422bcef102c1c29ab519af16f83d3ef7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 PACS Outside Radiology Dr Keith Foord Consultant Radiologist East Sussex Hospitals, UK
PACS Outside Radiology Dr Keith Foord Consultant Radiologist East Sussex Hospitals, UK
 `basic’ web viewers used in many clinical settings
`basic’ web viewers used in many clinical settings
 Radiology integration in the multi-disciplinary workplace
Radiology integration in the multi-disciplinary workplace
 Enterprise wide Multi-speciality PACS “In an Enterprise PACS Radiology images account for 30% or less of image volume…. It quickly became clear that many images sources outside of radiology were not being captured, and if they were not available for enterprise distribution, nor linked to the electronic patient record Another problem related to workflow. There was no RIS entry – no accession number and no entry on the DICOM MWL…. . Perhaps the biggest problem with expanding PACS is the lack of informatics standards in other departments. Some ophthalmology images are so proprietary that there is (essentially) no out put. ” Gary Wendt U Wisconsin SCAR 2005
Enterprise wide Multi-speciality PACS “In an Enterprise PACS Radiology images account for 30% or less of image volume…. It quickly became clear that many images sources outside of radiology were not being captured, and if they were not available for enterprise distribution, nor linked to the electronic patient record Another problem related to workflow. There was no RIS entry – no accession number and no entry on the DICOM MWL…. . Perhaps the biggest problem with expanding PACS is the lack of informatics standards in other departments. Some ophthalmology images are so proprietary that there is (essentially) no out put. ” Gary Wendt U Wisconsin SCAR 2005
 Enterprise PACS “One of the things we believe is that a radiology PACS, by itself, will not provide an adequate return on investment. The (enterprise) PACS must become part of the Electronic Patient Record to take advantage of electronic ordering, scheduling and reporting. To accommodate this we add 1. 5 to 2 TB of storage EACH MONTH” Ramin Khorasani MD, Director of Information Management for Radiology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
Enterprise PACS “One of the things we believe is that a radiology PACS, by itself, will not provide an adequate return on investment. The (enterprise) PACS must become part of the Electronic Patient Record to take advantage of electronic ordering, scheduling and reporting. To accommodate this we add 1. 5 to 2 TB of storage EACH MONTH” Ramin Khorasani MD, Director of Information Management for Radiology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
 Q. Who works with images? Image producers Image viewers – passive/learning Image interpreters and reporters Image interpreters / concurrent operators Image users – planning Image users – virtual endoscopy Image users – real time guided therapy and surgery A. Almost everyone, and if they don’t access to images would enrich their clinical lives
Q. Who works with images? Image producers Image viewers – passive/learning Image interpreters and reporters Image interpreters / concurrent operators Image users – planning Image users – virtual endoscopy Image users – real time guided therapy and surgery A. Almost everyone, and if they don’t access to images would enrich their clinical lives
