4e64a9825c7b54eabec101782f26eaf7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Page 1 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

IB Philosophy § The International Baccalaureate aims to develop inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people who help to create a better and more peaceful world through intercultural understanding and respect. § Our programs encourage students across the active, compassionate and lifelong learners who understand that world to become other people, with their differences, can also be right. Page 2 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

IB Mission The aim of all IB programs is to develop internationally minded people who, recognizing their common humanity and shared guardianship of the planet, help to create a better and more peaceful world. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

A continuum of international education Three programmes: one continuum © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
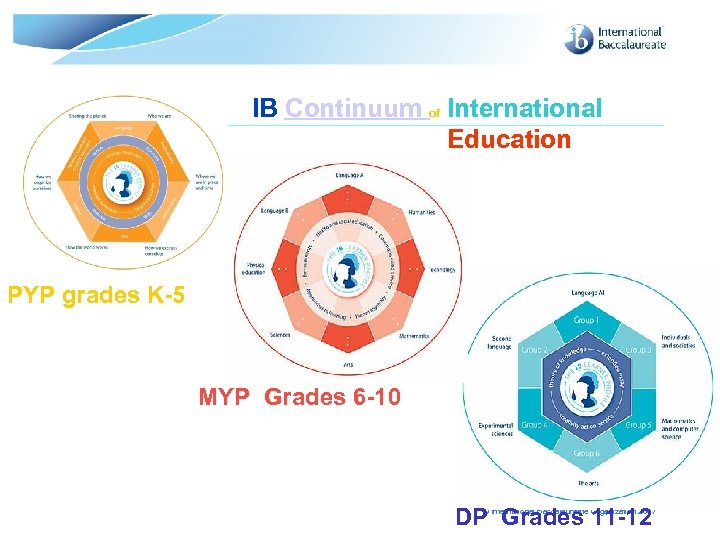
IB Continuum of International Education PYP grades K-5 MYP Grades 6 -10 DP Grades 11 -12 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
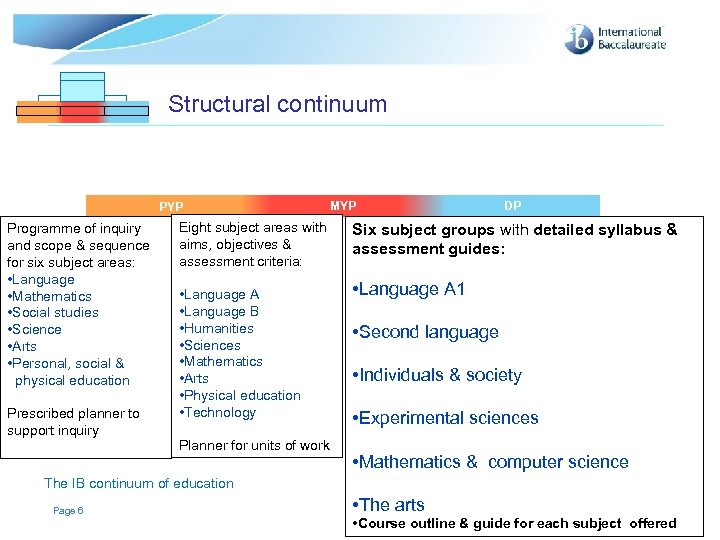
Structural continuum PYP Programme of inquiry and scope & sequence for six subject areas: • Language • Mathematics • Social studies • Science • Arts • Personal, social & physical education Prescribed planner to support inquiry MYP MYP Eight subject areas with aims, objectives & assessment criteria: • Language A • Language B • Humanities • Sciences • Mathematics • Arts • Physical education • Technology Planner for units of work DP DP DP Six subject groups with detailed syllabus & assessment guides: • Language A 1 • Second language • Individuals & society • Experimental sciences • Mathematics & computer science The IB continuum of education Page 6 • The arts © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007 • Course outline & guide for each subject offered

