A5 Psychology Level 3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Page 001 Level 3 FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE THEORETICAL PREPARATION PSYCHOLOGY STUDY NOTES Edition 1 / December 2001 Copyright FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE 2001 Rue de Oeuches 10 Case Postale 359 2740 MOUTIER 1 / Switzerland +41. 32. 494. 64. 10 Fax: +41. 32. 494. 64. 19 E-mail: info@fig-gymnastics. org http: //www. fig-gymnastics. com
Page 001 Level 3 FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE THEORETICAL PREPARATION PSYCHOLOGY STUDY NOTES Edition 1 / December 2001 Copyright FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE 2001 Rue de Oeuches 10 Case Postale 359 2740 MOUTIER 1 / Switzerland +41. 32. 494. 64. 10 Fax: +41. 32. 494. 64. 19 E-mail: info@fig-gymnastics. org http: //www. fig-gymnastics. com
 Page 002 PSYCHOLOGY Table of Contents Myths about PST Reasons Why PST is not Enhanced Properly 4 3 2 Level 3 The Phases of a PST PROGRAM 5 1 A Framework of Development PST Programs 6 PSYCHOLOGICAL SKILLS TRAINING (PST) Designing and Implementing PST programs Psychological Skills, Objectives, and Outcomes Needs Assessment Interpretation OMSAT – 3* Scales 12 11 10 9 8 7 Problems in Implementing PST Programs 14 PERFORMANCE PROFILING Mental