7fe44948413fe6f2970a6b0d15e4c41d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 PA Mammalian Predators
PA Mammalian Predators
 Eastern Coyote p. AKA brush wolf, prairie wolf, coy- dog p. Largest wild canine in PA p. During wolf bounties of 1800’s, many were turned in by mistake p. By 1990 populations had rebounded
Eastern Coyote p. AKA brush wolf, prairie wolf, coy- dog p. Largest wild canine in PA p. During wolf bounties of 1800’s, many were turned in by mistake p. By 1990 populations had rebounded
 Eastern Coyote: Identification Larger than Western Coyote: may be due to hybridization with wolves p Males: 45 -55 lbs. p Females: 35 to 40 pounds p Many different coat colors and patterns: tri -color (German shepherd-like), red, blonde and dark brown (appears black at a distance) p
Eastern Coyote: Identification Larger than Western Coyote: may be due to hybridization with wolves p Males: 45 -55 lbs. p Females: 35 to 40 pounds p Many different coat colors and patterns: tri -color (German shepherd-like), red, blonde and dark brown (appears black at a distance) p
 IDENTIFICATION p Tri-color p RED
IDENTIFICATION p Tri-color p RED
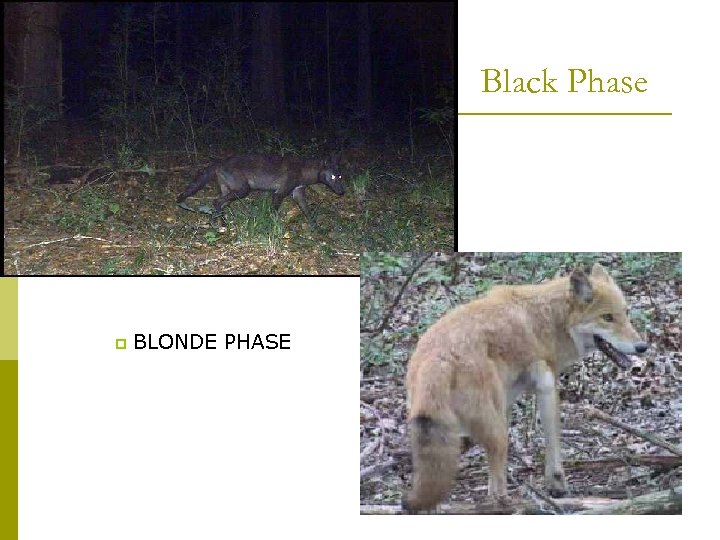 Black Phase p BLONDE PHASE
Black Phase p BLONDE PHASE
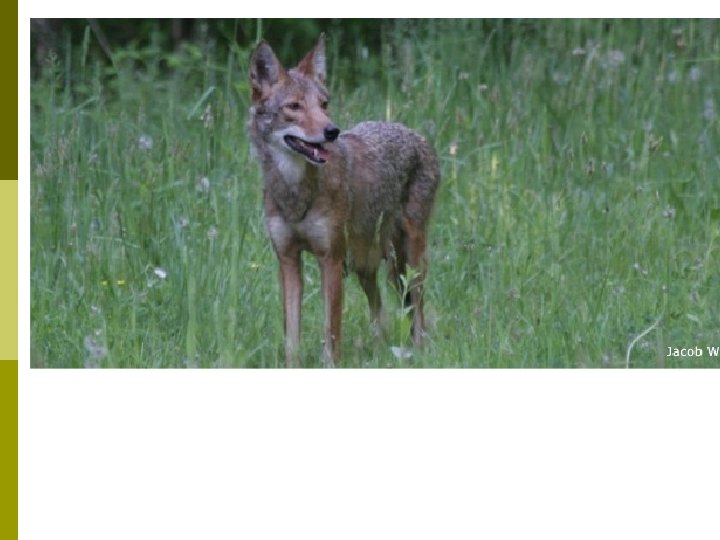

 Eastern Coyote: Diet Generalist: small mice, voles, deer, rabbits, wood chuck, birds, plant matter p Sometimes prey on domestic animals (sheep, chickens, ducks, dogs, cats) p
Eastern Coyote: Diet Generalist: small mice, voles, deer, rabbits, wood chuck, birds, plant matter p Sometimes prey on domestic animals (sheep, chickens, ducks, dogs, cats) p
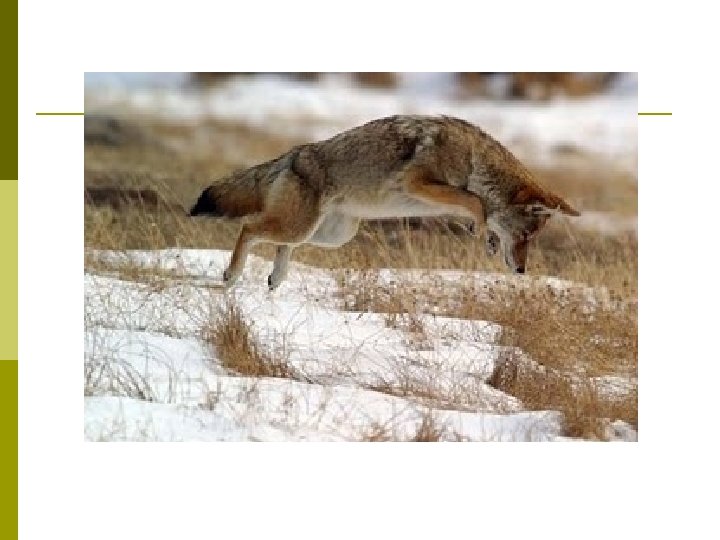

 Eastern Coyote: General Biology p Monogamous, but not for life May hunt alone or with family group, not a true pack animal like the wolf p Nocturnal p Smell and hearing are keen; very alert p Prefer heavy brush, edges p PA population estimated at 40, 000 p
Eastern Coyote: General Biology p Monogamous, but not for life May hunt alone or with family group, not a true pack animal like the wolf p Nocturnal p Smell and hearing are keen; very alert p Prefer heavy brush, edges p PA population estimated at 40, 000 p
 PA Game Commission Bag Limits p COYOTES: No closed season. Unlimited. Outside of any big game season (deer, bear, elk and turkey), coyotes may be taken with a hunting license or a furtaker license, and without wearing orange. During any big game season, coyotes may be taken while lawfully hunting big game or with a furtakers license.