 Image producers and many others The IT systems they use and how they record and manage images affects the remainder of the operation……
Image producers and many others The IT systems they use and how they record and manage images affects the remainder of the operation……
 Scanned Images Visual Light and Radiotherapy
Scanned Images Visual Light and Radiotherapy
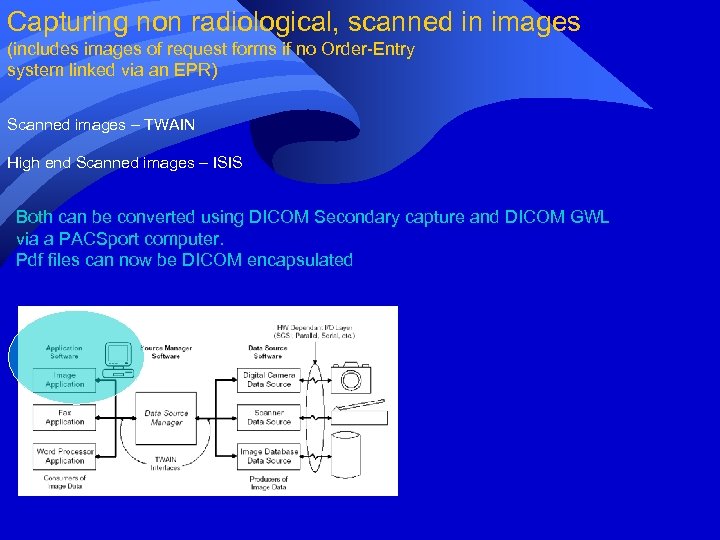 Capturing non radiological, scanned in images (includes images of request forms if no Order-Entry system linked via an EPR) Scanned images – TWAIN High end Scanned images – ISIS Both can be converted using DICOM Secondary capture and DICOM GWL via a PACSport computer. Pdf files can now be DICOM encapsulated
Capturing non radiological, scanned in images (includes images of request forms if no Order-Entry system linked via an EPR) Scanned images – TWAIN High end Scanned images – ISIS Both can be converted using DICOM Secondary capture and DICOM GWL via a PACSport computer. Pdf files can now be DICOM encapsulated
 Capturing Visual Light Images What is DICOM-VL? DICOM-Visible Light is an Supplement to integrate visible light images into DICOM Microscopy, endoscopy and digital photography. In particular, DICOM-VL specifies how to store preparation procedures and image-acquisition conditions in the image headers. It allows other ‘ologies’ to implement the DICOM standard, allowing their integration into EPRs It is the first real visible light image standard and allows display of these images next to radiological images on a DICOM viewing station. Part of the DICOM standard since 1999. DICOM minutes show struggle to obtain interest or expertise from medical VL companies, but better recently and DICOM MPEG 2 Video soon (? now)
Capturing Visual Light Images What is DICOM-VL? DICOM-Visible Light is an Supplement to integrate visible light images into DICOM Microscopy, endoscopy and digital photography. In particular, DICOM-VL specifies how to store preparation procedures and image-acquisition conditions in the image headers. It allows other ‘ologies’ to implement the DICOM standard, allowing their integration into EPRs It is the first real visible light image standard and allows display of these images next to radiological images on a DICOM viewing station. Part of the DICOM standard since 1999. DICOM minutes show struggle to obtain interest or expertise from medical VL companies, but better recently and DICOM MPEG 2 Video soon (? now)
 Pathology PACS…a rather special case! “Glass slides must be scanned at at least 400 x Generates up to 6 GB per slide Scanning a single slide can take up to 20 mins, but developments are expected to reduce this to 1 minute. Compression of 15: 1 can be applied, but will still generate 134 GB per day – 3 TB per month This will require 350 TB storage over 10 years” Kai Saeger, Charite Institute of Pathology, Berlin CARS 2003
Pathology PACS…a rather special case! “Glass slides must be scanned at at least 400 x Generates up to 6 GB per slide Scanning a single slide can take up to 20 mins, but developments are expected to reduce this to 1 minute. Compression of 15: 1 can be applied, but will still generate 134 GB per day – 3 TB per month This will require 350 TB storage over 10 years” Kai Saeger, Charite Institute of Pathology, Berlin CARS 2003
