5f028b250ced0cffb078e54049400ab2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Paperless Trade (e. TRADE) in India R K Arora Addl. General Manager, e. TRADE Department of Commerce rkarora@nic. in 1
Paperless Trade (e. TRADE) in India R K Arora Addl. General Manager, e. TRADE Department of Commerce rkarora@nic. in 1
 Outline 1. National e. Governance Plan 2. Need for paperless trade 3. e. TRADE - The Project - Objectives Stakeholders Services Covered Trade Process Flow Current Scenario 4. Status of the Project 5. Achievements 2
Outline 1. National e. Governance Plan 2. Need for paperless trade 3. e. TRADE - The Project - Objectives Stakeholders Services Covered Trade Process Flow Current Scenario 4. Status of the Project 5. Achievements 2
 National e. Governance Plan (Ne. GP) Ne. GP, takes a holistic view of e-Governance initiatives across the country, integrating them into a collective vision, a shared cause. The Government approved the National e-Governance Plan (Ne. GP), comprising of 27 Mission Mode Projects on May 18 2006. In the year 2011, 4 projects-Health, Education, PDS and Posts were introduced to make the list to 31. Central MMPs State MMPs Integrated MMPs • Banking • Central Excise & Customs • Income Tax (IT) • Insurance • MCA 21 • Passport • Immigration, Visa and Foreigners Registration & Tracking • Pension • e-Office • Posts • UID • Agriculture • Commercial Taxes • e−District • Employment Exchange • Land Records (NLRMP) • Municipalities • e-Panchayats • Police(CCTNS) • Road Transport • Treasuries Computerization • PDS • Education • Health • CSC • e-Biz • e-Courts • e-Procurement • EDI For e. Trade • National egovernance Service Delivery Gateway • India Portal 3
National e. Governance Plan (Ne. GP) Ne. GP, takes a holistic view of e-Governance initiatives across the country, integrating them into a collective vision, a shared cause. The Government approved the National e-Governance Plan (Ne. GP), comprising of 27 Mission Mode Projects on May 18 2006. In the year 2011, 4 projects-Health, Education, PDS and Posts were introduced to make the list to 31. Central MMPs State MMPs Integrated MMPs • Banking • Central Excise & Customs • Income Tax (IT) • Insurance • MCA 21 • Passport • Immigration, Visa and Foreigners Registration & Tracking • Pension • e-Office • Posts • UID • Agriculture • Commercial Taxes • e−District • Employment Exchange • Land Records (NLRMP) • Municipalities • e-Panchayats • Police(CCTNS) • Road Transport • Treasuries Computerization • PDS • Education • Health • CSC • e-Biz • e-Courts • e-Procurement • EDI For e. Trade • National egovernance Service Delivery Gateway • India Portal 3
