6662b5d7b11751721217dbe03233f1c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
 PACS introduction Facilitator: Edward Wong
PACS introduction Facilitator: Edward Wong
 What is the role of PACS Administrator?
What is the role of PACS Administrator?
 PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS § System Maintenance § Image and Information Management For a 200, 000 exams/year institution, 2 -8 full time PACS Administrator is available!
PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS § System Maintenance § Image and Information Management For a 200, 000 exams/year institution, 2 -8 full time PACS Administrator is available!
 PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS - Financial and workflow study - Request for Proposal and Tender drafting - Workflow modification including job reallocation and resource relocation - Training and Operation Manuals - Acceptance of system § System Maintenance § Image and Information Management
PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS - Financial and workflow study - Request for Proposal and Tender drafting - Workflow modification including job reallocation and resource relocation - Training and Operation Manuals - Acceptance of system § System Maintenance § Image and Information Management
 PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS § System Maintenance - Contingency plan - Incompatibility handling - First line support and problems escalating - System security and Performance monitoring § Image and Information Management
PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS § System Maintenance - Contingency plan - Incompatibility handling - First line support and problems escalating - System security and Performance monitoring § Image and Information Management
 PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS § System Maintenance § Image and Information Management - Maintain high Image Quality - Data Integrity - Quality Assurance program - Tele. Radiography - Anytime Available Storage Management
PACS Administrator’s roles § Implementing a PACS § System Maintenance § Image and Information Management - Maintain high Image Quality - Data Integrity - Quality Assurance program - Tele. Radiography - Anytime Available Storage Management
 What is PACS ? P: Picture, Images & Reports A: Archive, Online, Near line, Offline C: Communication, Networking, Transfer Protocols S: System, Components & Architecture PACS: for storage and distribution of images and information when necessary
What is PACS ? P: Picture, Images & Reports A: Archive, Online, Near line, Offline C: Communication, Networking, Transfer Protocols S: System, Components & Architecture PACS: for storage and distribution of images and information when necessary
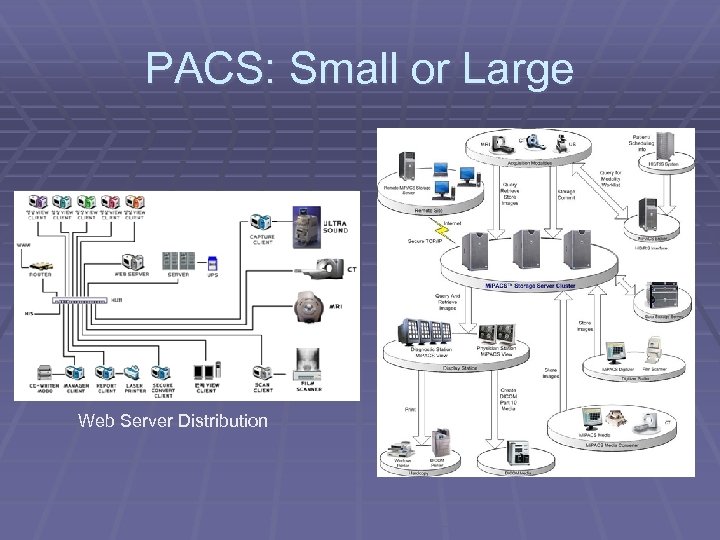 PACS: Small or Large Web Server Distribution
PACS: Small or Large Web Server Distribution
 Scale of PACS § No. of Beds in Hospital/ Exams per year § No. of Modalities § No. of Switches Considerations: System connectivity, expandability, reliability and cost-effectiveness
Scale of PACS § No. of Beds in Hospital/ Exams per year § No. of Modalities § No. of Switches Considerations: System connectivity, expandability, reliability and cost-effectiveness
 Types of images § 1 D, 2 D, 3 D, 4 D § Different DICOM Modality type: Cardiac / PET / 4 D § § § U/S…. . Image size: Resolution and bit depth Image quality: Bit Depth and resolution Color / Monochromatic Exam. Size: image size x no. of images Structured Reports New DICOM IOD: Endoscopic & Microscopic images / ECGs / Security Profiles…. .
Types of images § 1 D, 2 D, 3 D, 4 D § Different DICOM Modality type: Cardiac / PET / 4 D § § § U/S…. . Image size: Resolution and bit depth Image quality: Bit Depth and resolution Color / Monochromatic Exam. Size: image size x no. of images Structured Reports New DICOM IOD: Endoscopic & Microscopic images / ECGs / Security Profiles…. .
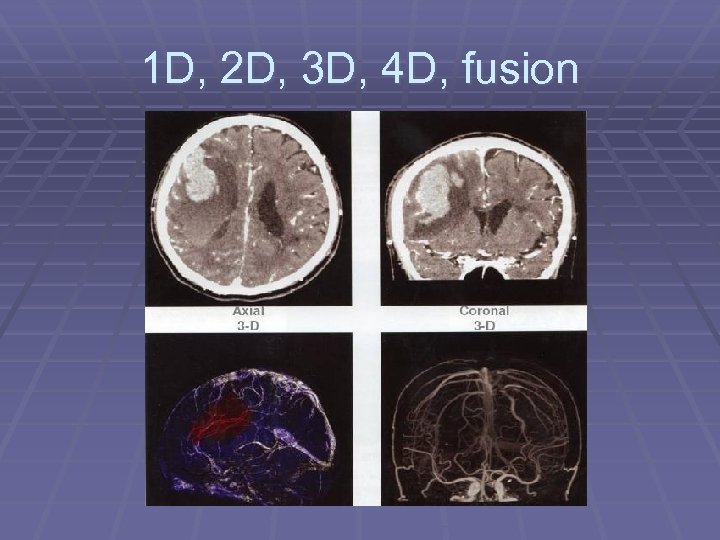 1 D, 2 D, 3 D, 4 D, fusion
1 D, 2 D, 3 D, 4 D, fusion