 “In the last few years, dynamic telepathology has been the only real digital application that has been able to transmit wide areas of microscopic preparations Dynamic telepathology is a real-time technology system. Only a few systems are able to store and create a database of the transmitted cases e. g. Bliss by Bacus. Labs. http: //www. bacuslabs. com//. A Web. Slide can be created either in uncompressed. bmp format or in. jpg format. These systems are very expensive because they work by means of a robotic microscope, and the software for image viewing and interaction is often sophisticated and only available with the purchase of apparatus. A Web. Slide can be created either in uncompressed. bmp format or in. jpg format” Each of these slides from one pathological specimen must be Scanned (Bacus. Labs system) Francesco Alfredo Zito 1, Franco Marzullo 1, Diego D'Errico 1, Cesare Salvatore 1, Rosanna Digirolamo 1, Angela Labriola 1 and Antonio Pellecchia 2 1 Division of Pathology 2 Division of Digestive Endoscopy, National Cancer Institute, Bari, Italy
“In the last few years, dynamic telepathology has been the only real digital application that has been able to transmit wide areas of microscopic preparations Dynamic telepathology is a real-time technology system. Only a few systems are able to store and create a database of the transmitted cases e. g. Bliss by Bacus. Labs. http: //www. bacuslabs. com//. A Web. Slide can be created either in uncompressed. bmp format or in. jpg format. These systems are very expensive because they work by means of a robotic microscope, and the software for image viewing and interaction is often sophisticated and only available with the purchase of apparatus. A Web. Slide can be created either in uncompressed. bmp format or in. jpg format” Each of these slides from one pathological specimen must be Scanned (Bacus. Labs system) Francesco Alfredo Zito 1, Franco Marzullo 1, Diego D'Errico 1, Cesare Salvatore 1, Rosanna Digirolamo 1, Angela Labriola 1 and Antonio Pellecchia 2 1 Division of Pathology 2 Division of Digestive Endoscopy, National Cancer Institute, Bari, Italy
 This is a 3 ´ 2 mm image of an endoscopic gastric biopsy. 7200 ´ 5200 pixel image was digitized at an objective The magnification of ´ 20. A total of 20 still pictures are required to generate a large image of 85 MB in TIFF format, which is then compressed into a 9 MB Quick Time VR file. process takes 60 min The entire digitization . The quality of the movie is related to the quality of initial images Quicktime virtual reality technology in light microscopy to support medical education in pathology Francesco Alfredo Zito 1, Franco Marzullo 1, Diego D'Errico 1, Cesare Salvatore 1, Rosanna Digirolamo 1, Angela Labriola 1 and Antonio Pellecchia 2 1 Division of Pathology 2 Division of Digestive Endoscopy, National Cancer Institute, Bari, Italy