Language learning continuum PYP Promotes mother-tongue development MYP MYP Promotes mothertongue/best language and/or Language A development Student’s learn an additional language from age seven Student’s second language (language B) Schools must develop a language policy DP DP DP Promotes mother-tongue development: school supported, self-taught language A 1 courses The IB continuum of education Page 7 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007 Promotes the
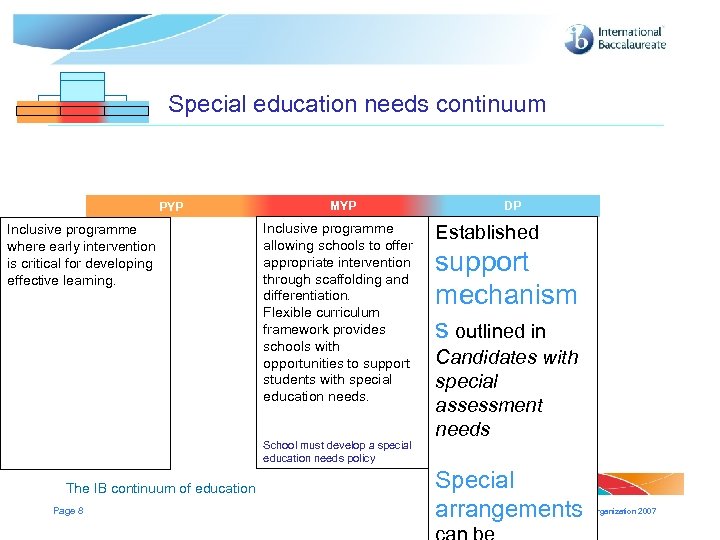
Special education needs continuum PYP Inclusive programme where early intervention is critical for developing effective learning. MYP MYP Inclusive programme allowing schools to offer appropriate intervention through scaffolding and differentiation. Flexible curriculum framework provides schools with opportunities to support students with special education needs. School must develop a special education needs policy The IB continuum of education Page 8 DP DP DP Established support mechanism s outlined in Candidates with special assessment needs Special arrangements © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Three Programs linked by the IB Learner Profile --the IB mission statement translated into a set of learning outcomes for the 21 st century. § Knowledgeable Inquirers Thinkers § Open-minded Principled Reflective § Communicators Risk-takers Balanced § Caring © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Diploma Programme The unique benefits of the DP
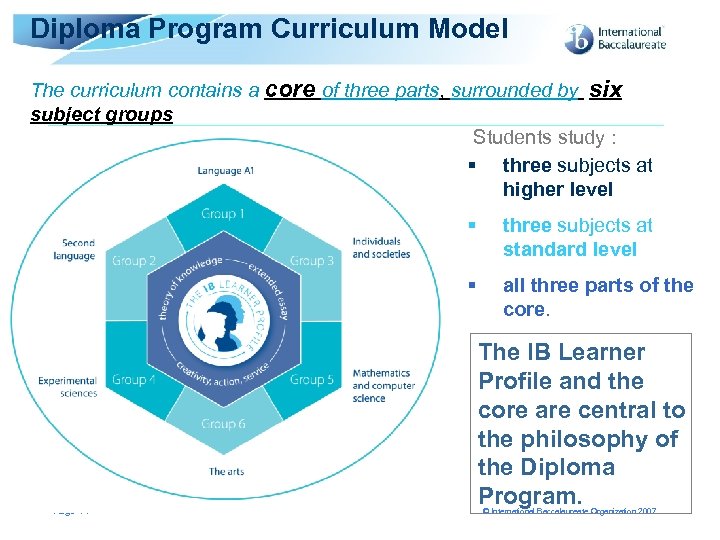
Diploma Program Curriculum Model The curriculum contains a core of three parts, surrounded by six subject groups Students study : § three subjects at higher level § § Page 11 three subjects at standard level all three parts of the core. The IB Learner Profile and the core are central to the philosophy of the Diploma Program. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Full Diploma CORE Requirements © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
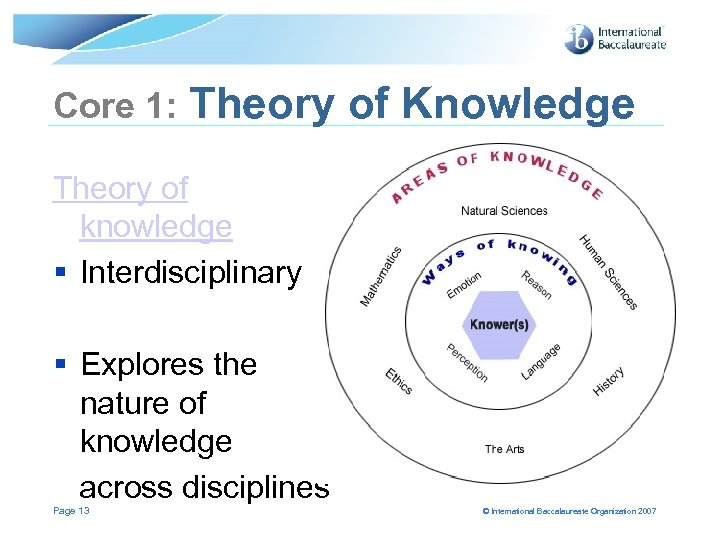