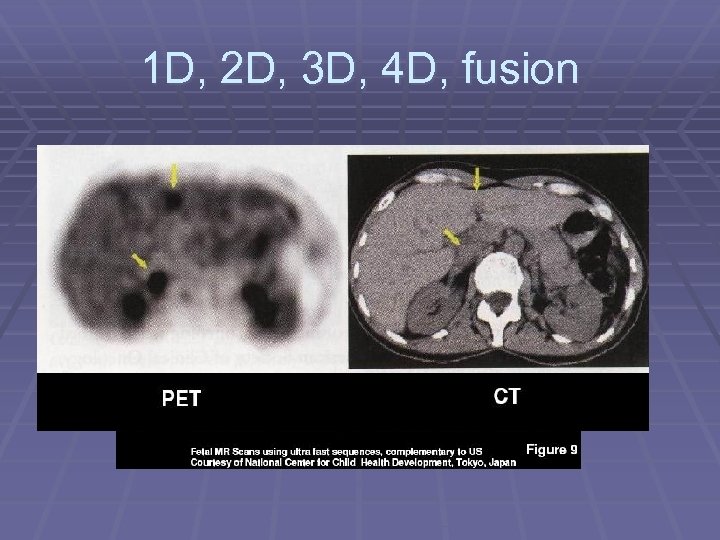 1 D, 2 D, 3 D, 4 D, fusion
1 D, 2 D, 3 D, 4 D, fusion
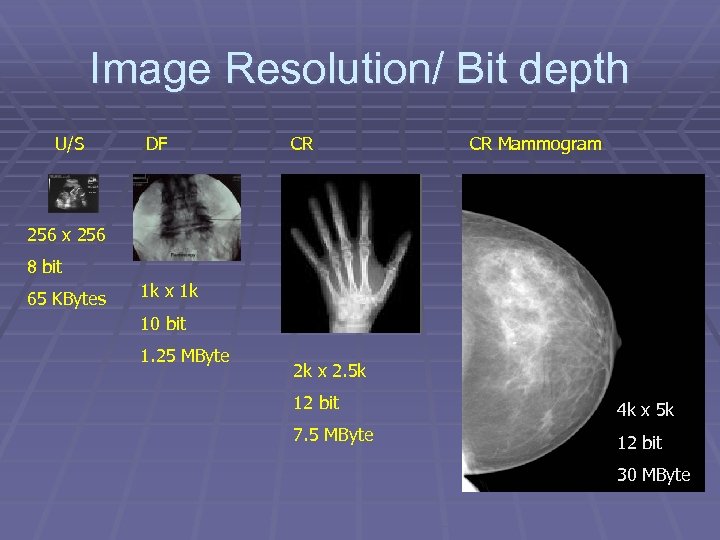 Image Resolution/ Bit depth U/S DF CR CR Mammogram 256 x 256 8 bit 65 KBytes 1 k x 1 k 10 bit 1. 25 MByte 2 k x 2. 5 k 12 bit 4 k x 5 k 7. 5 MByte 12 bit 30 MByte
Image Resolution/ Bit depth U/S DF CR CR Mammogram 256 x 256 8 bit 65 KBytes 1 k x 1 k 10 bit 1. 25 MByte 2 k x 2. 5 k 12 bit 4 k x 5 k 7. 5 MByte 12 bit 30 MByte
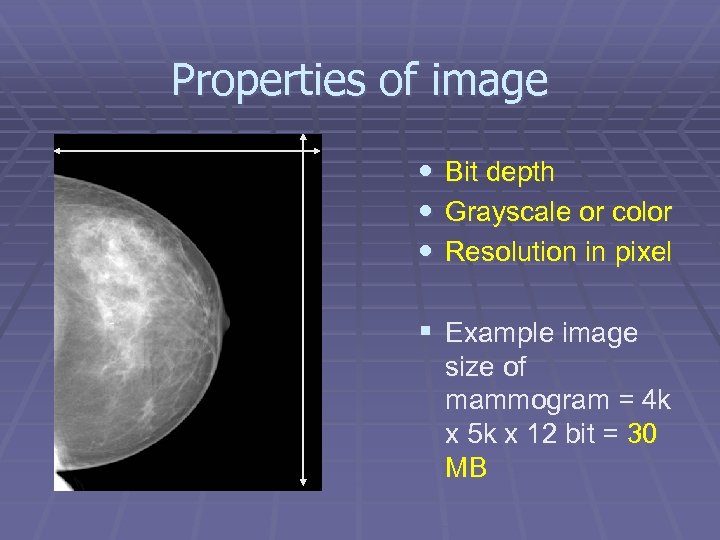 Properties of image • Bit depth • Grayscale or color • Resolution in pixel § Example image size of mammogram = 4 k x 5 k x 12 bit = 30 MB
Properties of image • Bit depth • Grayscale or color • Resolution in pixel § Example image size of mammogram = 4 k x 5 k x 12 bit = 30 MB
 PACS Architecture
PACS Architecture
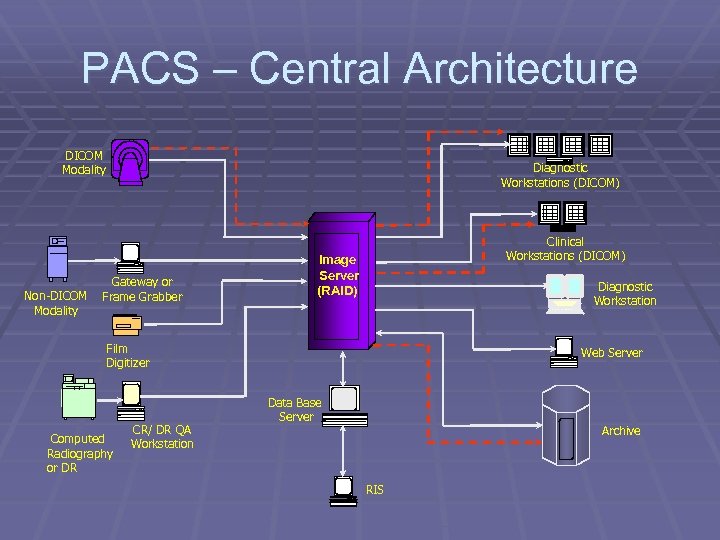 PACS – Central Architecture DICOM Modality Non-DICOM Modality Diagnostic Workstations (DICOM) Gateway or Frame Grabber Clinical Workstations (DICOM) Image Server (RAID) Diagnostic Workstation Film Digitizer Computed Radiography or DR CR/ DR QA Workstation Web Server Data Base Server Archive RIS
PACS – Central Architecture DICOM Modality Non-DICOM Modality Diagnostic Workstations (DICOM) Gateway or Frame Grabber Clinical Workstations (DICOM) Image Server (RAID) Diagnostic Workstation Film Digitizer Computed Radiography or DR CR/ DR QA Workstation Web Server Data Base Server Archive RIS
 Central Architecture § Image Server and Database Manager is the HEART § Any image, any where, any time § Unique central copy § Easy update of data § Requires high performance servers § Potential single point of failure at server § Bandwidth demanding
Central Architecture § Image Server and Database Manager is the HEART § Any image, any where, any time § Unique central copy § Easy update of data § Requires high performance servers § Potential single point of failure at server § Bandwidth demanding
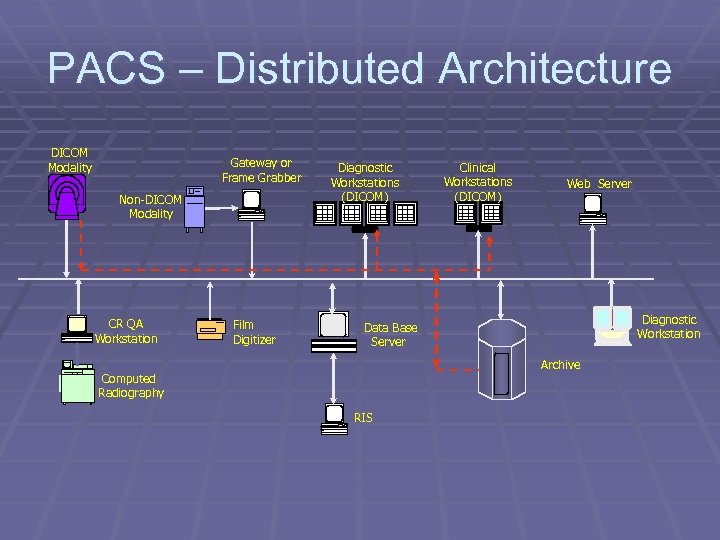 PACS – Distributed Architecture DICOM Modality Gateway or Frame Grabber Non-DICOM Modality CR QA Workstation Film Digitizer Diagnostic Workstations (DICOM) Clinical Workstations (DICOM) Web Server Diagnostic Workstation Data Base Server Archive Computed Radiography RIS
PACS – Distributed Architecture DICOM Modality Gateway or Frame Grabber Non-DICOM Modality CR QA Workstation Film Digitizer Diagnostic Workstations (DICOM) Clinical Workstations (DICOM) Web Server Diagnostic Workstation Data Base Server Archive Computed Radiography RIS
 Distributed Architecture § Exams are routed from modality to selected workstations § Complex routing algorithms based on department / user preference § Difficult to support concurrent review of images § Less destructive for failure at database server
Distributed Architecture § Exams are routed from modality to selected workstations § Complex routing algorithms based on department / user preference § Difficult to support concurrent review of images § Less destructive for failure at database server
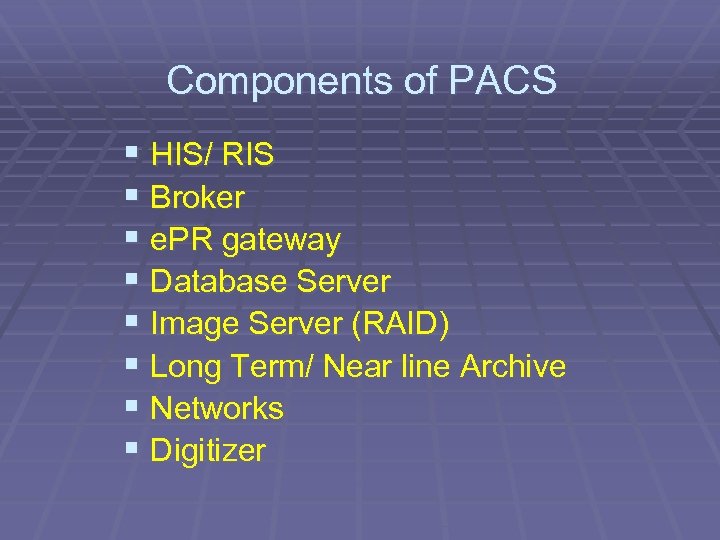 Components of PACS § HIS/ RIS § Broker § e. PR gateway § Database Server § Image Server (RAID) § Long Term/ Near line Archive § Networks § Digitizer
Components of PACS § HIS/ RIS § Broker § e. PR gateway § Database Server § Image Server (RAID) § Long Term/ Near line Archive § Networks § Digitizer
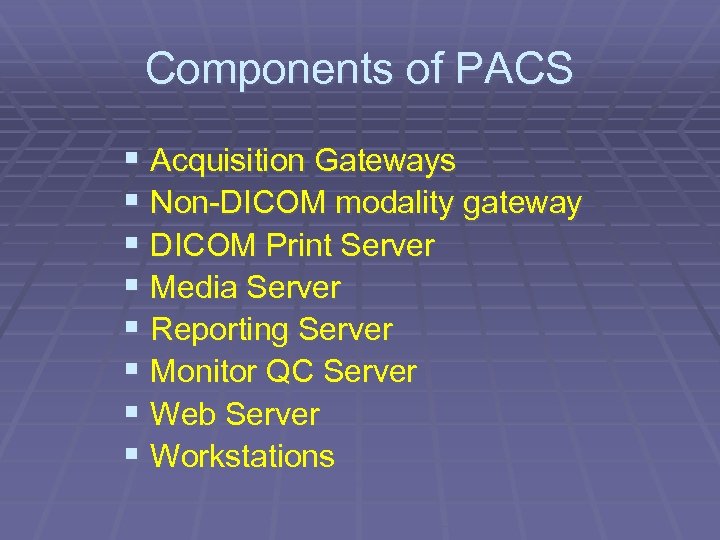 Components of PACS § Acquisition Gateways § Non-DICOM modality gateway § DICOM Print Server § Media Server § Reporting Server § Monitor QC Server § Web Server § Workstations
Components of PACS § Acquisition Gateways § Non-DICOM modality gateway § DICOM Print Server § Media Server § Reporting Server § Monitor QC Server § Web Server § Workstations
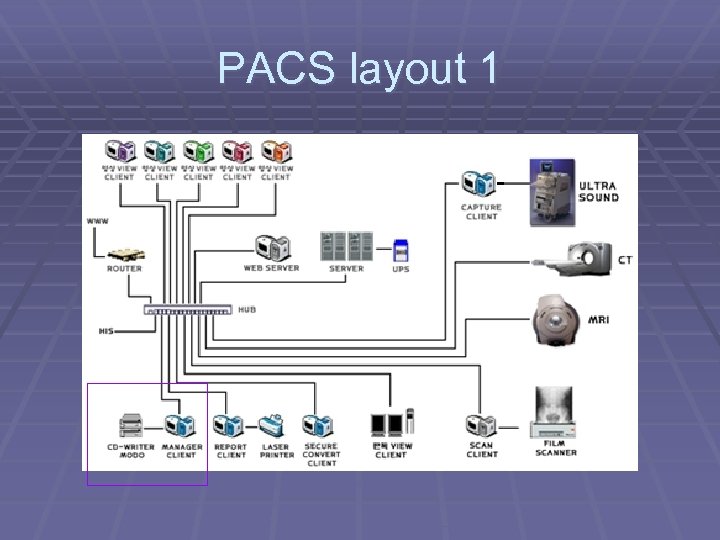 PACS layout 1
PACS layout 1
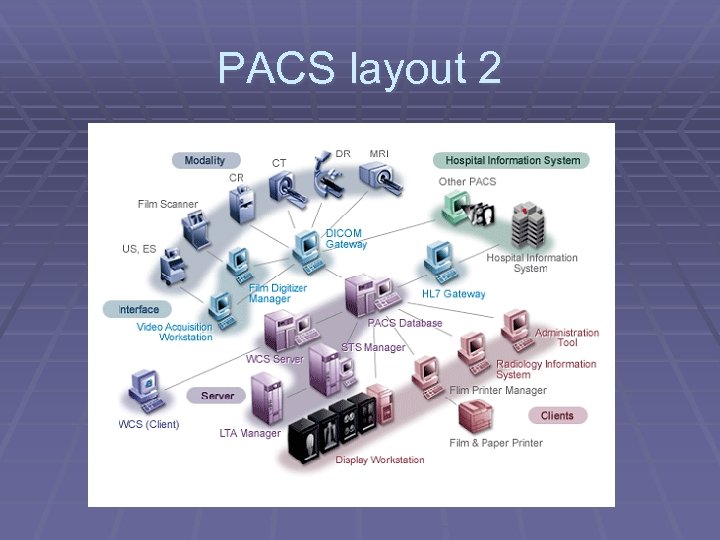 PACS layout 2
PACS layout 2
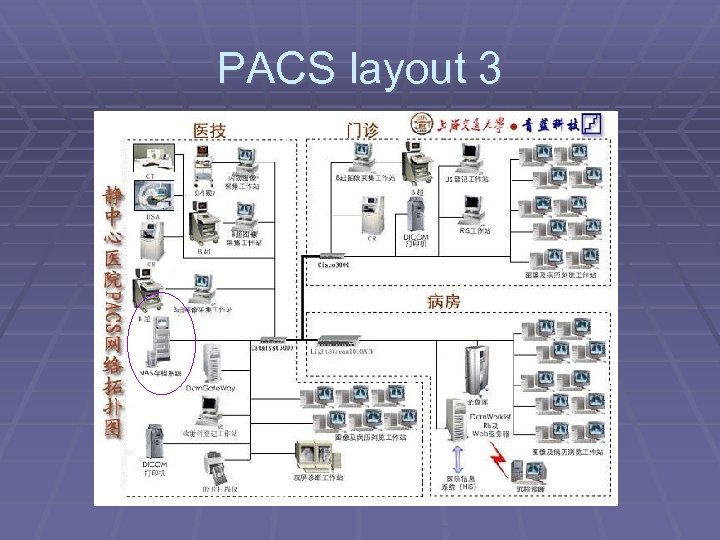 PACS layout 3
PACS layout 3