This is a 3 ´ 2 mm image of an endoscopic gastric biopsy. 7200 ´ 5200 pixel image was digitized at an objective The magnification of ´ 20. A total of 20 still pictures are required to generate a large image of 85 MB in TIFF format, which is then compressed into a 9 MB Quick Time VR file. process takes 60 min The entire digitization . The quality of the movie is related to the quality of initial images Quicktime virtual reality technology in light microscopy to support medical education in pathology Francesco Alfredo Zito 1, Franco Marzullo 1, Diego D'Errico 1, Cesare Salvatore 1, Rosanna Digirolamo 1, Angela Labriola 1 and Antonio Pellecchia 2 1 Division of Pathology 2 Division of Digestive Endoscopy, National Cancer Institute, Bari, Italy
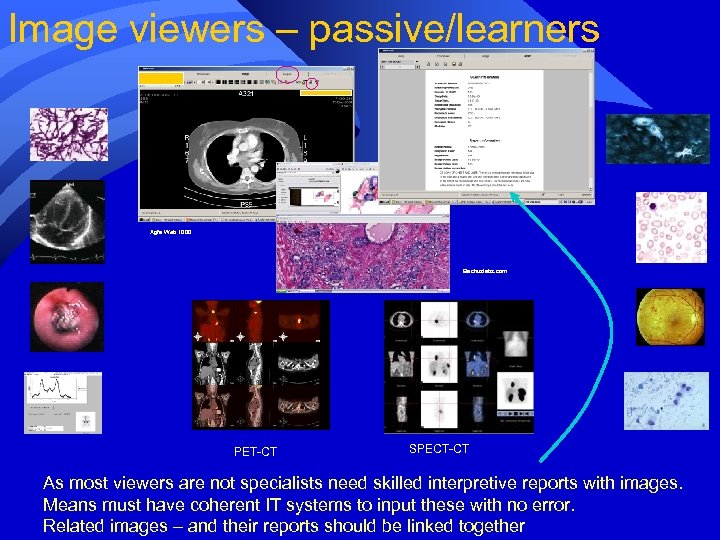 Image viewers – passive/learners Agfa Web 1000 Bachuslabs. com PET-CT SPECT-CT As most viewers are not specialists need skilled interpretive reports with images. Means must have coherent IT systems to input these with no error. Related images – and their reports should be linked together
Image viewers – passive/learners Agfa Web 1000 Bachuslabs. com PET-CT SPECT-CT As most viewers are not specialists need skilled interpretive reports with images. Means must have coherent IT systems to input these with no error. Related images – and their reports should be linked together
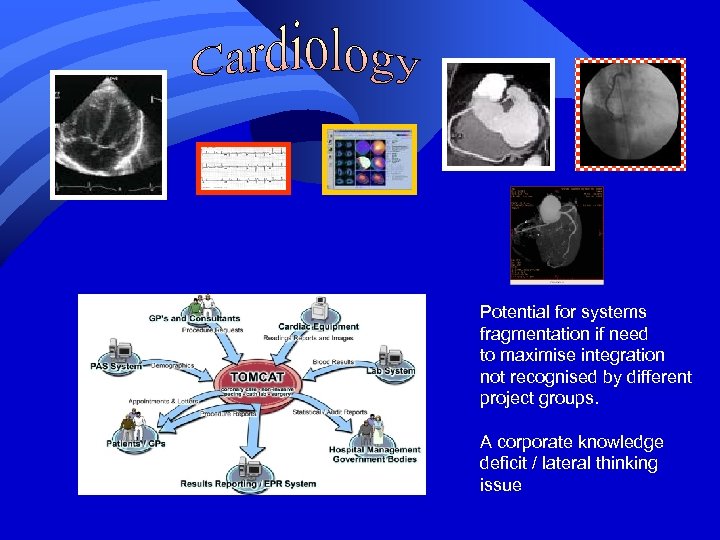 Potential for systems fragmentation if need to maximise integration not recognised by different project groups. A corporate knowledge deficit / lateral thinking issue
Potential for systems fragmentation if need to maximise integration not recognised by different project groups. A corporate knowledge deficit / lateral thinking issue
 Image interpreters and reporters
Image interpreters and reporters
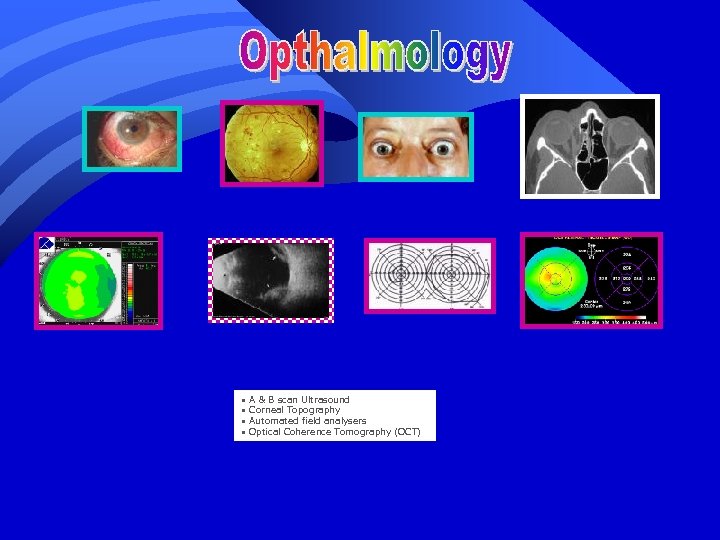 • A & B scan Ultrasound • Corneal Topography • Automated field analysers • Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
• A & B scan Ultrasound • Corneal Topography • Automated field analysers • Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
 Reminder…. “Perhaps the biggest problem with expanding PACS is the lack of informatics standards in other departments. Some ophthalmology images are so proprietary that there is (essentially) no out put. ” Gary Wendt U Wisconsin SCAR 2005
Reminder…. “Perhaps the biggest problem with expanding PACS is the lack of informatics standards in other departments. Some ophthalmology images are so proprietary that there is (essentially) no out put. ” Gary Wendt U Wisconsin SCAR 2005
 Image interpreters and concurrent operators. Use old images to plan, but dynamic image users in operation, recording new images - still and short video clips to be added to patient file
Image interpreters and concurrent operators. Use old images to plan, but dynamic image users in operation, recording new images - still and short video clips to be added to patient file
 Image users – planning
Image users – planning
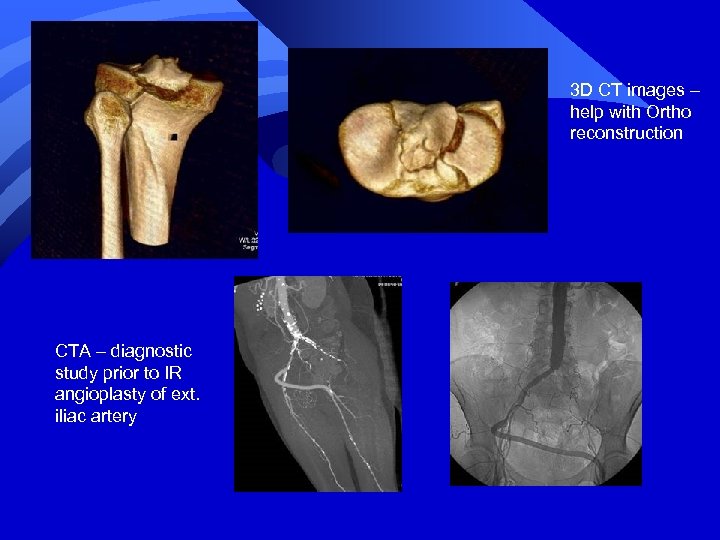 3 D CT images – help with Ortho reconstruction CTA – diagnostic study prior to IR angioplasty of ext. iliac artery
3 D CT images – help with Ortho reconstruction CTA – diagnostic study prior to IR angioplasty of ext. iliac artery
