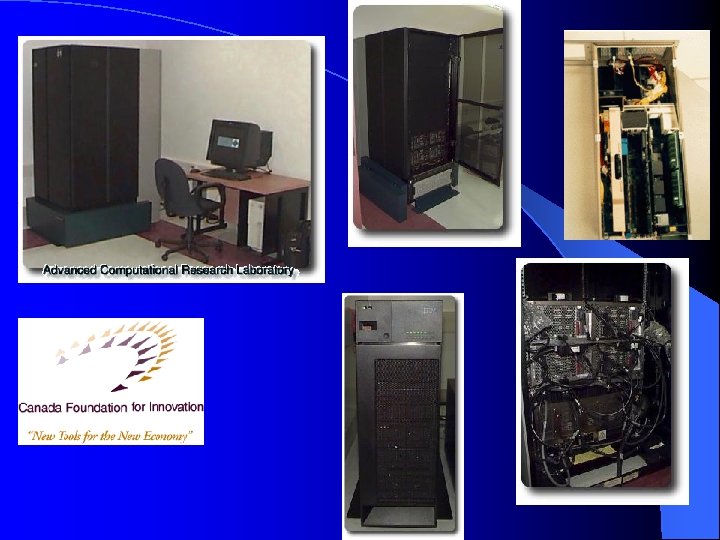


ACRL Facilities High Performance Multiprocessor (16 -processor) System - 24 GFLOPS (peak) performance - 72 GB internal disk storage - 109. 2 GB external disk storage Software for Computational Studies and Visualization Parallel Programming Tools E-Commerce Software, including datamining software Memorandum of Understanding between IBM and UNB (in process)

ACORN (Agent-based Community Oriented Retrieval Network) Architecture Steve Marsh, Institute for Information Technology, NRC Virendra C. Bhavsar, Ali A. Ghorbani, UNB - Keyphrase-based Information Sharing between Agents Hui Yu – MCS Thesis (UNB) MATA’ 2000 Paper - Performance Evaluation using Multiple Autonomous Virtual Users HPCS’ 2000 paper

ACORN Agent-Based Community-Oriented {Retrieval | Routing} Network l ACORN is a multi-agent based system for information diffusion and (limited) search in networks l In ACORN, all pieces of information are represented by semi-autonomous agents. . . - searches; documents; images, etc. l Intended to allow human users to collaborate closely

Degrees of Separation In the 1960’s, Stanley Milgram showed that everyone in the US was personally removed from everyone else by at most six degrees of separation l In communities, such as a research community, this is clear to all members: l – if you want to know something, you ask someone. – If they don’t know, they may know someone else to ask. . . – and so on l This also works when you have something to tell people. . . – if you want someone relevant to know, you tell people you know will be interested. . . – and they forward the information to people they know will be interested. . – and so on

Relation to Other Work l Search Engines – Alta Vista, Excite, Yahoo, Info. Seek, Lycos, etc. . . – We don’t aim to search the Web – If the user has to search, it’s because the information diffusion is l l l not fast enough not accurate enough Recommender Systems – Firefly (Maes), Fab (Balabanovic) – Content-based or Collaborative – ACORN’s agents are a radical new approach, and a mixture of both. . . – ACORN is distributed – ACORN levers direct human-human contact knowledge l Matchmakers

Relation to Other Work (cont. ) l Web Page Watchers and Push Technologies – Tierra, Marimba, Channels – ACORN is a means of pushing new data, reducing the need to watch for changes l Filtering Systems – The filtering in ACORN is implicit in what is recommended by humans l ‘Knowbots’ – Softbots (Washington, Etzioni, Weld), Nobots (Stanford, Shoham) – mobile agents for internet search – ACORN provides diffusion also

ACORN l Uses communication between agents representing pieces of information, ACORN automates some of the processes – Anyone can create agents, and direct them to parties they know will be interested – An Agent carries user profile – Agents can share information

The ACORN Mobile Agent l represents a unit of information l structure Mobile Agent Name: (Unique ID, timestamp) Owner Address Dublin Core Metadata Visited Recommended Known Lists of users (humans) and/or cafés the agent has visited, is due to visit, or ‘knows of’

The Dublin Core is a Metadata element set, first developed at a workshop in Dublin, Ohio l Includes author, title, date l Also includes l – Keywords; Publisher; type (e. g. home page, novel, poem) – format (of data) The Dublin Core presents a powerful structured medium for distributing human (and machine) readable metadata – It also presents an interesting query formulation tool l The DC home page can be found at: http: //purl. org/metadata/dublin_core

Agent Lifecycle l A mobile agent in ACORN (one which represents information) undergoes several stages in its lifecycle – Creation – Distribution Visiting a user l Mingling with other agents l Going to next site – Return l

The Café - Agent Recommendations User recommendations are not the only way an agent can expand its list of people to visit l Each site can have (between zero and many) cafés l A café is simply a meeting place for agents l Cafés can be generic or have specific topics (agents can be filtered before entering) l