PA Game Commission Bag Limits p COYOTES: No closed season. Unlimited. Outside of any big game season (deer, bear, elk and turkey), coyotes may be taken with a hunting license or a furtaker license, and without wearing orange. During any big game season, coyotes may be taken while lawfully hunting big game or with a furtakers license.

 Owl In an SUV grill http: //www. cnn. com/video/? hpt=hp_c 3#/vi deo/us/2013/02/11/dnt-owl-trapped-insuv. wsvn
Owl In an SUV grill http: //www. cnn. com/video/? hpt=hp_c 3#/vi deo/us/2013/02/11/dnt-owl-trapped-insuv. wsvn
 Mustelid Family Predators Examples: Mink, Otter, Fisher, Weasels p Others not in PA: Ferret, Badger, Wolverine p LEAST WEASEL
Mustelid Family Predators Examples: Mink, Otter, Fisher, Weasels p Others not in PA: Ferret, Badger, Wolverine p LEAST WEASEL
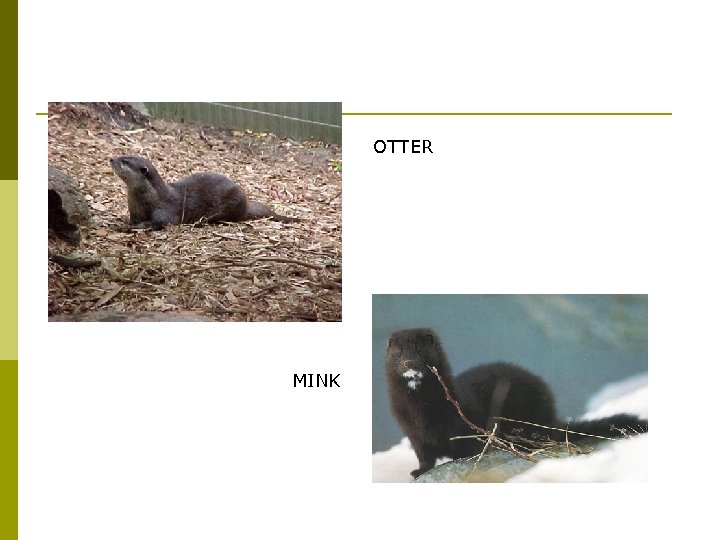 OTTER MINK
OTTER MINK
 FISHER
FISHER
 WEASELS p. Mustelid family p. Strong musk odor p. Found worldwide except Antarctica p 3 species in PA: ermine, long-tailed weasel, least weasel p. Long, slim bodies, short legs, 5 clawed toes
WEASELS p. Mustelid family p. Strong musk odor p. Found worldwide except Antarctica p 3 species in PA: ermine, long-tailed weasel, least weasel p. Long, slim bodies, short legs, 5 clawed toes
 WEASELS p ERMINE
WEASELS p ERMINE
 WEASELS p Least Weasel
WEASELS p Least Weasel
 WEASELS p Long tailed Weasel
WEASELS p Long tailed Weasel
 WEASELS: Diet Consummate Predators: kill and consume wide varieties of prey (including animals larger than themselves) p Mice, voles, rats, shrews, snakes, birds, insects p Very fast metabolism for size: eat 1/3 body weight every 24 hrs. p Keen smell, sight, hearing p
WEASELS: Diet Consummate Predators: kill and consume wide varieties of prey (including animals larger than themselves) p Mice, voles, rats, shrews, snakes, birds, insects p Very fast metabolism for size: eat 1/3 body weight every 24 hrs. p Keen smell, sight, hearing p
 WEASELS: Biology Aggressive and quick p Secretive and wary=difficult to study in nature p Delayed implantation: p n n n Mate in summer/fall Fertilized egg implants in uterus in spring WHY? ? ? 1. Assures litters arrive when prey is abundant p 2. Does not restrict mating to a short period p
WEASELS: Biology Aggressive and quick p Secretive and wary=difficult to study in nature p Delayed implantation: p n n n Mate in summer/fall Fertilized egg implants in uterus in spring WHY? ? ? 1. Assures litters arrive when prey is abundant p 2. Does not restrict mating to a short period p