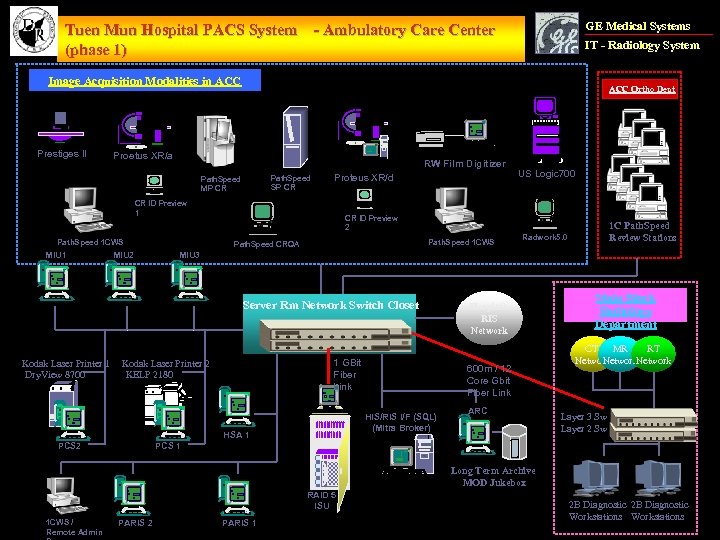 GE Medical Systems Tuen Mun Hospital PACS System - Ambulatory Care Center (phase 1) IT - Radiology System Image Acquisition Modalities in ACC Prestiges II ACC Ortho Dept Proetus XR/a RW Film Digitizer Path. Speed SP CR Path. Speed MP CR Proteus XR/d CR ID Preview 1 Path. Speed 1 CWS MIU 1 MIU 2 CR ID Preview 2 Path. Speed 1 CWS Path. Speed CRQA 1 GBit Fiber Link Kodak Laser Printer 2 KELP 2180 E 450 CPU HSA 1 PCS 2 1 C Path. Speed Review Stations Radwork 5. 0 MIU 3 Server Rm Network Switch Closet Kodak Laser Printer 1 Dry. View 8700 US Logic 700 Hospital RIS Network 600 m / 12 Core Gbit Fiber Link HIS/RIS I/F (SQL) (Mitra Broker) ARC Main Block Radiology Department CT MR RT Network Layer 3 Sw Layer 2 Sw PCS 1 Long Term Archive MOD Jukebox RAID 5 ISU 1 CWS / Remote Admin PARIS 2 PARIS 1 2 B Diagnostic Workstations
GE Medical Systems Tuen Mun Hospital PACS System - Ambulatory Care Center (phase 1) IT - Radiology System Image Acquisition Modalities in ACC Prestiges II ACC Ortho Dept Proetus XR/a RW Film Digitizer Path. Speed SP CR Path. Speed MP CR Proteus XR/d CR ID Preview 1 Path. Speed 1 CWS MIU 1 MIU 2 CR ID Preview 2 Path. Speed 1 CWS Path. Speed CRQA 1 GBit Fiber Link Kodak Laser Printer 2 KELP 2180 E 450 CPU HSA 1 PCS 2 1 C Path. Speed Review Stations Radwork 5. 0 MIU 3 Server Rm Network Switch Closet Kodak Laser Printer 1 Dry. View 8700 US Logic 700 Hospital RIS Network 600 m / 12 Core Gbit Fiber Link HIS/RIS I/F (SQL) (Mitra Broker) ARC Main Block Radiology Department CT MR RT Network Layer 3 Sw Layer 2 Sw PCS 1 Long Term Archive MOD Jukebox RAID 5 ISU 1 CWS / Remote Admin PARIS 2 PARIS 1 2 B Diagnostic Workstations
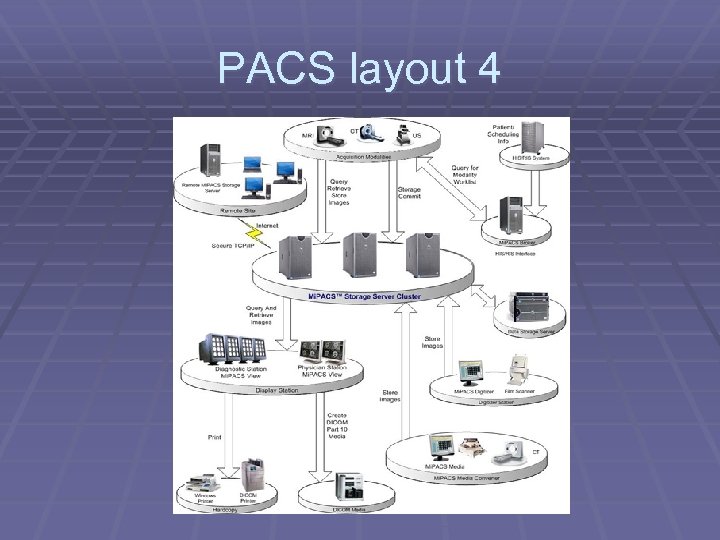 PACS layout 4
PACS layout 4
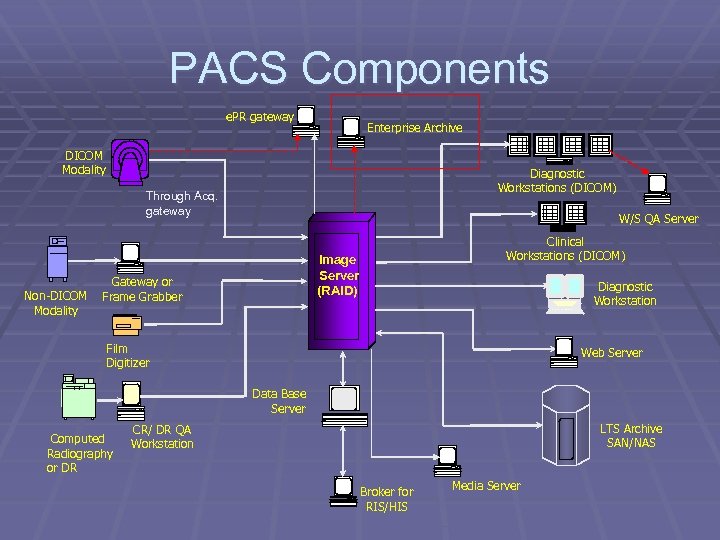 PACS Components e. PR gateway Enterprise Archive DICOM Modality Diagnostic Workstations (DICOM) Through Acq. gateway Non-DICOM Modality W/S QA Server Clinical Workstations (DICOM) Image Server (RAID) Gateway or Frame Grabber Diagnostic Workstation Film Digitizer Web Server Data Base Server Computed Radiography or DR LTS Archive SAN/NAS CR/ DR QA Workstation Broker for RIS/HIS Media Server
PACS Components e. PR gateway Enterprise Archive DICOM Modality Diagnostic Workstations (DICOM) Through Acq. gateway Non-DICOM Modality W/S QA Server Clinical Workstations (DICOM) Image Server (RAID) Gateway or Frame Grabber Diagnostic Workstation Film Digitizer Web Server Data Base Server Computed Radiography or DR LTS Archive SAN/NAS CR/ DR QA Workstation Broker for RIS/HIS Media Server
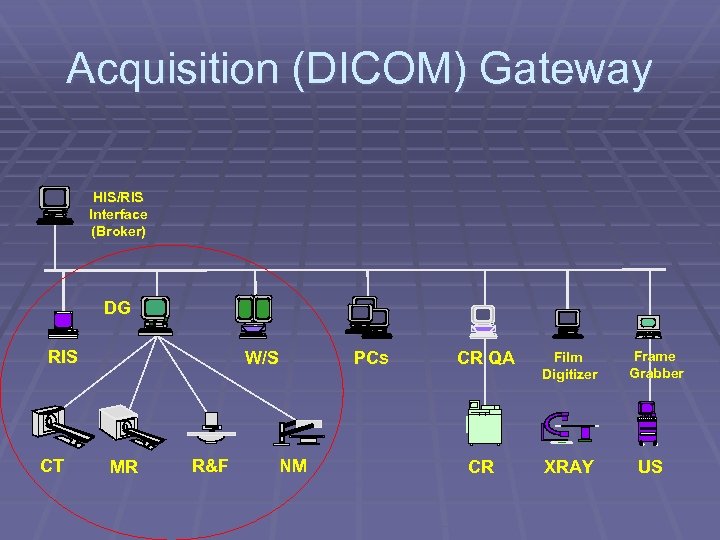 Acquisition (DICOM) Gateway HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
Acquisition (DICOM) Gateway HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
 Role of Acquisition gateway § Compression/ decompression and security § Check the images for integrity § Convert to PACS format (header, byteorder, matrix size) § Queue for images (priority) to database server (background) § Share the workload and no point of failure for multiple Acquisition gateway
Role of Acquisition gateway § Compression/ decompression and security § Check the images for integrity § Convert to PACS format (header, byteorder, matrix size) § Queue for images (priority) to database server (background) § Share the workload and no point of failure for multiple Acquisition gateway
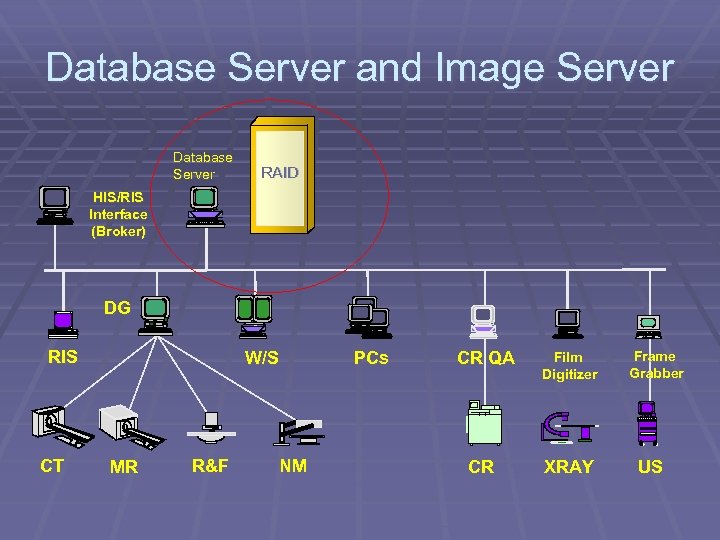 Database Server and Image Server Database Server RAID HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
Database Server and Image Server Database Server RAID HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
 Database Server (PACS controller) § The Heart of the system § Integration cross point between HIS/RIS and PACS (status update) § Create and manages patient folders § Manage reading worklists and user profiles § Manage data transfer within the system § Support data mining and teaching folders
Database Server (PACS controller) § The Heart of the system § Integration cross point between HIS/RIS and PACS (status update) § Create and manages patient folders § Manage reading worklists and user profiles § Manage data transfer within the system § Support data mining and teaching folders