strategies used by successful athletes What not to do ! Approaching and athlete with problems Signs or behavior which should concern Synopsis 20 19 18 17 16 15 Preventing eating disorders 21 EATING DISORDERS – Predisposing factors INJURY - A Model of Injury Causes 22 23 Stress – Injury relationship OVERTRAINING 30 25 Situational Factors Leading to Athlete Burnout 31 STALENESS Signs and Symptoms 35 26 Burnout in coaches 37 BURNOUT Treating and Preventing Burnout
Page 002 PSYCHOLOGY Table of Contents Myths about PST Reasons Why PST is not Enhanced Properly 4 3 2 Level 3 The Phases of a PST PROGRAM 5 1 A Framework of Development PST Programs 6 PSYCHOLOGICAL SKILLS TRAINING (PST) Designing and Implementing PST programs Psychological Skills, Objectives, and Outcomes Needs Assessment Interpretation OMSAT – 3* Scales 12 11 10 9 8 7 Problems in Implementing PST Programs 14 PERFORMANCE PROFILING Mental strategies used by successful athletes What not to do ! Approaching and athlete with problems Signs or behavior which should concern Synopsis 20 19 18 17 16 15 Preventing eating disorders 21 EATING DISORDERS – Predisposing factors INJURY - A Model of Injury Causes 22 23 Stress – Injury relationship OVERTRAINING 30 25 Situational Factors Leading to Athlete Burnout 31 STALENESS Signs and Symptoms 35 26 Burnout in coaches 37 BURNOUT Treating and Preventing Burnout