Café l At set intervals, agents present are compared, and relevant information exchanged – Keyphrase-based Information Sharing – Agents reside at cafés for set lengths of time (currently we have a default, but intend to make the length of time owner selectable) l The café represents a unique method of automating community based information sharing
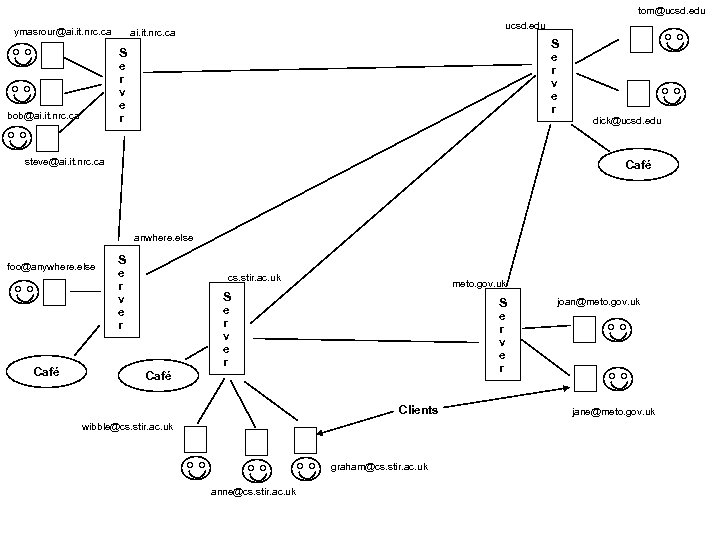
tom@ucsd. edu ymasrour@ai. it. nrc. ca ucsd. edu ai. it. nrc. ca S e r v e r bob@ai. it. nrc. ca steve@ai. it. nrc. ca dick@ucsd. edu Café anwhere. else foo@anywhere. else Café S e r v e r cs. stir. ac. uk meto. gov. uk S e r v e r Café Clients wibble@cs. stir. ac. uk graham@cs. stir. ac. uk anne@cs. stir. ac. uk joan@meto. gov. uk jane@meto. gov. uk
Testing and Deployment l A working implementation of ACORN in Sun’s Java language l Stress testing the architecture using large numbers of real users - problems l Multiple artificial users on a simulated network
Multiple Autonomous Virtual Users l Test-bed: Several Autonomous Servers, each serving autonomous virtual users Virtual User - capable of creating agents - picks up a topic from a client core’s interest - migrates to other servers - potential destinations l

Adaptation of ACORN: ~ >100 Java classes l Adaptation – Removal of user interaction classes – Removal of client behavior clases – Removal of other extraneous classes – Simulation of multiple client-server architecture: run more than one server on a single machine – Possibility of using multiple processor machines – Addition of a Site. Controller Class l
Adaptation of ACORN (cont. ) l Site. Controller Class – handles all communication between servers on a single machine – resolves agent migration requests – handles communication between different machines l Streamer Class – provides transport of agents across IP l Benefits – Removal of the need for continuous user interaction – Batch mode runs – Only ~30 Java classes

Experiments l Virtual Users Porting of ACORN to many machine architectures SGI Onyx. Power. PC, and PC l O(n 2) agent interactions in a Café, n - number of agents l

Future Research Work Bioinformatics -Canadian Potato Genomics Project Biological databases, multi-agent systems, pattern recognition § Multi-Agent Systems - ACORN and B 2 B – B 2 C extensions

Multi-Agent Systems B 2 B-B 2 C Extensions l ACORN and B 2 B – B 2 C extensions - User-driven personalisation - personalised and personalisable automatic delivery and search for information directed advertisements based on user profiles and preferences - directed programming (both these examples based on interactive TV facilities such as those offered by i. Magic. TV and Microsoft interactive TV). - agent learning - data mining over large distributed networks and databases,

Multi-Agent Systems B 2 B-B 2 C Extensions l ACORN and B 2 B – B 2 C extensions - the management of firms and user reputation (as in e. Bay's reputation manager, amongst others) finally leading into proposed standards and legal bases necessary for e. Commerce l Perceived and actual user privacy l Automated and manually-driven user profile generation and update

Multi-Agent Systems B 2 B-B 2 C Extensions Adaptation to Multi-processor machines at a single as well as multiple sites to exploit CA*NETIII l Usability Studies l XML objects instead of Java objects l

Trust In Information Systems - e. Commerce Formalization of Trust: Steve Marsh (early 1990 s) l Prototype version of an adaptable web site for e. Commerce transactions l Trust in information systems: - creation and sustainability - user interface technologies l - user perceptions, behaviors, etc. and how to l influence and use such user behaviors. l - automatic user profile generation, its use in agentbased interfaces such as the trust reasoning adaptive web sites l

Trust In Information Systems - e. Commerce Adaptive technologies in general for e. Commerce, education, entertainment l Personality in the user interface and how it can affect user trust and perceived satisfaction l
Multi-Agent Systems for Distributed Databases l Problem: Businesses are faced with continuous updating of their large and distributed databases connected on intranets and the Internet l Multi-Agent Systems - Very naturally satisfiy many requirements in such an environment - Provide a very flexible and open architecture - Scalability analysis with multiprocessor servers

Conclusion l l l l Parallel and Distributed Intelligent Systems Multi-Agent Systems and ACORN Applications in e-Commerce B 2 B and B 2 C Extensions Trust in Information Systems Multi-Agent Systems for Distributed Databases NRC Collaborations in the above and other areas (Software Engineering, Intelligent Systems, etc. )
de35097c5509067d9b6138709d312501.ppt