Core 1: Theory of Knowledge Theory of knowledge § Interdisciplinary § Explores the nature of knowledge across disciplines Page 13 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Learning to learn continuum MYP MYP PYP Learners constructing meaning Approaches to learning Promotes metacognitive knowledge (knowledge learners have about themselves and how they learn best) Promotes metacognitive performance (the ability to use self-knowledge to improve) The IB continuum of education Page 14 DP DP DP Theory of knowledge Promotes metacognitive knowledge --knowledge learners have about themselves and how they learn best Promotes metacognitive performance --the ability to use selfknowledge to improve © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
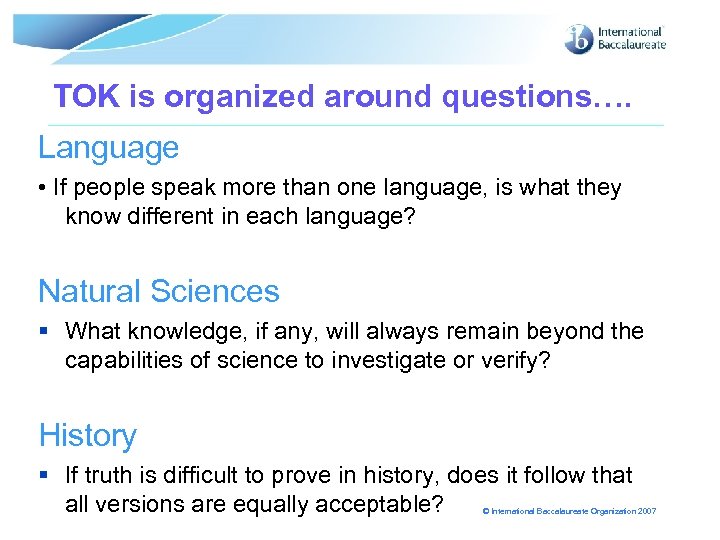
TOK is organized around questions…. Language • If people speak more than one language, is what they know different in each language? Natural Sciences § What knowledge, if any, will always remain beyond the capabilities of science to investigate or verify? History § If truth is difficult to prove in history, does it follow that all versions are equally acceptable? © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Core 2: The Extended Essay An independent, self-directed piece of research, culminating in a 4, 000 -word paper. …. the student has the opportunity to show knowledge, understanding and enthusiasm about a topic of his or her choice. Page 16 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
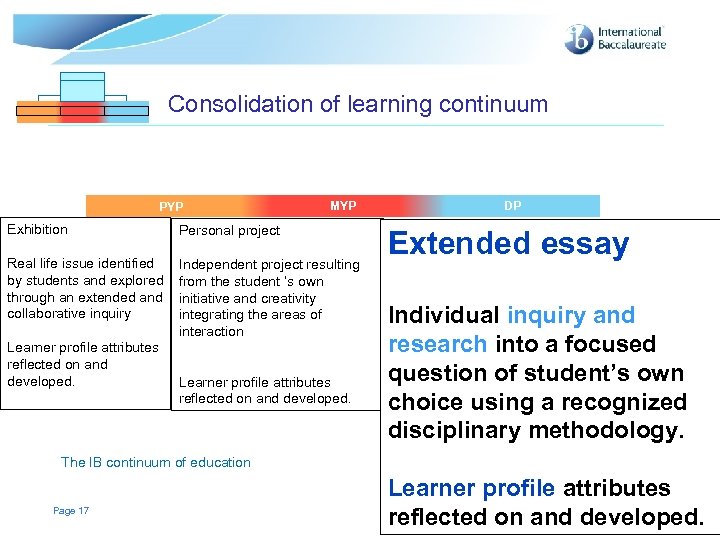
Consolidation of learning continuum PYP MYP MYP Exhibition Personal project Real life issue identified by students and explored through an extended and collaborative inquiry Independent project resulting from the student ‘s own initiative and creativity integrating the areas of interaction Learner profile attributes reflected on and developed. DP DP DP Extended essay Individual inquiry and research into a focused question of student’s own choice using a recognized disciplinary methodology. The IB continuum of education Page 17 Learner profile attributes reflected on and developed. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

