fb43dd8310a33b17302dcaab0eab2ee3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66

Paleolithic Era

But First! A Song!

Chinese Dynasties Song (Sung to Frere Jacques)

Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han Sui, Tang, Song

Yuan, Ming, Qing, Republic Mao Zedong, Mao Zedong

Zhou = joe Sui = sway x = sh (Xiaoping) q = ch (Qin & Qing = Chin & Ching)

• Time: • B. C. E = Before (the) Common Era • C. E. = Common Era • Prehistory (Prehistoric era) • Paleolithic – “Old Stone Age” • Paleo – “old”/Lithic – “stone”

Paleolithic Society • Hunting & Gathering – Social Class? • Men = Hunters • Women & Children = gatherers – Usually accounted for more calories • Nomadic Cycles – wandering or a plan?

Paleolithic Groups • Non-Nomadic • Natufian – 13, 500 B. C. E – Modern day Israel and Lebanon • Jomon – 10, 000 to 300 B. C. E. – Modern central Japan • Chinook – 3, 000 B. C. E. – Pacific Northwest – Washington, Oregon, British Columbia
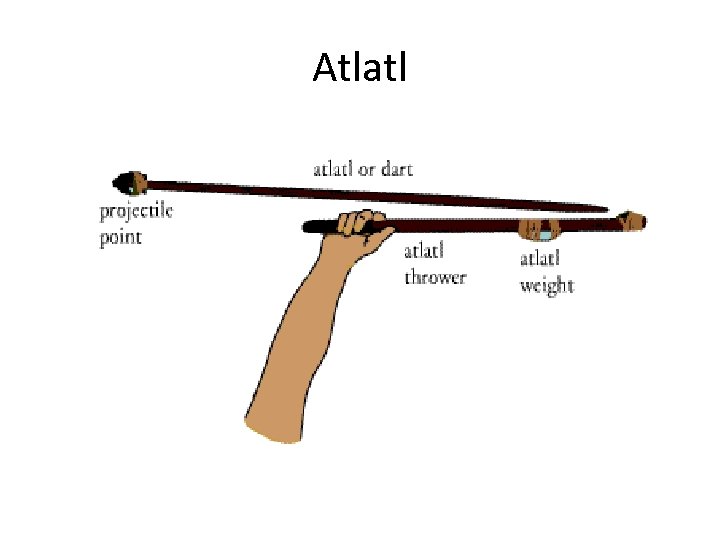
Atlatl

Cave Paintings • Lascaux in France • Altamira in Spain


Venus Figurines • Fertility • “Meaning of Life” questions

Your Task • What are the characteristics of the Paleolithic Age? The Neolithic Age? • What is the Agricultural Revolution (Transition)? • What were the major causes/reasons for the end of the Paleolithic and the beginning of the Neolithic?

Early Civilizations

Bronze Age Early Metallurgy: Copper + tin = Bronze First use? Mesopotamia circa 40003000 BCE By 1500 -1000 BCE Mesopotamia had developed iron weapons/tools Iron diffused throughout SW Asia Why?

Mesopotamia Tigris & Euphrates Tech: Irrigation -> increased food supply -> population increase City-State: Sumer (5000 BCE) “First” Cities: Ur and Babylon Historic breakthrough: First writing system – Sumerian cuneiform

Polytheistic Ziggurats Sumer was largest city-state – organized to maintain peace and stability Large public-works projects: Canals, bridges, & irrigation
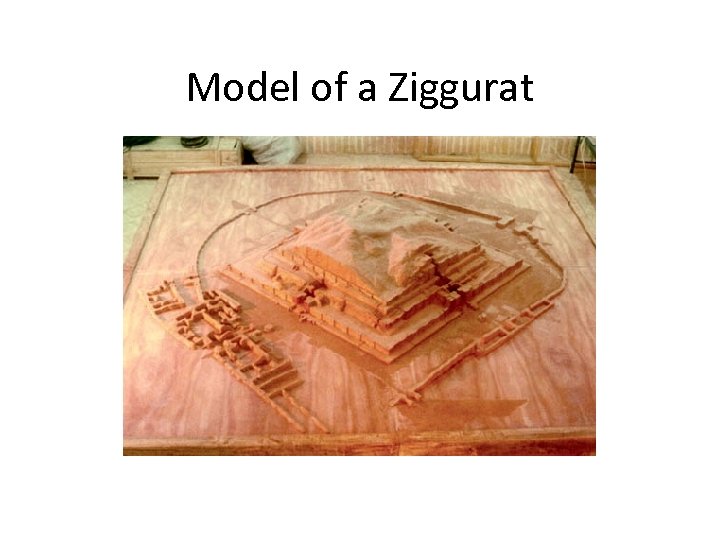
Model of a Ziggurat

