f4da03dc848cc09099f2b1690e3e6f24.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Parabola Unit Intro Algebra I Chapter 9
Introduction n Quadratic Functions Non-linear u y = ax 2 + bx + c u Physics Scenarios u n Graphs Symmetrical u Real-life applications u

Topics of Discussion n What parabolas look like Architecture u Sports u Natural u Engineering u n Algebraic investigation Graphs u Vocabulary u

Parabolas in Architecture n Parabolas can be found in architecture They are added for decorative purposes u They can also play a part in the support system for buildings u n Here are some examples

This one you know

Chicago Picasso Downtown Chicago
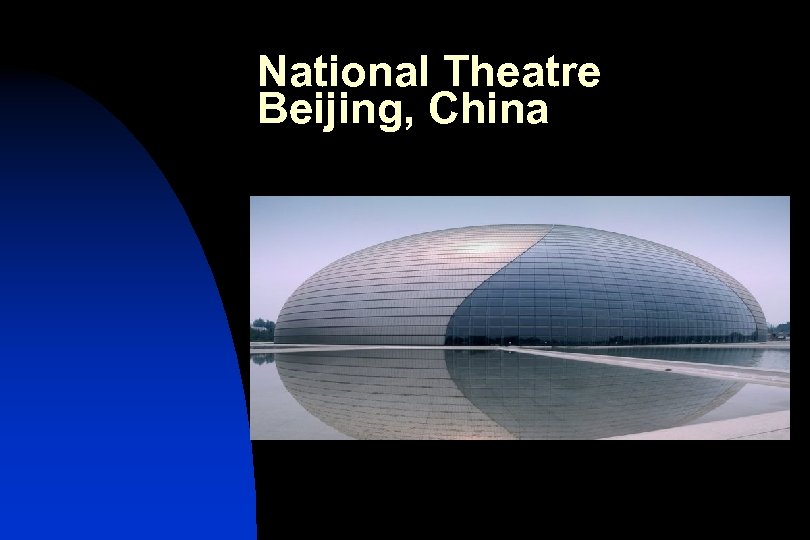
National Theatre Beijing, China

Athens Olympic Stadium Athens, Greece

Qwest Field Seattle, Washington

Qwest Field, another view.

Sculpture House Evergreen, Colorado

Gateway Arch St. Louis, Missouri

Tenerife Concert Hall Canary Islands, Spain

Parabolas in Sports n n Objects that are thrown in air naturally follow a parabolic curve Here are some examples

Falling Pong Ball

Ping Pong ball rolling down a tube
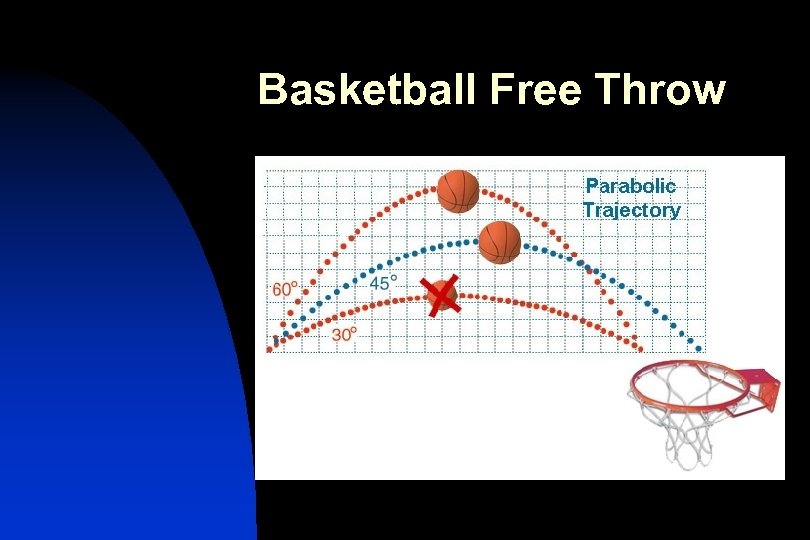
Basketball Free Throw

A Golf Shot

Another Golf Shot

Hammer Throw

Motorcycle Racing

Roller coasters

Parabolas in Nature n Parabolas occur naturally in the world n Here are some examples

Lamp Light bulbs

Rock Formations

Spinning Beaker

Rotates, and water reacts

More Water

Iceberg Arch

Another one

Rock Arch

Snow Thrower
Engineering n Parabolas are used in structures for support They are found a lot in bridges n Here a few examples n

Bridges…. .