 FISHER Size of a house cat 12 lbs. -30 lbs. p Males 2 times heavier than females p Appear black from a distance, really cream underneath; tri-colored hair p
FISHER Size of a house cat 12 lbs. -30 lbs. p Males 2 times heavier than females p Appear black from a distance, really cream underneath; tri-colored hair p
 FISHER: Habitat Climb trees very well: den in holes in the trees, rest in nests, pursue prey p Continuous forest areas p
FISHER: Habitat Climb trees very well: den in holes in the trees, rest in nests, pursue prey p Continuous forest areas p
 FISHER: Biology Low population densities and large home ranges: 30 square miles p Nocturnal p Produce 1 litter per year: 2 or 3 cubs p Born and raised in a tree cavity p Solitary and opportunistic predators: p Snowshoe hare and porcupine p RARELY EAT FISH!! p
FISHER: Biology Low population densities and large home ranges: 30 square miles p Nocturnal p Produce 1 litter per year: 2 or 3 cubs p Born and raised in a tree cavity p Solitary and opportunistic predators: p Snowshoe hare and porcupine p RARELY EAT FISH!! p
 FISHER: Population Widely distributed prior to 1800’s p Timber cutting and unregulated trapping almost eliminated by 1900’s p Reintroduced to Catskills, WV, PA p 1994 PSU and Game Commission released in Allegheny National Forest p
FISHER: Population Widely distributed prior to 1800’s p Timber cutting and unregulated trapping almost eliminated by 1900’s p Reintroduced to Catskills, WV, PA p 1994 PSU and Game Commission released in Allegheny National Forest p

 BOBCAT 36” long with a 6” tail p 15 -35 lbs. p Grey brown fur, dark spots and bars p Neck and belly white p Ruff of fur on ears p
BOBCAT 36” long with a 6” tail p 15 -35 lbs. p Grey brown fur, dark spots and bars p Neck and belly white p Ruff of fur on ears p
 Bobcat: Habitat Mountains, deep forest, swamp p Very elusive, prefer to stay away from people p Most common in North Central PA p In 2000 estimated pop. was 3500 adults p Very restricted hunting/trapping season p
Bobcat: Habitat Mountains, deep forest, swamp p Very elusive, prefer to stay away from people p Most common in North Central PA p In 2000 estimated pop. was 3500 adults p Very restricted hunting/trapping season p
 PA Game Commission Bag Limits p. BOBCAT (WMUs 2 A, 2 C, 2 E, 2 F, 2 G, 3 A, 3 B, 3 C, 3 D, 4 A, 4 C, 4 D and 4 E): Jan. 15 -Feb. 5. One bobcat per license year, but all licensed furtakers may obtain one permit.