 Need for e. Trade Substantial progress on policy front. Focus required on streamlining and standardisation of procedures. Large number of agencies involved in clearances for international trade. Multiple entry/exit points and complex management issues Cumbersome procedures Enormous documentation Need for extensive process re-engineering Different stages of automation Different priorities of organisations Non participation in community systems Need for adoption of standards 4
Need for e. Trade Substantial progress on policy front. Focus required on streamlining and standardisation of procedures. Large number of agencies involved in clearances for international trade. Multiple entry/exit points and complex management issues Cumbersome procedures Enormous documentation Need for extensive process re-engineering Different stages of automation Different priorities of organisations Non participation in community systems Need for adoption of standards 4
 e. TRADE - The Project Objectives of the Project: Efficient, transparent, secure delivery of services by Trade regulatory/facilitating agencies in 24 X 7 environment. Simplifying procedures and transaction cost and time. reducing the Introducing international standards and best practices. 5
e. TRADE - The Project Objectives of the Project: Efficient, transparent, secure delivery of services by Trade regulatory/facilitating agencies in 24 X 7 environment. Simplifying procedures and transaction cost and time. reducing the Introducing international standards and best practices. 5
 Stakeholders: Customs Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) Sea Ports Airports Container Corporation of India(CONCOR) / Central Warehousing Corporation (CWC) Banks Importers/Exporters Agents (Customs House Agents/ Freight Forwarders/ Air Cargo Agents etc. ) Airlines/Shipping lines Services Covered: E-delivery of services / clearances by community partners like Customs and Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports and ICD/CFSs, to exporter, importer, agents E-filing of export/import documents by exporter, importer, agents etc. to Customs and Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports and ICD/CFSs. Electronic exchange of documents between community partners i. e. Customs and Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports, ICD/CFSs. e-Payment by exporter, importer, agents for - Custom duties; - DGFT’s license fee and - Charges (handling/freight, etc) of Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports, ICD/CFSs. 6
Stakeholders: Customs Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) Sea Ports Airports Container Corporation of India(CONCOR) / Central Warehousing Corporation (CWC) Banks Importers/Exporters Agents (Customs House Agents/ Freight Forwarders/ Air Cargo Agents etc. ) Airlines/Shipping lines Services Covered: E-delivery of services / clearances by community partners like Customs and Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports and ICD/CFSs, to exporter, importer, agents E-filing of export/import documents by exporter, importer, agents etc. to Customs and Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports and ICD/CFSs. Electronic exchange of documents between community partners i. e. Customs and Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports, ICD/CFSs. e-Payment by exporter, importer, agents for - Custom duties; - DGFT’s license fee and - Charges (handling/freight, etc) of Custodians at Sea. Ports, Airports, ICD/CFSs. 6
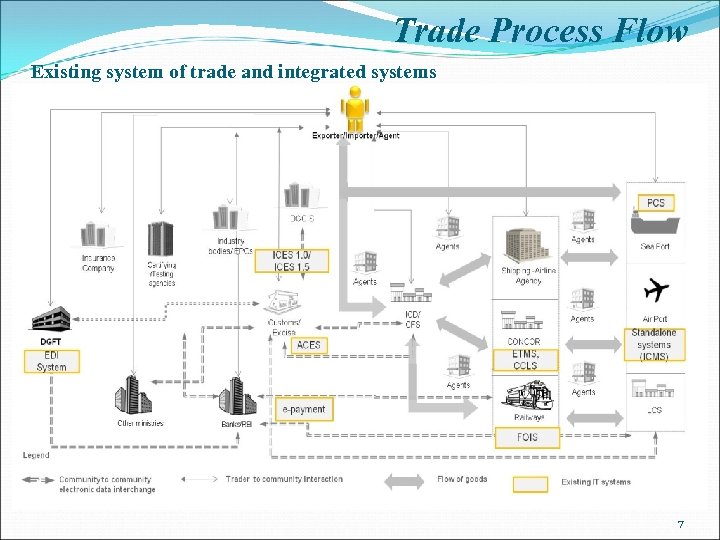 Trade Process Flow Existing system of trade and integrated systems 7
Trade Process Flow Existing system of trade and integrated systems 7
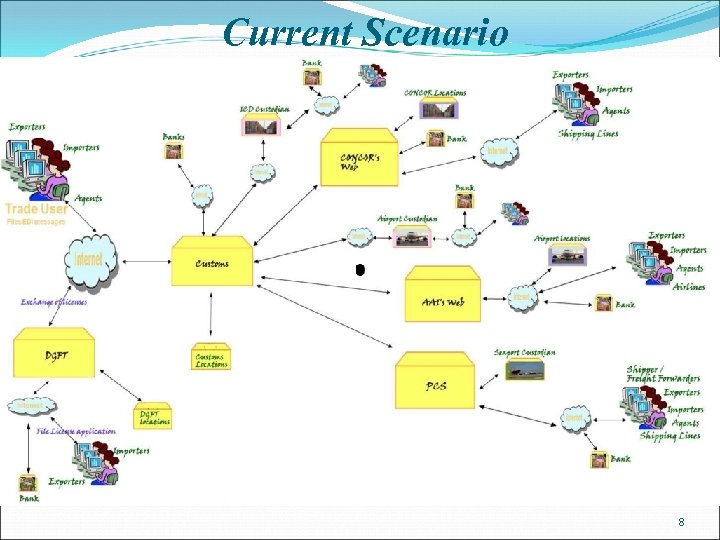 Current Scenario 8
Current Scenario 8
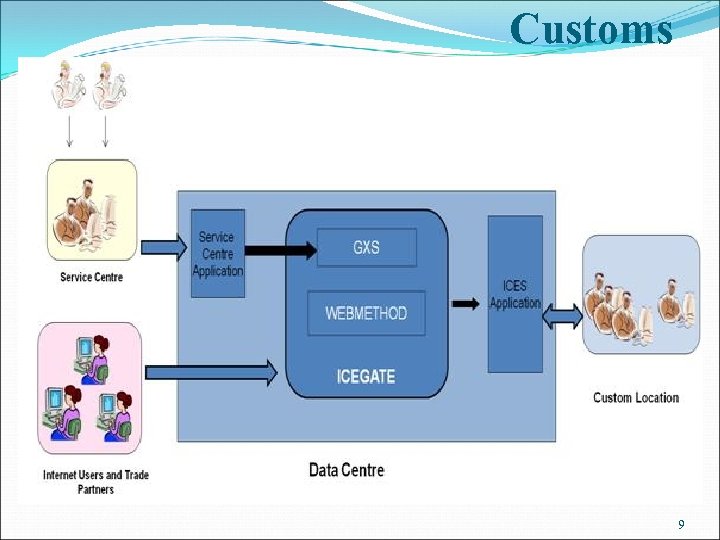 Customs 9
Customs 9
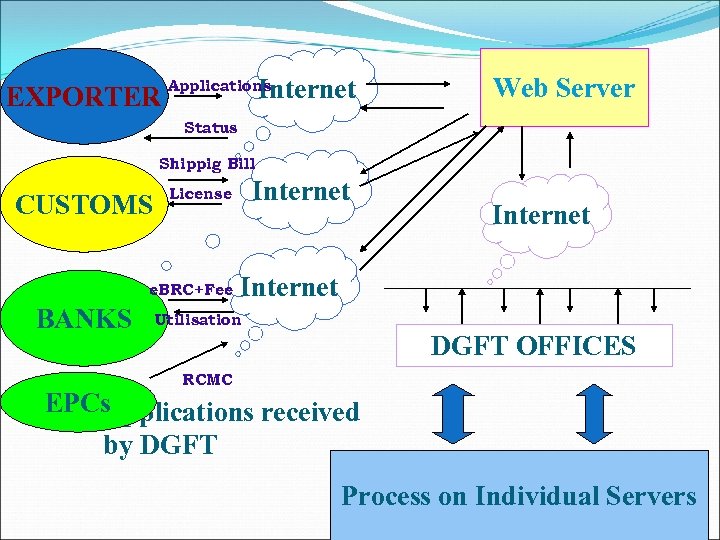 EXPORTER Internet Applications Web Server Status Shippig Bill CUSTOMS e. BRC+Fee BANKS Internet License Internet Utilisation DGFT OFFICES RCMC EPCs Applications received by DGFT Process on Individual Servers
EXPORTER Internet Applications Web Server Status Shippig Bill CUSTOMS e. BRC+Fee BANKS Internet License Internet Utilisation DGFT OFFICES RCMC EPCs Applications received by DGFT Process on Individual Servers
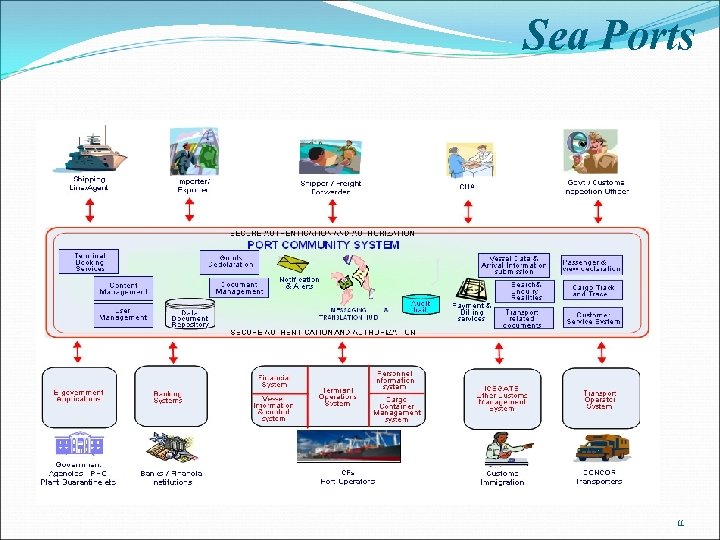 Sea Ports 11
Sea Ports 11
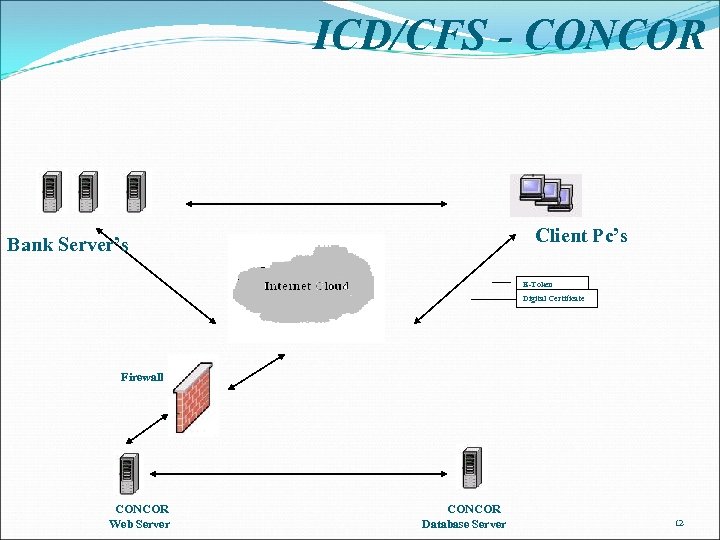 ICD/CFS - CONCOR Client Pc’s Bank Server’s E-Token Digital Certificate Firewall CONCOR Web Server CONCOR Database Server 12