Golden Gate Bridge San Francisco, California

Mackinac Bridge Mackinac, Michigan


Ferrari 550 Maranello
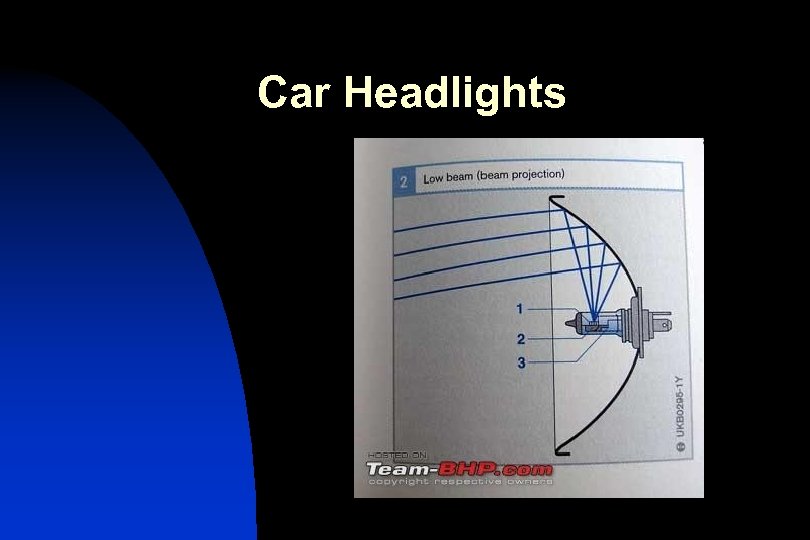
Car Headlights

Satellite Dishes….