The Extended Essay § Offers the opportunity to investigate a research question of individual interest § Familiarises students with the independent research and writing skills expected at university © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

The Extended Essay May 2009 E c o n o m i c s § To what extent does the extraction tax that Yanacocha pays contribute to Cajamarca's development? B i o l o g y § What effects are there on the potato tuber when disturbing the flow of water and nutrients? English LIterature § Romantic aspects in the characters of Victor Frankenstein and the monster of Mary Shelley's Frankenstein © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Core 3: Page 20 CAS: Creativity, Action Service A fundamental part of the Diploma program that takes seriously the importance of life outside the world of scholarship, providing a refreshing counterbalance to academic studies. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
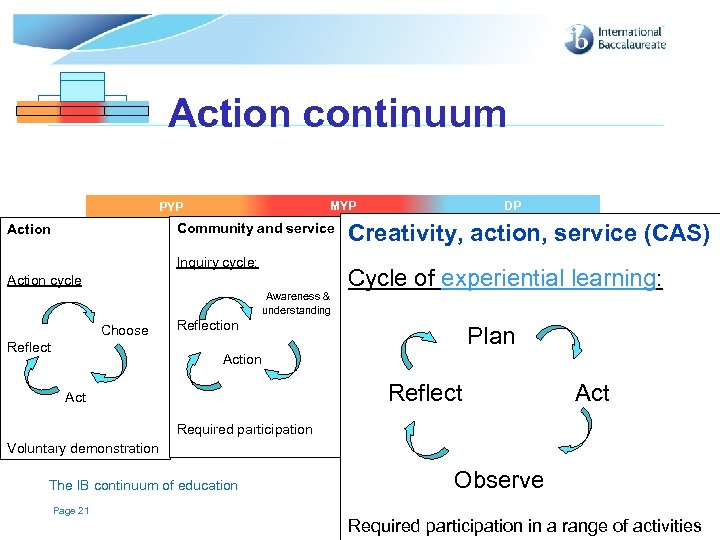
Action continuum MYP MYP PYP Community and service Action Inquiry cycle: Action cycle Awareness & understanding Choose Reflect DP DP DP Creativity, action, service (CAS) Cycle of experiential learning: Reflection Plan Action Reflect Act Required participation Voluntary demonstration The IB continuum of education Page 21 Observe © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007 Required participation in a range of activities

A good CAS program should be both challenging and enjoyable, a personal journey of self‑discovery © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

…. . students should have opportunities to choose their own CAS activities and to undertake activities in a local and international context as appropriate. This means that, as far as possible, students should “own” their personal CAS programs. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

CAS Learning Outcomes As a result of their CAS experience as a whole, there should be evidence that students have: § increased their awareness of their own strengths and areas for growth § undertaken new challenges § planned and initiated activities § worked collaboratively with others § shown perseverance and commitment in their activities § engaged with issues of global importance § considered the ethical implications of their actions § developed new skills © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

CAS Program at FDR thoughtful consideration § Incorporation of SMART goal proposals for all CAS Activities ownership , choice, challenge § Requires student choice and initiative in organizing a : CAS - Juniors 2008 -09 CAS service project meaningful reflection § Formalized summative assessment procedure © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