 Image Server (RAID) § Online (rapid access) exam storage and distribution device § Support simultaneous exam input and output transfer operations § Up to Three months of storage capacity § Scalable capacity
Image Server (RAID) § Online (rapid access) exam storage and distribution device § Support simultaneous exam input and output transfer operations § Up to Three months of storage capacity § Scalable capacity
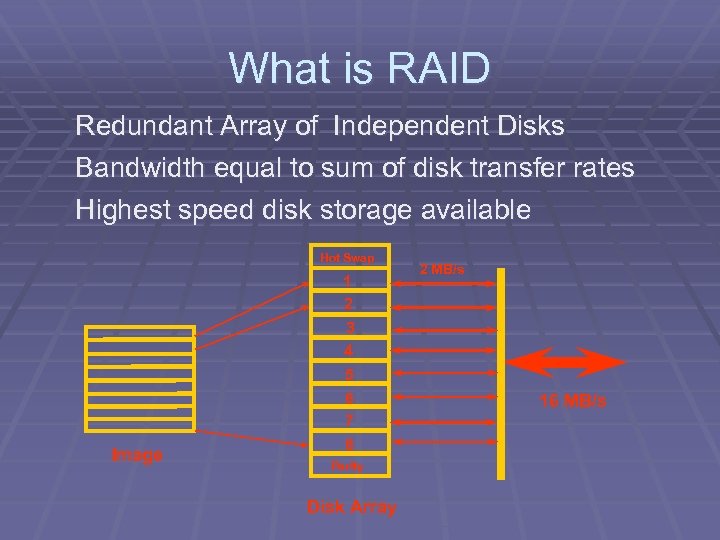 What is RAID Redundant Array of Independent Disks Bandwidth equal to sum of disk transfer rates Highest speed disk storage available Hot Swap Image 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Parity Disk Array 2 MB/s 16 MB/s
What is RAID Redundant Array of Independent Disks Bandwidth equal to sum of disk transfer rates Highest speed disk storage available Hot Swap Image 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Parity Disk Array 2 MB/s 16 MB/s
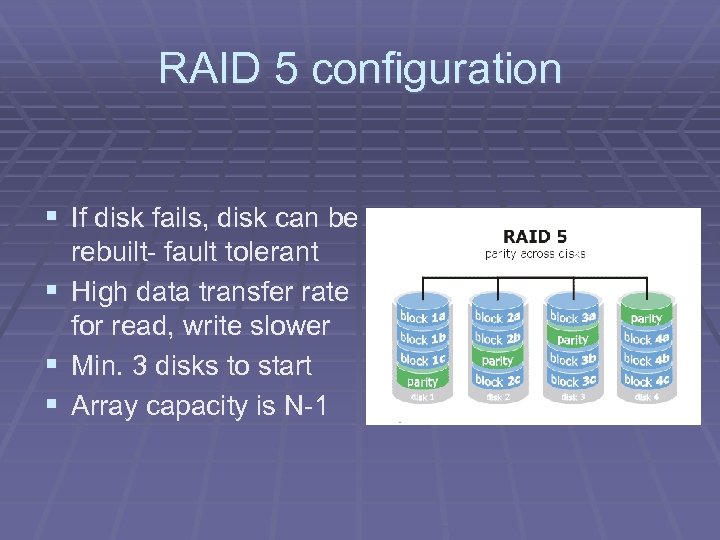 RAID 5 configuration § If disk fails, disk can be § § § rebuilt- fault tolerant High data transfer rate for read, write slower Min. 3 disks to start Array capacity is N-1
RAID 5 configuration § If disk fails, disk can be § § § rebuilt- fault tolerant High data transfer rate for read, write slower Min. 3 disks to start Array capacity is N-1
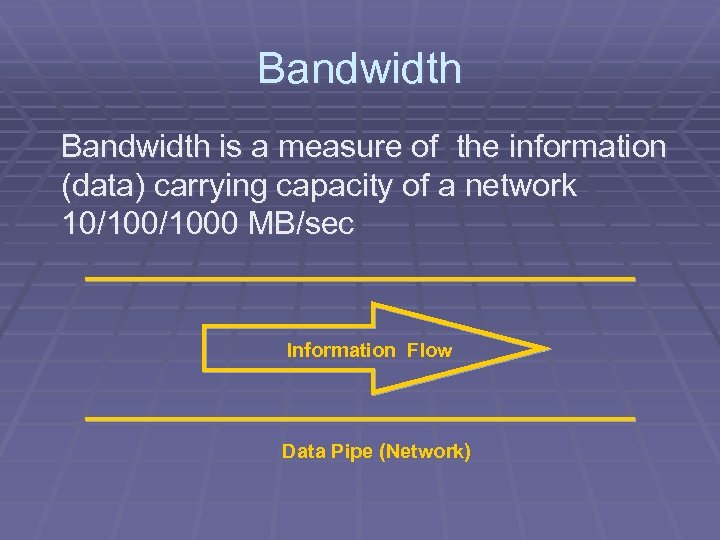 Bandwidth is a measure of the information (data) carrying capacity of a network 10/1000 MB/sec Information Flow Data Pipe (Network)
Bandwidth is a measure of the information (data) carrying capacity of a network 10/1000 MB/sec Information Flow Data Pipe (Network)
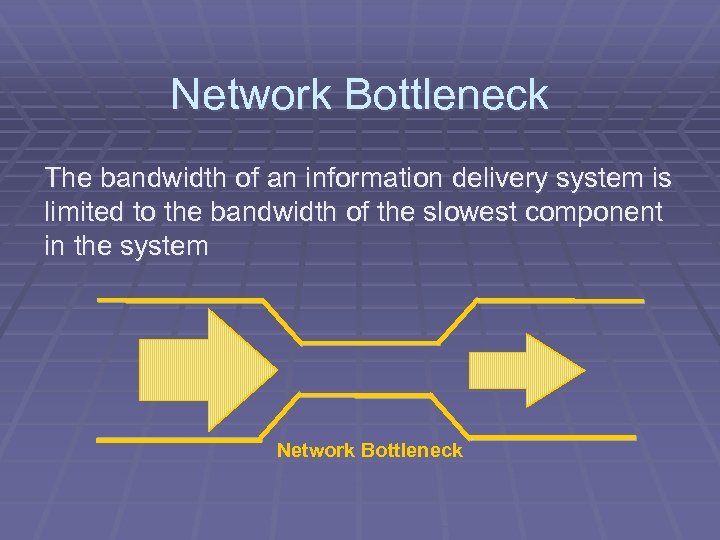 Network Bottleneck The bandwidth of an information delivery system is limited to the bandwidth of the slowest component in the system Network Bottleneck
Network Bottleneck The bandwidth of an information delivery system is limited to the bandwidth of the slowest component in the system Network Bottleneck
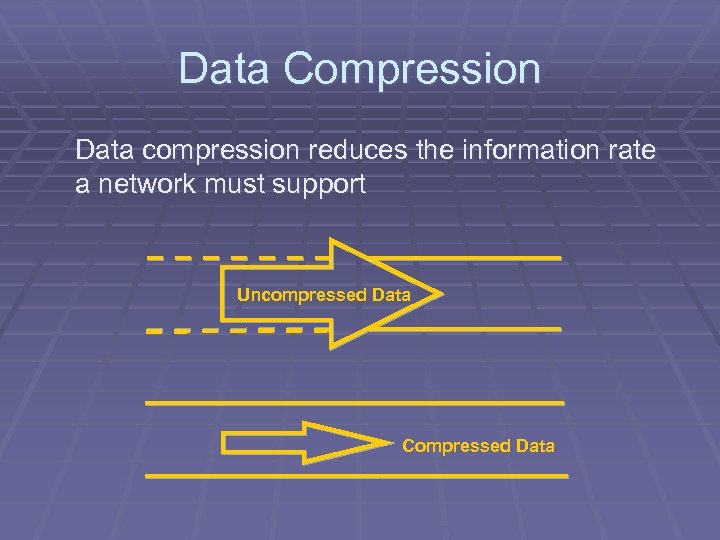 Data Compression Data compression reduces the information rate a network must support Uncompressed Data Compressed Data
Data Compression Data compression reduces the information rate a network must support Uncompressed Data Compressed Data
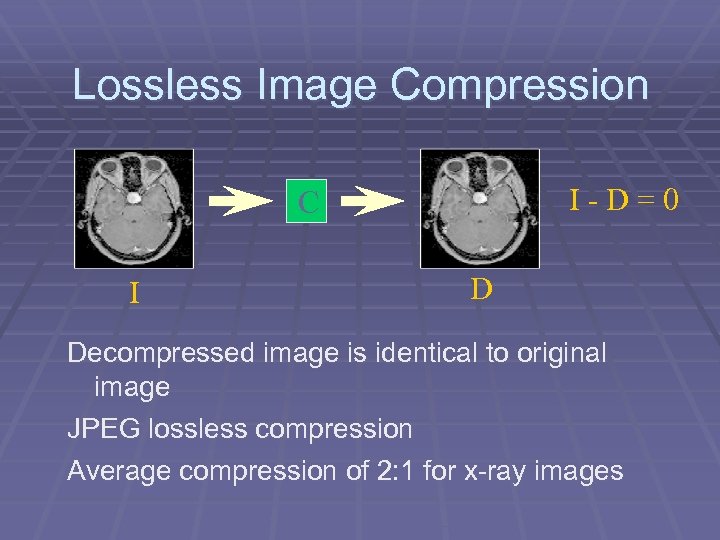 Lossless Image Compression I-D=0 C I D Decompressed image is identical to original image JPEG lossless compression Average compression of 2: 1 for x-ray images
Lossless Image Compression I-D=0 C I D Decompressed image is identical to original image JPEG lossless compression Average compression of 2: 1 for x-ray images
 JPEG 2000 Compression § Selected parts of the image can be defined as Regions of Interest, they can then be delivered before other parts of the image, or losslessly, whilst other parts of the image that are less critical use normal lossy compression § JPEG 2000 codestream can be ordered to deliver images of lower resolution before the full image can be transmitted § Motion JPEG 2000 does not have any form of extrapolation (and hence potential distortion) in the time domain. Each frame is a separate JPEG 2000 coded image
JPEG 2000 Compression § Selected parts of the image can be defined as Regions of Interest, they can then be delivered before other parts of the image, or losslessly, whilst other parts of the image that are less critical use normal lossy compression § JPEG 2000 codestream can be ordered to deliver images of lower resolution before the full image can be transmitted § Motion JPEG 2000 does not have any form of extrapolation (and hence potential distortion) in the time domain. Each frame is a separate JPEG 2000 coded image
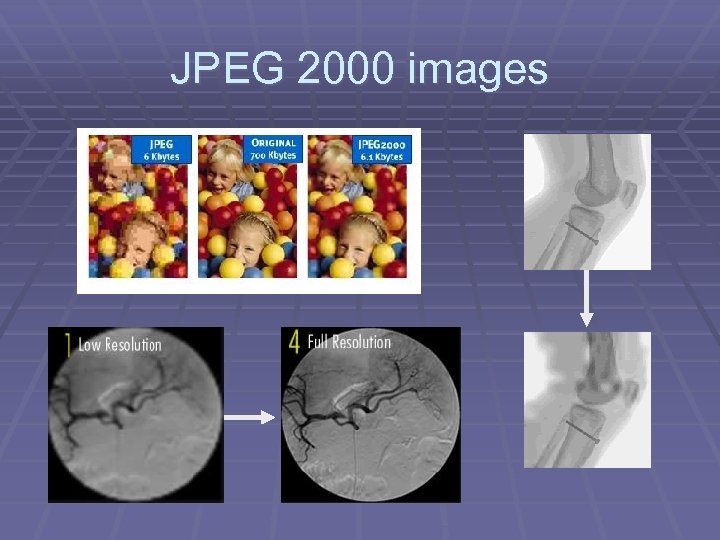 JPEG 2000 images
JPEG 2000 images
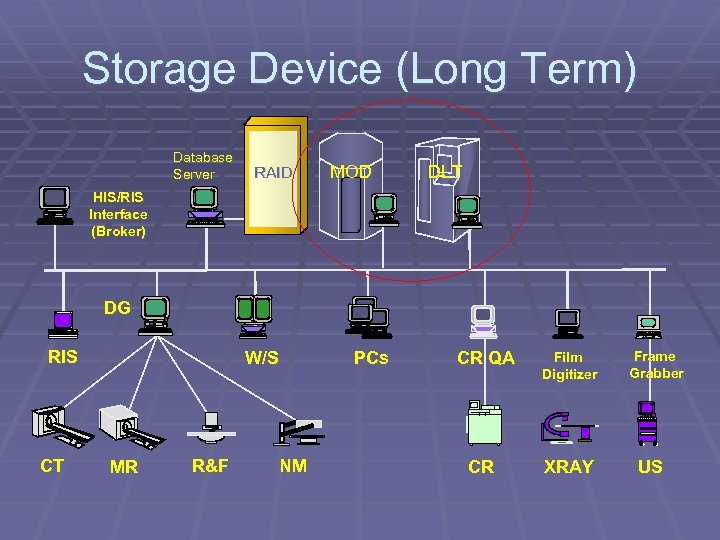 Storage Device (Long Term) Database Server RAID MOD DLT HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
Storage Device (Long Term) Database Server RAID MOD DLT HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