PA Game Commission Bag Limits p. BOBCAT (WMUs 2 A, 2 C, 2 E, 2 F, 2 G, 3 A, 3 B, 3 C, 3 D, 4 A, 4 C, 4 D and 4 E): Jan. 15 -Feb. 5. One bobcat per license year, but all licensed furtakers may obtain one permit.
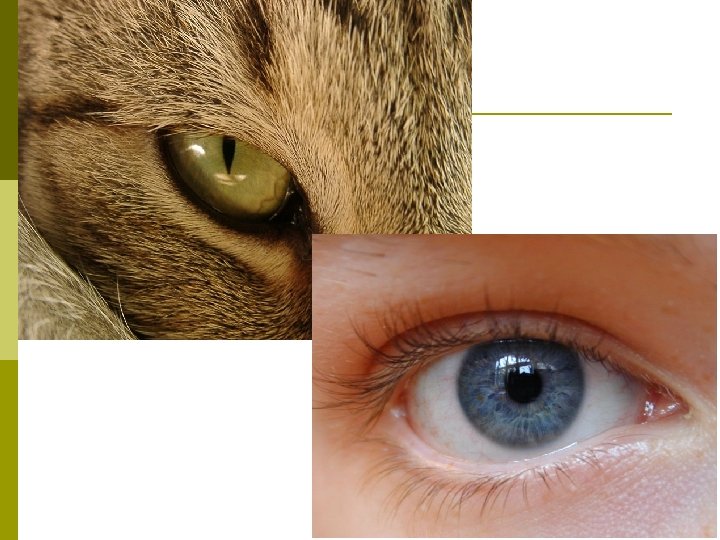
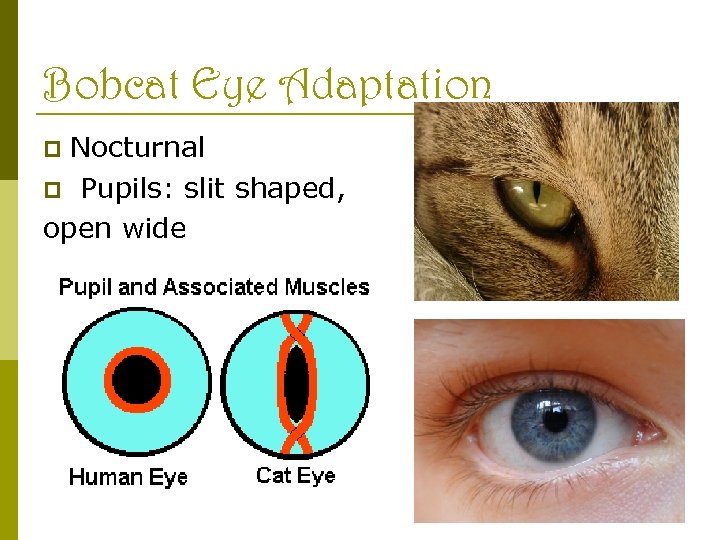 Bobcat Eye Adaptation Nocturnal p Pupils: slit shaped, open wide p
Bobcat Eye Adaptation Nocturnal p Pupils: slit shaped, open wide p

 Bobcat: Diet Mice, wood rat, shrew, squirrel, chipmunk, bird, rabbit, hare, porcupine, mink, muskrat, fish, frog p Sick/injured deer: cover and save carcass p
Bobcat: Diet Mice, wood rat, shrew, squirrel, chipmunk, bird, rabbit, hare, porcupine, mink, muskrat, fish, frog p Sick/injured deer: cover and save carcass p
 Bobcat: Breeding Males can travel up to 20 miles in a single night to find a female p Males play no part in raising young p Females guard litter; young often killed by males, owls, foxes p Mature bobcat has few enemies except man p
Bobcat: Breeding Males can travel up to 20 miles in a single night to find a female p Males play no part in raising young p Females guard litter; young often killed by males, owls, foxes p Mature bobcat has few enemies except man p
 Bobcat: Hunting Adaptations Sharp sight, smell and especially hearing p 4 large canines: pierce and hold p 5 retractable, hooked claws on front p 4 on rear p
Bobcat: Hunting Adaptations Sharp sight, smell and especially hearing p 4 large canines: pierce and hold p 5 retractable, hooked claws on front p 4 on rear p
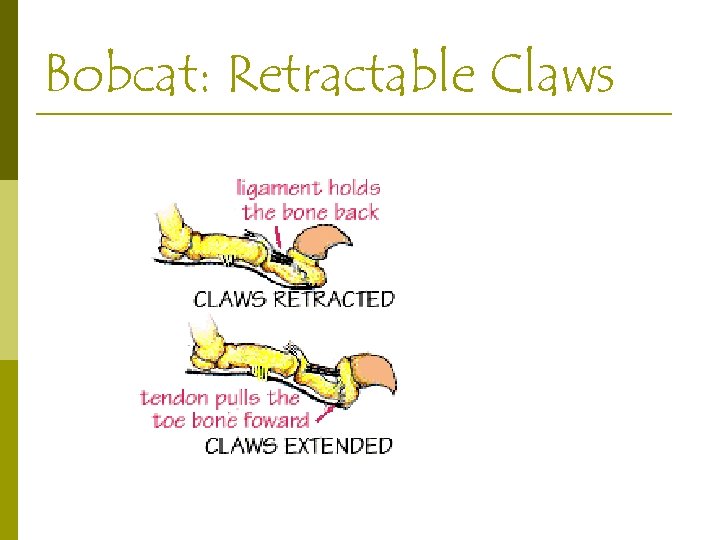 Bobcat: Retractable Claws
Bobcat: Retractable Claws
 Red Fox: Appearance
Red Fox: Appearance
 Gray Fox: Appearance
Gray Fox: Appearance
 Red Fox And Gray Fox Canidae family (coyote, wolf, domestic dog, fox) p Gray only member of Canidae to climb trees p