 Page 003
Page 003
 Page 004
Page 004
 Page 005
Page 005
 Page 006
Page 006
 Page 007
Page 007
 Page 008
Page 008
 Page 009
Page 009
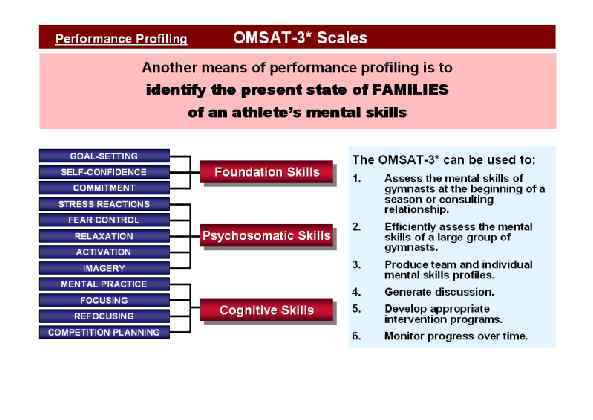 Page 010
Page 010
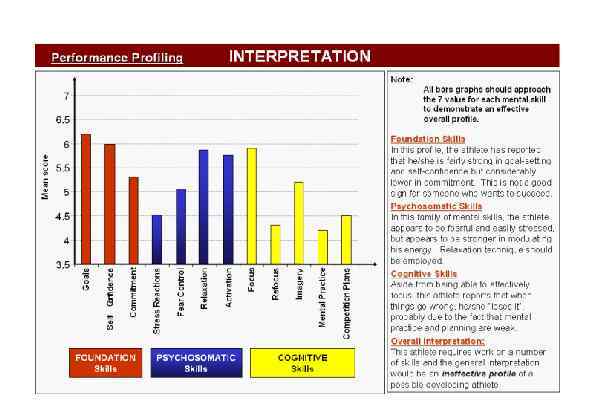 Page 011
Page 011
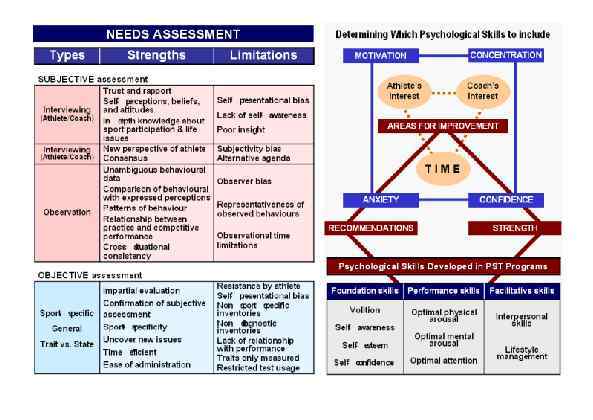 Page 012
Page 012
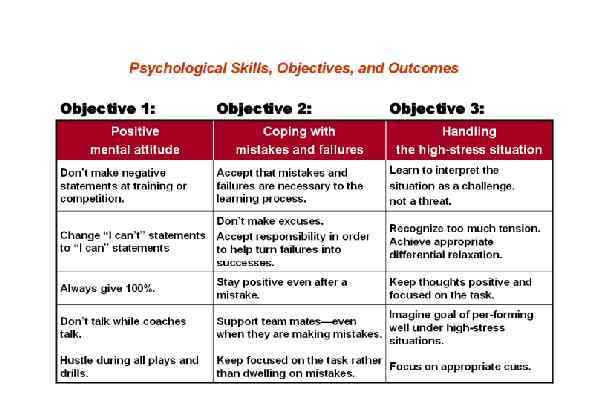 Page 013
Page 013
 Page 014
Page 014
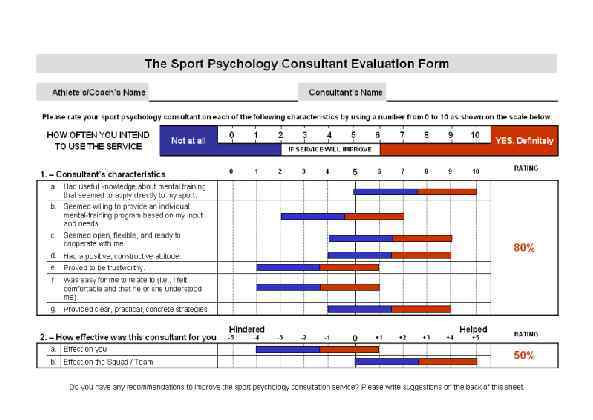 Page 015
Page 015
 Page 016
Page 016
 Page 017
Page 017
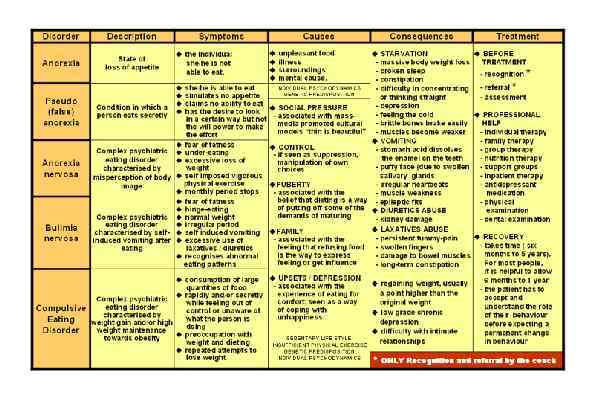 Page 018
Page 018
 Page 019
Page 019
 Page 020
Page 020
 Page 021
Page 021
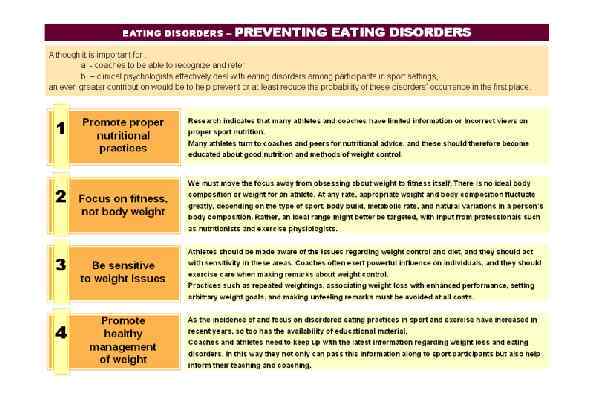 Page 022
Page 022
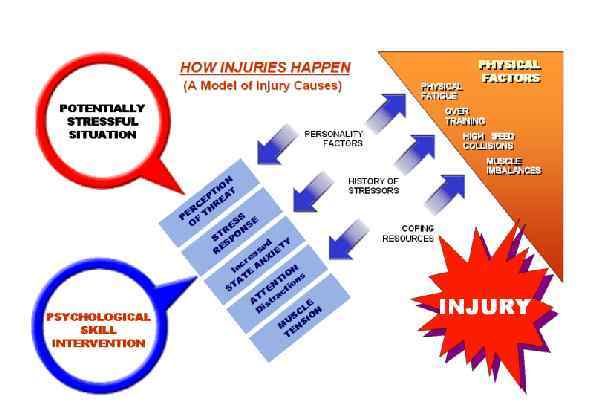 Page 023
Page 023
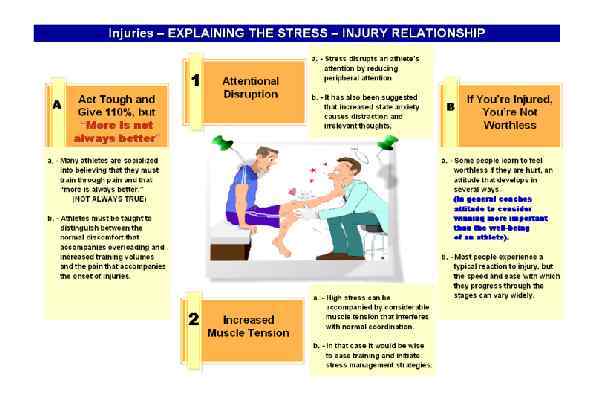 Page 024
Page 024
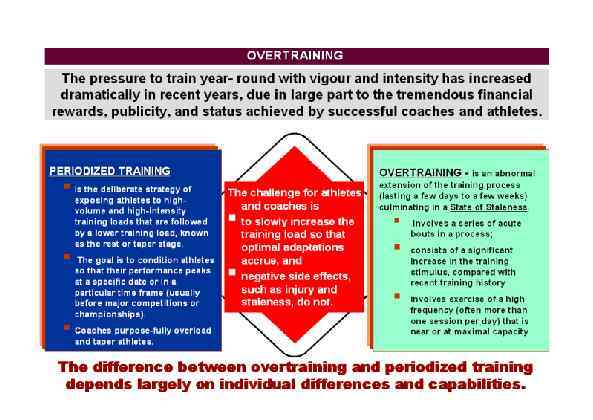 Page 025
Page 025
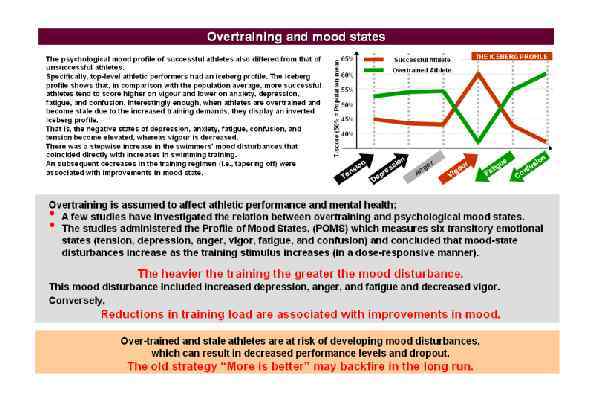 Page 026
Page 026
 Page 027
Page 027
 Page 028
Page 028
 Page 029
Page 029
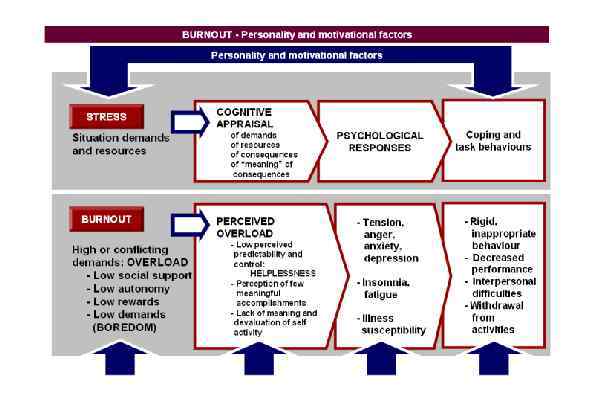 Page 030
Page 030
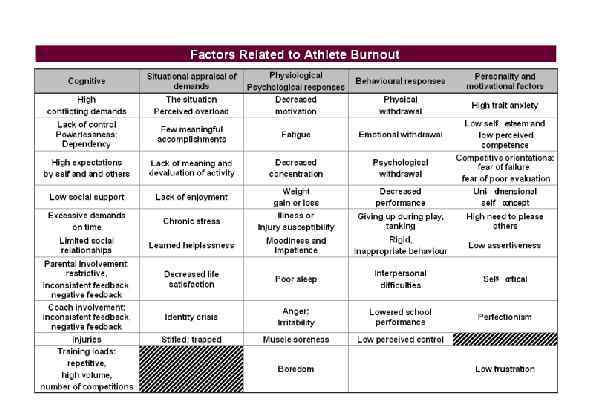 Page 031
Page 031
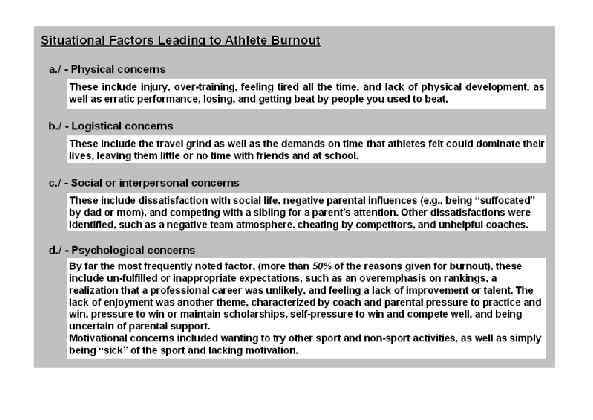 Page 032
Page 032
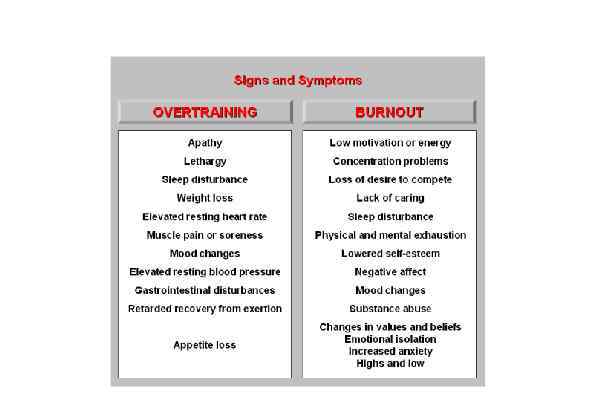 Page 033
Page 033
 Page 034
Page 034
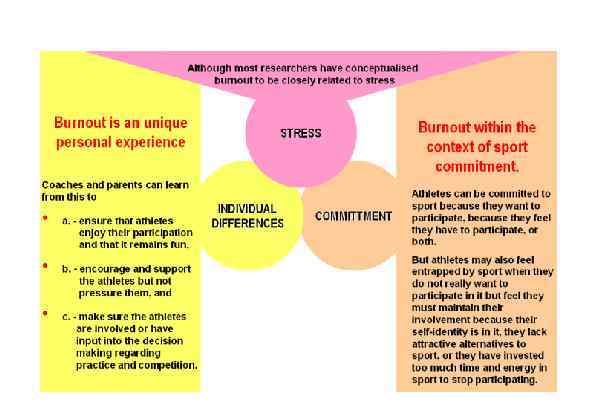 Page 035