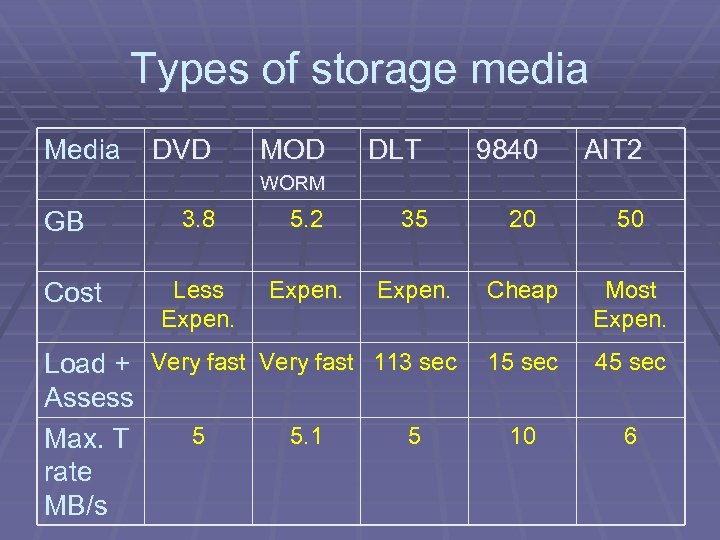 Types of storage media Media DVD MOD DLT 9840 AIT 2 WORM 3. 8 5. 2 35 20 50 Less Expen. Cheap Most Expen. Load + Very fast 113 sec Assess 5 5. 1 5 Max. T rate MB/s 15 sec 45 sec 10 6 GB Cost
Types of storage media Media DVD MOD DLT 9840 AIT 2 WORM 3. 8 5. 2 35 20 50 Less Expen. Cheap Most Expen. Load + Very fast 113 sec Assess 5 5. 1 5 Max. T rate MB/s 15 sec 45 sec 10 6 GB Cost
 Long Term Archive n n n Used to store digital data for longer periods of time Storage ranges from 100 MB to 10 TB Optical disk most common media - 5 1/4” MOD - 2. 6 GB and 5. 2 GB Capacity n n DLT used for longer term storage and redundancy ISP module
Long Term Archive n n n Used to store digital data for longer periods of time Storage ranges from 100 MB to 10 TB Optical disk most common media - 5 1/4” MOD - 2. 6 GB and 5. 2 GB Capacity n n DLT used for longer term storage and redundancy ISP module
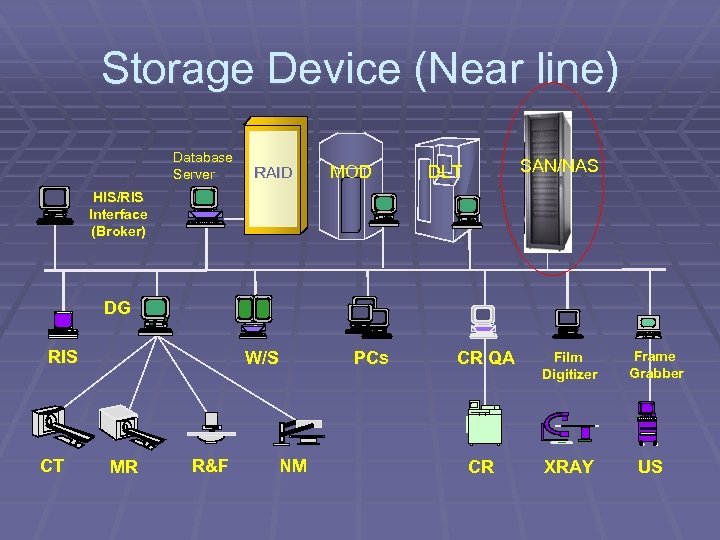 Storage Device (Near line) Database Server RAID MOD SAN/NAS DLT HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
Storage Device (Near line) Database Server RAID MOD SAN/NAS DLT HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
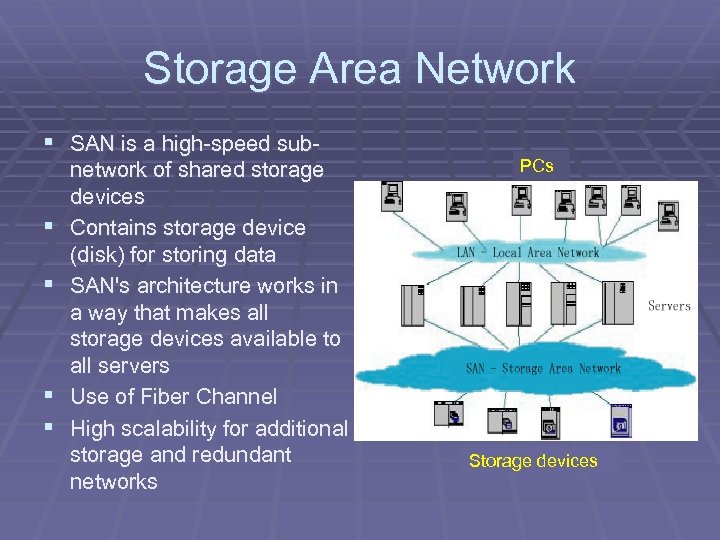 Storage Area Network § SAN is a high-speed sub§ § network of shared storage devices Contains storage device (disk) for storing data SAN's architecture works in a way that makes all storage devices available to all servers Use of Fiber Channel High scalability for additional storage and redundant networks PCs Storage devices
Storage Area Network § SAN is a high-speed sub§ § network of shared storage devices Contains storage device (disk) for storing data SAN's architecture works in a way that makes all storage devices available to all servers Use of Fiber Channel High scalability for additional storage and redundant networks PCs Storage devices
 Network Area Storage § NAS is a class of dedicated hard disk-based storage § § § devices which provide LAN users with additional disk storage through a standard network connection In most cases, a NAS device (or NAS server) receives an IP address, connects to the LAN through an Ethernet cable, and resides on the LAN as an independent network device Users are not demanding the server's processing time for mundane storage tasks -- often improving the performance of local application servers NAS systems also include some onboard memory (RAM) to cache network data to or from the disks
Network Area Storage § NAS is a class of dedicated hard disk-based storage § § § devices which provide LAN users with additional disk storage through a standard network connection In most cases, a NAS device (or NAS server) receives an IP address, connects to the LAN through an Ethernet cable, and resides on the LAN as an independent network device Users are not demanding the server's processing time for mundane storage tasks -- often improving the performance of local application servers NAS systems also include some onboard memory (RAM) to cache network data to or from the disks
 SAN Vs NAS § Difference between NAS and SAN is subtle § NAS devices are big, single purpose storage § § § appliances that you plug into network NAS sits between your application server and your file system As perform only 1 task, can serve files very fast NAS is network-centric SAN is a defined architecture that sits between your file system and your underlying physical storage SAN is data-centric
SAN Vs NAS § Difference between NAS and SAN is subtle § NAS devices are big, single purpose storage § § § appliances that you plug into network NAS sits between your application server and your file system As perform only 1 task, can serve files very fast NAS is network-centric SAN is a defined architecture that sits between your file system and your underlying physical storage SAN is data-centric
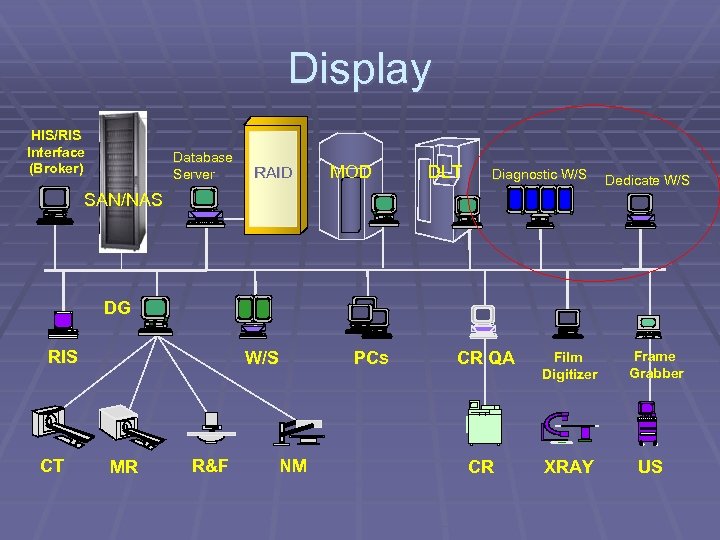 Display HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) Database Server RAID MOD DLT Diagnostic W/S Dedicate W/S SAN/NAS DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