Red Fox And Gray Fox Canidae family (coyote, wolf, domestic dog, fox) p Gray only member of Canidae to climb trees p
 Red Fox and Gray: Biology Males: “dogs” Females: “vixen” p Young are born in dens underground p Both parents care for young p Do not hibernate but will use bushy tail to conserve heat in severe weather p
Red Fox and Gray: Biology Males: “dogs” Females: “vixen” p Young are born in dens underground p Both parents care for young p Do not hibernate but will use bushy tail to conserve heat in severe weather p
 Red Fox and Gray: Biology Swift runners, can swim p Nocturnal p Opportunistic predators: mice, rabbits, woodchucks, opossum, cats, chickens, squirrels, fruits, grasses p Bury uneaten food in ground p
Red Fox and Gray: Biology Swift runners, can swim p Nocturnal p Opportunistic predators: mice, rabbits, woodchucks, opossum, cats, chickens, squirrels, fruits, grasses p Bury uneaten food in ground p
 Habitat Red: prefers rolling farmland, woods, marshes and streams p Gray: heavy woods, rugged, mountains p
Habitat Red: prefers rolling farmland, woods, marshes and streams p Gray: heavy woods, rugged, mountains p
 Exit Ticket…. . To leave this room you must answer these questions…. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. List one surprising new idea you learned about mammalian predators. Name 2 weasels found in PA. See #2. What is the common characteristic shared by the Mustelid family? Name 2 adaptations that help the canines locate prey.
Exit Ticket…. . To leave this room you must answer these questions…. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. List one surprising new idea you learned about mammalian predators. Name 2 weasels found in PA. See #2. What is the common characteristic shared by the Mustelid family? Name 2 adaptations that help the canines locate prey.