 Radiotherapy Planning DICOM RT is the extension of the DICOM 3. 0 standard which handles the Radiotherapy modality. It was developed to extend the current DICOM 3. 0 standard to include the RT modality, rather than produce a completely new standard Seven new objects define the RT modality DICOM-RT is not a separate standard - it is an extension, defining 7 new objects: - RT image - RT dose - RT structure set - RT plan - RT treatment record (beam session, brachy session, summary). Beams are defined with a system of "control points RT Image Includes all the normal RT images, DRRs, portal images, simulator images and radiograms RT Dose The total dose distributions from the planning system; dose matrix, dose points, isodose curves and dose volume histograms. RT Structure Set Patient related structures identified from diagnostic data, CT, virtual simulations and treatment planning systems. RT Plan This is the geometric and dosimetric data for course of external beam treatment or brachy-therapy. RT Treatment Records all the treatment session data.
Radiotherapy Planning DICOM RT is the extension of the DICOM 3. 0 standard which handles the Radiotherapy modality. It was developed to extend the current DICOM 3. 0 standard to include the RT modality, rather than produce a completely new standard Seven new objects define the RT modality DICOM-RT is not a separate standard - it is an extension, defining 7 new objects: - RT image - RT dose - RT structure set - RT plan - RT treatment record (beam session, brachy session, summary). Beams are defined with a system of "control points RT Image Includes all the normal RT images, DRRs, portal images, simulator images and radiograms RT Dose The total dose distributions from the planning system; dose matrix, dose points, isodose curves and dose volume histograms. RT Structure Set Patient related structures identified from diagnostic data, CT, virtual simulations and treatment planning systems. RT Plan This is the geometric and dosimetric data for course of external beam treatment or brachy-therapy. RT Treatment Records all the treatment session data.
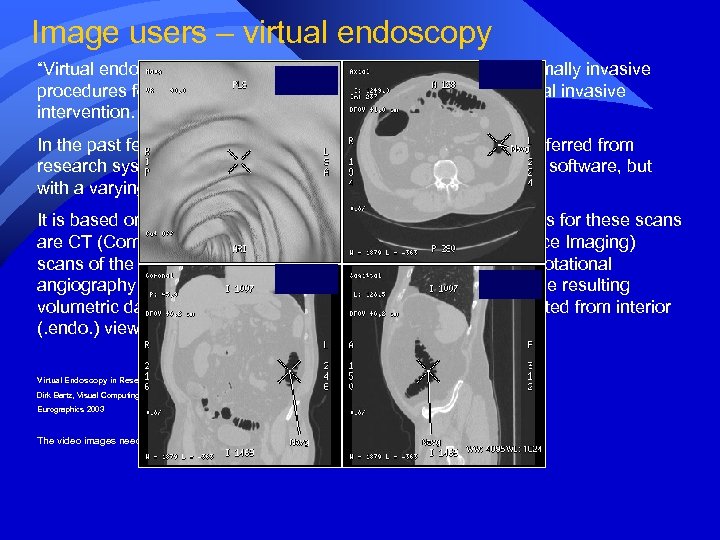 Image users – virtual endoscopy “Virtual endoscopy focuses on the virtual representation of minimally invasive procedures for training, planning, and diagnosis without an actual invasive intervention. In the past few years, virtual endoscopy modes have been transferred from research systems in virtually every commercial medical imaging software, but with a varying quality and exibility. It is based on a 3 D scan of the respective body region. Examples for these scans are CT (Computed Tomography) scans, MRI (Magnet Resonance Imaging) scans of the abdominal area, the heart, the head, the lungs, or rotational angiography of blood vessels in various body parts. Based on the resulting volumetric data, the organs of interest are visualized and inspected from interior (. endo. ) viewpoints. ” Virtual Endoscopy in Research and Clinical Practice Dirk Bartz, Visual Computing for Medicine Group, University of Tübingen Eurographics 2003 The video images need embedding in PACS…this video is 36 k. Bytes