Ziggurat in Iraq

Sumerian Cuneiform

Cuneiform Tablet



Mohenjo-Daro

Mohenjo-Daro Dancing Girl


Sanskrit


Egyptian Hieroglyphs

Rosetta Stone

Temple of Karnak

Aten Sun Disc

Terracota Soldier
Prehistoric Sites of Anatolia

Olmec Head Statues

Lion Gate of Mycenae
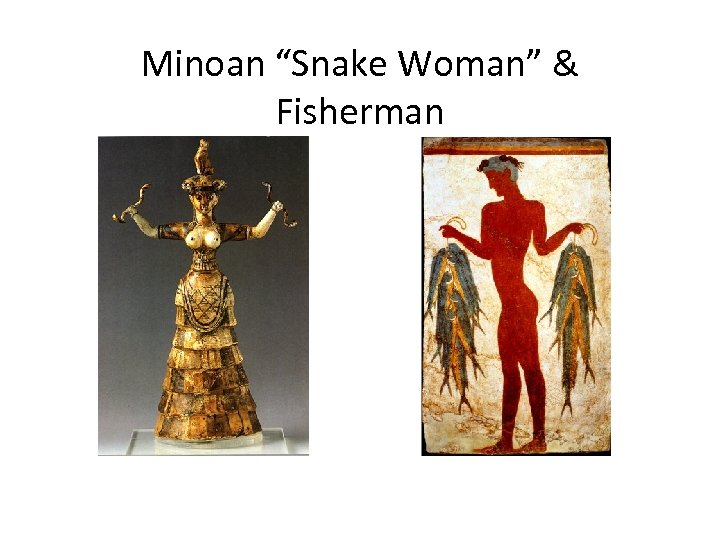


Minoan “Snake Woman” & Fisherman

Minoan Vase Art
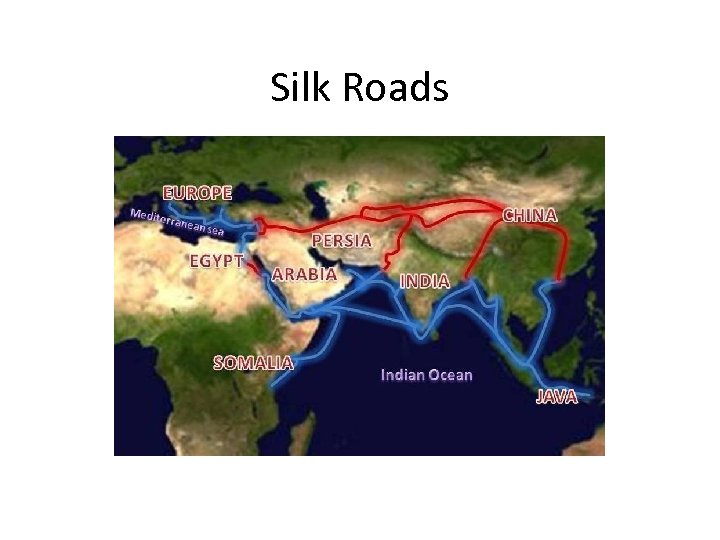
Silk Roads

The Assyrian Question

• Why have historians called the Assyrian Empire of the first millennium B. C. E. the first true empire? • How were the Assyrians able to conquer and control such a large and diverse empire?
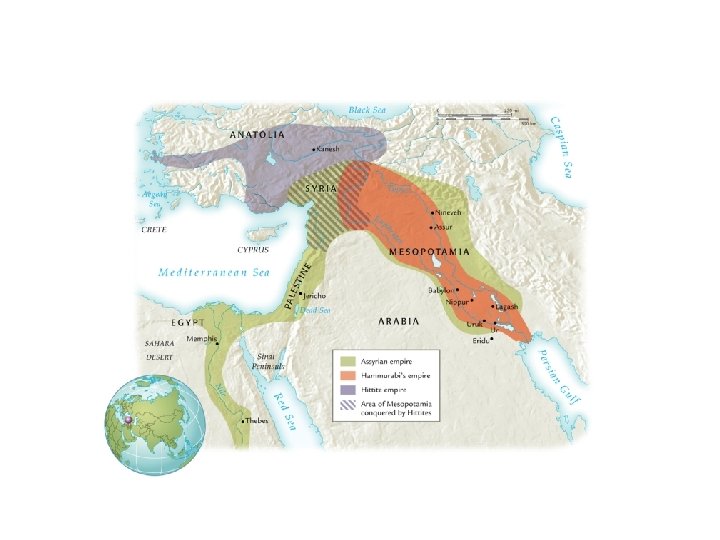

First “True” Empire • • • Diverse population Large land area Expansion - Self-defense - Trade - Resources

• Imperial Core & Periphery • Emergence of Capitals

How? • Military & Technology • Land distribution (Land grants, Theme System, “Fight for land”) • Diverse military • Technology – IRON!