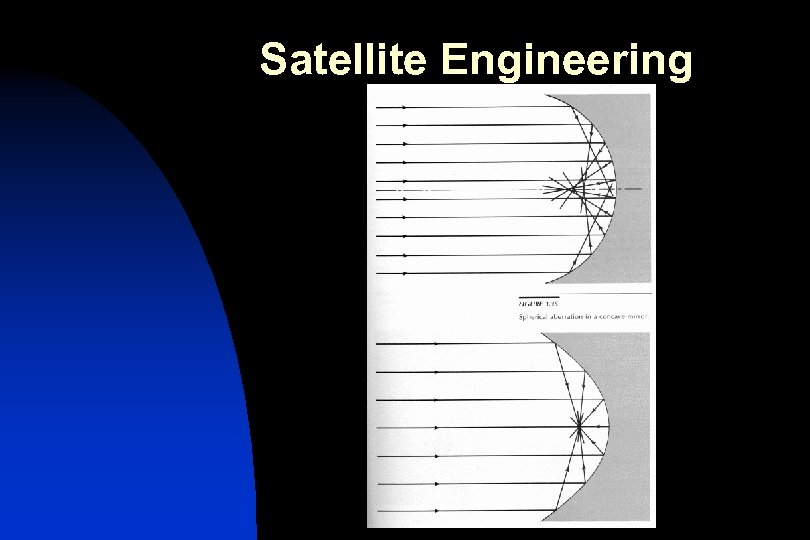
Satellite Engineering

Algebraic Side of Parabolas n n All parabolas are symmetrical around its axis of symmetry Each parabola has either a maximum point or a minimum point called the vertex
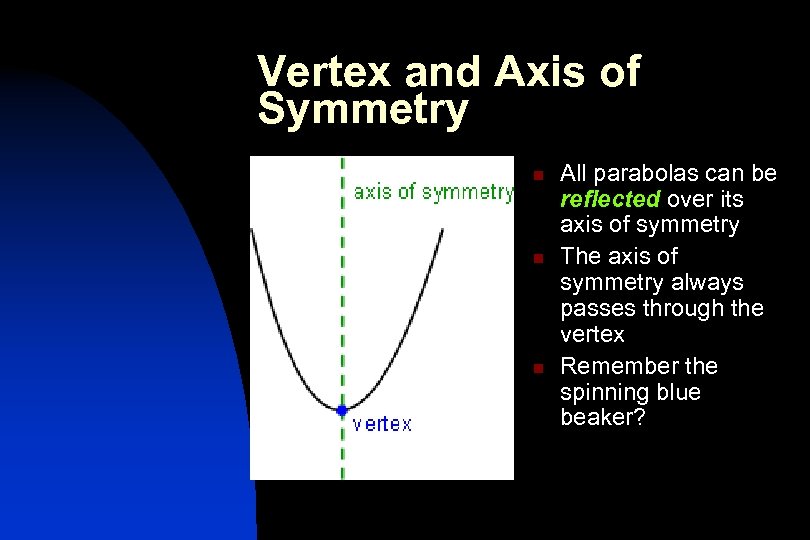
Vertex and Axis of Symmetry n n n All parabolas can be reflected over its axis of symmetry The axis of symmetry always passes through the vertex Remember the spinning blue beaker?
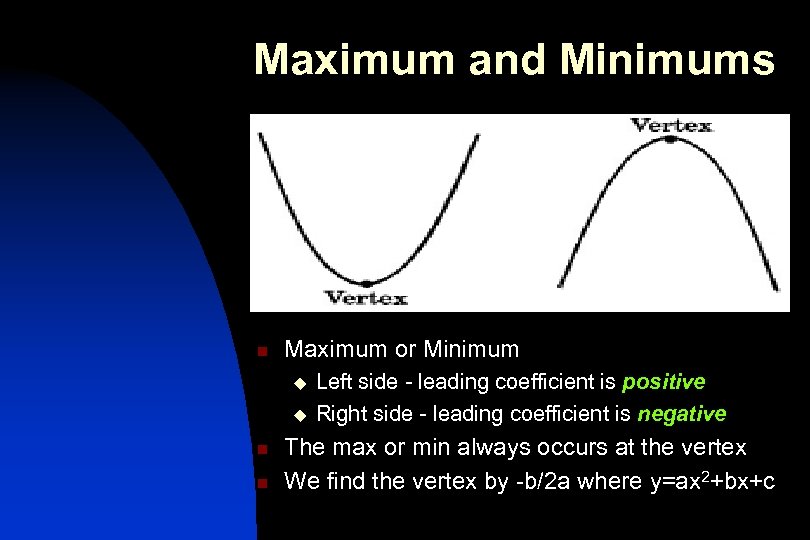
Maximum and Minimums n Maximum or Minimum u u n n Left side - leading coefficient is positive Right side - leading coefficient is negative The max or min always occurs at the vertex We find the vertex by -b/2 a where y=ax 2+bx+c
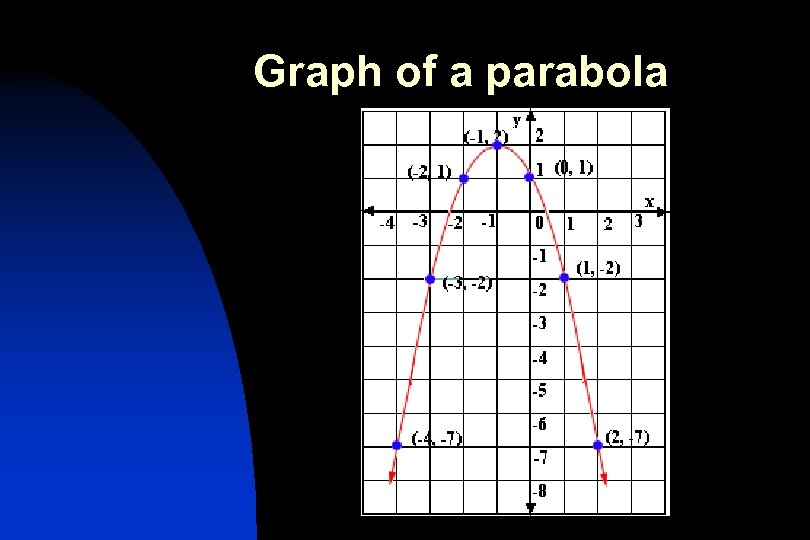
Graph of a parabola

Next Steps n n n We will find the vertex and axis of symmetry of parabolas We will determine if the parabola opens up or down based on its equation We will find the roots or zeros of a quadratic equation
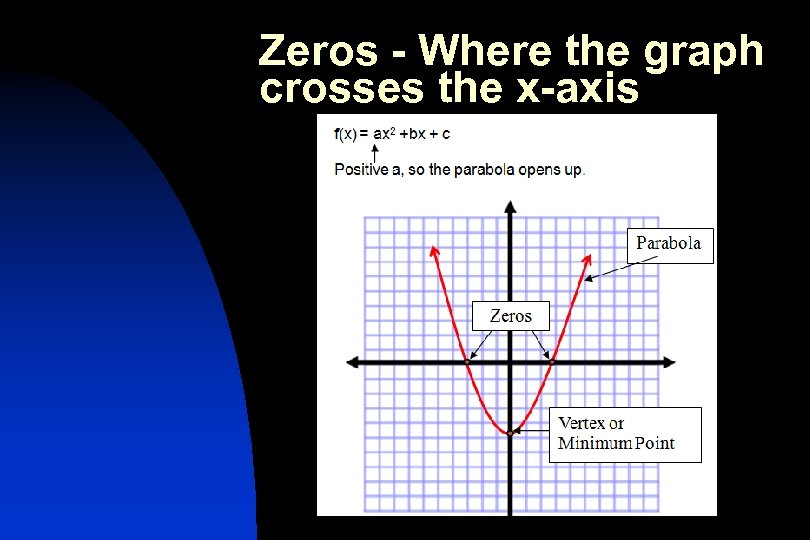
Zeros - Where the graph crosses the x-axis
f4da03dc848cc09099f2b1690e3e6f24.ppt