Display HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) Database Server RAID MOD DLT Diagnostic W/S Dedicate W/S SAN/NAS DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
 Workstations § Four Primary Categories - Advanced Analysis: Used by specialists for advanced diagnosis - 3 D, volume rendering - Diagnostic: For primary diagnosis; located in reading rooms; high-end 2 K monitors - Clinical: Used by clinicians and staff to consult; ICU / ER applications; less costly than diagnostic; 1 K monitors - At Home Review: low-end; PC based; cost-effective; review application; lossy compressed for faster transmit
Workstations § Four Primary Categories - Advanced Analysis: Used by specialists for advanced diagnosis - 3 D, volume rendering - Diagnostic: For primary diagnosis; located in reading rooms; high-end 2 K monitors - Clinical: Used by clinicians and staff to consult; ICU / ER applications; less costly than diagnostic; 1 K monitors - At Home Review: low-end; PC based; cost-effective; review application; lossy compressed for faster transmit
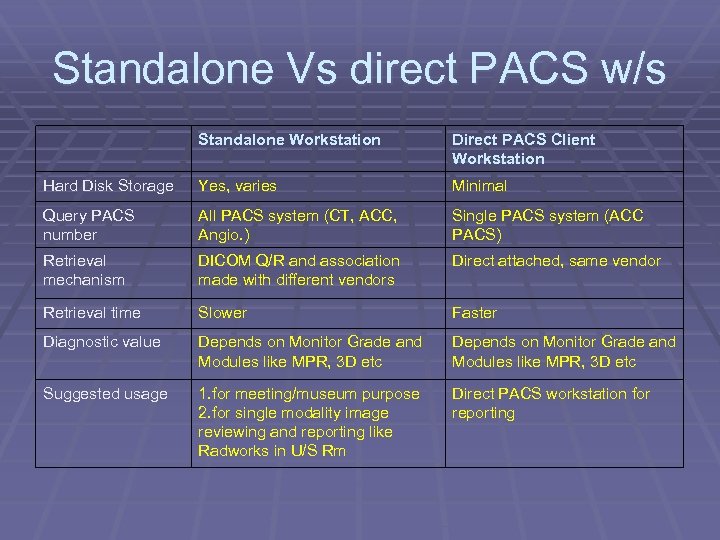 Standalone Vs direct PACS w/s Standalone Workstation Direct PACS Client Workstation Hard Disk Storage Yes, varies Minimal Query PACS number All PACS system (CT, ACC, Angio. ) Single PACS system (ACC PACS) Retrieval mechanism DICOM Q/R and association made with different vendors Direct attached, same vendor Retrieval time Slower Faster Diagnostic value Depends on Monitor Grade and Modules like MPR, 3 D etc Suggested usage 1. for meeting/museum purpose 2. for single modality image reviewing and reporting like Radworks in U/S Rm Direct PACS workstation for reporting
Standalone Vs direct PACS w/s Standalone Workstation Direct PACS Client Workstation Hard Disk Storage Yes, varies Minimal Query PACS number All PACS system (CT, ACC, Angio. ) Single PACS system (ACC PACS) Retrieval mechanism DICOM Q/R and association made with different vendors Direct attached, same vendor Retrieval time Slower Faster Diagnostic value Depends on Monitor Grade and Modules like MPR, 3 D etc Suggested usage 1. for meeting/museum purpose 2. for single modality image reviewing and reporting like Radworks in U/S Rm Direct PACS workstation for reporting
 Web distribution n n n High availability, low cost Reports / select images to referring physician desktop Point of integration with electronic patient record Lossy compression for performance Potential for Tele. Radiology Security issues to be resolved
Web distribution n n n High availability, low cost Reports / select images to referring physician desktop Point of integration with electronic patient record Lossy compression for performance Potential for Tele. Radiology Security issues to be resolved
 RIS, HIS, e. PR and PACS integration
RIS, HIS, e. PR and PACS integration
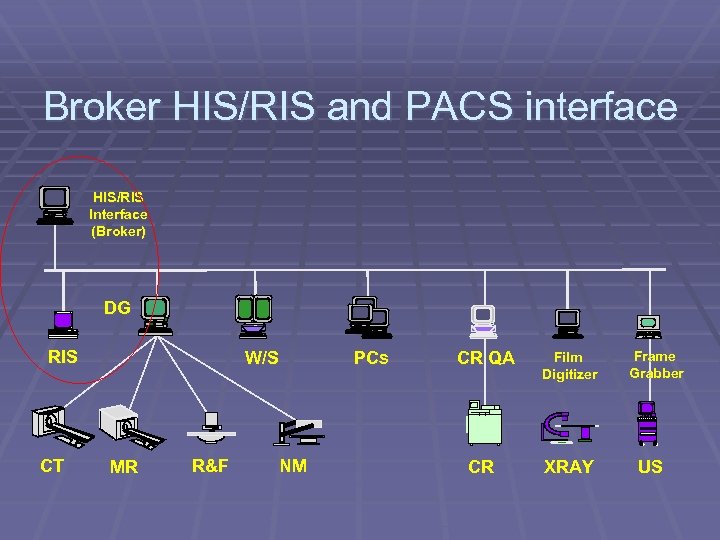 Broker HIS/RIS and PACS interface HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
Broker HIS/RIS and PACS interface HIS/RIS Interface (Broker) DG RIS CT W/S MR R&F PCs NM CR QA CR Film Digitizer XRAY Frame Grabber US
 Hospital Information System § Support clinical and medical patient care activities in the hospital § Administer the hospital’s daily business transactions like finance, payroll etc § Evaluate hospital performances and costs and make long-term forecast
Hospital Information System § Support clinical and medical patient care activities in the hospital § Administer the hospital’s daily business transactions like finance, payroll etc § Evaluate hospital performances and costs and make long-term forecast
 Clinical System in HA, HK § Patient Administration § § In-Patient and Out-Patient Administration System Accident & Emergency Information System Medical Record Abstract System Medical Record Tracking System § § Laboratory Information System Radiology Information System Pharmacy Management System Dietetics Catering Management System § § Clinical Management System (In-Patient) Discharge Summary Clinical Management System (Out-Patient) Electronic Patient Records Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System § Clinical Support § Clinical Management