Page 035
 Page 036
Page 036
 Page 037
Page 037
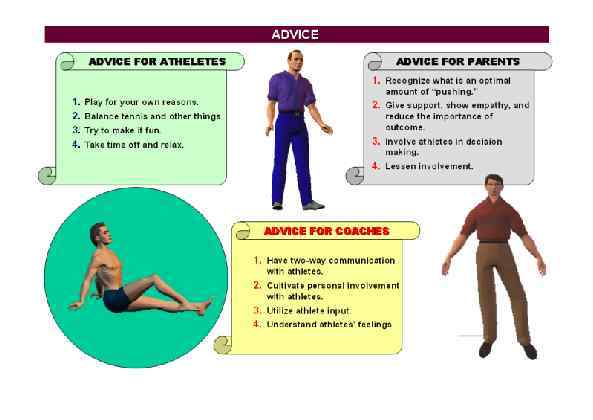 Page 038
Page 038
 Page 039
Page 039
 Page 040
Page 040
 Page 041 Weinberg, R. S. , & Gould, D. , (1998). Foundation of Sport and Exercise Psychology. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Martens, R. (1987). Coaches’ Guide to Sport Psychology. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Fink, H. , Kinsman, T. , Paradis, R. , Russell, K. , & Salmela, J. H. (1995). Athlete and Skill Development Model for Men’s Gymnastics, Ottawa: Canadian Gymnastics Federation, Men’s Technical Committee. Salmela, J. H. & Durand - Bush, N. , (2000). Age Group Development Program in Gymnastics. (CD-Rom). Moutier, (SUI), FIG SOURCES § § Côté, J. (1999). The influence of the family in the development of talent in sport. The Sport Psychologist, 13, 395 - 417 REFERENCES § § Côté, J. , Salmela, J. H. , Trudel, P. , Baria, A. , & Russell, S. J. (1995). The coaching model: A grounded assessment of expert gymnastic coaches’ knowledge. Journal pf Sport and Exercise Psychology, 17, 1 - 17. Adrian Stan, FIG, Moutier, (SUI) Dr. John H. Salmela, CENESP, UFMG, Belo Horizonte, (BRA) CONTRIBUTORS § § Prof. Lew Hardy (GBR) Prof. John H. Salmela, (BRA) REVIEW GROUP § §