• Bureaucracy • Terror • Mass Deportations

PERSIAN EGYPT (example) • • (P) – Politics (E) – Economics (R) – Religion (S) – Society (I) – Intellect (A) – Arts & Architecture (NG) – Near Geography Got it? Follow along!

Egypt – 1 of 4 River Valley civilizations Based on the Nile (NG) Flooding (NG) Small towns – occasional Mas projects (pyramids) (A) • Three Kingdoms – Old, Middle, New (P) • New Kingdom – height in 1400 BCE (P) • Nile to lower Turkey (P, NG) • •

Old Kingdom – Menes I (King Menes) (P) Memphis (P, NG) Unified Egypt = wealthy Egypt (P, E) Leader = Pharaoh – divine right/son of the gods (P, R) • Public works – pyramids (tombs), obelisks, irrigation & canals (R, A) • •

• Writing – hieroglyphs (spiritual writings) (R, I, A) • Led to: • Religious writing, record keeping, and early science: • Astronomy = calendar (I) • Trade (E)

• Akhenaten (Pharaoh Amenhotep IV – 13531335 BCE) (P, R) • Monotheism – Aten (previously poly – Amon. Re) • Capital city – Akhetaten (“Horizons of Aten”) • Monotheism ended with his death (R)

• Trade goods: timber, stone (marble), gold and spices (E) • Religion – polytheistic (R) • Afterlife (R) • Mummification (R) • Pyramids = tombs (R, A)

• Women (S) • Enjoyed high status, buy, sell, & inherit property. (S) • Give or “will” property (S) • Divorce for special circumstances (S) • Main role: birth (S) • Boys more educated than girls (S) • Queen Hatshepsut – expanded trade (P, E, S)
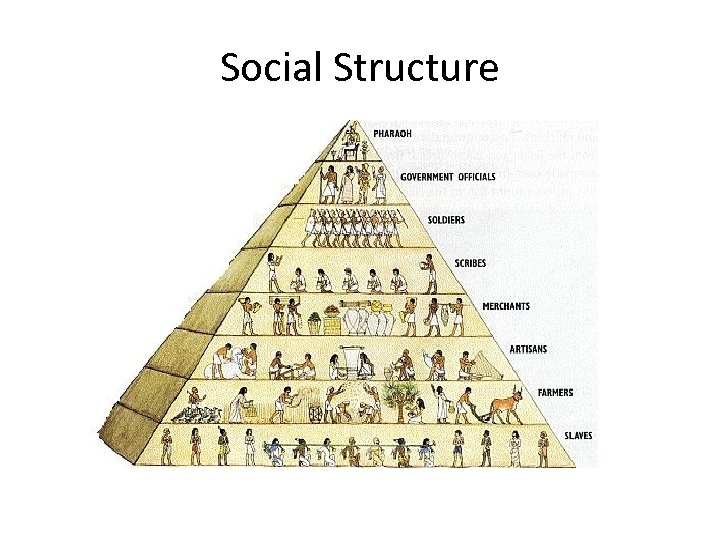
Social Structure

• • Lowest – peasants & slaves (S) Worked fields and projects (S, E, A) Half of labor to pharaoh (E, S) Slavery – heredity (S)

• Nubian Influence - agriculture • Nubia south of Egypt (modern day Sudan) (NG) • Heavy reliance on agriculture (E) • - Irrigation (I) • More food = more population (E) • Canals, dykes, crop rotations (E, I)

• • Nubia/Egypt relations – trade (E) Gold, ivory, & Precious stones (S, E) Tensions between (P, E) Nubia creates kingdom of Kush (capital of Kerma) (P, E)

Fall & Decline • • 1100 BCE – decline – why? Invasions: (P) Hyksos (Bronze, chariots/horse) Assyrians Persians Greeks Rome

• Task: • Describe the Rise and Fall of Ancient Egypt • Describe the Rise and Fall of (Insert Empire here)

• West Africa (NG) • River Valley civilizations? -> Niger and Benue river valleys (NG) • Mass migrations – Bantu (P, NG) • South & Eastern migrations (NG) • Why – climate issues? • Sahara

• • • Bantu language (I) 1500 BCE – next 2000 years Moved into nomadic areas (Nomads settled) Upper-Niger region – Jenne-Jeno (NG, A) 1 st African city? Jenne-Jeno – how is it different than other cultures?

Gender Issues in Unit I Paleolithic Women Neolithic Women • Child-birth and nurturing of children • Gathered food – berries, nuts, edible plants • Most of Paleolithic man’s diet was from gathering • Socialization/1 st teachers • Religious figures • Child-birth and nurturing of children • Worked farms • Family size increased due to farming • “Role” was established • Socialization/1 st teachers • Religious figures
fb43dd8310a33b17302dcaab0eab2ee3.ppt