Clinical System in HA, HK § Patient Administration § § In-Patient and Out-Patient Administration System Accident & Emergency Information System Medical Record Abstract System Medical Record Tracking System § § Laboratory Information System Radiology Information System Pharmacy Management System Dietetics Catering Management System § § Clinical Management System (In-Patient) Discharge Summary Clinical Management System (Out-Patient) Electronic Patient Records Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System § Clinical Support § Clinical Management
 Non-Clinical System in HA § Human Resources and Payroll Systems § Hospital Based Financial System § Materials Management System § Patient Billing and Revenue Collection System § Executive Information System Code 9 and view codes
Non-Clinical System in HA § Human Resources and Payroll Systems § Hospital Based Financial System § Materials Management System § Patient Billing and Revenue Collection System § Executive Information System Code 9 and view codes
 Radiology Information Systems § § § Similar to HIS but of smaller scale Interfaces to PACS based on HL 7 Department administrative management - Scheduling and Film tracking - Resource management and reporting - Monitor patient status n Link to Hospital Information System (HIS) - Billing and Master Record § Link to Clinical Management System (CMS) - Prefetch for Clinical visit - e. PR integration
Radiology Information Systems § § § Similar to HIS but of smaller scale Interfaces to PACS based on HL 7 Department administrative management - Scheduling and Film tracking - Resource management and reporting - Monitor patient status n Link to Hospital Information System (HIS) - Billing and Master Record § Link to Clinical Management System (CMS) - Prefetch for Clinical visit - e. PR integration
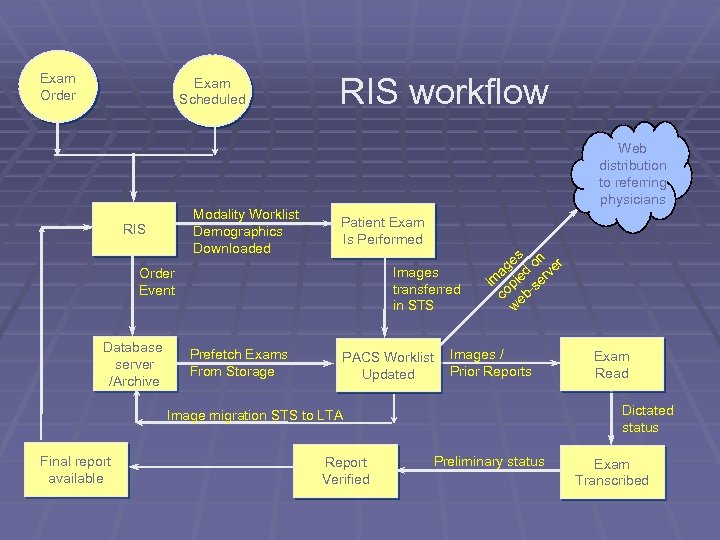 Exam Order Exam Scheduled RIS workflow Web distribution to referring physicians Modality Worklist Demographics Downloaded RIS Patient Exam Is Performed Images transferred in STS Order Event Database server /Archive Prefetch Exams From Storage PACS Worklist Updated s n ge d o ver a r Im pie -se o b c e w Images / Prior Reports Dictated status Image migration STS to LTA Final report available Report Verified Exam Read Preliminary status Exam Transcribed
Exam Order Exam Scheduled RIS workflow Web distribution to referring physicians Modality Worklist Demographics Downloaded RIS Patient Exam Is Performed Images transferred in STS Order Event Database server /Archive Prefetch Exams From Storage PACS Worklist Updated s n ge d o ver a r Im pie -se o b c e w Images / Prior Reports Dictated status Image migration STS to LTA Final report available Report Verified Exam Read Preliminary status Exam Transcribed
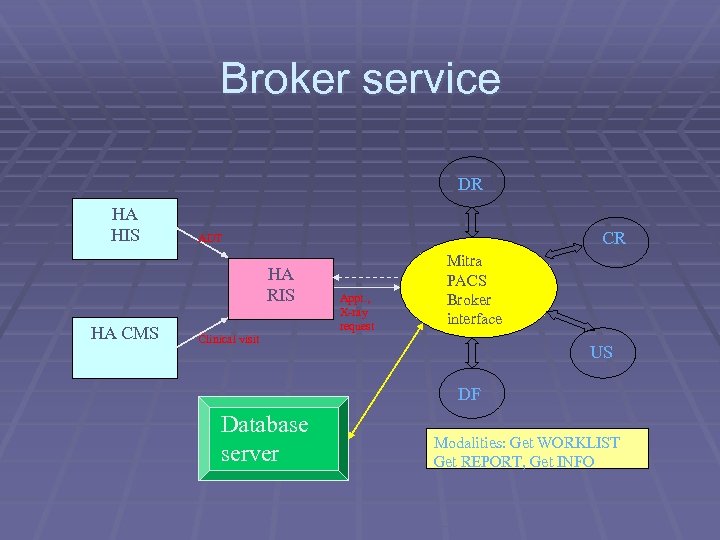 Broker service DR HA HIS CR ADT HA RIS HA CMS Clinical visit Appt. , X-ray request Mitra PACS Broker interface US DF Database server Modalities: Get WORKLIST Get REPORT, Get INFO
Broker service DR HA HIS CR ADT HA RIS HA CMS Clinical visit Appt. , X-ray request Mitra PACS Broker interface US DF Database server Modalities: Get WORKLIST Get REPORT, Get INFO
 Broker service § A restricted access account will be created at Sybase that gives limited authority for the DICOM Broker solely for the purpose of the interfaces § In general, for data flow from RIS to the Broker, the RIS write the supported events to the table, and the Broker polls against the events table and calls the associated stored procedures for the conversion to DICOM messages
Broker service § A restricted access account will be created at Sybase that gives limited authority for the DICOM Broker solely for the purpose of the interfaces § In general, for data flow from RIS to the Broker, the RIS write the supported events to the table, and the Broker polls against the events table and calls the associated stored procedures for the conversion to DICOM messages