Image users – virtual endoscopy “Virtual endoscopy focuses on the virtual representation of minimally invasive procedures for training, planning, and diagnosis without an actual invasive intervention. In the past few years, virtual endoscopy modes have been transferred from research systems in virtually every commercial medical imaging software, but with a varying quality and exibility. It is based on a 3 D scan of the respective body region. Examples for these scans are CT (Computed Tomography) scans, MRI (Magnet Resonance Imaging) scans of the abdominal area, the heart, the head, the lungs, or rotational angiography of blood vessels in various body parts. Based on the resulting volumetric data, the organs of interest are visualized and inspected from interior (. endo. ) viewpoints. ” Virtual Endoscopy in Research and Clinical Practice Dirk Bartz, Visual Computing for Medicine Group, University of Tübingen Eurographics 2003 The video images need embedding in PACS…this video is 36 k. Bytes
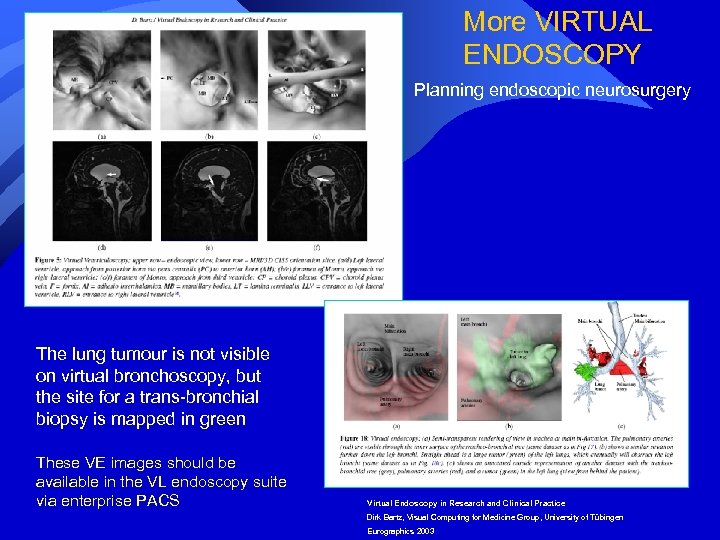 More VIRTUAL ENDOSCOPY Planning endoscopic neurosurgery The lung tumour is not visible on virtual bronchoscopy, but the site for a trans-bronchial biopsy is mapped in green These VE images should be available in the VL endoscopy suite via enterprise PACS Virtual Endoscopy in Research and Clinical Practice Dirk Bartz, Visual Computing for Medicine Group, University of Tübingen Eurographics 2003
More VIRTUAL ENDOSCOPY Planning endoscopic neurosurgery The lung tumour is not visible on virtual bronchoscopy, but the site for a trans-bronchial biopsy is mapped in green These VE images should be available in the VL endoscopy suite via enterprise PACS Virtual Endoscopy in Research and Clinical Practice Dirk Bartz, Visual Computing for Medicine Group, University of Tübingen Eurographics 2003
 Image users – real time guided therapy and surgery Sinus surgery. The cross lines show The position of the probe on the corresponding CT in x, y and z axes GE Medical Systems
Image users – real time guided therapy and surgery Sinus surgery. The cross lines show The position of the probe on the corresponding CT in x, y and z axes GE Medical Systems
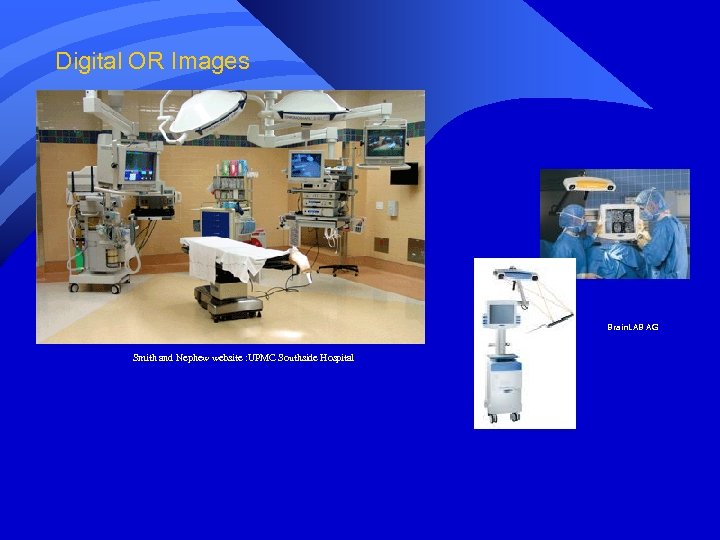 Digital OR Images Smith and Nephew website : UPMC Southside Hospital Brain. LAB AG
Digital OR Images Smith and Nephew website : UPMC Southside Hospital Brain. LAB AG
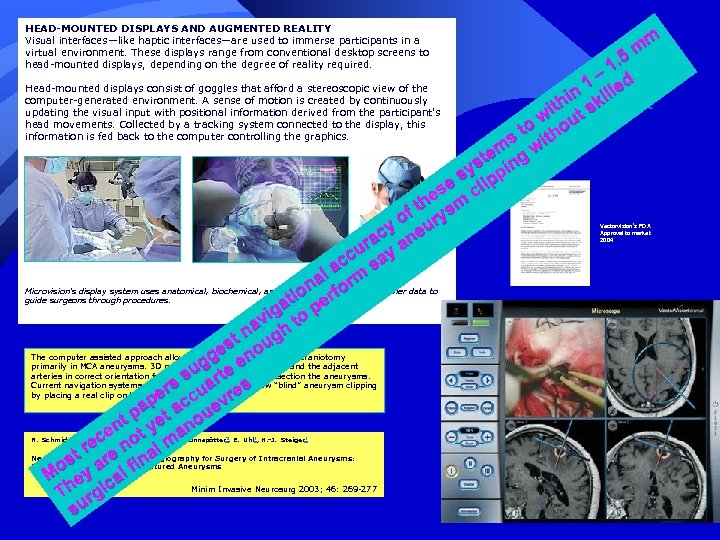 HEAD-MOUNTED DISPLAYS AND AUGMENTED REALITY Visual interfaces—like haptic interfaces—are used to immerse participants in a virtual environment. These displays range from conventional desktop screens to head-mounted displays, depending on the degree of reality required. m m 1. 5 1 – led Head-mounted displays consist of goggles that afford a stereoscopic view of the in il computer-generated environment. A sense of motion is created by continuously th t sk updating the visual input with positional information derived from the participant's wi u head movements. Collected by a tracking system connected to the display, this o o information is fed back to the computer controlling the graphics. s t ith m te n g w s sy ippi e l es m c h f t rys o cy neu a ur y a c ac sa l na formand other data to Microvision's display system uses anatomical, biochemical, and physiological images io guide surgeons through procedures. at per ig av h to n st oug The computer assisted approach allowed a smaller, exactly placed craniotomy ge en g primarily in MCA aneurysms. 