CAS Independent Projects May 2010 § Un Techo Para mi Pais § Fundacion ANAR § Descubriendo § Noche de Arte § In-site Entertainment © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Principled Inquirers • Consistently acts with integrity • Demonstrates an interest in the nature of learning and • Asks meaningful, relevant questions honesty • Enthusiastically engages in self-directed learning • Accepts responsibility for actions Thinkers • Demonstrates initiative and creativity in solving complex problems Risk-takers • Demonstrates the independence of spirit to explore new roles, ideas and strategies Caring Balanced • Actively chooses to participate in a variety of activities • Effectively applies organizational skills • Demonstrates empathy, compassion and respect for the needs and feelings of others • Demonstrates a personal commitment to © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007 service
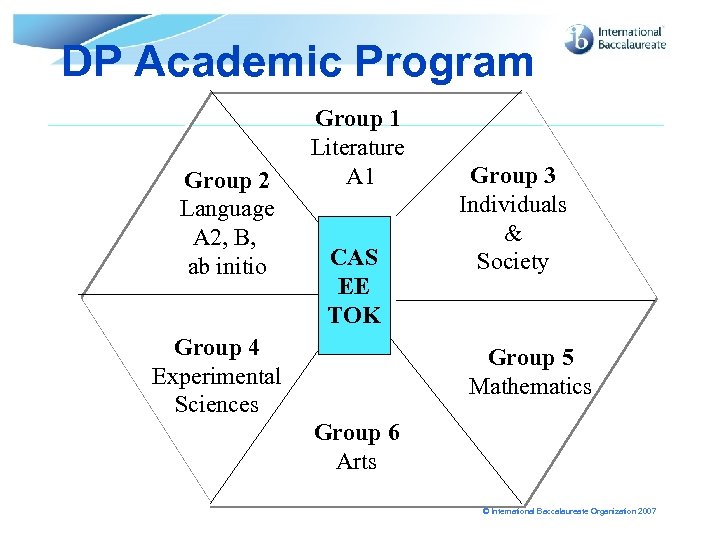
DP Academic Program Group 2 Language A 2, B, ab initio Group 1 Literature A 1 CAS EE EE TOK Group 4 Experimental Sciences Group 3 Individuals & Society Group 5 Mathematics Group 6 Arts © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
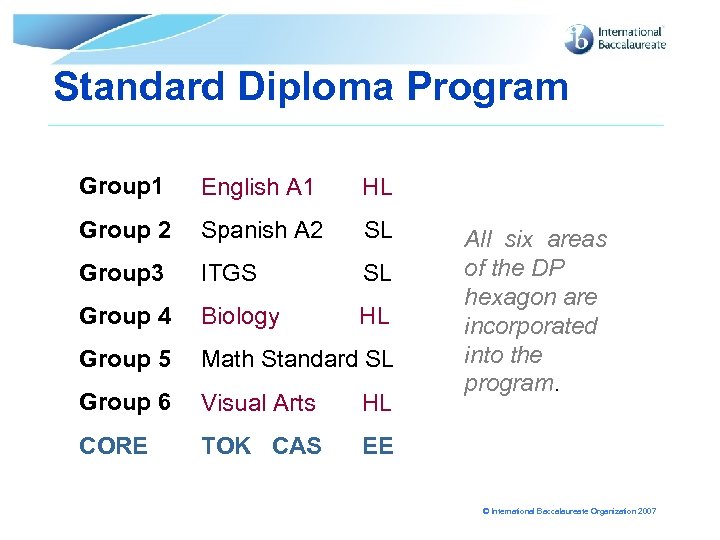
Standard Diploma Program Group 1 English A 1 HL Group 2 Spanish A 2 SL Group 3 ITGS SL Group 4 Biology HL Group 5 Math Standard SL Group 6 Visual Arts HL CORE TOK CAS EE All six areas of the DP hexagon are incorporated into the program. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
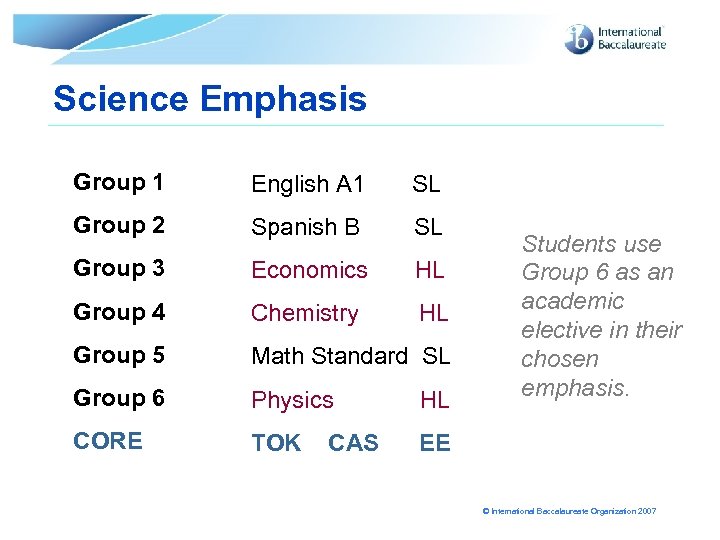
Science Emphasis Group 1 English A 1 SL Group 2 Spanish B SL Group 3 Economics HL Group 4 Chemistry HL Group 5 Math Standard SL Group 6 Physics HL CORE TOK EE CAS Students use Group 6 as an academic elective in their chosen emphasis. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Arts Emphasis Group 1 English A 1 HL Group 2 Spanish B Group 3/4 Environmental Systems SL Group 5 Math Studies SL Group 6 Theater HL Group 6 Music HL CORE TOK CAS SL EE Environmental Systems is used to meet the requirements for both groups 3 & 4, giving students the ability to include two arts in their program. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Peruvian Certificate + IB Diploma Group 1 Spanish A 1 HL Group 2 English A 2 SL Group 3 History HL Group 4 Chemistry HL Group 5 Math Standard SL Group 6 Visual Arts SL CORE TOK EE CAS OPP students may not use ITGS to meet the group 3 requirement. © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