ICD/CFS - CONCOR Client Pc’s Bank Server’s E-Token Digital Certificate Firewall CONCOR Web Server CONCOR Database Server 12
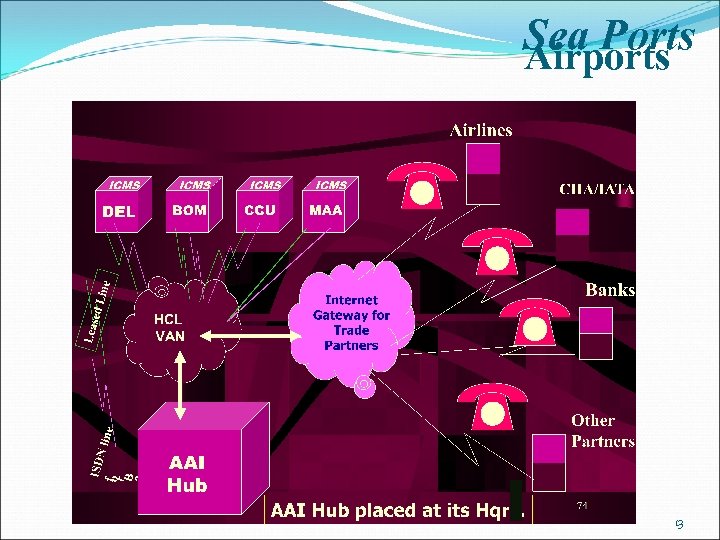 Sea Ports Airports 13
Sea Ports Airports 13
 e. TRADE MMP : Status DGFT · 99% Licenses issued through the web-based system using digital signatures/e. Payment through all 38 offices. · Digitally signed electronic message exchange with Customs for shipping bills and authorisations for schemes like DEPB, DES and EPCG. · Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate (e. BRC) made mandatory. Around 10 millions e. BRCs of approx. 500 billion USD uploaded till date, enhancing the productivity mainly of exporters, banks and DGFT, and saving a large amount of paper, time and stress. e-BRC won ‘e. ASIA Award 2013’. Customs · ICES 1. 5 (Customs Central Server System) is live at 120 locations. Automation covers 90% of India’s international trade 14
e. TRADE MMP : Status DGFT · 99% Licenses issued through the web-based system using digital signatures/e. Payment through all 38 offices. · Digitally signed electronic message exchange with Customs for shipping bills and authorisations for schemes like DEPB, DES and EPCG. · Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate (e. BRC) made mandatory. Around 10 millions e. BRCs of approx. 500 billion USD uploaded till date, enhancing the productivity mainly of exporters, banks and DGFT, and saving a large amount of paper, time and stress. e-BRC won ‘e. ASIA Award 2013’. Customs · ICES 1. 5 (Customs Central Server System) is live at 120 locations. Automation covers 90% of India’s international trade 14
 e. TRADE MMP : Status (Contd. ) · Electronic interface for critical messages with DGFT, Ports, Airports, Seaports, CONCOR. § Major international Airports, § Ports community system (PCS), and § CONCOR · e. Payment of duties mandatory for payments above Rs. 1 Lakh · Risk Management System(RMS) started at 89 locations for imports and exports · EDI clearance of Import Cargo started at Precious Cargo Customs Clearance Centre, Mumbai Airports · Web based Community partners system and Bar-code integration have been started at 6 airports out of 12 major airports. Seaports · The Centralized Port Community System (PCS), a single window interface for seaports community, is operational for 19 seaports including 15 all major and 6 non-major seaports.