3 D presentation of the aneurysms and the adjacent arteries in correct orientation facilitated identification and dissection the aneurysms. su rte Current navigation systems are not precise enough to allow “blind” aneurysm clipping s a by placing a real clip on the virtual aneurysm neck. er ccu vres p pa et a oue t en ot y an c re e n al m st ar fin Mo ey al Minim Invasive Neurosurg 2003; 46: 269 -277 Th rgic su Vectorvision’s FDA Approval to market 2004 R. Schmid-Elsaesser 1, A. Muacevic 1, M. Holtmannspötter 2, E. Uhl 1, H. -J. Steiger 1 Neuronavigation Based on CT Angiography for Surgery of Intracranial Aneurysms: Primary Experience with Unruptured Aneurysms
HEAD-MOUNTED DISPLAYS AND AUGMENTED REALITY Visual interfaces—like haptic interfaces—are used to immerse participants in a virtual environment. These displays range from conventional desktop screens to head-mounted displays, depending on the degree of reality required. m m 1. 5 1 – led Head-mounted displays consist of goggles that afford a stereoscopic view of the in il computer-generated environment. A sense of motion is created by continuously th t sk updating the visual input with positional information derived from the participant's wi u head movements. Collected by a tracking system connected to the display, this o o information is fed back to the computer controlling the graphics. s t ith m te n g w s sy ippi e l es m c h f t rys o cy neu a ur y a c ac sa l na formand other data to Microvision's display system uses anatomical, biochemical, and physiological images io guide surgeons through procedures. at per ig av h to n st oug The computer assisted approach allowed a smaller, exactly placed craniotomy ge en g primarily in MCA aneurysms. 3 D presentation of the aneurysms and the adjacent arteries in correct orientation facilitated identification and dissection the aneurysms. su rte Current navigation systems are not precise enough to allow “blind” aneurysm clipping s a by placing a real clip on the virtual aneurysm neck. er ccu vres p pa et a oue t en ot y an c re e n al m st ar fin Mo ey al Minim Invasive Neurosurg 2003; 46: 269 -277 Th rgic su Vectorvision’s FDA Approval to market 2004 R. Schmid-Elsaesser 1, A. Muacevic 1, M. Holtmannspötter 2, E. Uhl 1, H. -J. Steiger 1 Neuronavigation Based on CT Angiography for Surgery of Intracranial Aneurysms: Primary Experience with Unruptured Aneurysms
 Structured reporting DICOM SR – is an ‘envelope’, but within this useful structure is available. It allows linkage to other DICOM objects, including between associated radiological and other images and waveforms. CAD outputs can be in SR format. User decides how much structure to use and controls with templates the type of content, if it is mandatory or optional and modes of expression Incorporated into the report are captured images of key findings (which can be exploded to full screen presentation), structured diagnosis information, recorded video and audio, the ability to sort findings by anatomy or priority, to view prior findings associated with the corresponding patient and hyperlinks to related information. DICOM Structured Reporting", Dr. David A. Clunie, ISBN 09701369 -0 -0 Point. Dx