Page 041 Weinberg, R. S. , & Gould, D. , (1998). Foundation of Sport and Exercise Psychology. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Martens, R. (1987). Coaches’ Guide to Sport Psychology. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Fink, H. , Kinsman, T. , Paradis, R. , Russell, K. , & Salmela, J. H. (1995). Athlete and Skill Development Model for Men’s Gymnastics, Ottawa: Canadian Gymnastics Federation, Men’s Technical Committee. Salmela, J. H. & Durand - Bush, N. , (2000). Age Group Development Program in Gymnastics. (CD-Rom). Moutier, (SUI), FIG SOURCES § § Côté, J. (1999). The influence of the family in the development of talent in sport. The Sport Psychologist, 13, 395 - 417 REFERENCES § § Côté, J. , Salmela, J. H. , Trudel, P. , Baria, A. , & Russell, S. J. (1995). The coaching model: A grounded assessment of expert gymnastic coaches’ knowledge. Journal pf Sport and Exercise Psychology, 17, 1 - 17. Adrian Stan, FIG, Moutier, (SUI) Dr. John H. Salmela, CENESP, UFMG, Belo Horizonte, (BRA) CONTRIBUTORS § § Prof. Lew Hardy (GBR) Prof. John H. Salmela, (BRA) REVIEW GROUP § §
 Page 042 IMPORTANT ! These notes have been produced for Education purposes ONLY Design and Compilation ADRIAN STAN
Page 042 IMPORTANT ! These notes have been produced for Education purposes ONLY Design and Compilation ADRIAN STAN