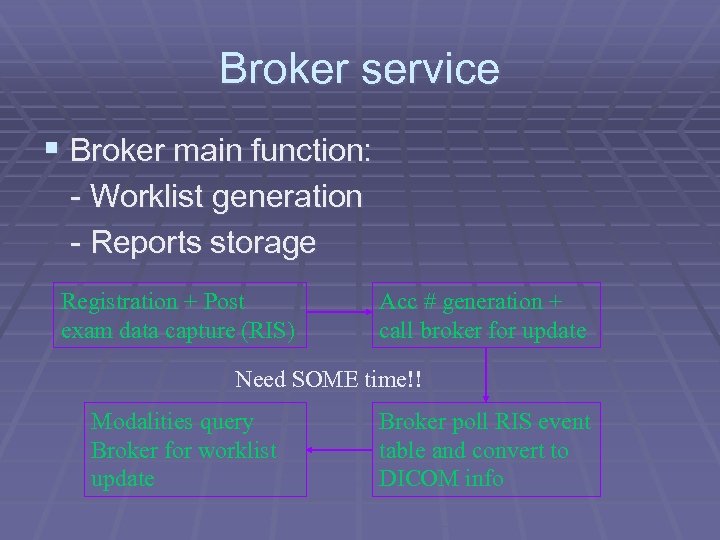 Broker service § Broker main function: - Worklist generation - Reports storage Registration + Post exam data capture (RIS) Acc # generation + call broker for update Need SOME time!! Modalities query Broker for worklist update Broker poll RIS event table and convert to DICOM info
Broker service § Broker main function: - Worklist generation - Reports storage Registration + Post exam data capture (RIS) Acc # generation + call broker for update Need SOME time!! Modalities query Broker for worklist update Broker poll RIS event table and convert to DICOM info
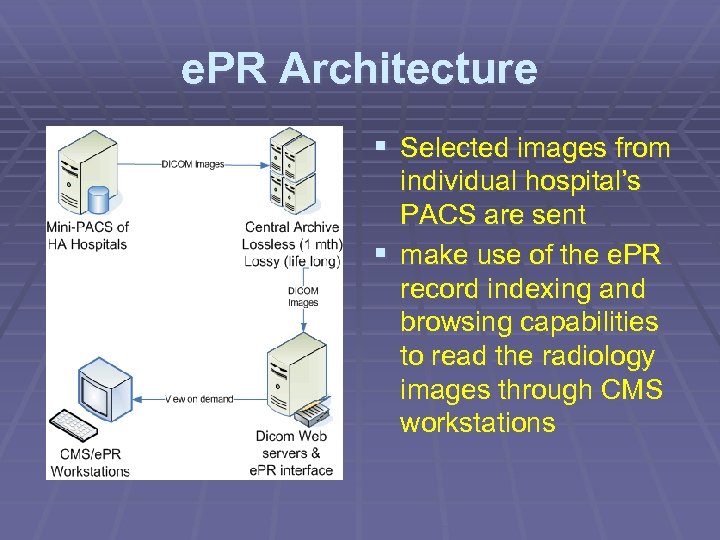 e. PR Architecture § Selected images from individual hospital’s PACS are sent § make use of the e. PR record indexing and browsing capabilities to read the radiology images through CMS workstations
e. PR Architecture § Selected images from individual hospital’s PACS are sent § make use of the e. PR record indexing and browsing capabilities to read the radiology images through CMS workstations
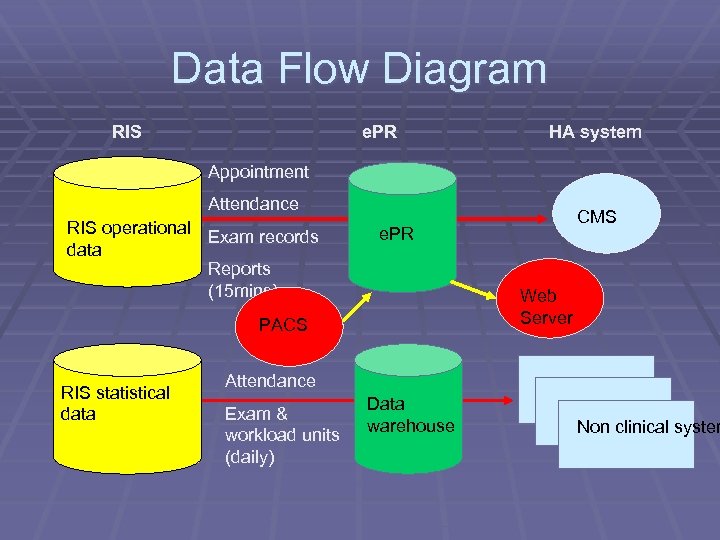 Data Flow Diagram RIS e. PR HA system Appointment Attendance RIS operational Exam records data Reports (15 mins) e. PR Web Server PACS RIS statistical data CMS Attendance Exam & workload units (daily) Data warehouse Non clinical system
Data Flow Diagram RIS e. PR HA system Appointment Attendance RIS operational Exam records data Reports (15 mins) e. PR Web Server PACS RIS statistical data CMS Attendance Exam & workload units (daily) Data warehouse Non clinical system
 Characteristics of e. PR § Near instant image review § Web distribution can be within hospital, to other hospitals or even private clinics § Tele. Radiography possible § Update of patient information § Lossy Vs lossless § Broken pathway § 15 minutes time lag
Characteristics of e. PR § Near instant image review § Web distribution can be within hospital, to other hospitals or even private clinics § Tele. Radiography possible § Update of patient information § Lossy Vs lossless § Broken pathway § 15 minutes time lag
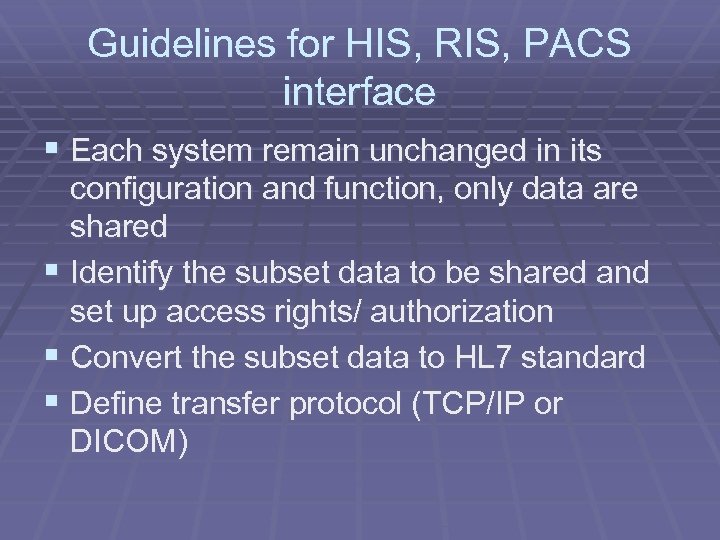 Guidelines for HIS, RIS, PACS interface § Each system remain unchanged in its configuration and function, only data are shared § Identify the subset data to be shared and set up access rights/ authorization § Convert the subset data to HL 7 standard § Define transfer protocol (TCP/IP or DICOM)
Guidelines for HIS, RIS, PACS interface § Each system remain unchanged in its configuration and function, only data are shared § Identify the subset data to be shared and set up access rights/ authorization § Convert the subset data to HL 7 standard § Define transfer protocol (TCP/IP or DICOM)
 Typical patient and data flow § § § Admission: Patient registration, notify HIS (HL 7) Order entry/Arrival: Schedule exam and notify RIS Broker notified and PACS database server updated (prefetch) DICOM worklist to modality Exam completed: data to DICOM gateway (MPPS) Information/images to database/image server through gateway (DICOM store) Images stored in PACS archive Images to workstations from PACS archive Dictation, transcription etc: workstation to RIS/PACS RIS reporting and PACS updated for reports Transfer: HIS/RIS to PACS, images to other PACS Discharge: HIS/RIS to PACS, images rub out
Typical patient and data flow § § § Admission: Patient registration, notify HIS (HL 7) Order entry/Arrival: Schedule exam and notify RIS Broker notified and PACS database server updated (prefetch) DICOM worklist to modality Exam completed: data to DICOM gateway (MPPS) Information/images to database/image server through gateway (DICOM store) Images stored in PACS archive Images to workstations from PACS archive Dictation, transcription etc: workstation to RIS/PACS RIS reporting and PACS updated for reports Transfer: HIS/RIS to PACS, images to other PACS Discharge: HIS/RIS to PACS, images rub out
 http: //www. pacs. hk Thanks!
http: //www. pacs. hk Thanks!