e. TRADE MMP : Status (Contd. ) · Electronic interface for critical messages with DGFT, Ports, Airports, Seaports, CONCOR. § Major international Airports, § Ports community system (PCS), and § CONCOR · e. Payment of duties mandatory for payments above Rs. 1 Lakh · Risk Management System(RMS) started at 89 locations for imports and exports · EDI clearance of Import Cargo started at Precious Cargo Customs Clearance Centre, Mumbai Airports · Web based Community partners system and Bar-code integration have been started at 6 airports out of 12 major airports. Seaports · The Centralized Port Community System (PCS), a single window interface for seaports community, is operational for 19 seaports including 15 all major and 6 non-major seaports.
 e. TRADE MMP : Status (Contd. ) · Integration of 4 more non-major seaports of Gujarat Maritime Board is under integration and other seaports are also being pursued. · Automation at major seaports accounts for 75% of trade by sea route. ICDs/CFSs · CONCOR implemented a centralized web-based community partner interface system for its 38 EXIM locations. · Central Warehouse Corporation (CWC) has started web-based community partner interface at 9 out of 30 locations. e. Payments facilitation has been introduced by Customs, DGFT, Seaports and major airports. 16
e. TRADE MMP : Status (Contd. ) · Integration of 4 more non-major seaports of Gujarat Maritime Board is under integration and other seaports are also being pursued. · Automation at major seaports accounts for 75% of trade by sea route. ICDs/CFSs · CONCOR implemented a centralized web-based community partner interface system for its 38 EXIM locations. · Central Warehouse Corporation (CWC) has started web-based community partner interface at 9 out of 30 locations. e. Payments facilitation has been introduced by Customs, DGFT, Seaports and major airports. 16
 Achievements · Uniformity and simplification of procedures · Re-engineered inter agency interfaces · Digital signature integration · e. Payment integration § Significant reduction in transaction time of services like §License application (30 days to 1 day), §Flight manifest at airports (4 Hrs to 15 minutes), §Vessel profile submission and approval at seaports (48 Hrs to 1 -2 hrs) etc. · Reduction and early detection of frauds 17
Achievements · Uniformity and simplification of procedures · Re-engineered inter agency interfaces · Digital signature integration · e. Payment integration § Significant reduction in transaction time of services like §License application (30 days to 1 day), §Flight manifest at airports (4 Hrs to 15 minutes), §Vessel profile submission and approval at seaports (48 Hrs to 1 -2 hrs) etc. · Reduction and early detection of frauds 17
 THANK YOU 18
THANK YOU 18
 Custom - DGFT message exchange (earlier scenario) 19
Custom - DGFT message exchange (earlier scenario) 19
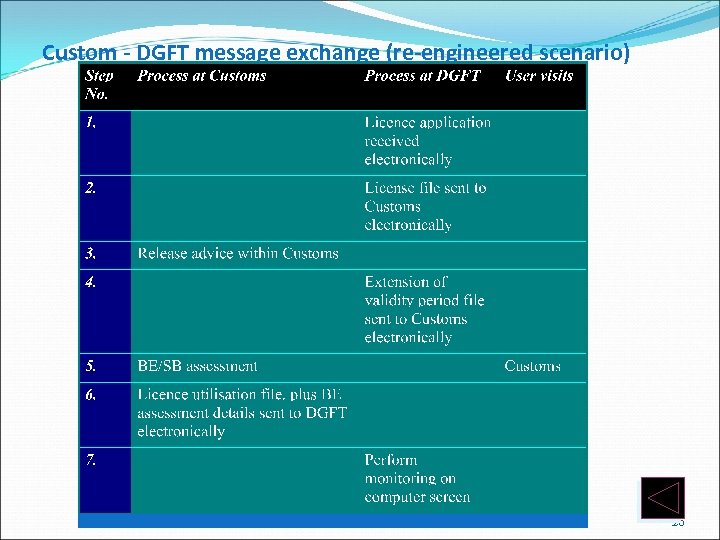 Custom - DGFT message exchange (re-engineered scenario) 20
Custom - DGFT message exchange (re-engineered scenario) 20