Structured reporting DICOM SR – is an ‘envelope’, but within this useful structure is available. It allows linkage to other DICOM objects, including between associated radiological and other images and waveforms. CAD outputs can be in SR format. User decides how much structure to use and controls with templates the type of content, if it is mandatory or optional and modes of expression Incorporated into the report are captured images of key findings (which can be exploded to full screen presentation), structured diagnosis information, recorded video and audio, the ability to sort findings by anatomy or priority, to view prior findings associated with the corresponding patient and hyperlinks to related information. DICOM Structured Reporting", Dr. David A. Clunie, ISBN 09701369 -0 -0 Point. Dx
 Dilemma – products from many different vendors – hardware & software incompatibility Goal – prevent being vendor dependent - consumer locked into specific products – component interoperability “plug and play” – seamless integration with “other” IT John A. Carrino, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Information Management Group Jefferson Health System
Dilemma – products from many different vendors – hardware & software incompatibility Goal – prevent being vendor dependent - consumer locked into specific products – component interoperability “plug and play” – seamless integration with “other” IT John A. Carrino, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Information Management Group Jefferson Health System
 ISSUES for Enterprise PACS • • Image data set size – MDCT/Pathology Image storage volumes Networking Integration • RIS becomes IIS within EPR, but preferably an integrated component of the EPR • Image and data Protocols • Lack of protocol standards and expertise with some vendors • • DICOM & IHE Corporate awareness and lateral thinking
ISSUES for Enterprise PACS • • Image data set size – MDCT/Pathology Image storage volumes Networking Integration • RIS becomes IIS within EPR, but preferably an integrated component of the EPR • Image and data Protocols • Lack of protocol standards and expertise with some vendors • • DICOM & IHE Corporate awareness and lateral thinking
 Quite clearly if we do not all eat and think together Enterprise wide PACS may be a very long time coming
Quite clearly if we do not all eat and think together Enterprise wide PACS may be a very long time coming
 “Perhaps the biggest problem with expanding PACS is the lack of informatics standards in other departments. ”Gary Wendt U Wisconsin SCAR 2005 Vendors of all medical imaging equipment, not just in radiology, must be brought into the IHE and DICOM fraternities. We need to educate hospital operators and image users in all clinical specialities not to buy bespoke IT solutions. Keith Foord Conquest Hospital UK CARS 2005 Cf. H looking to integrate other ‘ologies’ within 2 to 4 years
“Perhaps the biggest problem with expanding PACS is the lack of informatics standards in other departments. ”Gary Wendt U Wisconsin SCAR 2005 Vendors of all medical imaging equipment, not just in radiology, must be brought into the IHE and DICOM fraternities. We need to educate hospital operators and image users in all clinical specialities not to buy bespoke IT solutions. Keith Foord Conquest Hospital UK CARS 2005 Cf. H looking to integrate other ‘ologies’ within 2 to 4 years