IB assessment Assessment tasks are designed to support and encourage good classroom teaching and learning. They measure advanced academic skills: § analyzing and presenting information § evaluating and constructing arguments § solving problems creatively Page 33 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
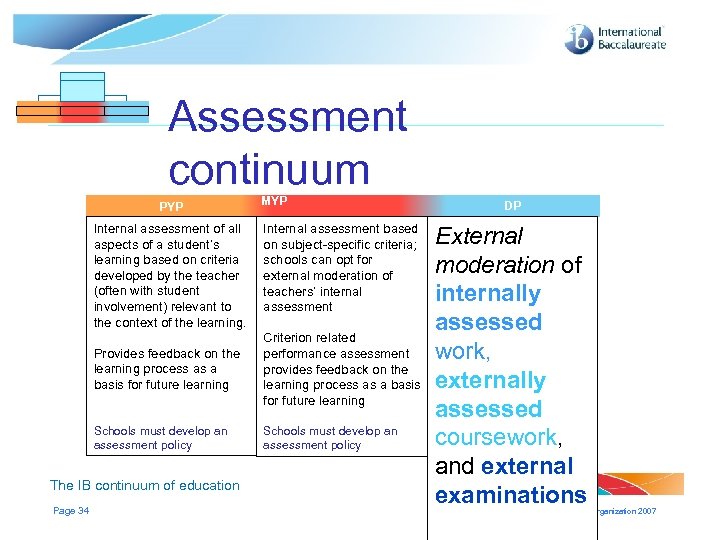
Assessment continuum PYP Internal assessment of all aspects of a student’s learning based on criteria developed by the teacher (often with student involvement) relevant to the context of the learning. MYP MYP DP DP Internal assessment based on subject-specific criteria; schools can opt for external moderation of teachers’ internal assessment External moderation of internally assessed work, externally assessed coursework, and external examinations Provides feedback on the learning process as a basis for future learning Criterion related performance assessment provides feedback on the learning process as a basis for future learning Schools must develop an assessment policy The IB continuum of education Page 34 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Internal vs External Assessment Internal Assessment consists of various forms of coursework: oral performances, written tasks, presentation; this work is marked by FDR teachers External Assessment comprises all of the May exams along with some coursework; all are marked by IBO appointed examiners In all cases, student results are determined by performance against set criteria and moderated against an international standard © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

Award of the Diploma © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

The IB diploma is widely recognized by the world’s leading universities. The IB works closely with universities in all regions of the world to gain recognition for the IB diploma: § Recognition in over 100 countries § Recognition by over 2, 000 universities § A database of university admission policies on www. ibo. org § Some universities offer scholarships and advanced placement for IB students Page 37 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

IBO Transcripts © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

to IB or not to IB…. . The program demands a great deal of self-discipline, organizational skills and motivation which are of at least equal importance to academic competence. Page 39 © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

To successfully undertake the full IB Diploma at FDR, a student should therefore have demonstrated: § Previous competence in a majority of the six subjects to be studied § Evidence of the necessary study skills and maturity to take on increasing responsibility for their education. § Awareness of the goals of the IB Diploma program § Willingness to participate in school life beyond the classroom © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

IB Certificates § Students who have demonstrated academic competence/interest in specific subjects § desire for the advantages the official IB exam results provide § would like more flexibility with the make-up of their academic program § have yet to fully embrace the IB goals and objectives © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007

IB Values © International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
4e64a9825c7b54eabec101782f26eaf7.ppt